Today
目录
Course Goals
·Introduction to computer science and software development
·Present methods for problem solving
·Acquiring Python 3 programming skills
Learning and understanding tools for problem solving using a computer in science and engineering.
?
Motivation
Why do I need this?How would this course benefit me?
?
Problem Solving

Mathematics, Statistics
Monte Carlo Method – Using randomness in problem solving
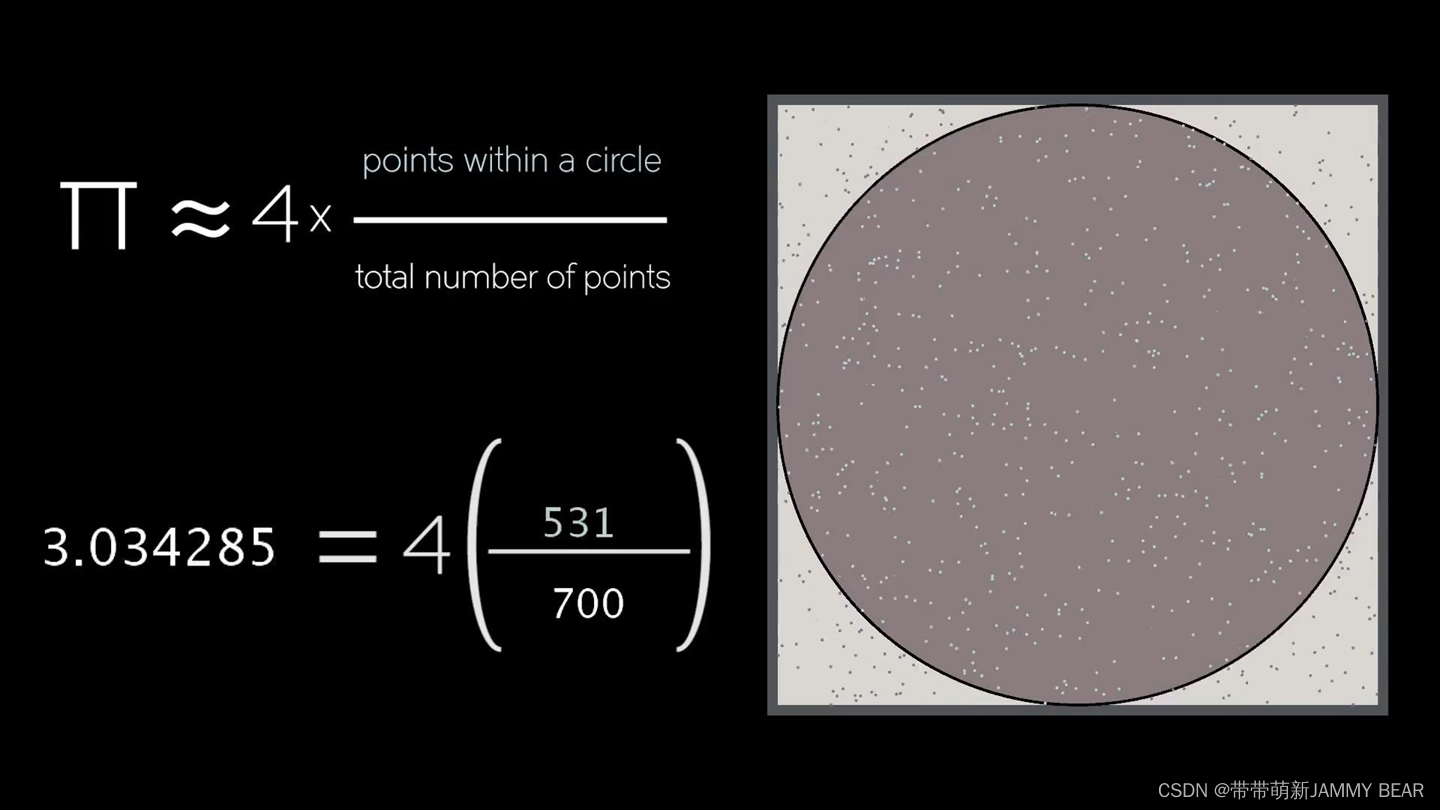 ? ??
? ??

Data Visualization?

?
Physics: DEM and CFD
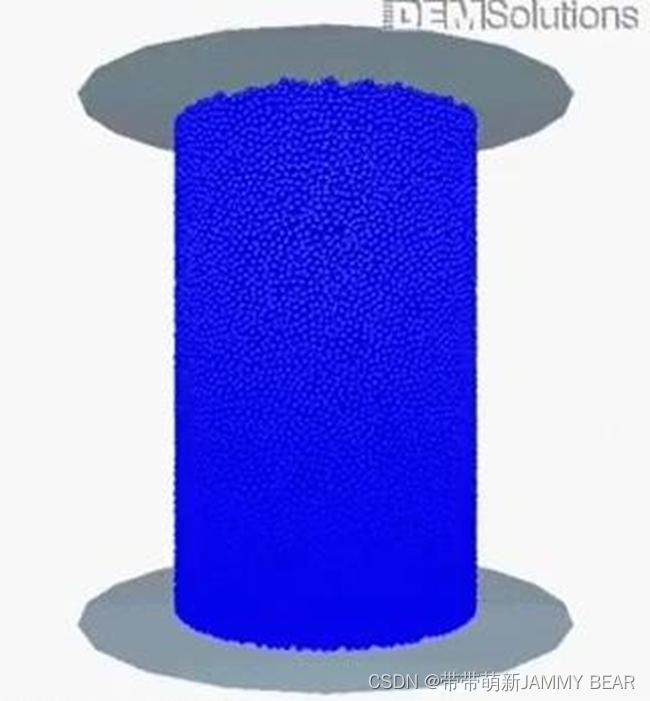
Discrete Element Method (DEM) for simulating structural failure?
 Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulation?for evaluating air velocity around a cyclist
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulation?for evaluating air velocity around a cyclist
Physics: Evolution of a Cough

?
 ?
?
Biology: Protein Folding

?
Neural Style Transfer

?Machine Learning
Genetic Algorithms (GA) are a mathematical model inspired by the famous Charles Darwin’s idea of natural selection. The natural selection preserves only the fittest individuals, over the different generations.

 ?
?
WHAT IS A COMPUTER??
Where did it All Begin?
- Historically, there was always a need to make calculation? faster and more accurately.
- Abacus:
- Better than counting fingers
- “Remembers” results
- Can be used for: × ÷ + ?
- Origin: China
 ?
?
?
Mechanical Calculator
- Blaise Pascal - Famous French scientist. Made significant discoveries in the fields of Physics and Mathematics.
- Invented in 1642 (aged 19) the “Pascalin”: a mechanical calculator for addition and subtraction.
 ?
?
?Mechanical Computer

- Charles Babbage’s “Difference Engine” – 1822, built after his death.
- Calculation speed: 12 operations per minute!



- In 1833, together with Ada Lovelace (historically, the first “computer programmer”) invented an “analytical engine” capable of running instructions based on punch-cards.
- A computer is a device that manipulates information or data.
- Can receive input, perform calculations and display or store the results.
- Does exactly what it is instructed to do, not less and not more.
- Can be mechanical or electronic.
?
?Hardware and Software
Hardware:
? ? ?The physical components of a computer
? ? ?Inside the computer:
Processor (CPU), memory, GPU.
? ? ?Outside the computer:
Mouse, keyboard, display, speakers
? ? ?Software:![]()
![]()

![]()

? ? ?Sequence of commands that use the hardware.
?
?HARDWARE COMPONENTS
?CPU – ? Central Processing Unit
- The main component responsible of computation (Central Processing Unit)
- Receives commands for processing:
- Arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.)
- Input/output operations (reading memory)
- Evaluating conditions (if some condition met, then do something)
 ?
?

?
?Memory
The Memory is a special hardware component in which the CPU can read from and write to.
Difference between types of memory:
- Capacity – how much information can be stored.
- Mobility – memory is connected permanently or can be used between different computers.
- Survivability – information is stored or deleted after turning off the machine.
- Price.
Main Memory - RAM?
- Fast
- Expensive
- Compact (compared to secondary memory)
- Common Capacity: 4GB, 8GB, 16GB, 32GB
 ?
?
?
?Secondary Memory
- Slow
- Cheap
- Higher capacity: 1TB - 12TB
 ?
?

?
?
 ?
?
 ?
?
?
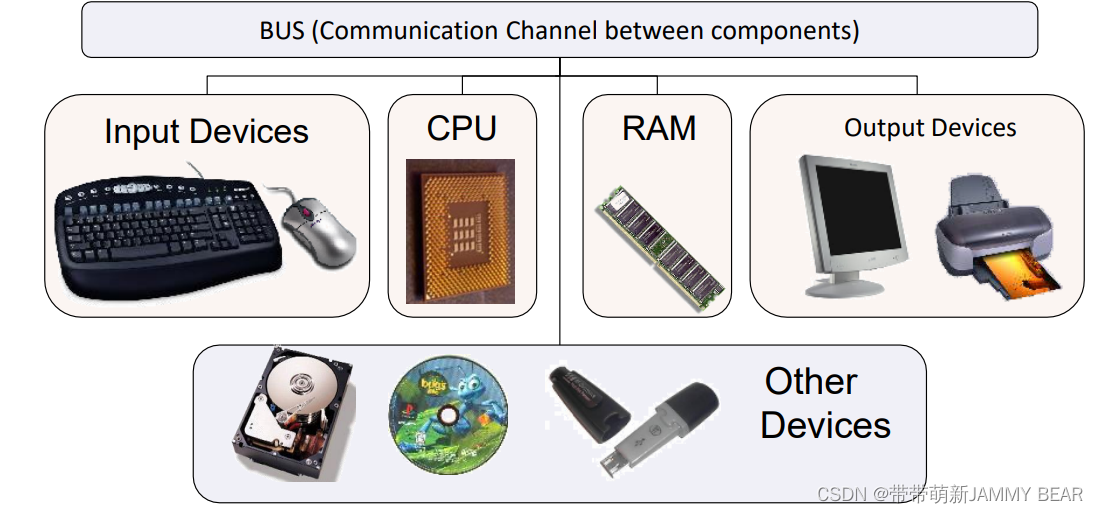
Communication? Channel? (BUS)?
- Different hardware uses the same communication channel to pass information.
?
OPERATING SYSTEM?
?
- The “glue” between hardware and software
- Passes information
- For example: reading words from a file stored in memory
- Passes commands:
- For example: command to present an image on the screen
?

?Operating System: Example
What happens when you type the string “Hello” in a Word document?
- The Keyboard recognizes a keystroke
- The Keyboard passes the corresponding character to the Operating System
- The Operating System passes the character to the Word Application
- The Word Application sends via the Operation System a request to display the types character.
- The Operating System passes the request to the Display
?

?
DATA IN MEMORY
What is Data?
- Anything we would like to store
- Images
- Music
- Movies
- Documents
- Computer code, software, applications
- The operating system, Microsoft Office, drivers
How is Data Stored??
- We all know that computers need power.
- How can we use that power to represent data?

?
?
- Computer memory is made of ones (1) and zeros (0) which are called bits. Generally, 0 is represented by low voltage and high voltage represents 1.
- Different types of data are stored using encoding.
- Binary encoding – using sequences of bits to store more complicated types of data.
 ?
?
?
?Base-10 Number Representation
?
- The numeral system we use since ancient civilizations. Likely since there are ten fingers on two hands.
- Each digit has 10 possible values: 0-9
-

- Exercise:
What is the representation of 452 in powers of 10?
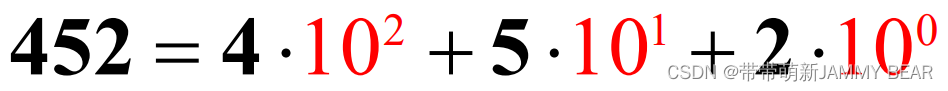
?
Base-2 Number Representation?
?
?
?
Binary System?
- Each bit is given different weight based on location.
- This is known as the Binary System (base 2).
- In binary, instead of using powers of 10 to define the “weight” of a digit, we use powers of 2:
 ?
?
?
- It is possible to represent any number in this system.
Binary Number Representation
 ?
?
?More Examples
 ?
?
?
?Byte
- For sake of simplicity, a sequence of 8-bits is referred to as a single Byte.
- A Byte can get 256 different values. These values are 0-255.
 ?
?
?
?Numbers in Memory
- Bit is the smallest unit of memory inside a computer. A bit represents a binary digit.
- Byte is a unit composed of 8 bits.
- Every piece of information is stored as a sequence of ones and zeros. Whole numbers are represented in Binary as discussed before.
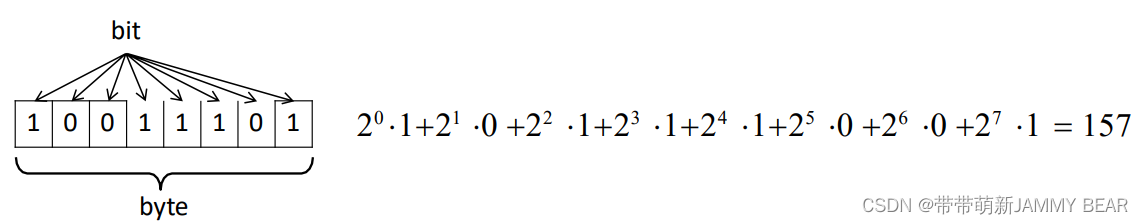
 ?
?
 ?
?
?Other Types of Data
- Thus far we discussed representation of numbers inside the computer.
- How can we represent other types of data in a computer?
?

?
Images?
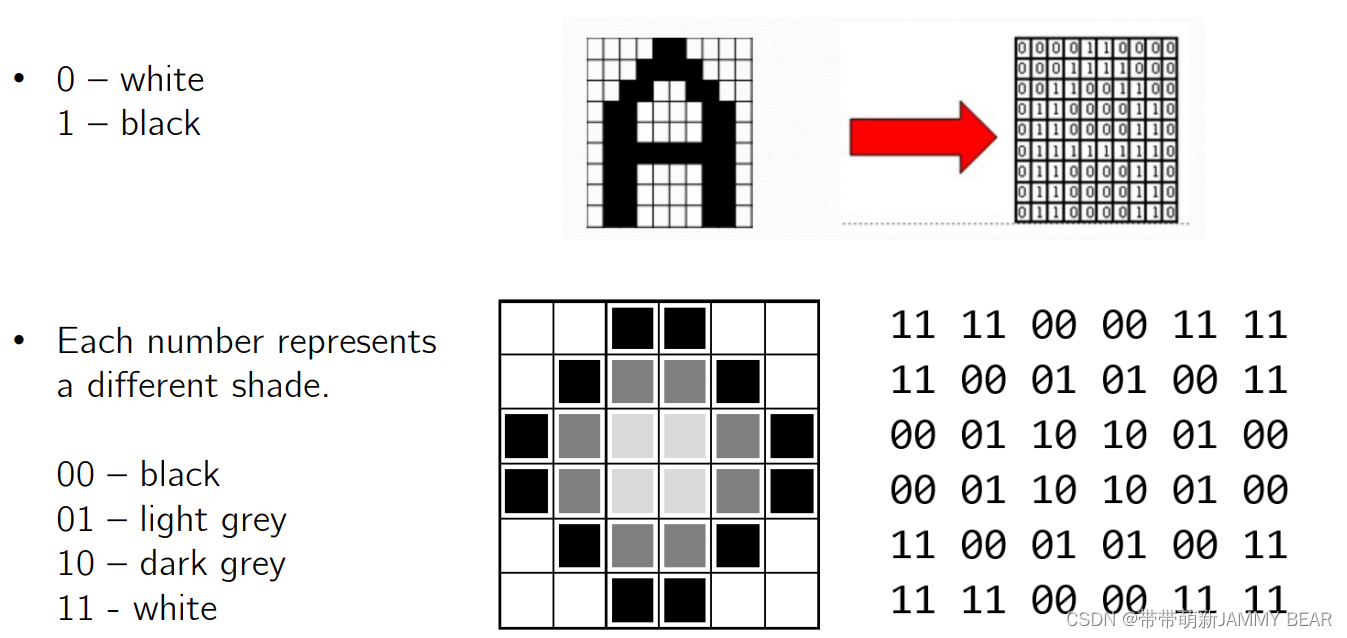
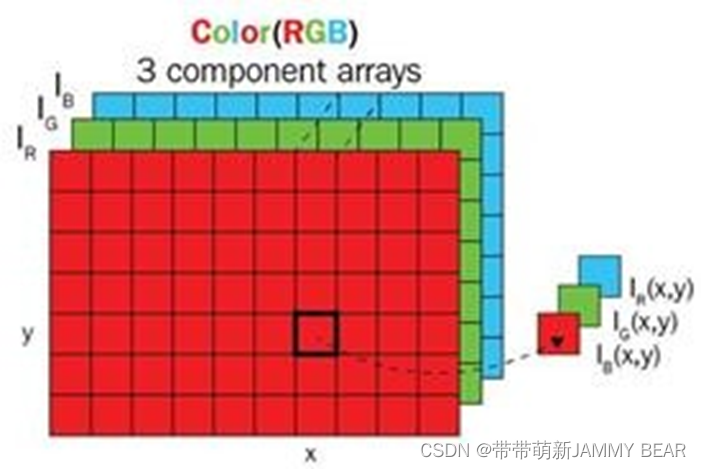
?Images - RGB?
- Each number represents a different color or shade: 0 – black, 255 - white
 ?
?
?
?Music
- Each number represents different note pitch and length
?
?
?Most Important – ?Code!
- It is possible to represent different commands using binary encoding. For example:
0 – read a number from memory 1 – add two numbers
01 – write number to memory 10 – subtract two numbers
- Each CPU has its own “language” – numbers that resemble CPU operations.
This is called Machine Code.
- This is the only language a processor can “understand”.
PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES?
Machine Code
- Machine code is the language in which hardware uses for communication.
- Operations such as writing\reading from memory, multiplication, etc.
- It is incredibly difficult to write software in machine code.
- This is easy for a computer, hard for a human.
 ?
?
High-Level Programming Language?

- High-Level Programming Languages allow us to write programs in an easier and more human-readable way.
- There are special tools that translate high-level code into lower-level code or machine code so that the computer will understand what operations it needs to execute.
- We will use a high-level programming language called Python 3.
?
?
A program that displays the text “Hello World!” in different programming languages:
- In C:
 ?
?
- In Java:
 ?
?
?
- And now in Python:
print(‘Hello world!’)
?
PYTHON 3
Simple Example

- Code:

- Output:
 ?
?
?
STEPS IN PROBLEM SOLVING
Problem Solving: The Steps
- Understand the problem. Identify the Input à Output

- Design an algorithm (a recipe) to? solve it
- Start coding
?
?
?
Problem Solving: Cashier?
Example:
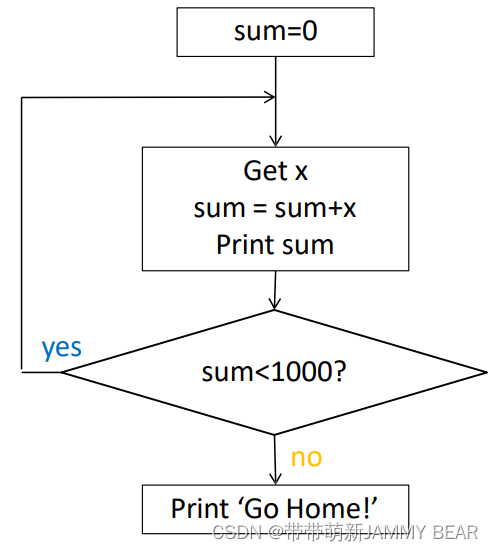
Write a program which receives a series of purchases, prints the current total and tells the cashier to go home when the total reaches over $1000.
?Problem Solving: Algorithm
? ? ?1.Define a counter which keeps track of the current sum.
? ? ?2.Get the cost as input? Add the cost to the sum Display the sum
? ? ?3.If the sum is smaller than $1000, repeat
?????4.If not, display “Go Home!”
?
?
Problem Solving: Code
 ?
?
?
?Actual Coding and Debugging?
Soon….

?

?