01
Metropolis-Hastings算法
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
## 设置参数
mu = 0.5
sigma = 0.1
skip = 700 ## 设置收敛步长
num = 100000 ##采样点数
def Gussian(x,mu,sigma):
return 1/(np.sqrt(2*np.pi)*sigma)*np.exp(-np.square((x-mu))/(2*np.square(sigma)))
def M_H(num):
x_0 = 0
samples = []
j = 1
while(len(samples) <= num):
while True:
x_1 = random.random() # 转移函数(转移矩阵)
q_i = Gussian(x_0,mu,sigma)
q_j = Gussian(x_1,mu,sigma)
alpha = min(1,q_i/q_j)
u = random.random()
if u <= alpha:
x_0 = x_1
if j >= skip:
samples.append(x_1)
j = j + 1
break
return samples
norm_samples = M_H(num)
X = np.array(norm_samples)
px = Gussian(X,mu,sigma)
plt.scatter(X,px)
plt.show()
结果
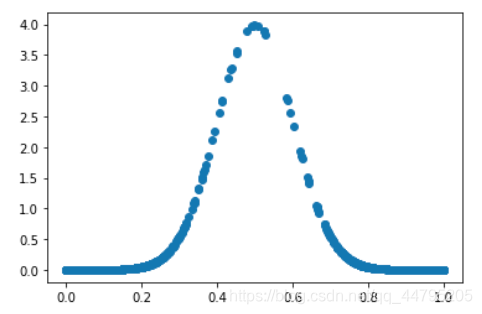
02
基础知识学习
2.1概率论与数理统计
# pi的估计问题
import numpy as np
def pi_estimate(n):
'''
n为投点的数量
'''
n_rand_X = np.random.uniform(-1.0,1.0,n)
n_rand_Y = np.random.uniform(-1.0,1.0,n)
## 判断是否在圆内
distance = np.sqrt(n_rand_X**2 + n_rand_Y**2)
dis_n = float(len(distance[distance<=1.0]))
return 4 * (dis_n / n)
for i in [10,50,100,500,1000,5000,10000,50000,100000,500000,10000000]:
print("pi的估计值为",pi_estimate(i))
# 电子元件寿命问题
import numpy as np
def ele_life(n,c,h,t,lamb):
"""
参数n:模拟实验的次数
参数c:每次试验中的c个元件
参数t:每c个元件中规定的合格品数量
参数h:小时数
"""
times = 0.0
for i in range(n):
c_rand = np.random.exponential(1/lamb,c)
c_rand_t = len(c_rand[c_rand>h])
if c_rand_t > t:
times = times + 1
return times / n
ele_life(10000,1000,18,20,0.2)
# 三门问题
import numpy.random as random
def MontyHallProblem(n_test):
#测试次数
winning_door = random.randint(0,3,n_test)
first_get = 0
change_get = 0
for winning_doors in winning_door:
act_door = random.randint(0,3)
if winning_doors == act_door:
first_get += 1
else :
change_get += 1
first_pro = first_get / n_test
change_pro = change_get / n_test
compar1 = round(change_get / first_get,2)
print ("在%d次测试中,坚持原则第一次就选中的次数是%d,改变决定选择另一扇门中奖的次数是%d"% (n_test,first_get,change_get))
print ("概率分别是{0}和{1},改变决定选择另一扇门中奖几率是坚持选择的{2}倍".format(first_pro,change_pro,compar1))
MontyHallProblem(100000)
03
随机过程
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.style.use("ggplot")
# 模拟泊松过程
def poisson_process(n,lmd,times):
## n是模拟的次数,lmd是泊松过程的强度,times是每次模拟发生的次数
fin_list = []
y_list = []
for i in range(n):
mid_list = []
mid_list_y = []
y = 1
for time in range(times):
mid_ans = np.random.exponential(lmd)
mid_list.append(mid_ans)
mid_list_y.append(y)
y = y+1
y_list.append(mid_list_y)
for p,mid in enumerate(mid_list):
if p == 0:
pass
else:
mid_list[p] = sum(mid_list[0:p+1])
fin_list.append(mid_list)
for li,y_li in zip(fin_list,y_list):
li.insert(0,0)
y_li.insert(0,0)
plt.step(li,y_li)
## 开始模拟
poisson_process(10000,0.05,10)
04
高等数学
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def f(x):
return np.power(x, 2)
def d_f_1(x):
'''
求导数的方式1
'''
return 2.0 * x
def d_f_2(f, x, delta=1e-4):
'''
求导数的第二种方法
'''
return (f(x+delta) - f(x-delta)) / (2 * delta)
# plot the function
xs = np.arange(-10, 11)
plt.plot(xs, f(xs))
learning_rate = 0.1
max_loop = 30
x_init = 10.0
x = x_init
lr = 0.1
x_list = []
for i in range(max_loop):
#d_f_x = d_f_1(x)
d_f_x = d_f_2(f, x)
x = x - learning_rate * d_f_x
x_list.append(x)
x_list = np.array(x_list)
plt.scatter(x_list,f(x_list),c="r")
plt.show()
print('initial x =', x_init)
print('arg min f(x) of x =', x)
print('f(x) =', f(x))
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
%matplotlib inline
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
class Rosenbrock():
def __init__(self):
self.x1 = np.arange(-100, 100, 0.0001)
self.x2 = np.arange(-100, 100, 0.0001)
#self.x1, self.x2 = np.meshgrid(self.x1, self.x2)
self.a = 1
self.b = 1
self.newton_times = 1000
self.answers = []
self.min_answer_z = []
# 准备数据
def data(self):
z = np.square(self.a - self.x1) + self.b * np.square(self.x2 - np.square(self.x1))
#print(z.shape)
return z
# 随机牛顿
def snt(self,x1,x2,z,alpha):
rand_init = np.random.randint(0,z.shape[0])
x1_init,x2_init,z_init = x1[rand_init],x2[rand_init],z[rand_init]
x_0 =np.array([x1_init,x2_init]).reshape((-1,1))
#print(x_0)
for i in range(self.newton_times):
x_i = x_0 - np.matmul(np.linalg.inv(np.array([[12*x2_init**2-4*x2_init+2,-4*x1_init],[-4*x1_init,2]])),np.array([4*x1_init**3-4*x1_init*x2_init+2*x1_init-2,-2*x1_init**2+2*x2_init]).reshape((-1,1)))
x_0 = x_i
x1_init = x_0[0,0]
x2_init = x_0[1,0]
answer = x_0
return answer
# 绘图
def plot_data(self,min_x1,min_x2,min_z):
x1 = np.arange(-100, 100, 0.1)
x2 = np.arange(-100, 100, 0.1)
x1, x2 = np.meshgrid(x1, x2)
a = 1
b = 1
z = np.square(a - x1) + b * np.square(x2 - np.square(x1))
fig4 = plt.figure()
ax4 = plt.axes(projection='3d')
ax4.plot_surface(x1, x2, z, alpha=0.3, cmap='winter') # 生成表面, alpha 用于控制透明度
ax4.contour(x1, x2, z, zdir='z', offset=-3, cmap="rainbow") # 生成z方向投影,投到x-y平面
ax4.contour(x1, x2, z, zdir='x', offset=-6, cmap="rainbow") # 生成x方向投影,投到y-z平面
ax4.contour(x1, x2, z, zdir='y', offset=6, cmap="rainbow") # 生成y方向投影,投到x-z平面
ax4.contourf(x1, x2, z, zdir='y', offset=6, cmap="rainbow") # 生成y方向投影填充,投到x-z平面,contourf()函数
ax4.scatter(min_x1,min_x2,min_z,c='r')
# 设定显示范围
ax4.set_xlabel('X')
ax4.set_ylabel('Y')
ax4.set_zlabel('Z')
plt.show()
# 开始
def start(self):
times = int(input("请输入需要随机优化的次数:"))
alpha = float(input("请输入随机优化的步长"))
z = self.data()
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(times):
answer = self.snt(self.x1,self.x2,z,alpha)
self.answers.append(answer)
min_answer = np.array(self.answers)
for i in range(times):
self.min_answer_z.append((1-min_answer[i,0,0])**2+(min_answer[i,1,0]-min_answer[i,0,0]**2)**2)
optimal_z = np.min(np.array(self.min_answer_z))
optimal_z_index = np.argmin(np.array(self.min_answer_z))
optimal_x1,optimal_x2 = min_answer[optimal_z_index,0,0],min_answer[optimal_z_index,1,0]
end_time = time.time()
running_time = end_time-start_time
print("优化的时间:%.2f秒!" % running_time)
self.plot_data(optimal_x1,optimal_x2,optimal_z)
if __name__ == '__main__':
snt = Rosenbrock()
snt.start()
05
线性代数
向量和矩阵计算
本次学习内容来源Datawhale组织