文章目录
使用API
学习如何编写一个独立的程序,并对其进行可视化。
利用Web应用编程接口(API)自动请求网站的特定信息而不是整个网页,再对信息进行可视化,这样即使数据瞬息万变,程序呈现的信息也是最新的。
1. 使用Web API
API调用 : Web API是网站的一部分,用于与使用非常具体的URL请求特定信息的程序交互。请求得到的数据将以易于处理的格式(JOSN, CSV)返回。
实战: 使用GitHub的API请求有关该网站中的python信息,使用Pygal生成交互可视化,呈现这些项目的受欢迎程度。
1.1 使用API调用请求数据
打开如下网址
https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q=language:python&sort=starts
这个调用返回GitHub当前托管了多少个python项目,还有有关最受欢迎的python仓库的信息。
解释调用:
https://api.github.com/ 将请求发送到GitHub网站中相应API调用的部分
search/repositories 搜索所有GitHub上的仓库
q= q表示查询 =指定查询
language:python 使用语言为python的仓库项目信息
&sort=starts 将项目按所获得的星级排序
下面显示了相应的前几行。从响应可知,该URL并不适合人工输入
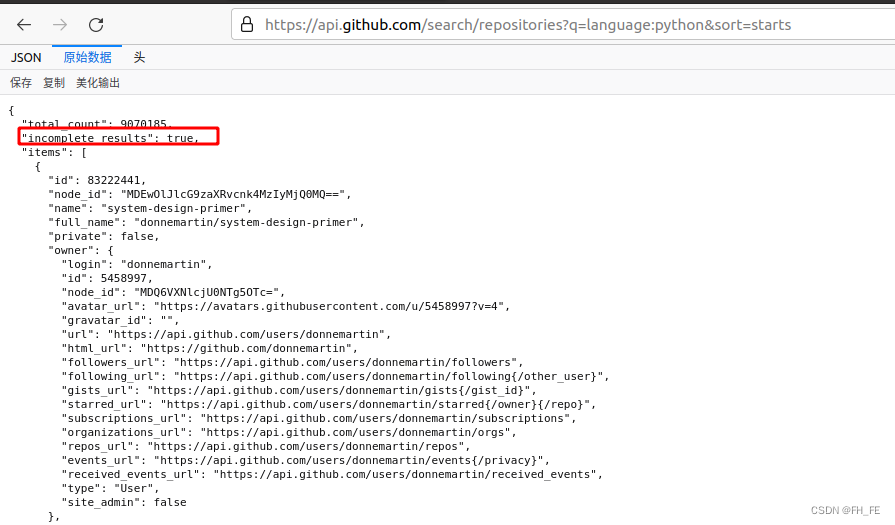 “total_count”: 9070185, 写该文章的时刻,GitHub共9070185个python项目
“total_count”: 9070185, 写该文章的时刻,GitHub共9070185个python项目
“incomplete_results”: true, 请求成功。true,GitHub无法全面处理该API;若为false,则代表请求并非完整
item 其中包含GitHub上最受欢迎的Python项目的详细信息
1.2 安装requests
requests包向网站请求信息并检查返回的响应
先查看自己的conda环境
conda env list
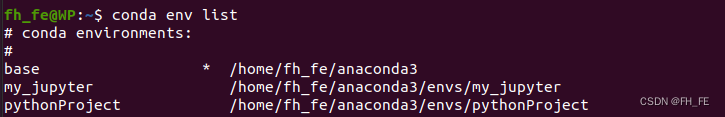
激活要使用的环境
conda activate pythonProject
安装requests包
pip install --user requests
1.3 处理API响应
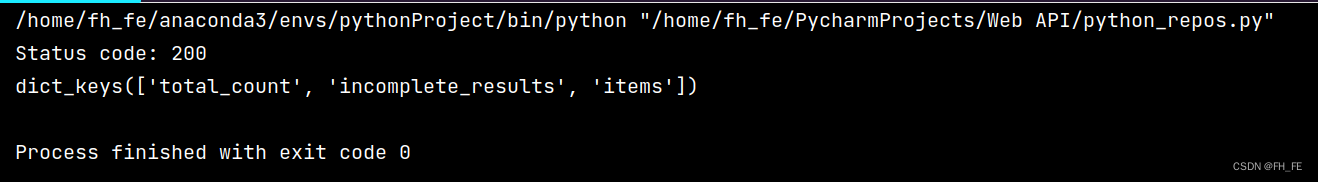
编写一个程序, 执行API调用,并处理结果,找出GitHub上星级最高的Python项目:
import requests
# 执行API调用并存储响应
url = 'https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q=language:python&sort=starts'
# 将url传递给r,再将响应对象存储在变量r中
r = requests.get(url)
# 通过查看响应对象的一个status_code属性,知道了请求是否成功(状态码200表示请求成功)
print("Status code:", r.status_code)
# 将API响应存储在一个变量中(将返回的json格式信息转化为python字典)
response_dict = r.json()
# 处理结果,查看有哪些键值
print(response_dict.keys())
调用程序查看结果
1.4 处理响应字典
python_repos.py
import requests
# 执行API调用并存储响应
url = 'https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q=language:python&sort=starts'
# 将url传递给r,再将响应对象存储在变量r中
r = requests.get(url)
# 通过查看响应对象的一个status_code属性,知道了请求是否成功(状态码200表示请求成功)
print("Status code:", r.status_code)
# 将API响应存储在一个变量中(将返回的json格式信息转化为python字典)
response_dict = r.json()
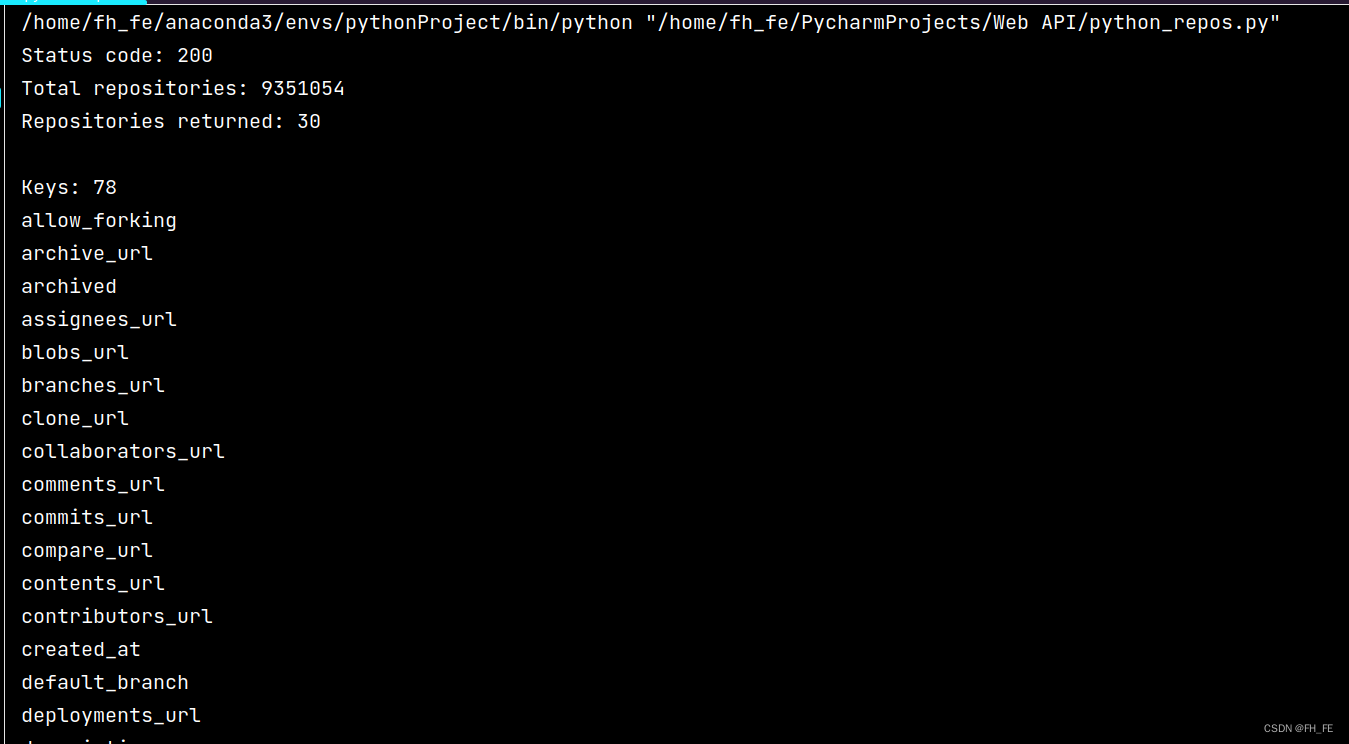
print("Total repositories:", response_dict['total_count']) # 查看共有多少个仓库
# 探索有关仓库的信息
repo_dicts = response_dict['items'] # 每个与items相关的字典都包含一个有关python仓库的信息
print("Repositories returned:", len(repo_dicts)) # 查看得到了多少个仓库的信息
# 研究第一个仓库
repo_dict = repo_dicts[0]
print("\nKeys:", len(repo_dict)) # 查看第一个仓库中有多少信息
for key in sorted(repo_dict.keys()): # 打印所有信息的建
print(key)
下面提取repo_dict中与一些键相关联的值:
python_repos.py
--snip--
# 研究第一个仓库
repo_dict = repo_dicts[0]
print("\nSelected information about first repository:")
print('Name:', repo_dict['name']) # 项目名称
print('Owner:', repo_dict['owner']['login']) # ['owner']获取项目所有者的字典 ['login']获取项目所有者的登录名
print('Stars:', repo_dict['stargazers_count']) # 获得的star数
print('Repository:', repo_dict['html_url'])
print('Created:', repo_dict['created_at']) # 建库时间
print('UPdate:', repo_dict['updated_at']) # 最近更新时间
print('Description:', repo_dict['description'])
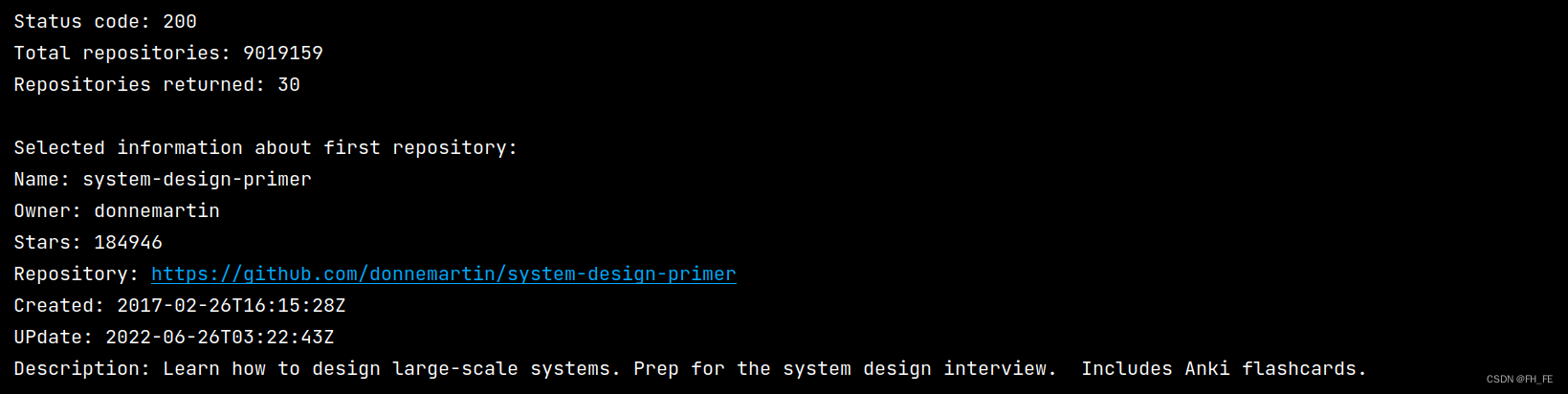 写文章此刻,最受欢迎的项目是system-design-primer
写文章此刻,最受欢迎的项目是system-design-primer
1.5 概述最受欢迎的仓库
查看每一个仓库的信息
python_repos.py
--snip--
# 研究有关仓库的信息
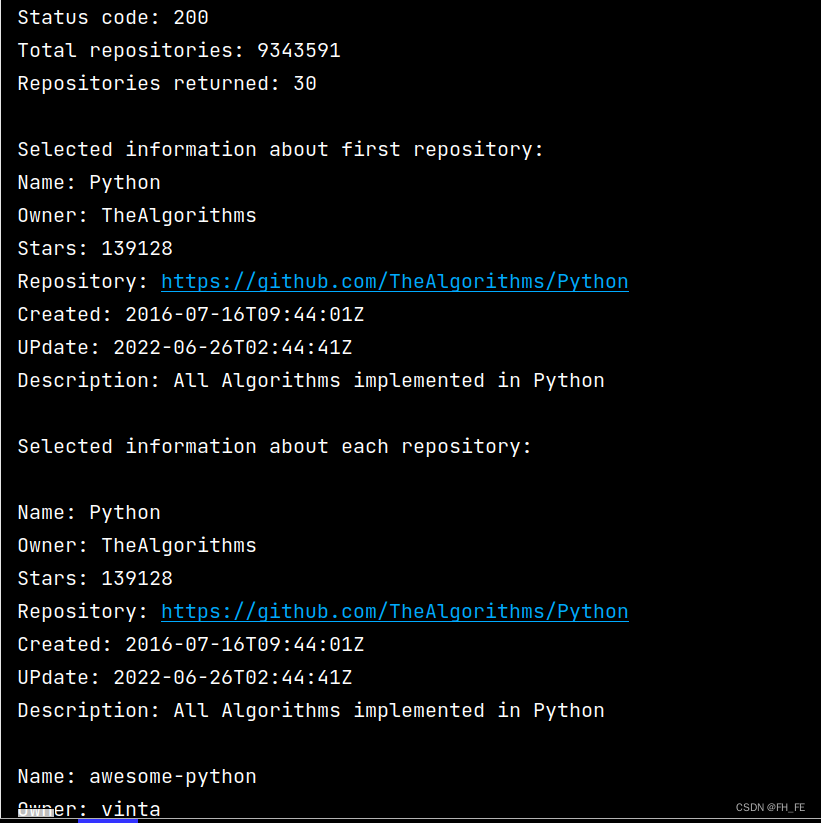
print("\nSelected information about each repository:")
# 打印一条说明性的信息
for repo_dict in repo_dicts:
print('\nName:', repo_dict['name']) # 项目名称
print('Owner:', repo_dict['owner']['login']) # ['owner']获取项目所有者的字典 ['login']获取项目所有者的登录名
print('Stars:', repo_dict['stargazers_count']) # 获得的star数
print('Repository:', repo_dict['html_url'])
print('Created:', repo_dict['created_at']) # 建库时间
print('UPdate:', repo_dict['updated_at']) # 最近更新时间
print('Description:', repo_dict['description'])
1.6 监视API的速率限制
大多数API都存在速率限制,即在特定时间内的可执行的请求数存在限制。
要获悉自己是否接近了GitHub的限制,可以输入如下网址查看
https://api.github.com/rate_limit
将看到如下响应
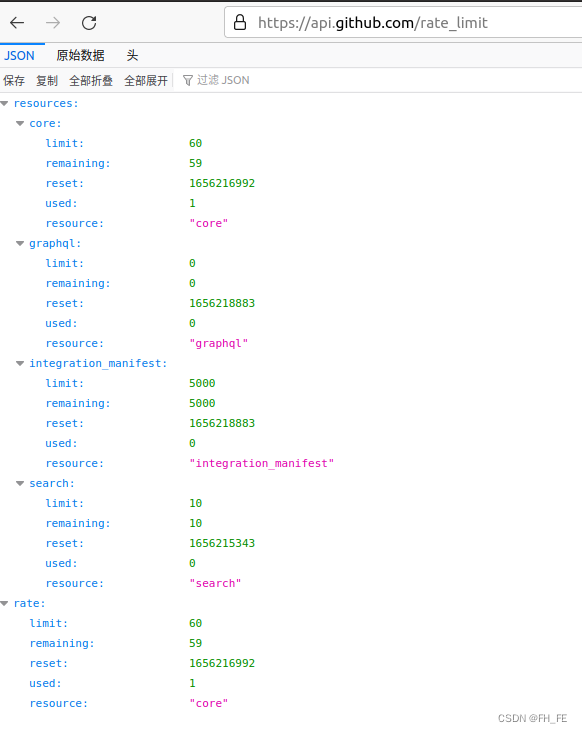
我们关心的信息是搜索API的速度限制
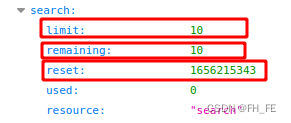
limit极限为每分钟10个请求
remaining当前这一分钟内还可再执行8个请求
reset配额将重置的时Unix时间或新纪元时间(1970年1月1日午夜后多少秒)
用完配额后,将收到一条简单的响应,由此知道已达到API极限。到达极限后必须等待配额重置。
注意:很多API都要求注册获得API密钥后才能执行API调用,GitHub没有这样的要求,但是获得API密钥后,配额将高得多。
2. 使用Pygal可视化仓库
python_repos.py
import requests
import pygal
from pygal.style import LightColorizedStyle as LCS, LightStyle as LS
# 执行API调用并存储响应
url = 'https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q=language:python&sort=starts'
# 将url传递给r,再将响应对象存储在变量r中
r = requests.get(url)
# 通过查看响应对象的一个status_code属性,知道了请求是否成功(状态码200表示请求成功)
print("Status code:", r.status_code)
# 将API响应存储在一个变量中(将返回的json格式信息转化为python字典)
response_dict = r.json()
print("Total repositories:", response_dict['total_count']) # 查看共有多少个仓库
# 探索有关仓库的信息
repo_dicts = response_dict['items'] # 每个与items相关的字典都包含一个有关python仓库的信息
# print("Repositories returned:", len(repo_dicts)) # 查看得到了多少个仓库的信息
names, stars = [], []
for repo_dict in repo_dicts:
names.append(repo_dict['name'])
stars.append(repo_dict['stargazers_count'])
# 可视化
my_style = LS # 使用LightenStyle类作为Bar的基本格式
chart = pygal.Bar(style=my_style, x_label_rotation=45, show_legend=False) #标签绕x轴转45度,并隐藏了图例
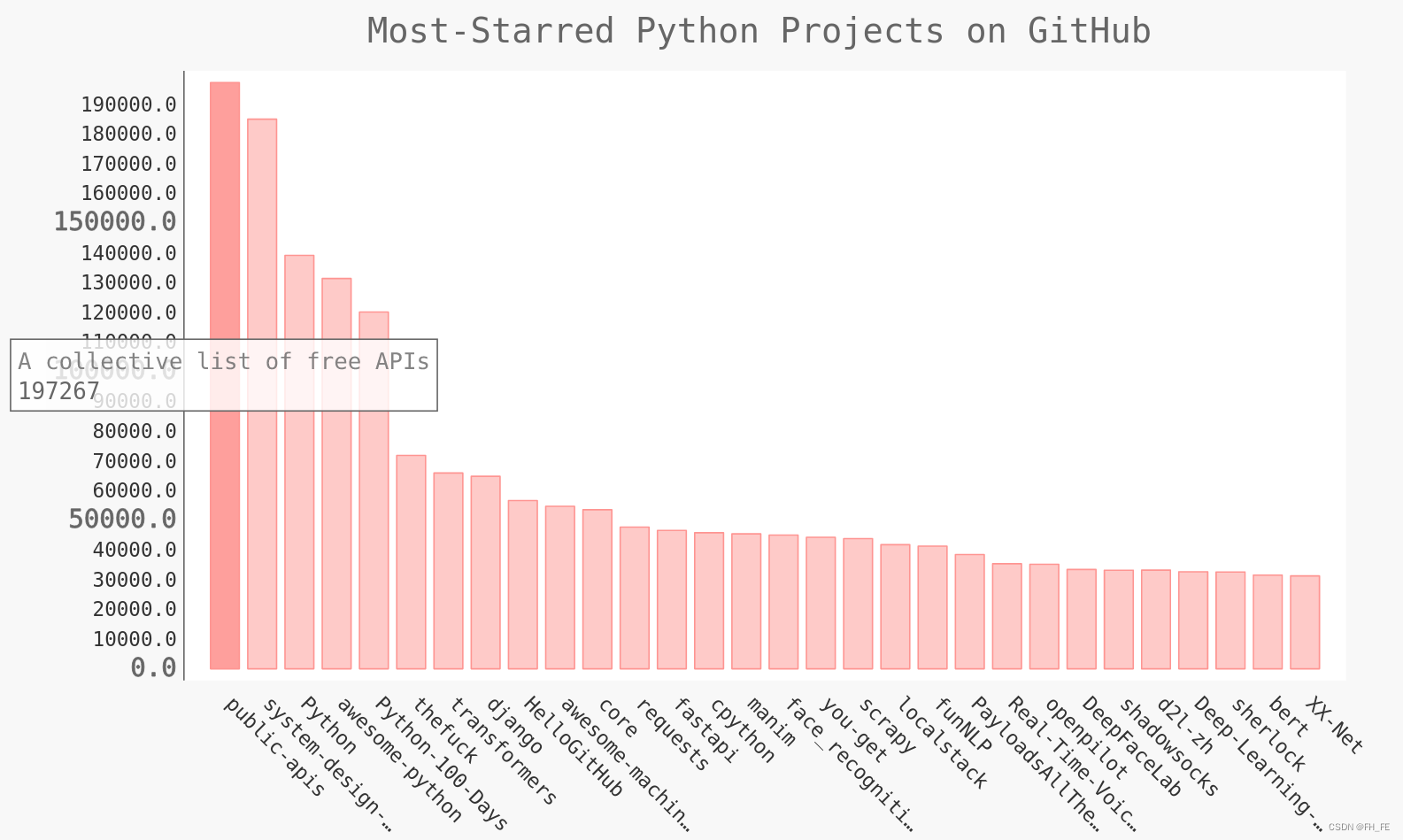
chart.title = 'Most-Starred Python Projects on GitHub'
chart.x_labels = names
chart.add('', stars) # 添加数据时,将标签设置为空字符串
chart.render_to_file('python_repos.svg')
用浏览器打开生成的python_repos.svg
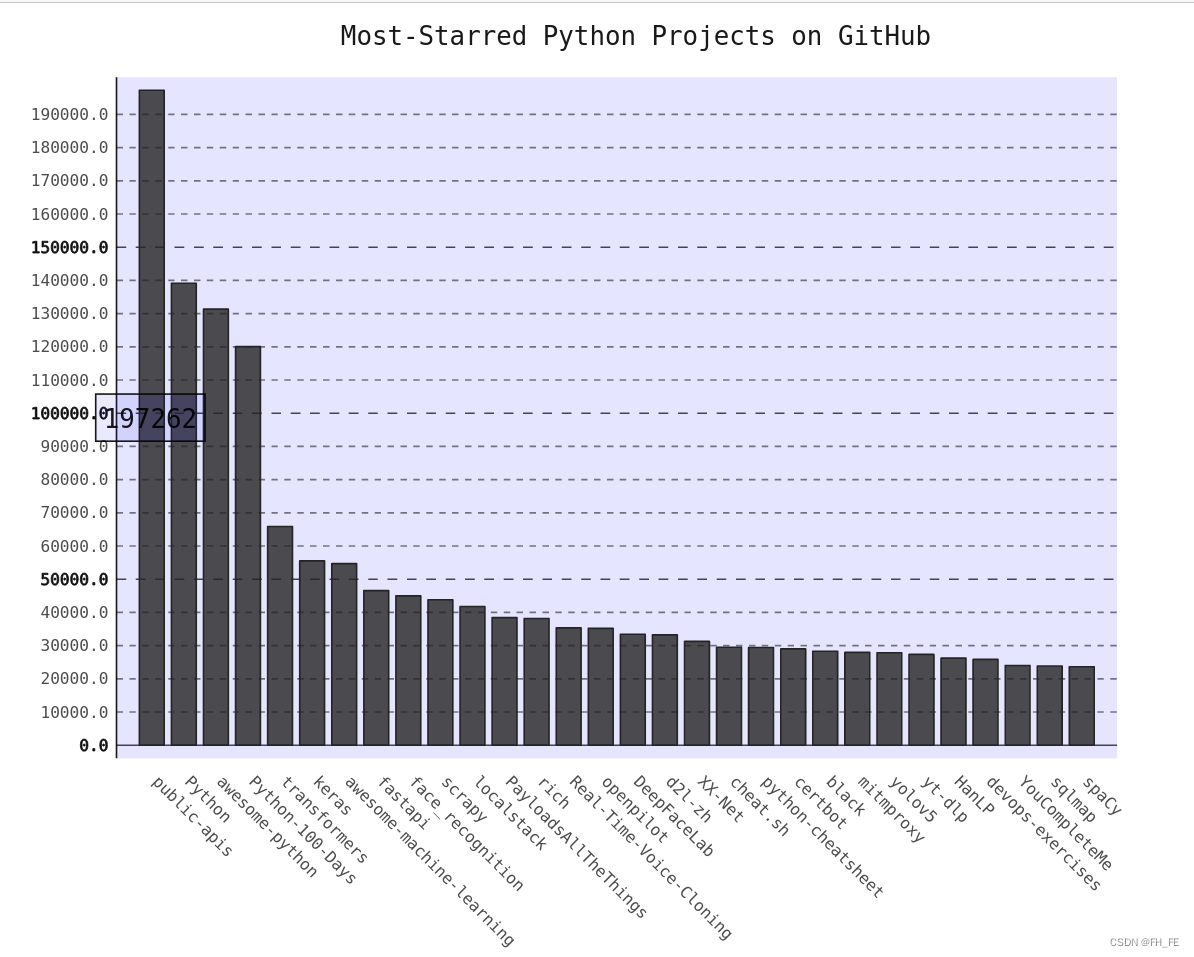
2.1 改进Pygal图表
设置图表标题,副标题和主标签的字体大小
副标题: x轴上的项目名称,以及y轴上的大部分数字
主标签: y轴上5000的整数倍刻度
truncate_label: 将较长的项目名缩短为15个字符(如果将鼠标指向屏幕上被截短的项目名,将显式完整的项目名)
show_y_guides: 设置为False,以隐藏图表中的水平线
import requests
import pygal
from pygal.style import LightColorizedStyle as LCS, LightStyle as LS
# 执行API调用并存储响应
url = 'https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q=language:python&sort=starts'
# 将url传递给r,再将响应对象存储在变量r中
r = requests.get(url)
# 通过查看响应对象的一个status_code属性,知道了请求是否成功(状态码200表示请求成功)
print("Status code:", r.status_code)
# 将API响应存储在一个变量中(将返回的json格式信息转化为python字典)
response_dict = r.json()
print("Total repositories:", response_dict['total_count']) # 查看共有多少个仓库
# 探索有关仓库的信息
repo_dicts = response_dict['items'] # 每个与items相关的字典都包含一个有关python仓库的信息
# print("Repositories returned:", len(repo_dicts)) # 查看得到了多少个仓库的信息
names, stars = [], []
for repo_dict in repo_dicts:
names.append(repo_dict['name'])
stars.append(repo_dict['stargazers_count'])
# 可视化
my_style = LS # 使用LightenStyle类,并设置基调为蓝色
my_config = pygal.Config() # 创建一个Pygal类Config的实例
my_config.x_label_rotation = 45
my_config.show_legend = True
my_config.title_font_size = 24
my_config.label_font_size = 14
my_config.major_label_font_size = 18
my_config.truncate_label = 15
my_config.show_y_guides = False
my_config.width = 1000
chart = pygal.Bar(my_config, style=my_style) #标签绕x轴转45度,并隐藏了图例
chart.title = 'Most-Starred Python Projects on GitHub'
chart.x_labels = names
chart.add('', stars) # 添加数据时,将标签设置为空字符串
chart.render_to_file('python_repos.svg')
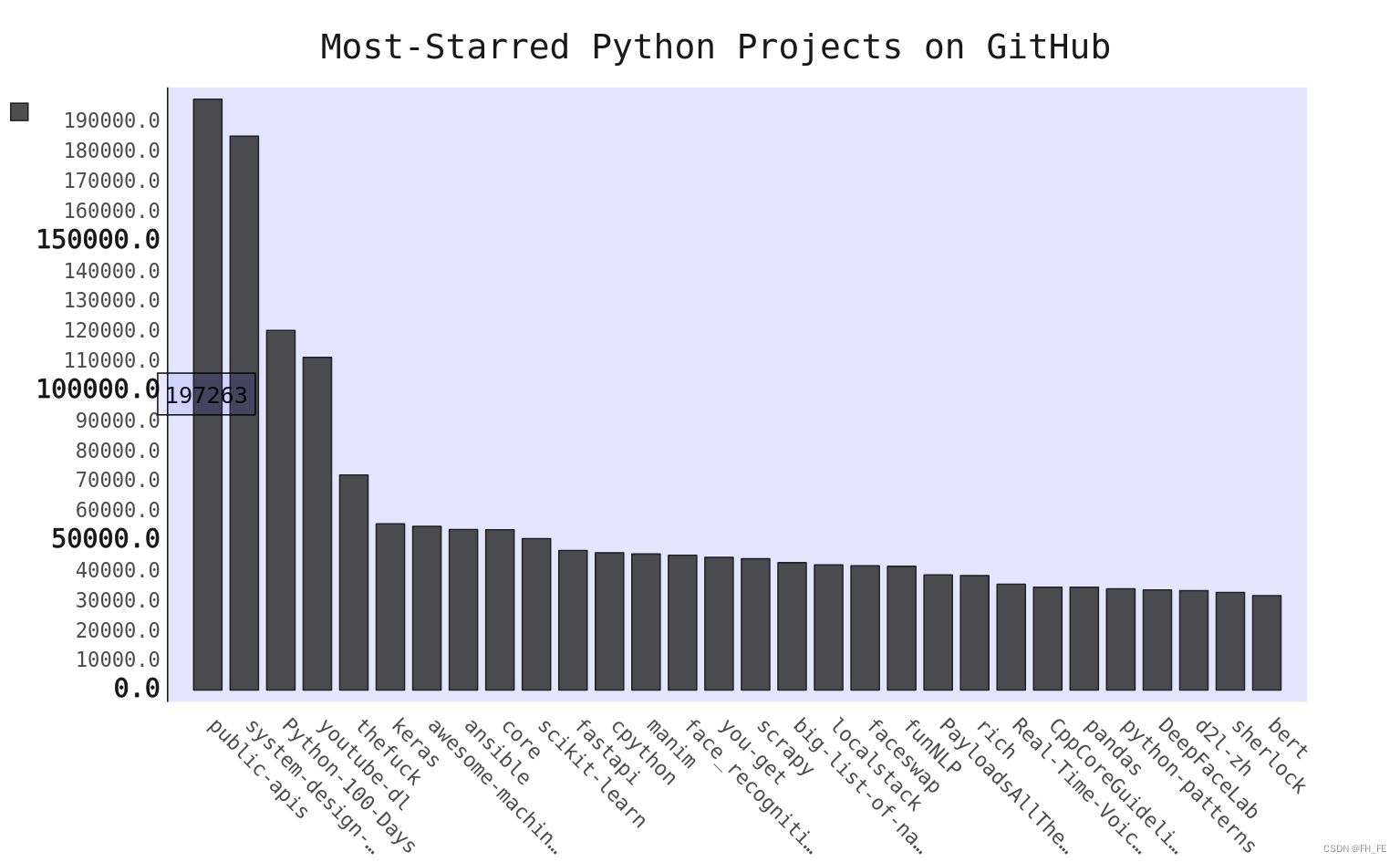
my_config.show_legend = False
隐藏图例
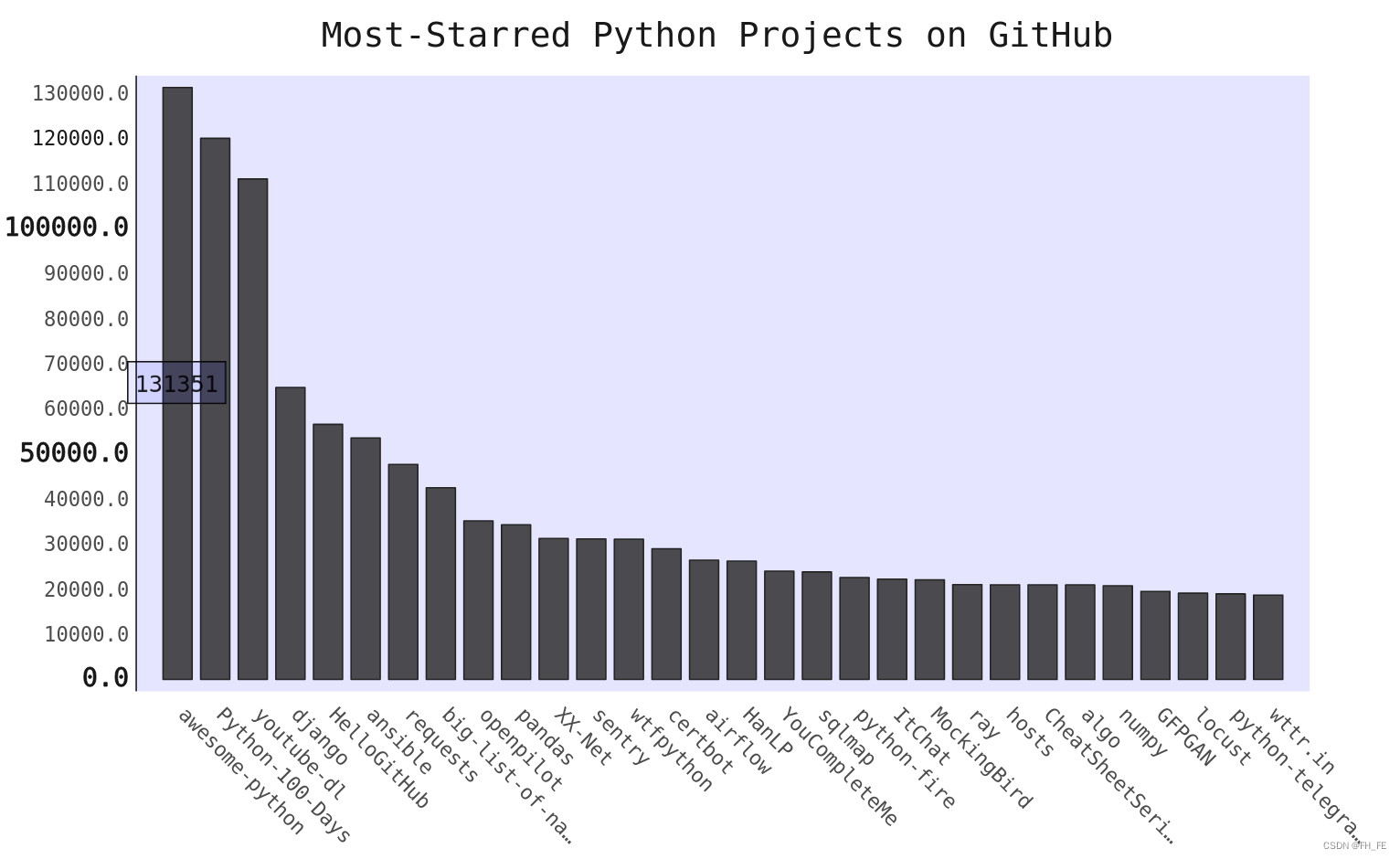
2.2 添加自定义工具提示
工具提示: 在Pygal中将鼠标指向条形,将显示它表示的信息
下面创建一个自定义工具提示,以显示项目的描述
bar_discriptions.py
import pygal
from pygal.style import LightColorizedStyle as LCS, LightStyle as LS
my_style = LS
chart = pygal.Bar(style=my_style, x_label_rotation=45, show_Legend=False)
chart.title = 'Python Projects'
chart.x_labels = ['httpie', 'django', 'flask']
plot_dicts = [
{'value': 16101, 'label': 'Description of httpie.'},
{'value':15028, 'label': 'Descripiton of django'},
{'value': 14798, 'label': 'Description of flask'},
]
chart.add('', plot_dicts)
chart.render_to_file('bar_descriptions.svg')
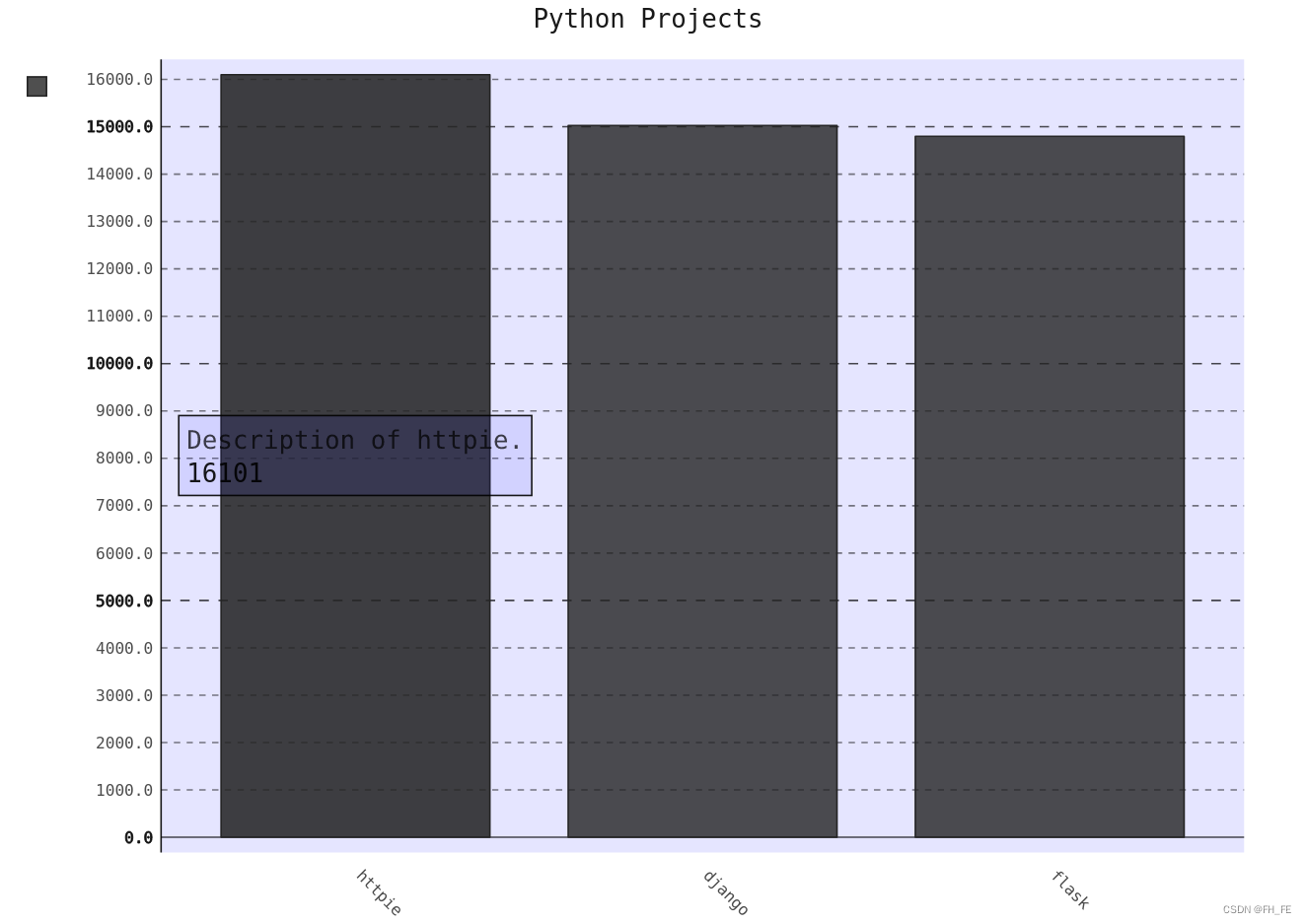
2.3 根据数据绘图
自动生成plot_dicts,其中包含API返回的30个项目
python_repos.py
# 探索有关仓库的信息
repo_dicts = response_dict['items'] # 每个与items相关的字典都包含一个有关python仓库的信息
print("Number of items:", len(repo_dicts)) # 查看得到了多少个仓库的信息
names, plot_dicts = [], []
for repo_dict in repo_dicts:
names.append(repo_dict['name'])
plot_dict = {'value': repo_dict['stargazers_count'], 'label': repo_dict['description']}
plot_dicts.append(plot_dict)
# 可视化
my_style = LCS # 使用LightenStyle类,并设置基调为蓝色
--snip--
chart = pygal.Bar(my_config, style=my_style) #标签绕x轴转45度,并隐藏了图例
chart.title = 'Most-Starred Python Projects on GitHub'
chart.x_labels = names
chart.add('', plot_dicts) # 添加数据时,将标签设置为空字符串
chart.render_to_file('python_repos_bar_descriptions.svg')
2.4 在图表中添加可单击的链接
Pygal允许将图表中的每个条形用作网站的链接,只需要在为每个项目创建的字典中,添加一个键对‘xlink’:
python_repos.py
--snip--
names, plot_dicts = [], []
for repo_dict in repo_dicts:
names.append(repo_dict['name'])
plot_dict = {'value': repo_dict['stargazers_count'],
'label': repo_dict['description'],
'xlink': repo_dict['html_url'],
}
plot_dicts.append(plot_dict)
--snip--
此时打开图表,再单击每一个条形,都会在新的窗口中跳转到对应github项目地址!
3. Hacker News API
为探索如何使用其他网站的API调用,我们来看看Hacker News(http://news.ycombinator.com/)。
在Hacker News网站,用户分享编程技巧方面的文章, 并就此展开积极的讨论。Hacker News的API让你能够访问有关该网站所有文章和评论的信息,且不要求你通过注册获得密钥。
https://hacker-news.firebaseio.com/v0/item/9884165.json
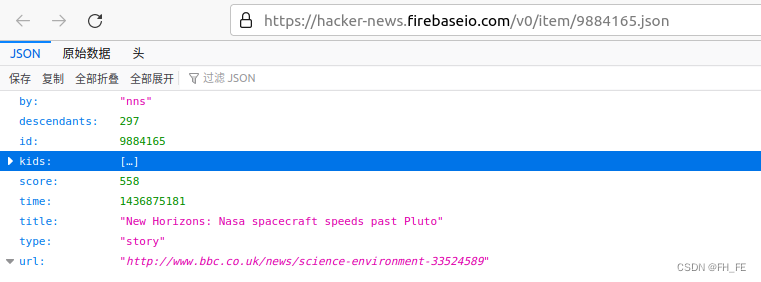
响应是一个字典,包含ID为9884165的文章信息
import requests
from operator import itemgetter
# 执行API调用并存储响应
url = 'https://hacker-news.firebaseio.com/v0/topstories.json'
r = requests.get(url) # 其中包含了Hacker News上当前最热门的500片篇文章的ID
print("Status code", r.status_code)
# 处理有关每篇文章的信息
submission_ids = r.json()
submission_dicts = []
for submission_id in submission_ids[:30]:
# 对于每篇文章,都执行一个API调用
url = ('https://hacker-news.firebaseio.com/v0/item/' + str(submission_id) + '.json')
submission_r = requests.get(url)
print(submission_r.status_code) # 判断请求状态是否成功
response_dict = submission_r.json()
submission_dict = {
'title': response_dict['title'],
'link': 'http://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=' + str(submission_id),
'comments': response_dict.get('descendants', 0) #当评论数为0时,就没有comments这一项
}
submission_dicts.append(submission_dict)
submission_dicts = sorted(submission_dicts, key=itemgetter('comments'), reverse=True)
for submission_dict in submission_dicts:
print("\nTitle:", submission_dict['title'])
print("Discussion link:", submission_dict['link'])
print("Comments:", submission_dict['comments'])
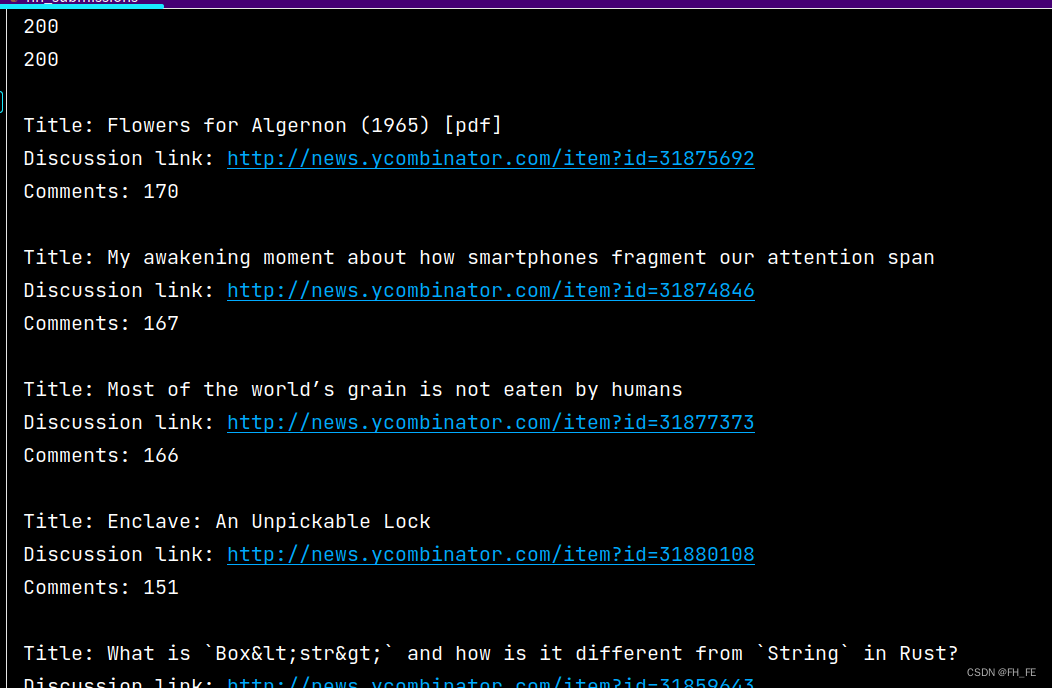
使用任何API来访问和分析信息时,流程都与此类似。有了数据后,就可以进行数据可视化了。