Pytorch网络参数初始化的方法
- 常用的参数初始化方法
| 方法(均省略前缀 torch.nn.init.) | 功能 |
|---|---|
| uniform_(tensor, a=0.0, b=1.0) | 从均匀分布 U(a,b) 中生成值,填充输入的张量 |
| normal_(tensor, mean=0.0, std=1.0) | 从给定均值 mean 和标准差 std 的正态分布中生成值,填充输入的张量 |
| constant_(tensor, val) | 用 val 的值填充输入的张量 |
| ones_(tensor) | 用 1 填充输入的张量 |
| zeros_(tensor) | 用 0 填充输入的张量 |
| eye_(tensor) | 用单位矩阵填充输入的二维张量 |
| dirac_(tensor, groups=1) | 用 Dirac delta 函数来填充 {3,4,5} 维输入张量。在卷积层中尽可能多地保存输入通道特性 |
| xavier_uniform_(tensor, gain=1.0) | 使用 Glorot initialization 方法均匀分布生成值,生成随机数填充张量 |
| xavier_normal_(tensor, gain=1.0) | 使用 Glorot initialization 方法正态分布生成值,生成随机数填充张量 |
| kaiming_uniform_(tensor, a=0, mode=‘fan_in’, nonlinearity=‘leaky_relu’) | 使用 He initialization 方法均匀分布生成值,生成随机数填充张量 |
| kaiming_normal_(tensor, a=0, mode=‘fan_in’, nonlinearity=‘leaky_relu’) | 使用 He initialization 方法正态分布生成值,生成随机数填充张量 |
| orthogonal_(tensor, gain=1) | 使用正交矩阵填充张量进行初始化 |
针对某一层的权重初始化
以卷积层为例:
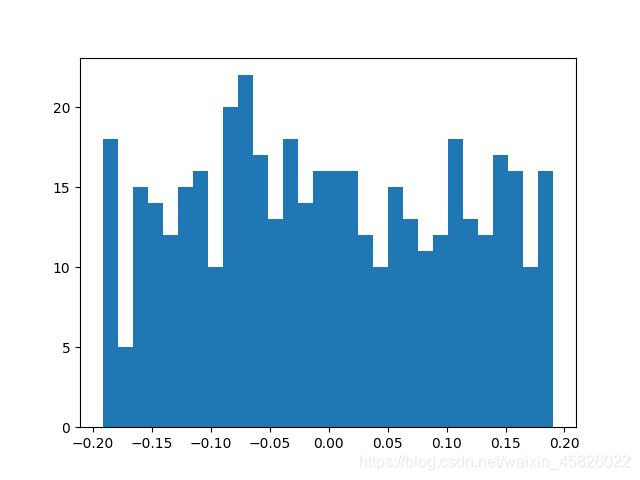
- 绘制权重默认的分布
import os # 不加会报错 Initializing libiomp5md.dll, but found libiomp5md.dll already initialized
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"] = "TRUE"
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
conv = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, 3, 2)
# 绘制权重分布图
plt.hist(conv.weight.data.numpy().reshape(-1, 1), bins=30)
plt.show()
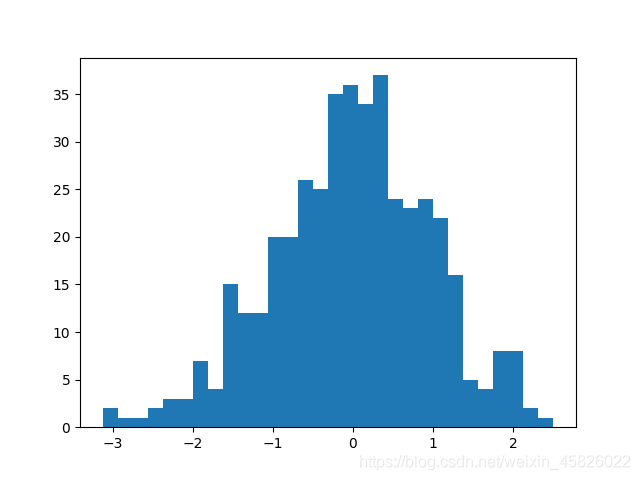
- 对权重设置初始化
import os
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"] = "TRUE"
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
conv = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, 3, 2)
# 为 conv 层的权重设置均值为0,标准差为1的正态分布初始化
nn.init.normal_(conv.weight, mean=0, std=1)
# 绘制权重分布图
plt.hist(conv.weight.data.numpy().reshape(-1, 1), bins=30)
plt.show()
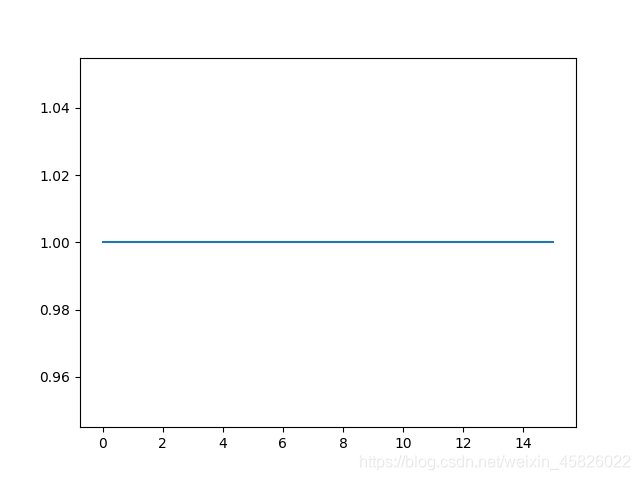
- 对偏置设置初始化
import os
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"] = "TRUE"
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
conv = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, 3, 2)
# 为 conv 层的偏置设置全1初始化
nn.init.constant_(conv.bias, 1)
# 绘制偏置分布
plt.plot(conv.bias.data.numpy().reshape(-1, 1))
plt.show()
针对整个模型的权重初始化
- 先任意定义一个网络
import os
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"] = "TRUE"
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class LeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LeNet, self).__init__()
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 128, 5, 1),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 5, 1),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 5, 1),
nn.ReLU(True),
)
self.classifer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(128, 84),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(0.1),
nn.Linear(84, 10),
nn.Softmax(-1)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = nn.ZeroPad2d((2, 2, 2, 2))(x)
x = self.features(x)
x = self.classifer(x)
return x
model = LeNet()
print(model)
LeNet(
(features): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(1, 128, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(3): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(4): ReLU(inplace=True)
(5): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(6): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(7): ReLU(inplace=True)
)
(classifer): Sequential(
(0): Flatten(start_dim=1, end_dim=-1)
(1): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=84, bias=True)
(2): ReLU(inplace=True)
(3): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
(4): Linear(in_features=84, out_features=10, bias=True)
(5): Softmax(dim=-1)
)
)
- 针对不同类型的层,可以采用不同的初始化方法。
只需定义一个函数。
def init_weights(layer):
# 如果为卷积层,使用正态分布初始化
if type(layer) == nn.Conv2d:
nn.init.normal_(layer.weight, mean=0, std=0.5)
# 如果为全连接层,权重使用均匀分布初始化,偏置初始化为0.1
elif type(layer) == nn.Linear:
nn.init.uniform_(layer.weight, a=-0.1, b=0.1)
nn.init.constant_(layer.bias, 0.1)
- 对网络进行参数初始化
# 只需要使用apply函数即可
# torch.manual_seed(2021) # 设置随机种子
model.apply(init_weights)