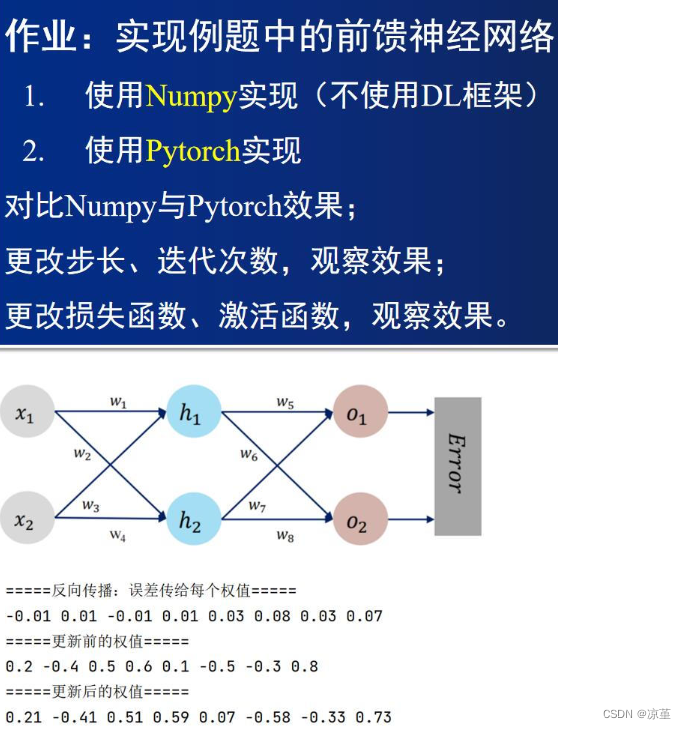
目录
1、对比【numpy】和【pytorch】程序,总结并陈述。
2、激活函数Sigmoid用PyTorch自带函数torch.sigmoid(),观察、总结并陈述。
3、激活函数Sigmoid改变为Relu,观察、总结并陈述。
4、损失函数MSE用PyTorch自带函数 t.nn.MSELoss()替代,观察、总结并陈述。
7、权值w1-w8初始值换为随机数,对比“指定权值”的结果,观察、总结并陈述。
题目
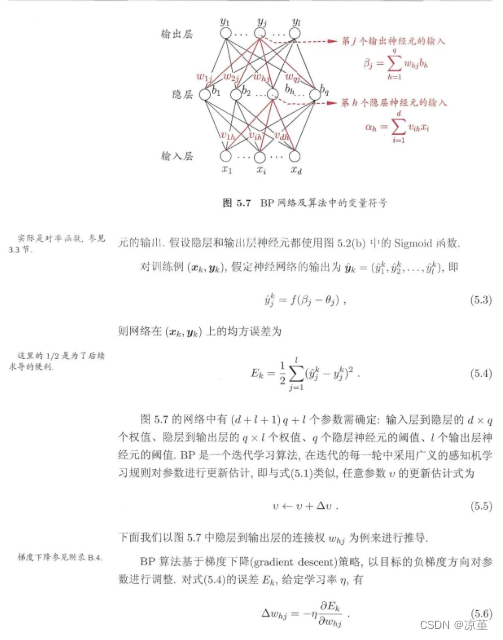
一、过程推导 - 了解BP原理
西瓜书相关内容:
由此可得:
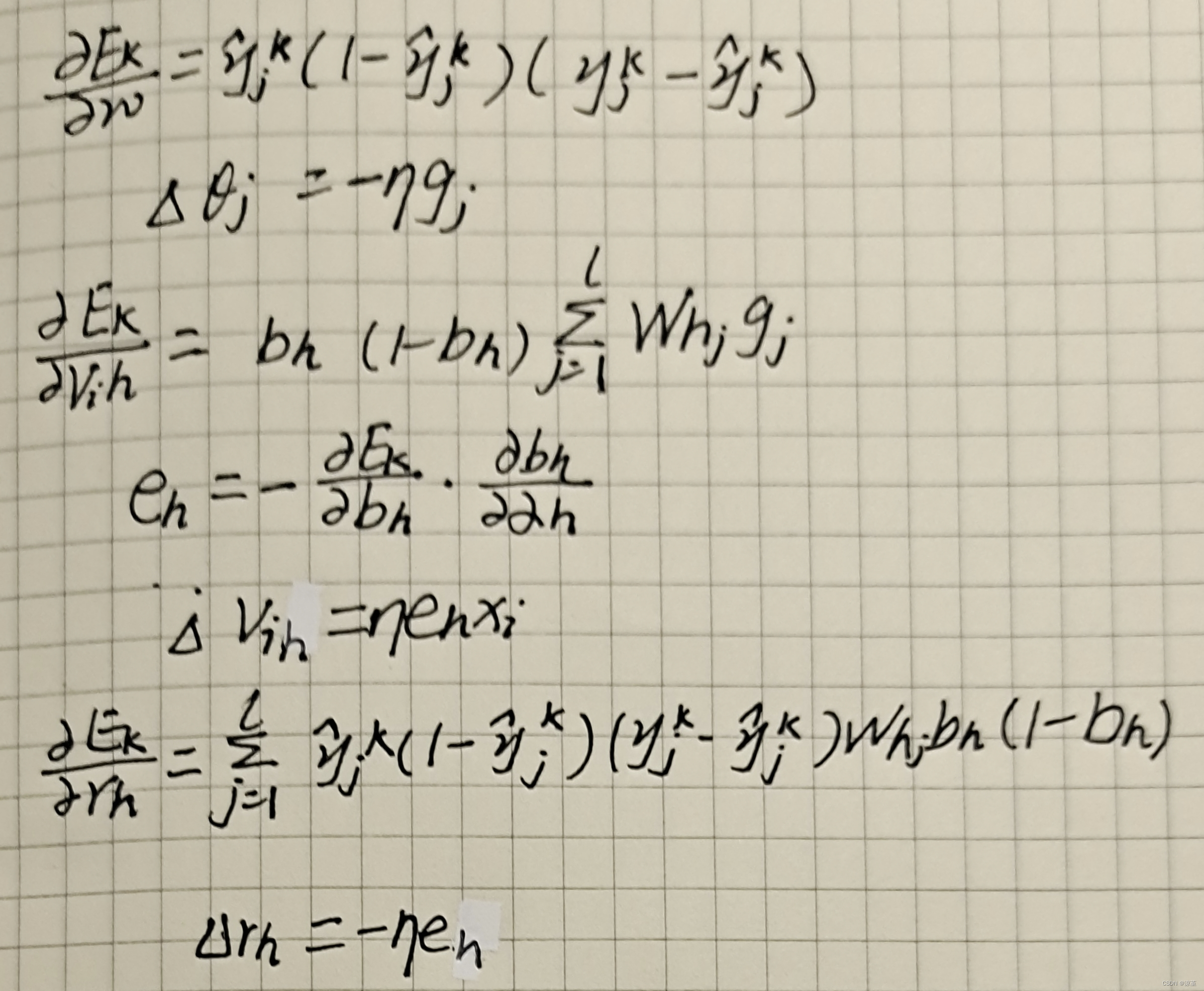
?
二、数值计算 - 手动计算,掌握细节
?
?
三、代码实现 - numpy手推 + pytorch自动
1、对比【numpy】和【pytorch】程序,总结并陈述。
使用numpy实现
import numpy as np
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = 0.2, -0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.1, -0.5, -0.3, 0.8
x1, x2 = 0.5, 0.3
y1, y2 = 0.23, -0.07
print("输入值 x0, x1:")
print(x1, x2)
print("输出值 y0, y1:")
print(y1, y2)
def sigmoid(z):
a = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
return a
def forward_propagate(x1, x2, y1, y2, w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8):
in_h1 = w1 * x1 + w3 * x2
out_h1 = sigmoid(in_h1)
in_h2 = w2 * x1 + w4 * x2
out_h2 = sigmoid(in_h2)
in_o1 = w5 * out_h1 + w7 * out_h2
out_o1 = sigmoid(in_o1)
in_o2 = w6 * out_h1 + w8 * out_h2
out_o2 = sigmoid(in_o2)
print("正向计算:预测值o1 ,o2为")
print(round(out_o1, 5), round(out_o2, 5))
error = (1 / 2) * (out_o1 - y1) ** 2 + (1 / 2) * (out_o2 - y2) ** 2
print("损失函数(均方误差):",round(error, 5))
return out_o1, out_o2, out_h1, out_h2
def back_propagate(out_o1, out_o2, out_h1, out_h2):
# 反向传播
d_o1 = out_o1 - y1
d_o2 = out_o2 - y2
d_w5 = d_o1 * out_o1 * (1 - out_o1) * out_h1
d_w7 = d_o1 * out_o1 * (1 - out_o1) * out_h2
d_w6 = d_o2 * out_o2 * (1 - out_o2) * out_h1
d_w8 = d_o2 * out_o2 * (1 - out_o2) * out_h2
d_w1 = (d_o1 * out_h1 * (1 - out_h1) * w5 + d_o2 * out_o2 * (1 - out_o2) * w6) * out_h1 * (1 - out_h1) * x1
d_w3 = (d_o1 * out_h1 * (1 - out_h1) * w5 + d_o2 * out_o2 * (1 - out_o2) * w6) * out_h1 * (1 - out_h1) * x2
d_w2 = (d_o1 * out_h1 * (1 - out_h1) * w7 + d_o2 * out_o2 * (1 - out_o2) * w8) * out_h2 * (1 - out_h2) * x1
d_w4 = (d_o1 * out_h1 * (1 - out_h1) * w7 + d_o2 * out_o2 * (1 - out_o2) * w8) * out_h2 * (1 - out_h2) * x2
print("反向传播:误差传给每个权值", round(d_w1, 5), round(d_w2, 5), round(d_w3, 5), round(d_w4, 5), round(d_w5, 5), round(d_w6, 5),
round(d_w7, 5), round(d_w8, 5))
return d_w1, d_w2, d_w3, d_w4, d_w5, d_w6, d_w7, d_w8
def update_w(w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8):
# 步长
step = 1
w1 = w1 - step * d_w1
w2 = w2 - step * d_w2
w3 = w3 - step * d_w3
w4 = w4 - step * d_w4
w5 = w5 - step * d_w5
w6 = w6 - step * d_w6
w7 = w7 - step * d_w7
w8 = w8 - step * d_w8
return w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("更新前的权值:",round(w1, 2), round(w2, 2), round(w3, 2), round(w4, 2), round(w5, 2), round(w6, 2), round(w7, 2),
round(w8, 2))
for i in range(1):
print("第" + str(i+1) + "轮:")
out_o1, out_o2, out_h1, out_h2 = forward_propagate(x1, x2, y1, y2, w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8)
d_w1, d_w2, d_w3, d_w4, d_w5, d_w6, d_w7, d_w8 = back_propagate(out_o1, out_o2, out_h1, out_h2)
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = update_w(w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8)
print("更新后的权值w:", round(w1, 2), round(w2, 2), round(w3, 2), round(w4, 2), round(w5, 2), round(w6, 2), round(w7, 2),运行结果
输入值 x0, x1:
0.5 0.3
输出值 y0, y1:
0.23 -0.07
更新前的权值: 0.2 -0.4 0.5 0.6 0.1 -0.5 -0.3 0.8
第1轮:
正向计算:预测值o1 ,o2为
0.47695 0.5287
损失函数(均方误差): 0.20971
反向传播:误差传给每个权值 -0.00843 0.01264 -0.00506 0.00758 0.03463 0.08387 0.03049 0.07384
更新后的权值w: 0.21 -0.41 0.51 0.59 0.07 -0.58 -0.33 0.73
使用pytorch实现
import torch
x1, x2 = torch.Tensor([0.5]), torch.Tensor([0.3])
y1, y2 = torch.Tensor([0.23]), torch.Tensor([-0.07])
print("=====输入值:x1, x2;真实输出值:y1, y2=====")
print(x1, x2, y1, y2)
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = torch.Tensor([0.2]), torch.Tensor([-0.4]), torch.Tensor([0.5]), torch.Tensor(
[0.6]), torch.Tensor([0.1]), torch.Tensor([-0.5]), torch.Tensor([-0.3]), torch.Tensor([0.8]) # 权重初始值
w1.requires_grad = True
w2.requires_grad = True
w3.requires_grad = True
w4.requires_grad = True
w5.requires_grad = True
w6.requires_grad = True
w7.requires_grad = True
w8.requires_grad = True
def sigmoid(z):
a = 1 / (1 + torch.exp(-z))
return a
def forward_propagate(x1, x2):
in_h1 = w1 * x1 + w3 * x2
out_h1 = sigmoid(in_h1) # out_h1 = torch.sigmoid(in_h1)
in_h2 = w2 * x1 + w4 * x2
out_h2 = sigmoid(in_h2) # out_h2 = torch.sigmoid(in_h2)
in_o1 = w5 * out_h1 + w7 * out_h2
out_o1 = sigmoid(in_o1) # out_o1 = torch.sigmoid(in_o1)
in_o2 = w6 * out_h1 + w8 * out_h2
out_o2 = sigmoid(in_o2) # out_o2 = torch.sigmoid(in_o2)
print("正向计算:o1 ,o2")
print(out_o1.data, out_o2.data)
return out_o1, out_o2
def loss_fuction(x1, x2, y1, y2): # 损失函数
y1_pred, y2_pred = forward_propagate(x1, x2) # 前向传播
loss = (1 / 2) * (y1_pred - y1) ** 2 + (1 / 2) * (y2_pred - y2) ** 2 # 考虑 : t.nn.MSELoss()
print("损失函数(均方误差):", loss.item())
return loss
def update_w(w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8):
# 步长
step = 1
w1.data = w1.data - step * w1.grad.data
w2.data = w2.data - step * w2.grad.data
w3.data = w3.data - step * w3.grad.data
w4.data = w4.data - step * w4.grad.data
w5.data = w5.data - step * w5.grad.data
w6.data = w6.data - step * w6.grad.data
w7.data = w7.data - step * w7.grad.data
w8.data = w8.data - step * w8.grad.data
w1.grad.data.zero_() # 注意:将w中所有梯度清零
w2.grad.data.zero_()
w3.grad.data.zero_()
w4.grad.data.zero_()
w5.grad.data.zero_()
w6.grad.data.zero_()
w7.grad.data.zero_()
w8.grad.data.zero_()
return w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("=====更新前的权值=====")
print(w1.data, w2.data, w3.data, w4.data, w5.data, w6.data, w7.data, w8.data)
for i in range(1):
print("=====第" + str(i) + "轮=====")
L = loss_fuction(x1, x2, y1, y2) # 前向传播,求 Loss,构建计算图
L.backward() # 自动求梯度,不需要人工编程实现。反向传播,求出计算图中所有梯度存入w中
print("\tgrad W: ", round(w1.grad.item(), 2), round(w2.grad.item(), 2), round(w3.grad.item(), 2),
round(w4.grad.item(), 2), round(w5.grad.item(), 2), round(w6.grad.item(), 2), round(w7.grad.item(), 2),
round(w8.grad.item(), 2))
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = update_w(w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8)
print("更新后的权值")
print(w1.data, w2.data, w3.data, w4.data, w5.data, w6.data, w7.data, w8.data)
运行结果
=====输入值:x1, x2;真实输出值:y1, y2=====
tensor([0.5000]) tensor([0.3000]) tensor([0.2300]) tensor([-0.0700])
=====更新前的权值=====
tensor([0.2000]) tensor([-0.4000]) tensor([0.5000]) tensor([0.6000]) tensor([0.1000]) tensor([-0.5000]) tensor([-0.3000]) tensor([0.8000])
=====第0轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.4769]) tensor([0.5287])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.2097097933292389
grad W: -0.01 0.01 -0.01 0.01 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.07
更新后的权值
tensor([0.2084]) tensor([-0.4126]) tensor([0.5051]) tensor([0.5924]) tensor([0.0654]) tensor([-0.5839]) tensor([-0.3305]) tensor([0.7262])
通过观察发现,两种方法的结果都十分相近,因此可认为两种方法的求解效果基本相同。但是numpy相对复杂,也不太系统,而pytorch实现通过调用函数代码较为简单。
2、激活函数Sigmoid用PyTorch自带函数torch.sigmoid(),观察、总结并陈述。
训练50轮:
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.2758]) tensor([0.1304])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.02112446539103985
grad W: -0.01 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 0.01 0.01 0.0 0.01
更新后的权值
tensor([0.7606]) tensor([-0.3133]) tensor([0.8363]) tensor([0.6520]) tensor([-0.7251]) tensor([-2.3611]) tensor([-0.9798]) tensor([-0.7355])
训练100轮:
=====第99轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.2378]) tensor([0.0736])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.010342842899262905
grad W: -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 0.0 0.01 0.0 0.01
更新后的权值
tensor([0.9865]) tensor([-0.2037]) tensor([0.9719]) tensor([0.7178]) tensor([-0.8628]) tensor([-2.8459]) tensor([-1.0866]) tensor([-1.1112])
Sigmoid函数的导数是其本身的函数,由上可知,使用Sigmoid函数和使用Pytorch自带函数torch.sigmoid()没较为明显的差距。
3、激活函数Sigmoid改变为Relu,观察、总结并陈述。
训练50轮:
=====第49轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.2300]) tensor([0.])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.0024500000290572643
grad W: -0.0 0.0 -0.0 0.0 -0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
更新后的权值
tensor([0.4287]) tensor([-0.4000]) tensor([0.6372]) tensor([0.6000]) tensor([0.5672]) tensor([-0.5000]) tensor([-0.3000]) tensor([0.8000])
训练100轮:
=====第99轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.2300]) tensor([0.])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.0024500000290572643
grad W: -0.0 0.0 -0.0 0.0 -0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
更新后的权值
tensor([0.4287]) tensor([-0.4000]) tensor([0.6372]) tensor([0.6000]) tensor([0.5672]) tensor([-0.5000]) tensor([-0.3000]) tensor([0.8000])
Relu函数其实就是分段的线性函数,作用是把所有的负值都变为0,而正值保持不变。
Relu激活函数收敛速度要优于使用sigmoid激活函数。
4、损失函数MSE用PyTorch自带函数 t.nn.MSELoss()替代,观察、总结并陈述。
def loss_fuction(x1, x2, y1, y2): # 损失函数
y1_pred, y2_pred = forward_propagate(x1, x2) # 前向传播
# loss = (1 / 2) * (y1_pred - y1) ** 2 + (1 / 2) * (y2_pred - y2) ** 2 # 考虑 : t.nn.MSELoss()
loss = torch.nn.MSELoss()
loss1 = loss(y1_pred,y1)
loss2 = loss(y2_pred,y2)
loss = loss1 + loss2
print("损失函数(均方误差):", loss.item())
return loss
训练50轮:
=====第49轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.2300]) tensor([0.])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.004900000058114529
grad W: -0.0 0.0 -0.0 0.0 -0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
更新后的权值
tensor([0.4236]) tensor([-0.4000]) tensor([0.6342]) tensor([0.6000]) tensor([0.5720]) tensor([-0.5000]) tensor([-0.3000]) tensor([0.8000])
训练100轮:
=====第99轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.2300]) tensor([0.])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.004900000058114529
grad W: -0.0 0.0 -0.0 0.0 -0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
更新后的权值
tensor([0.4236]) tensor([-0.4000]) tensor([0.6342]) tensor([0.6000]) tensor([0.5720]) tensor([-0.5000]) tensor([-0.3000]) tensor([0.8000])
MSELoss是均方误差,是预测值与真实值之差的平方和的平均值。
通过观察结果发现自带函数和编写的函数运行结果相同。
5、损失函数MSE改变为交叉熵,观察、总结并陈述。
def loss_fuction(x1, x2, y1, y2):
y1_pred, y2_pred = forward_propagate(x1, x2)
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 创建交叉熵损失函数
y_pred = torch.stack([y1_pred, y2_pred], dim=1)
y = torch.stack([y1, y2], dim=1)
loss = loss_func(y_pred, y) # 计算
print("损失函数(交叉熵损失):", loss.item())
return loss
训练50轮:
=====第49轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([13.3109]) tensor([0.])
损失函数(交叉熵损失): -0.9317622780799866
grad W: -0.17 0.0 -0.1 0.0 -0.2 0.0 0.0 0.0
更新后的权值
tensor([4.1027]) tensor([-0.4000]) tensor([2.8416]) tensor([0.6000]) tensor([4.9657]) tensor([-0.5000]) tensor([-0.3000]) tensor([0.8000])
训练100轮;
=====第99轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([727.1639]) tensor([0.])
损失函数(交叉熵损失): -50.9014778137207
grad W: -1.24 0.0 -0.74 0.0 -1.44 0.0 0.0 0.0
更新后的权值
tensor([31.3506]) tensor([-0.4000]) tensor([19.1903]) tensor([0.6000]) tensor([36.7545]) tensor([-0.5000]) tensor([-0.3000]) tensor([0.8000])
改为交叉熵之后损失函数出现负数。
6、改变步长,训练次数,观察、总结并陈述。
步长为0.5
训练50轮:
=====第49轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.2758]) tensor([0.1304])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.0422489307820797
grad W: -0.01 -0.01 -0.01 -0.0 0.01 0.03 0.01 0.02
更新后的权值
tensor([0.7606]) tensor([-0.3133]) tensor([0.8363]) tensor([0.6520]) tensor([-0.7251]) tensor([-2.3611]) tensor([-0.9798]) tensor([-0.7355])
训练100轮:
=====第99轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.2378]) tensor([0.0736])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.02068568579852581
grad W: -0.01 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 0.0 0.01 0.0 0.01
更新后的权值
tensor([0.9865]) tensor([-0.2037]) tensor([0.9719]) tensor([0.7178]) tensor([-0.8628]) tensor([-2.8459]) tensor([-1.0866]) tensor([-1.1112])
步长为3
训练50轮:
=====第49轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.2283]) tensor([0.0290])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.009809560142457485
grad W: -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 0.0 -0.0 0.0
更新后的权值
tensor([1.2860]) tensor([-0.0748]) tensor([1.1516]) tensor([0.7951]) tensor([-0.8526]) tensor([-3.5755]) tensor([-1.0837]) tensor([-1.6757])
训练100轮:
=====第99轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.2293]) tensor([0.0157])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.007349265739321709
grad W: -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 0.0 -0.0 0.0
更新后的权值
tensor([1.4843]) tensor([0.0442]) tensor([1.2706]) tensor([0.8665]) tensor([-0.8113]) tensor([-3.9912]) tensor([-1.0526]) tensor([-1.9894])
如果选取合适的step并不会影响最优解的取得,反而会减少迭代的次数,提高时间效率。
7、权值w1-w8初始值换为随机数,对比“指定权值”的结果,观察、总结并陈述。
import torch
torch.manual_seed(20)
x1, x2 = torch.Tensor([0.5]), torch.Tensor([0.3])
y1, y2 = torch.Tensor([0.23]), torch.Tensor([-0.07])
print("=====输入值:x1, x2;真实输出值:y1, y2=====")
print(x1, x2, y1, y2)
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 =torch.rand(1), torch.rand(1), torch.rand(1), torch.rand(1), torch.rand(1),torch.rand(1), torch.rand(1), torch.rand(1)
w1.requires_grad = True
w2.requires_grad = True
w3.requires_grad = True
w4.requires_grad = True
w5.requires_grad = True
w6.requires_grad = True
w7.requires_grad = True
w8.requires_grad = True
def sigmoid(z):
a = 1 / (1 + torch.exp(-z))
return a
def forward_propagate(x1, x2):
in_h1 = w1 * x1 + w3 * x2
out_h1 = torch.relu(in_h1) # out_h1 = torch.sigmoid(in_h1)
in_h2 = w2 * x1 + w4 * x2
out_h2 = torch.relu(in_h2) # out_h2 = torch.sigmoid(in_h2)
in_o1 = w5 * out_h1 + w7 * out_h2
out_o1 = torch.relu(in_o1) # out_o1 = torch.sigmoid(in_o1)
in_o2 = w6 * out_h1 + w8 * out_h2
out_o2 = torch.relu(in_o2) # out_o2 = torch.sigmoid(in_o2)
print("正向计算:o1 ,o2")
print(out_o1.data, out_o2.data)
return out_o1, out_o2
def loss_fuction(x1, x2, y1, y2): # 损失函数
y1_pred, y2_pred = forward_propagate(x1, x2) # 前向传播
loss = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 考虑 : t.nn.MSELoss()
y_pred = torch.stack([y1_pred, y2_pred], dim=1)
y = torch.stack([y1, y2], dim=1)
loss = loss(y_pred,y)
print("损失函数(CrossEntropyLoss):", loss.item())
return loss
def update_w(w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8):
# 步长
step = 2
w1.data = w1.data - step * w1.grad.data
w2.data = w2.data - step * w2.grad.data
w3.data = w3.data - step * w3.grad.data
w4.data = w4.data - step * w4.grad.data
w5.data = w5.data - step * w5.grad.data
w6.data = w6.data - step * w6.grad.data
w7.data = w7.data - step * w7.grad.data
w8.data = w8.data - step * w8.grad.data
w1.grad.data.zero_() # 注意:将w中所有梯度清零
w2.grad.data.zero_()
w3.grad.data.zero_()
w4.grad.data.zero_()
w5.grad.data.zero_()
w6.grad.data.zero_()
w7.grad.data.zero_()
w8.grad.data.zero_()
return w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("=====更新前的权值=====")
print(w1.data, w2.data, w3.data, w4.data, w5.data, w6.data, w7.data, w8.data)
for i in range(2):
print("=====第" + str(i) + "轮=====")
L = loss_fuction(x1, x2, y1, y2) # 前向传播,求 Loss,构建计算图
L.backward() # 自动求梯度,不需要人工编程实现。反向传播,求出计算图中所有梯度存入w中
print("\tgrad W: ", round(w1.grad.item(), 2), round(w2.grad.item(), 2), round(w3.grad.item(), 2),
round(w4.grad.item(), 2), round(w5.grad.item(), 2), round(w6.grad.item(), 2), round(w7.grad.item(), 2),
round(w8.grad.item(), 2))
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = update_w(w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8)
print("更新后的权值")
print(w1.data, w2.data, w3.data, w4.data, w5.data, w6.data, w7.data, w8.data)
训练50轮:
=====第49轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([1648.7810]) tensor([0.])
损失函数(CrossEntropyLoss): -115.4146728515625
grad W: -1.1 -1.5 -0.66 -0.9 -1.29 0.0 -1.75 0.0
更新后的权值
tensor([29.0125]) tensor([39.6298]) tensor([17.8853]) tensor([24.0010]) tensor([34.0791]) tensor([0.2528]) tensor([46.3349]) tensor([-0.2410])
训练100轮:
=====第99轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([4218611.]) tensor([0.])
损失函数(CrossEntropyLoss): -295302.78125
grad W: -55.78 -75.84 -33.47 -45.5 -65.05 0.0 -88.44 0.0
更新后的权值
tensor([1477.9680]) tensor([2009.5591]) tensor([887.2587]) tensor([1205.9587]) tensor([1723.8379]) tensor([0.2528]) tensor([2343.6436]) tensor([-0.2410])
权重的初始化不会影响收敛的结果,均方误差的下降速度与指定权值时相比有所降低,收敛速度小于指定权值。
8、权值w1-w8初始值换为0,观察、总结并陈述。
将tensor中的数全部换为0
训练100轮:
=====第99轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.]) tensor([0.])
损失函数(CrossEntropyLoss): 0.1109035536646843
grad W: 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
更新后的权值
tensor([0.]) tensor([0.]) tensor([0.]) tensor([0.]) tensor([0.]) tensor([0.]) tensor([0.]) tensor([0.])
权重初始值只影响收敛速度,并不会影响收敛结果。
四、全面总结反向传播原理和编码实现,认真写心得体会。
首先回顾了反向传播的计算流程,自己手推一遍真的让人印象深刻。
其次就是通过修改代码中激活函数、损失函数、步长、训练次数、权重等的值,运行观察了修改这些值对收敛速度、结果的影响。大部分的修改都是影响了收敛的速度,但它们的结果都大致相同。
参考文献:
NNDL 作业3:分别使用numpy和pytorch实现FNN例题_HBU_David的博客-CSDN博客
【2021-2022 春学期】人工智能-作业2:例题程序复现_HBU_David的博客-CSDN博客
【2021-2022 春学期】人工智能-作业3:例题程序复现 PyTorch版_HBU_David的博客-CSDN博客
【人工智能导论:模型与算法】MOOC 8.3 误差后向传播(BP) 例题 编程验证 Pytorch版本 - HBU_DAVID - 博客园