1、过程推导 - 了解BP原理
BP网络是在输入层与输出层之间增加若干层(一层或多层)神经元,这些神经元称为隐单元,它们与外界没有直接的联系,但其状态的改变,则能影响输入与输出之间的关系,每一层可以有若干个节点。
BP神经网络的计算过程由正向计算过程和反向计算过程组成。正向传播过程,输入模式从输入层经隐单元层逐层处理,并转向输出层,每一层神经元的状态只影响下一层神经元的状态。如果在输出层不能得到期望的输出,则转入反向传播,将误差信号沿原来的连接通路返回,通过修改各神经元的权值,使得误差信号最小。
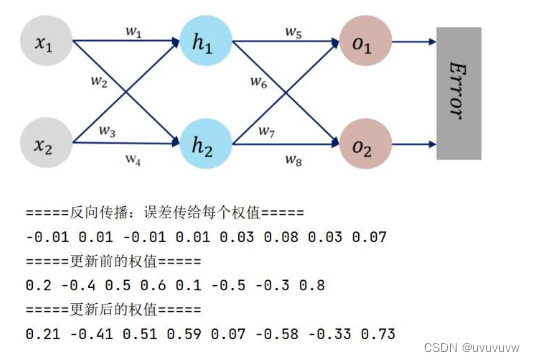
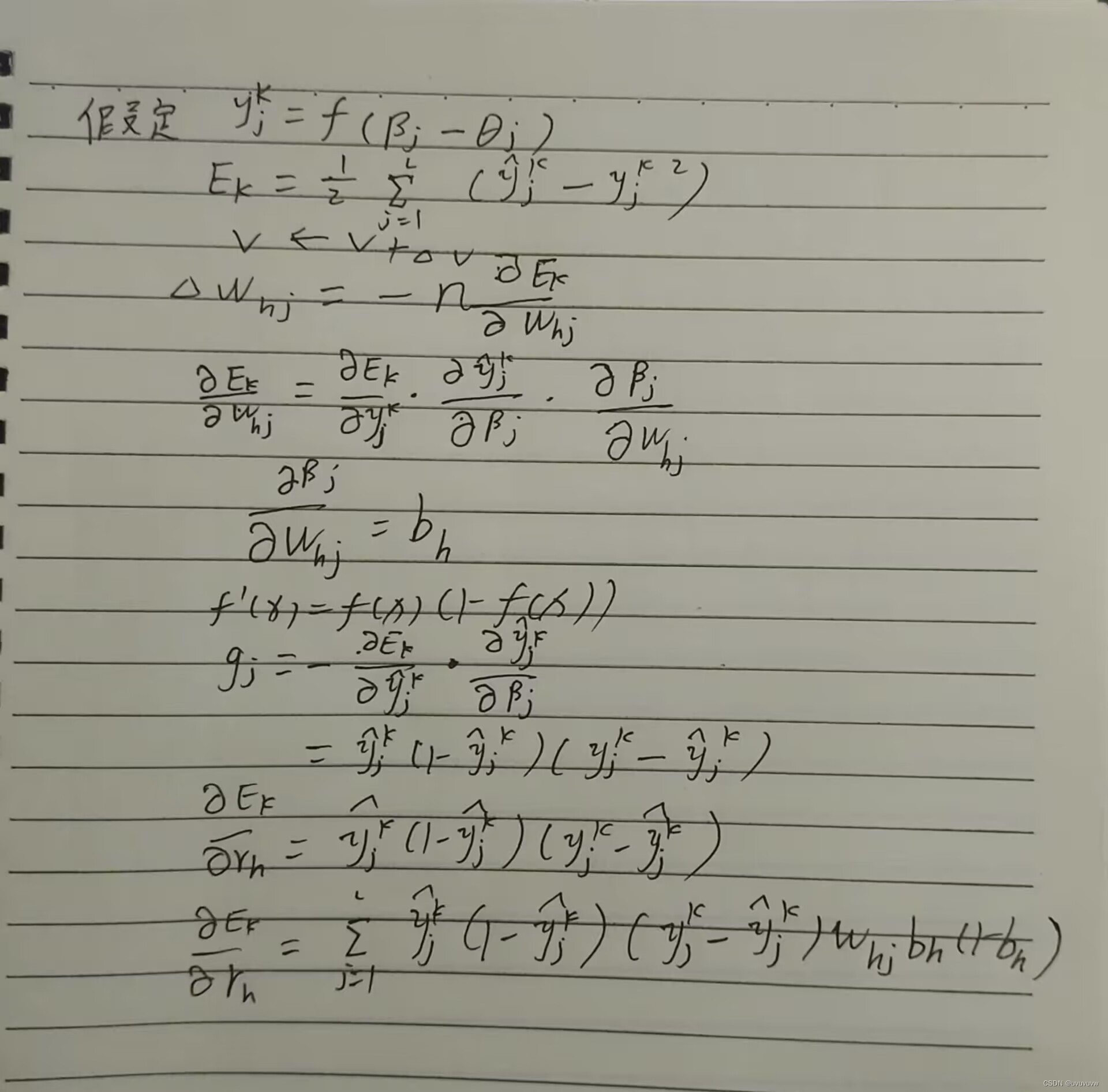
?
2、数值计算 - 手动计算,掌握细节
3、代码实现 - numpy手推 + pytorch自动
3.1 对比【numpy】和【pytorch】程序,总结并陈述。
代码实现:
numpy:
import numpy as np
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = 0.2, -0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.1, -0.5, -0.3, 0.8
x1, x2 = 0.5, 0.3
y1, y2 = 0.23, -0.07
print("输入值 x0, x1:", x1, x2)
print("输出值 y0, y1:", y1, y2)
def sigmoid(z):
a = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
return a
def forward_propagate(x1, x2, y1, y2, w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8):
in_h1 = w1 * x1 + w3 * x2
out_h1 = sigmoid(in_h1)
in_h2 = w2 * x1 + w4 * x2
out_h2 = sigmoid(in_h2)
in_o1 = w5 * out_h1 + w7 * out_h2
out_o1 = sigmoid(in_o1)
in_o2 = w6 * out_h1 + w8 * out_h2
out_o2 = sigmoid(in_o2)
print("正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:", end="")
print(round(out_h1, 5), round(out_h2, 5))
print("正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:", end="")
print(round(out_o1, 5), round(out_o2, 5))
error = (1 / 2) * (out_o1 - y1) ** 2 + (1 / 2) * (out_o2 - y2) ** 2
print("损失函数(均方误差):",round(error, 5))
return out_o1, out_o2, out_h1, out_h2
def back_propagate(out_o1, out_o2, out_h1, out_h2):
# 反向传播
d_o1 = out_o1 - y1
d_o2 = out_o2 - y2
d_w5 = d_o1 * out_o1 * (1 - out_o1) * out_h1
d_w7 = d_o1 * out_o1 * (1 - out_o1) * out_h2
d_w6 = d_o2 * out_o2 * (1 - out_o2) * out_h1
d_w8 = d_o2 * out_o2 * (1 - out_o2) * out_h2
d_w1 = (d_o1 * out_h1 * (1 - out_h1) * w5 + d_o2 * out_o2 * (1 - out_o2) * w6) * out_h1 * (1 - out_h1) * x1
d_w3 = (d_o1 * out_h1 * (1 - out_h1) * w5 + d_o2 * out_o2 * (1 - out_o2) * w6) * out_h1 * (1 - out_h1) * x2
d_w2 = (d_o1 * out_h1 * (1 - out_h1) * w7 + d_o2 * out_o2 * (1 - out_o2) * w8) * out_h2 * (1 - out_h2) * x1
d_w4 = (d_o1 * out_h1 * (1 - out_h1) * w7 + d_o2 * out_o2 * (1 - out_o2) * w8) * out_h2 * (1 - out_h2) * x2
print("w的梯度:",round(d_w1, 2), round(d_w2, 2), round(d_w3, 2), round(d_w4, 2), round(d_w5, 2), round(d_w6, 2),
round(d_w7, 2), round(d_w8, 2))
return d_w1, d_w2, d_w3, d_w4, d_w5, d_w6, d_w7, d_w8
def update_w(w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8):
# 步长
step = 1
w1 = w1 - step * d_w1
w2 = w2 - step * d_w2
w3 = w3 - step * d_w3
w4 = w4 - step * d_w4
w5 = w5 - step * d_w5
w6 = w6 - step * d_w6
w7 = w7 - step * d_w7
w8 = w8 - step * d_w8
return w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("权值w0-w7:",round(w1, 2), round(w2, 2), round(w3, 2), round(w4, 2), round(w5, 2), round(w6, 2), round(w7, 2),
round(w8, 2))
for i in range(5):
print("=====第" + str(i+1) + "轮=====")
out_o1, out_o2, out_h1, out_h2 = forward_propagate(x1, x2, y1, y2, w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8)
d_w1, d_w2, d_w3, d_w4, d_w5, d_w6, d_w7, d_w8 = back_propagate(out_o1, out_o2, out_h1, out_h2)
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = update_w(w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8)
print("更新后的权值w:",round(w1, 2), round(w2, 2), round(w3, 2), round(w4, 2), round(w5, 2), round(w6, 2), round(w7, 2),
round(w8, 2))
结果如下:
输入值 x0, x1: 0.5 0.3
输出值 y0, y1: 0.23 -0.07
权值w0-w7: 0.2 -0.4 0.5 0.6 0.1 -0.5 -0.3 0.8
=====第1轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:0.56218 0.495
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:0.47695 0.5287
损失函数(均方误差): 0.20971
w的梯度: -0.01 0.01 -0.01 0.01 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.07
=====第2轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:0.56359 0.49285
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:0.46853 0.50721
损失函数(均方误差): 0.19503
w的梯度: -0.01 0.01 -0.01 0.01 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.07
=====第3轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:0.56524 0.49104
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:0.46042 0.48642
损失函数(均方误差): 0.18135
w的梯度: -0.01 0.01 -0.01 0.01 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.07
=====第4轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:0.5671 0.48954
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:0.45261 0.46642
损失函数(均方误差): 0.16865
w的梯度: -0.01 0.01 -0.01 0.0 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.07
=====第5轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:0.56913 0.48832
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:0.44506 0.44726
损失函数(均方误差): 0.1569
w的梯度: -0.01 0.01 -0.01 0.0 0.03 0.07 0.03 0.06
更新后的权值w: 0.25 -0.44 0.53 0.57 -0.06 -0.89 -0.44 0.46
进程已结束,退出代码为 0
pytorch:
import torch
x = [0.5, 0.3] # x0, x1 = 0.5, 0.3
y = [0.23, -0.07] # y0, y1 = 0.23, -0.07
print("输入值 x0, x1:", x[0], x[1])
print("输出值 y0, y1:", y[0], y[1])
w = [torch.Tensor([0.2]), torch.Tensor([-0.4]), torch.Tensor([0.5]), torch.Tensor(
[0.6]), torch.Tensor([0.1]), torch.Tensor([-0.5]), torch.Tensor([-0.3]), torch.Tensor([0.8])] # 权重初始值
for i in range(0, 8):
w[i].requires_grad = True
print("权值w0-w7:")
for i in range(0, 8):
print(w[i].data, end=" ")
def forward_propagate(x): # 计算图
in_h1 = w[0] * x[0] + w[2] * x[1]
out_h1 = torch.sigmoid(in_h1)
in_h2 = w[1] * x[0] + w[3] * x[1]
out_h2 = torch.sigmoid(in_h2)
in_o1 = w[4] * out_h1 + w[6] * out_h2
out_o1 = torch.sigmoid(in_o1)
in_o2 = w[5] * out_h1 + w[7] * out_h2
out_o2 = torch.sigmoid(in_o2)
print("正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:", end="")
print(out_h1.data, out_h2.data)
print("正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:", end="")
print(out_o1.data, out_o2.data)
return out_o1, out_o2
def loss(x, y): # 损失函数
y_pre = forward_propagate(x) # 前向传播
loss_mse = (1 / 2) * (y_pre[0] - y[0]) ** 2 + (1 / 2) * (y_pre[1] - y[1]) ** 2 # 考虑 : t.nn.MSELoss()
print("损失函数(均方误差):", loss_mse.item())
return loss_mse
if __name__ == "__main__":
for k in range(5):
print("\n=====第" + str(k+1) + "轮=====")
l = loss(x, y) # 前向传播,求 Loss,构建计算图
l.backward() # 反向传播,求出计算图中所有梯度存入w中. 自动求梯度,不需要人工编程实现。
print("w的梯度: ", end=" ")
for i in range(0, 8):
print(round(w[i].grad.item(), 2), end=" ") # 查看梯度
step = 1 # 步长
for i in range(0, 8):
w[i].data = w[i].data - step * w[i].grad.data # 更新权值
w[i].grad.data.zero_() # 注意:将w中所有梯度清零
print("\n更新后的权值w:")
for i in range(0, 8):
print(w[i].data, end=" ")
结果如下:
输入值 x0, x1: 0.5 0.3
输出值 y0, y1: 0.23 -0.07
权值w0-w7:
tensor([0.2000]) tensor([-0.4000]) tensor([0.5000]) tensor([0.6000]) tensor([0.1000]) tensor([-0.5000]) tensor([-0.3000]) tensor([0.8000])
=====第1轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:tensor([0.5622]) tensor([0.4950])
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:tensor([0.4769]) tensor([0.5287])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.2097097933292389
w的梯度: -0.01 0.01 -0.01 0.01 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.07
更新后的权值w:
tensor([0.2084]) tensor([-0.4126]) tensor([0.5051]) tensor([0.5924]) tensor([0.0654]) tensor([-0.5839]) tensor([-0.3305]) tensor([0.7262])
=====第2轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:tensor([0.5636]) tensor([0.4929])
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:tensor([0.4685]) tensor([0.5072])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.19503259658813477
w的梯度: -0.01 0.01 -0.01 0.01 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.07
更新后的权值w:
tensor([0.2183]) tensor([-0.4232]) tensor([0.5110]) tensor([0.5861]) tensor([0.0319]) tensor([-0.6652]) tensor([-0.3598]) tensor([0.6550])
=====第3轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:tensor([0.5652]) tensor([0.4910])
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:tensor([0.4604]) tensor([0.4864])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.1813509315252304
w的梯度: -0.01 0.01 -0.01 0.01 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.07
更新后的权值w:
tensor([0.2294]) tensor([-0.4321]) tensor([0.5177]) tensor([0.5808]) tensor([-0.0005]) tensor([-0.7437]) tensor([-0.3879]) tensor([0.5868])
=====第4轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:tensor([0.5671]) tensor([0.4896])
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:tensor([0.4526]) tensor([0.4664])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.16865134239196777
w的梯度: -0.01 0.01 -0.01 0.0 0.03 0.08 0.03 0.07
更新后的权值w:
tensor([0.2416]) tensor([-0.4392]) tensor([0.5250]) tensor([0.5765]) tensor([-0.0317]) tensor([-0.8195]) tensor([-0.4149]) tensor([0.5214])
=====第5轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:tensor([0.5691]) tensor([0.4883])
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:tensor([0.4451]) tensor([0.4473])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.15690487623214722
w的梯度: -0.01 0.01 -0.01 0.0 0.03 0.07 0.03 0.06
更新后的权值w:
tensor([0.2547]) tensor([-0.4447]) tensor([0.5328]) tensor([0.5732]) tensor([-0.0620]) tensor([-0.8922]) tensor([-0.4408]) tensor([0.4590])
进程已结束,退出代码为 03.2 激活函数Sigmoid用PyTorch自带函数torch.sigmoid(),观察、总结并陈述。
sigmoid函数表达式
通过3.1中手动和自动对比,当训练次数增加到500次时:
手动:
=====第500轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:0.75099 0.57172
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:0.22916 0.01856
损失函数(均方误差): 0.00392
w的梯度: -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 0.0 -0.0 0.0
更新后的权值w: 1.46 0.05 1.25 0.87 -0.82 -3.85 -1.05 -1.88自动:
=====第500轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:tensor([0.7507]) tensor([0.5705])
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:tensor([0.2292]) tensor([0.0186])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.003923574462532997
w的梯度: -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 0.0 -0.0 0.0
更新后的权值w:
tensor([1.4539]) tensor([0.0472]) tensor([1.2523]) tensor([0.8683]) tensor([-0.8166]) tensor([-3.8563]) tensor([-1.0516]) tensor([-1.8817]) 可以看出,二者几乎相同
3.3 激活函数Sigmoid改变为Relu,观察、总结并陈述。
import torch
x = [0.5, 0.3] # x0, x1 = 0.5, 0.3
y = [0.23, -0.07] # y0, y1 = 0.23, -0.07
print("输入值 x0, x1:", x[0], x[1])
print("输出值 y0, y1:", y[0], y[1])
w = [torch.Tensor([0.2]), torch.Tensor([-0.4]), torch.Tensor([0.5]), torch.Tensor(
[0.6]), torch.Tensor([0.1]), torch.Tensor([-0.5]), torch.Tensor([-0.3]), torch.Tensor([0.8])] # 权重初始值
for i in range(0, 8):
w[i].requires_grad = True
print("权值w0-w7:")
for i in range(0, 8):
print(w[i].data, end=" ")
def forward_propagate(x): # 计算图
in_h1 = w[0] * x[0] + w[2] * x[1]
out_h1 = torch.relu(in_h1)
in_h2 = w[1] * x[0] + w[3] * x[1]
out_h2 = torch.relu(in_h2)
in_o1 = w[4] * out_h1 + w[6] * out_h2
out_o1 = torch.relu(in_o1)
in_o2 = w[5] * out_h1 + w[7] * out_h2
out_o2 = torch.relu(in_o2)
print("正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:", end="")
print(out_h1.data, out_h2.data)
print("正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:", end="")
print(out_o1.data, out_o2.data)
return out_o1, out_o2
def loss(x, y): # 损失函数
y_pre = forward_propagate(x) # 前向传播
loss_mse = (1 / 2) * (y_pre[0] - y[0]) ** 2 + (1 / 2) * (y_pre[1] - y[1]) ** 2 # 考虑 : t.nn.MSELoss()
print("损失函数(均方误差):", loss_mse.item())
return loss_mse
if __name__ == "__main__":
for k in range(5):
print("\n=====第" + str(k + 1) + "轮=====")
l = loss(x, y) # 前向传播,求 Loss,构建计算图
l.backward() # 反向传播,求出计算图中所有梯度存入w中. 自动求梯度,不需要人工编程实现。
print("w的梯度: ", end=" ")
for i in range(0, 8):
print(round(w[i].grad.item(), 2), end=" ") # 查看梯度
step = 1 # 步长
for i in range(0, 8):
w[i].data = w[i].data - step * w[i].grad.data # 更新权值
w[i].grad.data.zero_() # 注意:将w中所有梯度清零
print("\n更新后的权值w:")
for i in range(0, 8):
print(w[i].data, end=" ")
运行结果:
输入值 x0, x1: 0.5 0.3
输出值 y0, y1: 0.23 -0.07
权值w0-w7:
tensor([0.2000]) tensor([-0.4000]) tensor([0.5000]) tensor([0.6000]) tensor([0.1000]) tensor([-0.5000]) tensor([-0.3000]) tensor([0.8000])
=====第1轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:tensor([0.2500]) tensor([0.])
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:tensor([0.0250]) tensor([0.])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.023462500423192978
w的梯度: -0.01 0.0 -0.01 0.0 -0.05 0.0 -0.0 0.0
更新后的权值w:
tensor([0.2103]) tensor([-0.4000]) tensor([0.5062]) tensor([0.6000]) tensor([0.1513]) tensor([-0.5000]) tensor([-0.3000]) tensor([0.8000])
=====第2轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:tensor([0.2570]) tensor([0.])
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:tensor([0.0389]) tensor([0.])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.020715968683362007
w的梯度: -0.01 0.0 -0.01 0.0 -0.05 0.0 0.0 0.0
更新后的权值w:
tensor([0.2247]) tensor([-0.4000]) tensor([0.5148]) tensor([0.6000]) tensor([0.2004]) tensor([-0.5000]) tensor([-0.3000]) tensor([0.8000])
=====第3轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:tensor([0.2668]) tensor([0.])
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:tensor([0.0535]) tensor([0.])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.01803365722298622
w的梯度: -0.02 0.0 -0.01 0.0 -0.05 0.0 0.0 0.0
更新后的权值w:
tensor([0.2424]) tensor([-0.4000]) tensor([0.5254]) tensor([0.6000]) tensor([0.2475]) tensor([-0.5000]) tensor([-0.3000]) tensor([0.8000])
=====第4轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:tensor([0.2788]) tensor([0.])
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:tensor([0.0690]) tensor([0.])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.015410471707582474
w的梯度: -0.02 0.0 -0.01 0.0 -0.04 0.0 0.0 0.0
更新后的权值w:
tensor([0.2623]) tensor([-0.4000]) tensor([0.5374]) tensor([0.6000]) tensor([0.2924]) tensor([-0.5000]) tensor([-0.3000]) tensor([0.8000])
=====第5轮=====
正向计算,隐藏层h1 ,h2:tensor([0.2924]) tensor([0.])
正向计算,预测值o1 ,o2:tensor([0.0855]) tensor([0.])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.012893404811620712
w的梯度: -0.02 0.0 -0.01 0.0 -0.04 0.0 0.0 0.0
更新后的权值w:
tensor([0.2834]) tensor([-0.4000]) tensor([0.5501]) tensor([0.6000]) tensor([0.3346]) tensor([-0.5000]) tensor([-0.3000]) tensor([0.8000])
进程已结束,退出代码为 0
与sigmod函数对比可得,relu函数准确率更高
3.4 损失函数MSE用PyTorch自带函数 torch.nn.MSELoss()替代,观察、总结并陈述。
代码实现:
import torch
x1, x2 = torch.Tensor([0.5]), torch.Tensor([0.3])
y1, y2 = torch.Tensor([0.23]), torch.Tensor([-0.07])
print("=====输入值:x1, x2;真实输出值:y1, y2=====")
print(x1, x2, y1, y2)
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = torch.Tensor([0.2]), torch.Tensor([-0.4]), torch.Tensor([0.5]), torch.Tensor(
[0.6]), torch.Tensor([0.1]), torch.Tensor([-0.5]), torch.Tensor([-0.3]), torch.Tensor([0.8]) # 权重初始值
w1.requires_grad = True
w2.requires_grad = True
w3.requires_grad = True
w4.requires_grad = True
w5.requires_grad = True
w6.requires_grad = True
w7.requires_grad = True
w8.requires_grad = True
def sigmoid(z):
a = 1 / (1 + torch.exp(-z))
return a
def forward_propagate(x1, x2):
in_h1 = w1 * x1 + w3 * x2
out_h1 = sigmoid(in_h1) # out_h1 = torch.sigmoid(in_h1)
in_h2 = w2 * x1 + w4 * x2
out_h2 = sigmoid(in_h2) # out_h2 = torch.sigmoid(in_h2)
in_o1 = w5 * out_h1 + w7 * out_h2
out_o1 = sigmoid(in_o1) # out_o1 = torch.sigmoid(in_o1)
in_o2 = w6 * out_h1 + w8 * out_h2
out_o2 = sigmoid(in_o2) # out_o2 = torch.sigmoid(in_o2)
print("正向计算:o1 ,o2")
print(out_o1.data, out_o2.data)
return out_o1, out_o2
def loss_fuction(x1, x2, y1, y2):
y1_pred, y2_pred = forward_propagate(x1, x2)
t = torch.nn.MSELoss()
loss = t(y1_pred,y1) + t(y2_pred,y2)
print("损失函数(均方误差):", loss.item())
return loss
def update_w(w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8):
# 步长
step = 1
w1.data = w1.data - step * w1.grad.data
w2.data = w2.data - step * w2.grad.data
w3.data = w3.data - step * w3.grad.data
w4.data = w4.data - step * w4.grad.data
w5.data = w5.data - step * w5.grad.data
w6.data = w6.data - step * w6.grad.data
w7.data = w7.data - step * w7.grad.data
w8.data = w8.data - step * w8.grad.data
w1.grad.data.zero_() # 注意:将w中所有梯度清零
w2.grad.data.zero_()
w3.grad.data.zero_()
w4.grad.data.zero_()
w5.grad.data.zero_()
w6.grad.data.zero_()
w7.grad.data.zero_()
w8.grad.data.zero_()
return w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("=====更新前的权值=====")
print(w1.data, w2.data, w3.data, w4.data, w5.data, w6.data, w7.data, w8.data)
for i in range(5):
print("=====第" + str(i+1) + "轮=====")
L = loss_fuction(x1, x2, y1, y2) # 前向传播,求 Loss,构建计算图
L.backward() # 自动求梯度,不需要人工编程实现。反向传播,求出计算图中所有梯度存入w中
print("\tgrad W: ", round(w1.grad.item(), 2), round(w2.grad.item(), 2), round(w3.grad.item(), 2),
round(w4.grad.item(), 2), round(w5.grad.item(), 2), round(w6.grad.item(), 2), round(w7.grad.item(), 2),
round(w8.grad.item(), 2))
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = update_w(w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8)
print("更新后的权值")
print(w1.data, w2.data, w3.data, w4.data, w5.data, w6.data, w7.data, w8.data)
其中的损失函数为:
def loss_fuction(x1, x2, y1, y2):
y1_pred, y2_pred = forward_propagate(x1, x2)
t = torch.nn.MSELoss()
loss = t(y1_pred,y1) + t(y2_pred,y2)
print("损失函数(均方误差):", loss.item())
return loss运行结果:
=====第50轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.2376]) tensor([0.0736])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.02068198285996914
grad W: -0.01 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 0.0 0.01 0.0 0.01
更新后的权值
tensor([0.9834]) tensor([-0.2099]) tensor([0.9701]) tensor([0.7141]) tensor([-0.8661]) tensor([-2.8555]) tensor([-1.0899]) tensor([-1.1204])=====第500轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.2296]) tensor([0.0098])
损失函数(均方误差): 0.006369990762323141
grad W: -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 0.0 -0.0 0.0
更新后的权值
tensor([1.6478]) tensor([0.1706]) tensor([1.3687]) tensor([0.9424]) tensor([-0.7806]) tensor([-4.2782]) tensor([-1.0250]) tensor([-2.2036])由上图可以看出,50轮是一样,但是最终收敛结果不一样,手写的要比torch.nn.MSELoss()收敛的结果好些。
3.5 损失函数MSE改变为交叉熵,观察、总结并陈述。
代码实现:
def loss_fuction(x1, x2, y1, y2):
y1_pred, y2_pred = forward_propagate(x1, x2)
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 创建交叉熵损失函数
y_pred = torch.stack([y1_pred, y2_pred], dim=1)
y = torch.stack([y1, y2], dim=1)
loss = loss_func(y_pred, y) # 计算
print("损失函数(交叉熵损失):", loss.item())
return loss
运行结果:
=====第50轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.7090]) tensor([0.2902])
损失函数(交叉熵损失): 0.051561735570430756
grad W: -0.01 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.02 0.02 -0.01 0.01
更新后的权值
tensor([0.5132]) tensor([-0.4629]) tensor([0.6879]) tensor([0.5623]) tensor([1.0764]) tensor([-1.4770]) tensor([0.5131]) tensor([-0.0136])=====第500轮=====
正向计算:o1 ,o2
tensor([0.9827]) tensor([0.0174])
损失函数(交叉熵损失): -0.01593960076570511
grad W: -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 -0.0 0.0 -0.0 0.0
更新后的权值
tensor([1.9505]) tensor([0.3587]) tensor([1.5503]) tensor([1.0552]) tensor([3.3073]) tensor([-3.6951]) tensor([2.2004]) tensor([-1.6912])当训练次数较多时,损失函数小于0
3.6 改变步长,训练次数,观察、总结并陈述。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
x1, x2 = torch.Tensor([0.5]), torch.Tensor([0.3])
y1, y2 = torch.Tensor([0.23]), torch.Tensor([-0.07])
print("=====输入值:x1, x2;真实输出值:y1, y2=====")
print(x1, x2, y1, y2)
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = torch.Tensor([0.2]), torch.Tensor([-0.4]), torch.Tensor([0.5]), torch.Tensor(
[0.6]), torch.Tensor([0.1]), torch.Tensor([-0.5]), torch.Tensor([-0.3]), torch.Tensor([0.8]) # 权重初始值
w1.requires_grad = True
w2.requires_grad = True
w3.requires_grad = True
w4.requires_grad = True
w5.requires_grad = True
w6.requires_grad = True
w7.requires_grad = True
w8.requires_grad = True
def sigmoid(z):
a = 1 / (1 + torch.exp(-z))
return a
def forward_propagate(x1, x2):
in_h1 = w1 * x1 + w3 * x2
out_h1 = sigmoid(in_h1) # out_h1 = torch.sigmoid(in_h1)
in_h2 = w2 * x1 + w4 * x2
out_h2 = sigmoid(in_h2) # out_h2 = torch.sigmoid(in_h2)
in_o1 = w5 * out_h1 + w7 * out_h2
out_o1 = sigmoid(in_o1) # out_o1 = torch.sigmoid(in_o1)
in_o2 = w6 * out_h1 + w8 * out_h2
out_o2 = sigmoid(in_o2) # out_o2 = torch.sigmoid(in_o2)
print("正向计算:o1 ,o2")
print(out_o1.data, out_o2.data)
return out_o1, out_o2
def loss_fuction(x1, x2, y1, y2): # 损失函数
y1_pred, y2_pred = forward_propagate(x1, x2) # 前向传播
loss = (1 / 2) * (y1_pred - y1) ** 2 + (1 / 2) * (y2_pred - y2) ** 2 # 考虑 : t.nn.MSELoss()
print("损失函数(均方误差):", loss.item())
return loss
def update_w(w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8):
# 步长
step = 1
w1.data = w1.data - step * w1.grad.data
w2.data = w2.data - step * w2.grad.data
w3.data = w3.data - step * w3.grad.data
w4.data = w4.data - step * w4.grad.data
w5.data = w5.data - step * w5.grad.data
w6.data = w6.data - step * w6.grad.data
w7.data = w7.data - step * w7.grad.data
w8.data = w8.data - step * w8.grad.data
w1.grad.data.zero_() # 注意:将w中所有梯度清零
w2.grad.data.zero_()
w3.grad.data.zero_()
w4.grad.data.zero_()
w5.grad.data.zero_()
w6.grad.data.zero_()
w7.grad.data.zero_()
w8.grad.data.zero_()
return w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("=====更新前的权值=====")
print(w1.data, w2.data, w3.data, w4.data, w5.data, w6.data, w7.data, w8.data)
Y = []
X = []
for i in range(10):
print("=====第" + str(i + 1) + "轮=====")
L = loss_fuction(x1, x2, y1, y2) # 前向传播,求 Loss,构建计算图
L.backward() # 自动求梯度,不需要人工编程实现。反向传播,求出计算图中所有梯度存入w中
print("\tgrad W: ", round(w1.grad.item(), 2), round(w2.grad.item(), 2), round(w3.grad.item(), 2),
round(w4.grad.item(), 2), round(w5.grad.item(), 2), round(w6.grad.item(), 2), round(w7.grad.item(), 2),
round(w8.grad.item(), 2))
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = update_w(w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8)
Y.append(L.item())
X.append(i)
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 可以plt绘图过程中中文无法显示的问题
plt.plot(X, Y)
plt.xlabel('迭代次数')
plt.ylabel('Loss,step=1')
plt.show()
print("更新后的权值")
print(w1.data, w2.data, w3.data, w4.data, w5.data, w6.data, w7.data, w8.data)
实验结果:
步长为1,训练5次
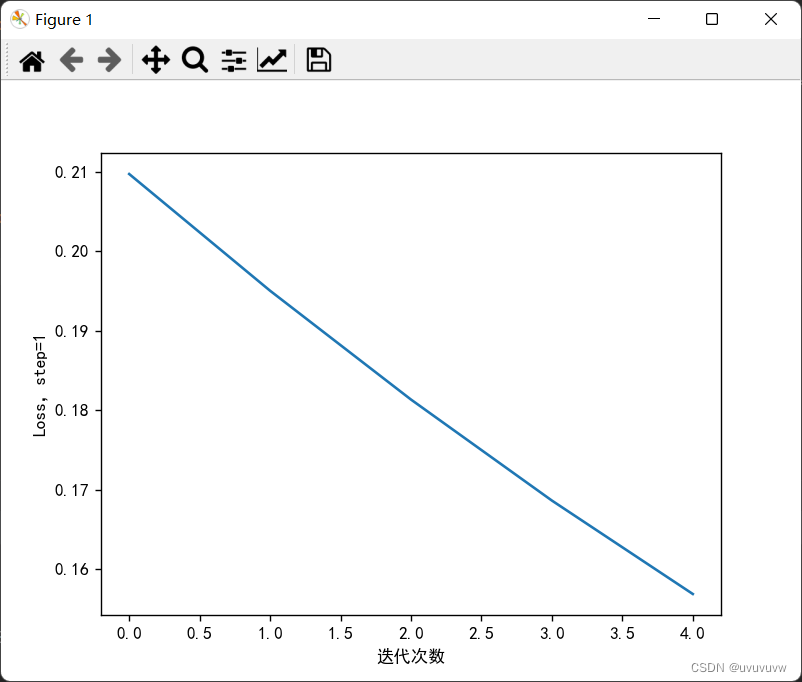
?步长为1,训练50次
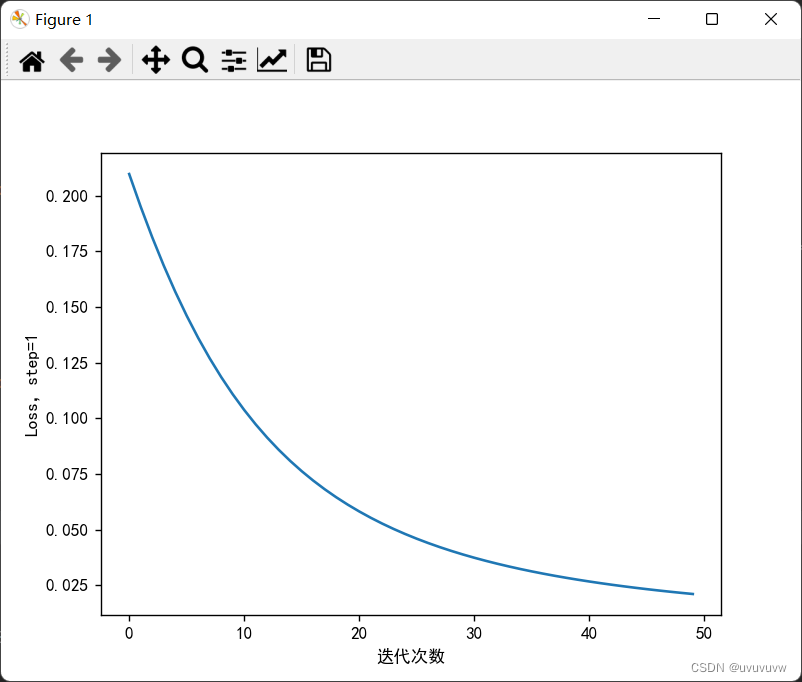
?
步长为10,训练50次
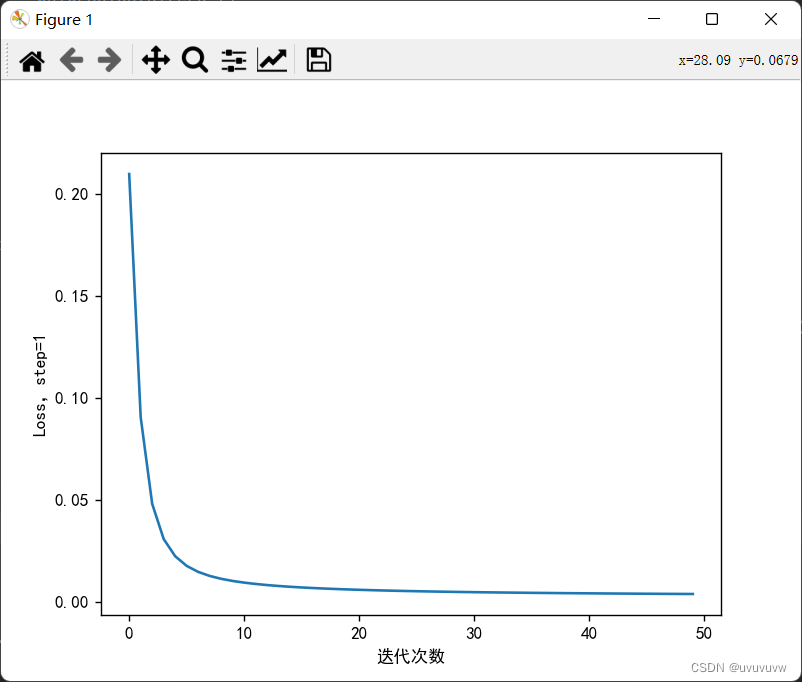
3.7 权值w1-w8初始值换为随机数,对比“指定权值”的结果,观察、总结并陈述。
?w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = torch.randn(1), torch.randn(1), torch.randn(1), torch.randn(1), \
torch.randn(1), torch.randn(1), torch.randn(1), torch.randn(1)
结果如图
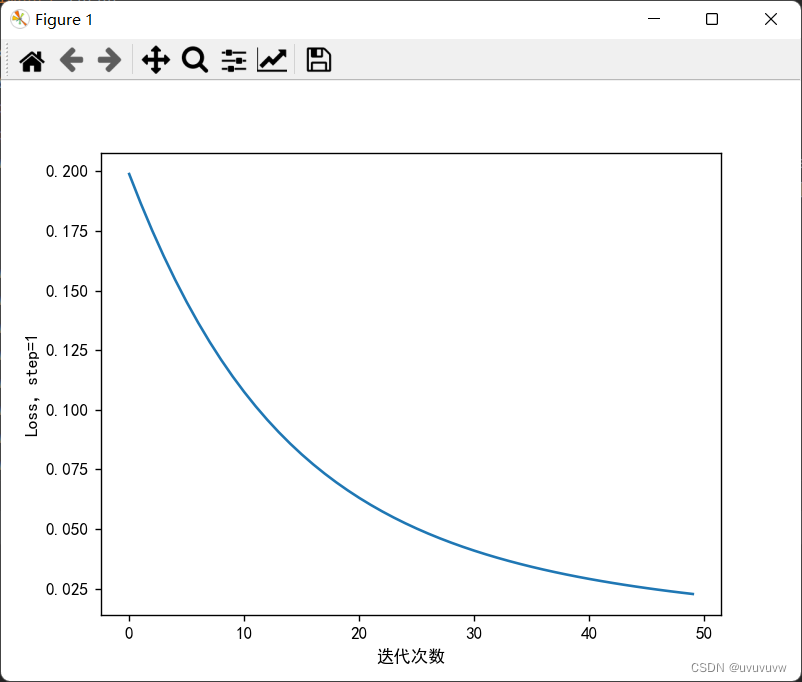
 3.8 权值w1-w8初始值换为0,观察、总结并陈述。
3.8 权值w1-w8初始值换为0,观察、总结并陈述。
?代码实现:
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = torch.Tensor([0]), torch.Tensor([0]), torch.Tensor([0]), torch.Tensor(
[0]), torch.Tensor([0]), torch.Tensor([0]), torch.Tensor([0]), torch.Tensor([0])
结果如图:
?3.9 全面总结反向传播原理和编码实现,认真写心得体会。
反向传播算法将训练集数据输入到ANN的输入层,经过隐藏层,最后达到输出层并输出结果,这是ANN的前向传播过程;由于ANN的输出结果与实际结果有误差,则先计算估计值与实际值之间的误差,并将该误差从输出层向隐藏层反向传播,直至传播到输入层;在反向传播的过程中,根据误差调整各种参数的值;不断迭代上述过程,直至收敛。
?