1:闭包 closure
若要访问funB,则需要访问funA,如何不通过在funA函数内部访问funB来打印funB的值?
?
将funB函数作为返回值返回,注意函数作为返回值时,不需要加括号。
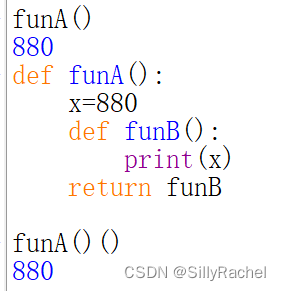
?2:闭包的含义,工厂函数
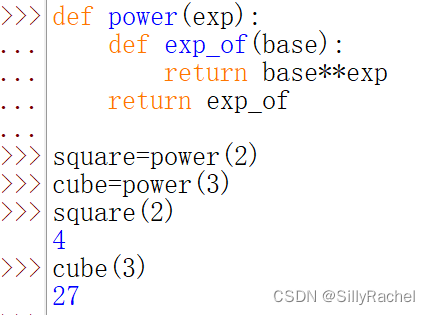
nonlocal实现带记忆功能的函数

3.小案例,位置移动
origin=(0,0) #这个是原点
legal_x=[-100,100] #限定x的移动范围
legal_y=[-100,100] #限定y轴的移动范围
def creat(pos_x=0,pos_y=0): #坐标位置
def moving(direction,step): #两个参数,一个代表移动的方向,一个代表步数
nonlocal pos_x,pos_y #实现坐标记忆功能
new_x=pos_x+direction[0]*step
new_y=pos_x+direction[1]*step
if new_x < legal_x[0]:
pos_x=legal_x[0]-(new_x-legal_x[0]) #超出规定范围,撞墙反弹
elif new_x > legal_x[1]:
pos_x=legal_x[1]-(new_x-legal_x[1])
else:
pos_x=new_x
if new_y < legal_y[0]:
pos_y=legal_y[0]-(new_y-legal_y[0])
elif new_y > legal_y[1]:
pos_y=legal_y[1]-(new_y-legal_y[1])
else:
pos_y=new_y
return pos_x,pos_y
return moving
move=creat()
print("向右移动120步后,坐标位置是:",move([1,0],120))向右移动120步后: (80, 0)
4.把一个函数作为一个参数传递给另一个函数

?5:装饰器
import time
def time_master(func):
def call_func():
print("开始运行程序")
start=time.time()
func()
stop=time.time()
print("程序结束运行")
print(f"一共耗费了{(stop-start):.2f}秒")
return call_func
@time_master
def myfunc():
time.sleep(2)
print("Hello,world")
myfunc()上面的@time_master 相当于:
import time
def time_master(func):
def call_func():
print("开始运行程序")
start=time.time()
func()
stop=time.time()
print("程序结束运行")
print(f"一共耗费了{(stop-start):.2f}秒")
return call_func
def myfunc():
time.sleep(2)
print("Hello,world")
myfunc=time_master(myfunc)
#把myfunc作为一个参数传进去.
#上面time_master函数相当于一个闭包,并不执行call_fun,而将其返回再把内部返回的call_fun赋值给myfunc
myfunc()
#调用myfunc()相当于调用call_func()?6:多个装饰器用在同一函数上
def add(func):
def inner():
x=func()
return x+1
return inner
def cube(func):
def inner():
x=func()
return x*x*x
return inner
def square(func):
def inner():
x=func()
return x*x
return inner
@add
@cube
@square
def test():
return 2
print(test())?输出:65
装饰器执行顺序,按靠近函数顺序执行,执行时由外而内。
7:如何给装饰器传递参数
import time
def logger(msg):
def time_master(func):
def call_func():
start=time.time()
func()
stop=time.time()
print(f"[{msg}]一共耗费了{(stop-start):.2f}")
return call_func
return time_master
@logger(msg="A")
def funA():
time.sleep(1)
print("正在调用funA")
@logger(msg="B")
def funB():
time.sleep(1)
print("正在调用funB")
funA()
funB()?还原为不含装饰器的代码:
import time
def logger(msg):
def time_master(func):
def call_func():
start=time.time()
func()
stop=time.time()
print(f"[{msg}]一共耗费了{(stop-start):.2f}")
return call_func
return time_master
def funA():
time.sleep(1)
print("正在调用funA")
def funB():
time.sleep(1)
print("正在调用funB")
funA=logger(msg="A")(funA)
funB=logger(msg="B")(funB)
funA()
funB()