Today?
?? ? ?Constants, Variables, Identifiers
? ? ? Types
? ? ? Type Casting
? ? ? Expressions, Operators
? ? ? Assignments, Statements
CONSTANTS, VARIALBES, IDENTIFIERS?
Reminder: Cashier Program?
? ? ? Write a program which receives a series of purchases, prints the?
current total and tells the cashier to go home when the total reaches?
over $1000.?
1. ?Define and initialize a counter, which keeps track?
of the current sum.
2. ?While the counter did not reach 1000:
????????1. ?Get the cost as input
????????2. ?Add the cost to the sum
????????3. ?Display the sum
3. ?Display “Go Home!”?
sum = 0
while sum < 1000:
x = int(input("Enter cost: "))
sum += x
print("Current Total:", sum)
print("Go Home!")?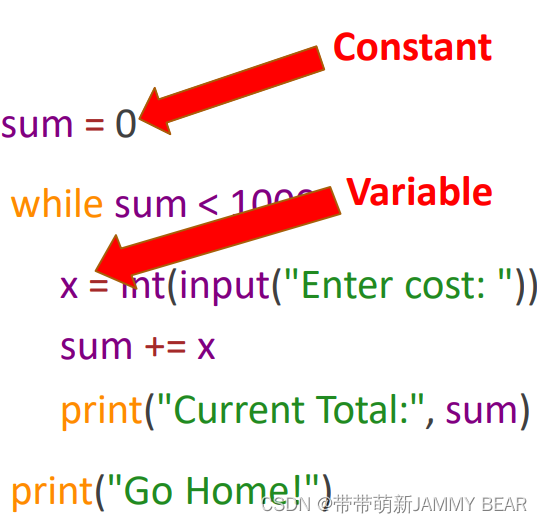
Elements of Code: Constants?
? ? ? Number:
????????? 5
????????? -10
????????? 17.5
? Boolean:
????????? True
????????? False?
?? ? ? String:
????????? “Hello World”
????????? ‘Some String’
?? ? ? List:
????????? [1, 2, 3]
????????? [‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’]
Constants: Examples?
sum = 0
while sum < 1000:
x = int(input("Enter cost: "))
sum += x
print("Current Total:", sum)
print("Go Home!")
Elements of Code: Variables?
? Holds a value inside
? Its contents can be changed (variable – it “varies”)?
Variables: Examples?

? Note: each variable is marked the first time it appears in the code.?
Elements of Code: Identifiers?
? Refers to components inside the code, like a name.
? Enables us to use the component.
? Examples to such components:
????????? Variables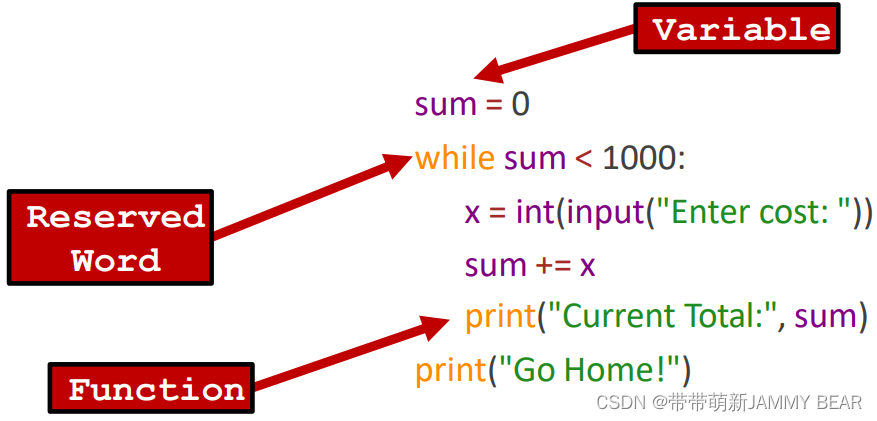
????????? Reserved words
????????? Functions?
Reserved Words: Examples?
Constants, Variables, Identifiers?
>>> a = 3?
>>> b = 1?
>>> c = 9?

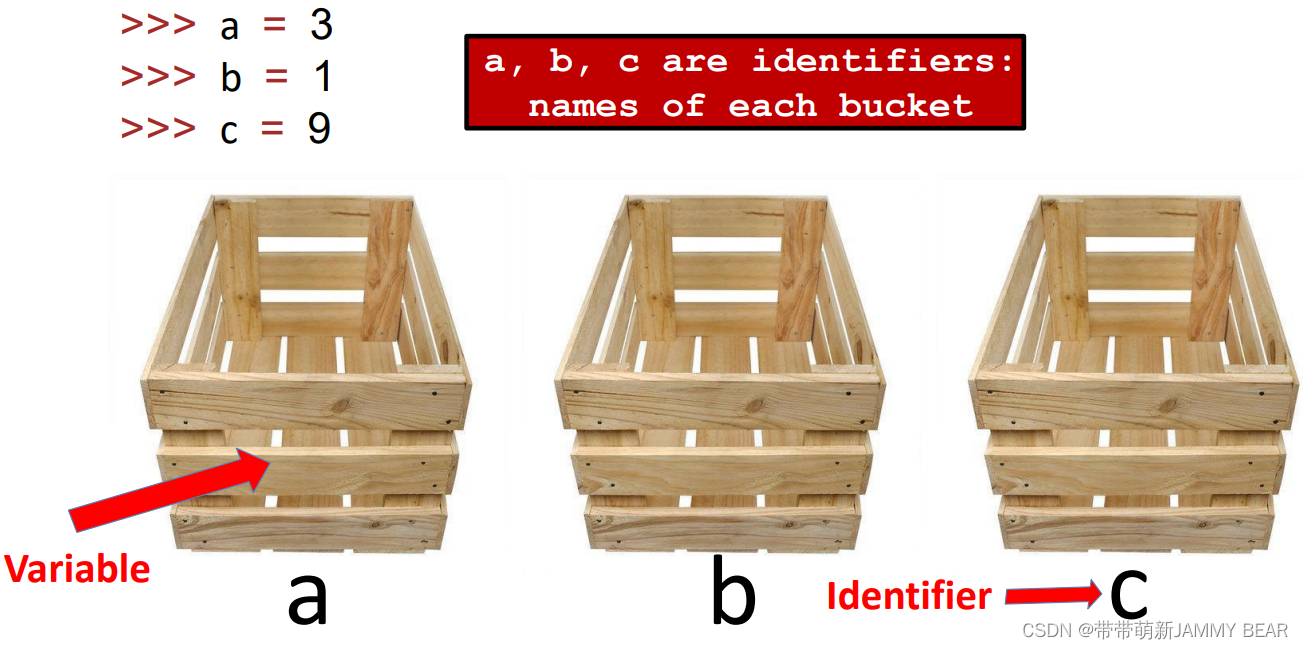
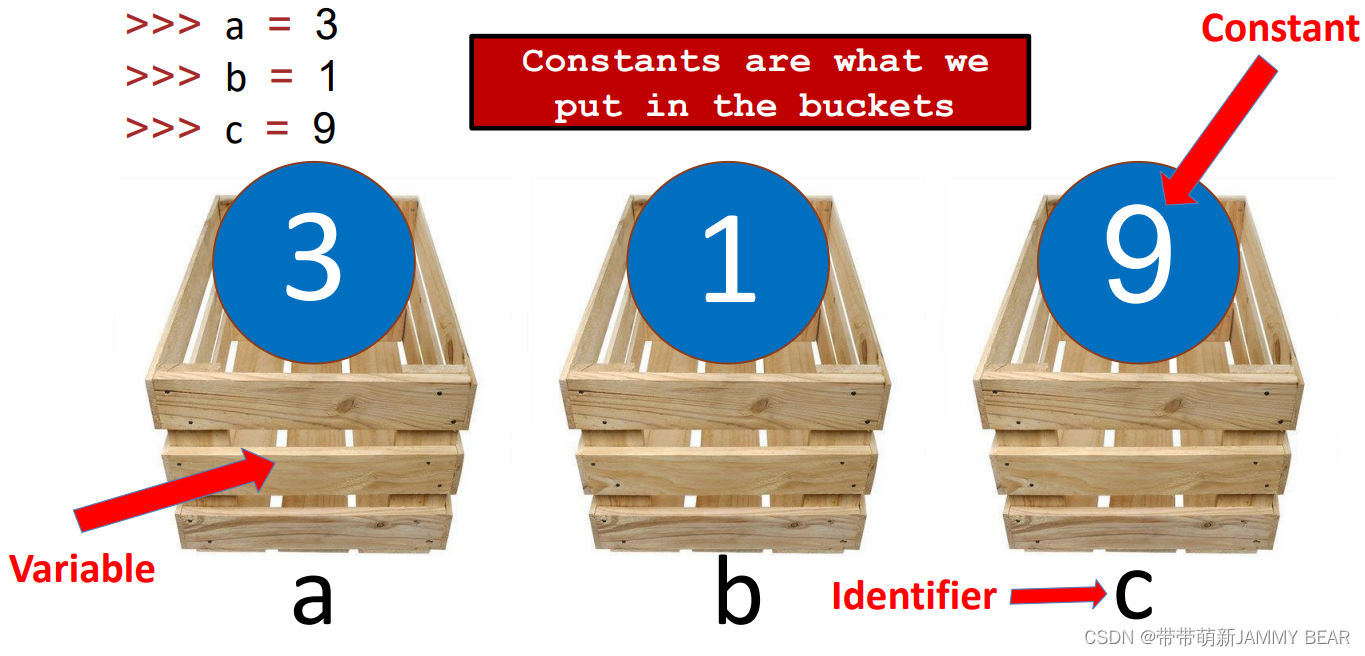
Rules for Identifiers?
?Identifiers are like names, but not every name is acceptable.?
Rules for Identifiers in Python 3:
1. Must contain non-empty sequence of characters.
2. Only English letters (lowercase or UPPERCASE), digits or?
underscore (_)
3. Cannot start with a digit
4. Cannot be a reserved word
Identifiers: Examples?

Meaningful Identifiers?
? It is important to give meaningful names for identifiers.
? ? ? Good naming will help make your code more readable!
? ? ? Compare these examples:
t = p * tr?
sA = gr + fff
tax ?= ?price * tax_rate
grade_of_semester_A = test_grade + factor?
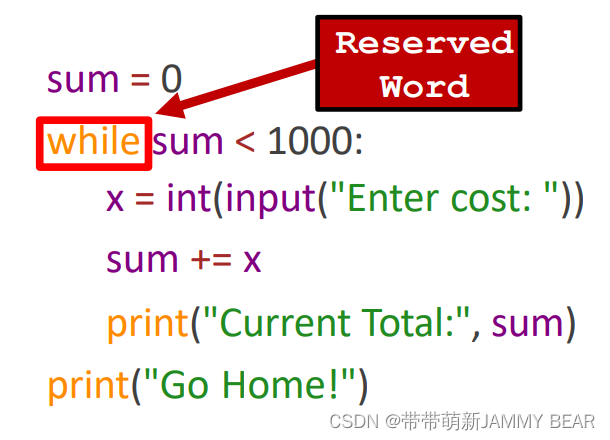
Reserved Words??
? These are special identifiers reserved for built-in Python components.
? Cannot be used as identifiers for variables!?
? ? ? These special keywords are a part of the Python language and?
cannot be used as identifiers:
>>> False = 4
File "<stdin>", line 1
SyntaxError: can't assign to keyword
TYPES?
? ? ? Every value in Python has a Type.?
????????>>> type(5)
????????int
????????>>> type("Hello World")?
????????str
????????>>> type(True)?
????????bool
????????>>> type(1.0)?
????????float
? ? ? What is a type in Python?
? ? ? The type defines what are the relevant operations that can be done?
with the value:
????????>>> 5 * 5?
????????25
????????>>> 'hi' * 5?
????????'hihihihihi'?
????????>>> 'hi' * 'hi'
????????Traceback (most recent call last): ?File?
????????"<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
????????TypeError: can't multiply sequence by non-int of type 'str'
????????>>> 'hi' + 'hi'?
????????'hihi'
????????>>> 5 + 'hi'
????????Traceback (most recent call last): ?File?
????????"<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
????????TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for +: 'int' and 'str'????????
Type Casting?
? ? ? Python has special functions that convert values from one type to?
another. This explicit way of changing the type of a value is called Type?
Casting.
? ? ? Examples:
>>> ? int('17')?
17
>>> ? str(20)?
'20'
>>> ? float(1)?
1.0
>>> ? int(2.5)
2
>>> ? int(2.3)
2
>>> ? str(float(1))?
'1.0'
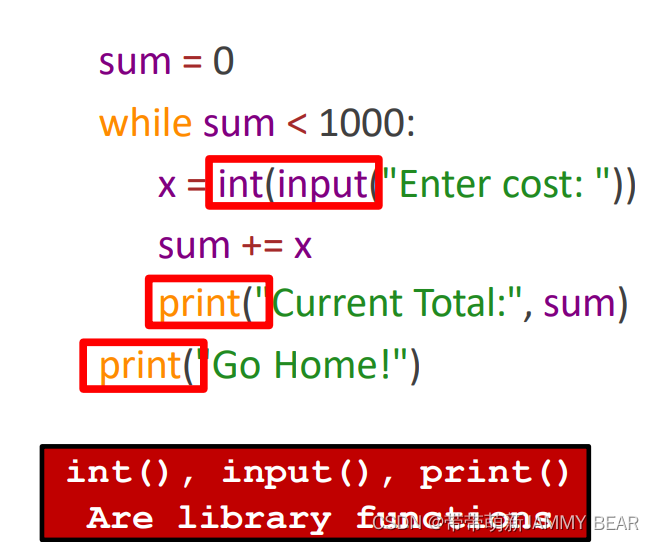
? ? ? We saw that already. Back to our Cashier problem:

? ? ? The input function always receives a string as keyboard input from?
the user. Type casting is used to convert the string to a number we can?
add to sum.?
Types and Variables?
?? ? ? A variable at one point can store a value of one type and later store?
a value of another type:
????????>>> x = 5?
????????>>> type(x)?
????????int
????????>>> x ?= "hello"?
????????>>> type(x)?
????????str
PYTHON TYPES?
Integer
? ? ? Integers (whole numbers) are numbers without fractions.
? ? ? Integers are represented in Python by the type int.
? ? ? In contrast with other programming languages, there isn’t a limit on?how large a number you can store in Python (apart for the size of?computer memory…)
>>> 2**300
203703597633448608626844568840937816105146839366?
5936250636140449354381299763336706183397376?
Float?
? ? ? Real numbers are stored as type float.
? ? ? The representation of these numbers in memory is implemented by?the Floating-Point ??????Method.
? ? ? Does not guarantee to always be 100% accurate:?
?
Complex Number?
? ? ? Python also supports Complex Numbers.
? ? ? Those numbers are of type complex.
? ? ? Defined with the letter j (lower or uppercase).
? ? ? All the relevant arithmetic operations are implemented in Python:?
????????>>> x = 2 + 7j
????????>>> (1+2j)* (2+3j)?
????????(-4+7j)
String?
? ? ? A String is a sequence of characters.
? ? ? Each character is represented by a special numerical value according?to the Unicode ??????Standard. Will be discussed later in the course.
? ? ? Python identifies strings by double quotes and single-quotes:
? ? ? ?Double Quotes: ? my_string = “Hello”
? ? ? ?Single Quotes: ? ? my_string = ‘hello’?
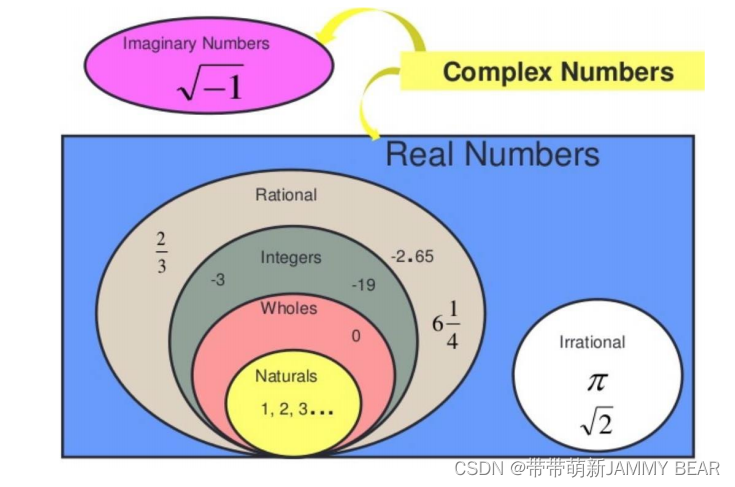
?Basic Python Types
? ? ? Numbers:
? ? ? int – whole numbers
0, 1, 2, 5, 10, 100, 2352, -100….
? ? ? float – real numbers?
4.3, 0.5, 4e7, .4
? ? ? complex – complex numbers?
0j, 2+8j, 1j, 1J
? ? ?Strings:
? ? ? ‘I am a string’
? ? ? ‘‘
? ? ? “Another string ? ?“
EXPRESSIONS, OPERATORS?
?Expressions
?? ? ? For expressions we can use constants, variables and operators.
? It is possible to create complex expressions by combining multiple?operators:
????????7
????????‘this_is_a_string’?
????????y=x+9
????????x=3
? ? ? There are different types of operators:?
? ? ? ?Unary:????????-x
? ? ? ?Binary:????????a*b
? ?????Trinary:? ? ? ?a if (a>0) else -a
Arithmetic Operators?
?? ? ? Operators on numbers: +, -, *, /
? ? ? Contrary to many other programming languages, dividing two?numbers always returns a real? ? ? ? ?number (float).? ?
????????>>> ? x ?= ?4/2?
????????2.0
????????>>> ? type(x)?
????????<class ? ?'float'>?
????????>>> ? 7/4
????????1.75?
Special Arithmetic Operators?
? ? ? Power operator: **?
>>> ? 2**7?
128?
? Modulo – operator for remainder of division: %?
>>> ? 128 ? % ?10?
8
>>> ? 11 ? ? % ? ?3?
2?
? ? ? Floor division – operator for rounded-down division: //?
>>> ? 7/4?
1.75
>>> ? 7//4?
1?
?Arithmetic Operators Priority
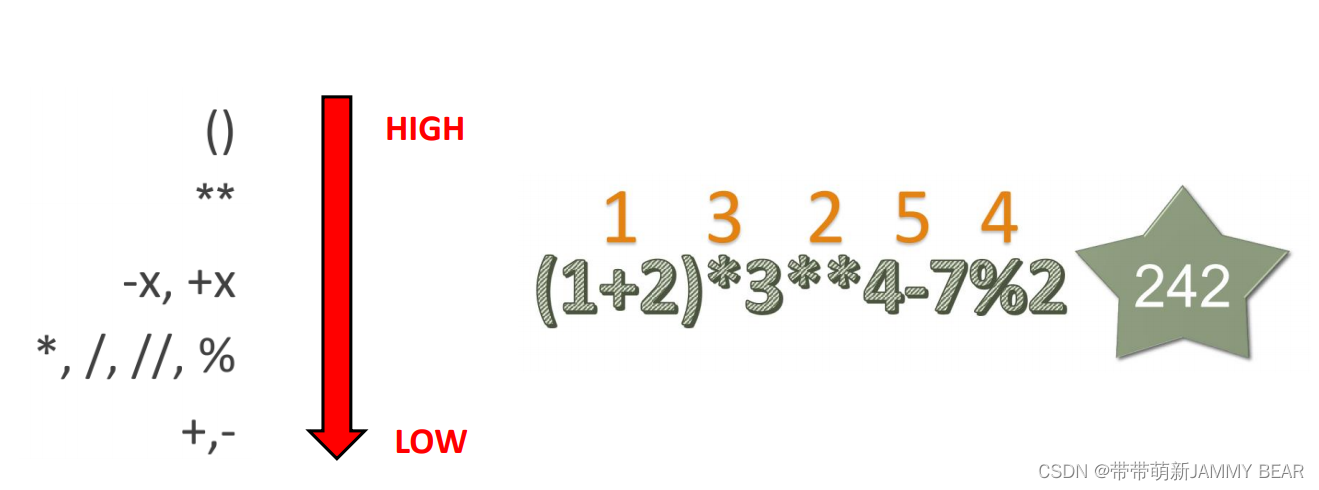
ASSINGMENT, STATEMENTS?
Assignment Operator?
?? ? ? The value of the expression on the right is saved in the variable on?
the left.
????????>>> ? x ?= ?3
????????>>> y = x + 9?
? ? ? First, the expression on the right is evaluated. Then it is saved in the?
variable on the left.?
????????>>> ? y ?= ?y ?+ ?3?
? ? ? Assignment can appear more than once in an expression.?
For example, all variables get the same value of 0:?
????????>>> ? a ?= ?b ?= ?c ?= ?0?
Assignment?
? ? ? Special syntax for combining assignment with an arithmetic?
operation:?

Exercise: Solution?
Write a program which receives a 3-digit number as input from the user?
and calculates the sum of its digits.?
????????>>> dsum ?= 0
????????>>> x = int(input("Enter a number between 100 and 999"))?
????????>>> dsum ?+= x%10
????????>>> x //= 10
????????>>> dsum ?+= x%10?
????????>>> x //= 10
????????>>> dsum ?+= x%10?
