文章目录
一、PyTorch安装
??https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html下载对应cuda版本或cpu,对应pytorch版本,对应python版本、对应电脑系统的文件,然后在对应的虚拟环境下pip安装。下面对文件命名进行解释
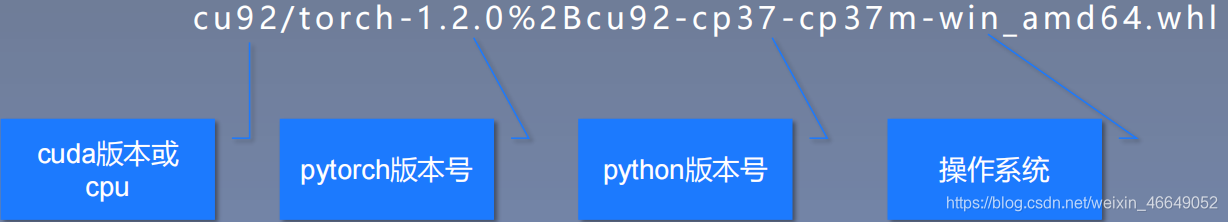
在https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html中使用crtl+f进行搜索
基于我的电脑配置,我选择这两个文件进行下载

在对应文件夹下分别pip
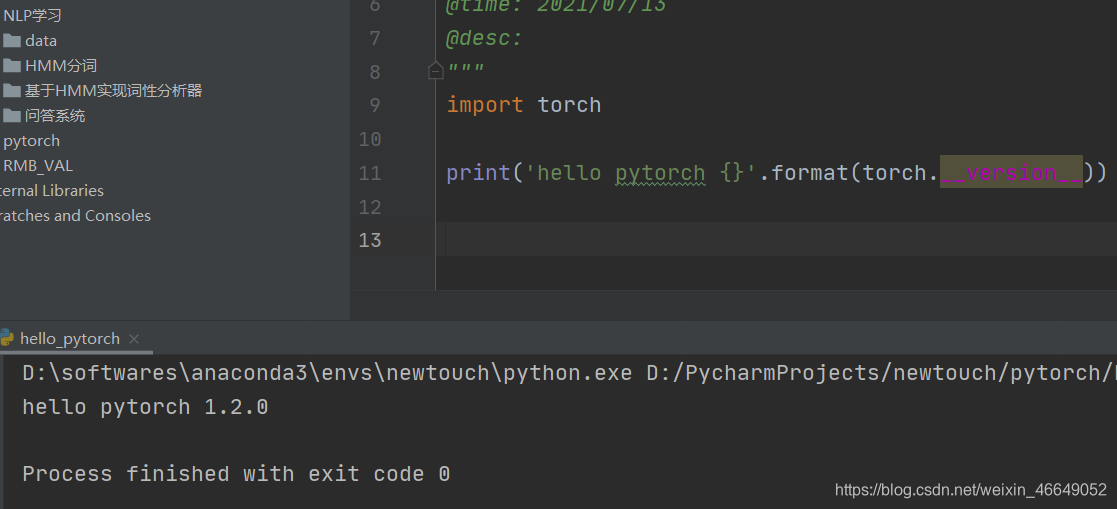
(newtouch) D:\softwares\anaconda3\envs>pip install torch-1.2.0-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl
Processing d:\softwares\anaconda3\envs\torch-1.2.0-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl
Requirement already satisfied: numpy in d:\softwares\anaconda3\envs\newtouch\lib\site-packages (from torch==1.2.0) (1.19.5)
Installing collected packages: torch
Successfully installed torch-1.2.0
(newtouch) D:\softwares\anaconda3\envs>pip install torchvision-0.4.0-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl
Processing d:\softwares\anaconda3\envs\torchvision-0.4.0-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl
Requirement already satisfied: numpy in d:\softwares\anaconda3\envs\newtouch\lib\site-packages (from torchvision==0.4.0) (1.19.5)
Requirement already satisfied: torch in d:\softwares\anaconda3\envs\newtouch\lib\site-packages (from torchvision==0.4.0) (1.2.0)
Requirement already satisfied: pillow>=4.1.1 in d:\softwares\anaconda3\envs\newtouch\lib\site-packages (from torchvision==0.4.0) (8.2.0)
Requirement already satisfied: six in d:\softwares\anaconda3\envs\newtouch\lib\site-packages (from torchvision==0.4.0) (1.16.0)
Installing collected packages: torchvision
Successfully installed torchvision-0.4.0
二、PyTorch的张量Tensor
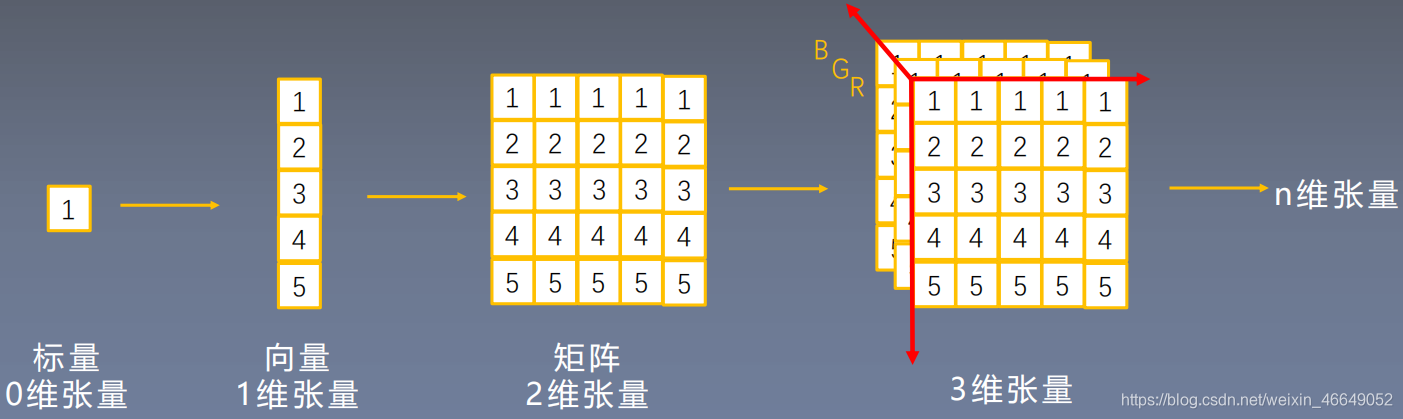
1.Tensor的概念
??张量是一个多维数组,它是标量、向量、矩阵的高维拓展。
??Variable是PyTorch0.4.0之前的重要数据类型,在PyTorch0.4.0之后已经并入到Tensor中。但是我们还要了解Variable这一数据类型,因为了解Variable对了解Tensor是十分有帮助的。Variable是torch.autograd中的数据类型,进行自动求导。
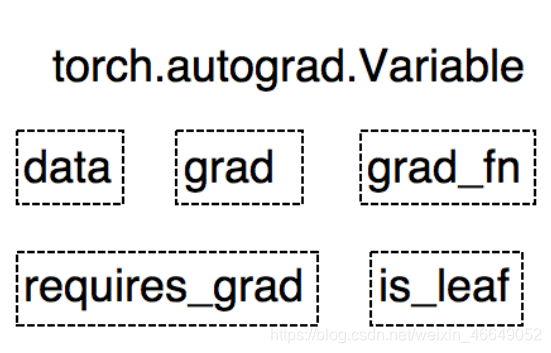
- data:被包装的Tensor
- grad: data的梯度
- grad_fn:创建Tensor的Function,是自动求导的关键
- requires_grad:指示是否需要梯度
- is_lea f:指示是否是叶子结点(张量)
??PyTorch0.4.0版开始,Variable并入Tensor。在并入之后,Tensor有8个属性:
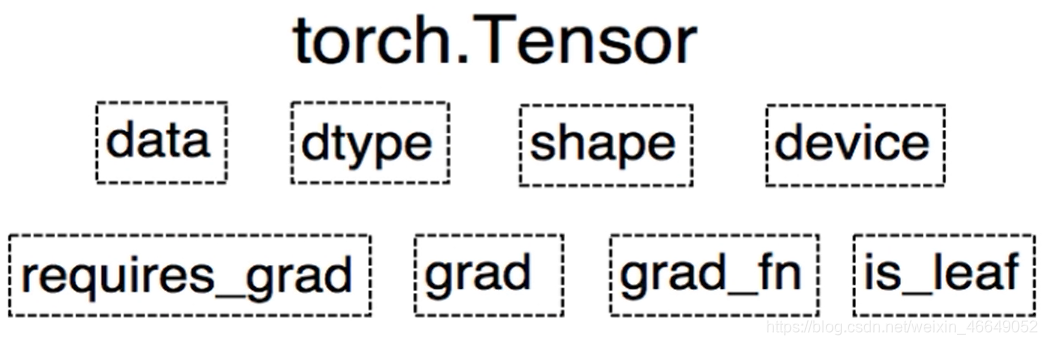
- data:被包装的Tensor
- dtype:张量的数据类型,如torch.FloatTensor, torch.cuda.FloatTensor(表示数据放到了GPU上)
- shape:张量的形状,如(64,3,224,224)
- device:张量所在设备,GPU/CPU,是加速的关键
- grad: data的梯度
- grad_fn:创建Tensor的Function,是自动求导的关键
- requires_grad:指示是否需要梯度
- is_lea f:指示是否是叶子结点(张量)
2. Tensor的创建
2.1 直接创建
??通过torch.tensor创建张量
torch.tensor(data, dtype=None, device=None, requires_grad=False,pin_memory=False)
功能:从data创建tensor
- data:数据,可以是list,numpy
- dtype:数据类型,默认与data的一致
- device :所在设备,cuda/cpu
- requires_grad:是否需要梯度
- pin_memory:是否存于锁页内存(这与转换效率有关)
# 直接创建Tensor
arr = np.ones((3, 3))
t = torch.tensor(arr)
print(t)
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]], dtype=torch.float64)
??通过torch.from_numpy()创建张量
torch.from_numpy(ndarray)
注意事项:从torch.from_numpy创建的tensor与原ndarray共享内存,当修改其中一个的数据,另外一个也将会被改动。
# 从ndarray创建Tensor
arr = np.ones((2, 2))
t1 = torch.from_numpy(arr)
print(arr)
print(t1)
[[1. 1.]
[1. 1.]]
tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]], dtype=torch.float64)
2.2 依据数值创建
??torch.zeros()
torch.zeros(*size,
out=None,dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:依size创建全0张量
- size:张量的形状,如(3,3)、(3,224,224)
- out:输出的张量
- layout :内存中布局形式,有strided,sparse_coo等
- device :所在设备,gpu/cpu
- requires_grad:是否需要梯度
??torch.zeros_like()
torch.zeros_like( input,
dtype=None,layout=None,device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:依input形状创建全0张量
- intput:创建与input同形状的全0张量
- dtype:数据类型
- layout :内存中布局形式
??torch.ones(),torch.ones_like()
torch.ones( *size,
out=None,dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:依size创建全1张量
torch.ones_like( input,
dtype=None,layout=None,device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:依input形状创建全1张量
- size:张量的形状,如(3,3)、(3,224,224)
- dtype:数据类型
- layout :内存中布局形式
- device :所在设备,gpu/cpu
- requires_grad:是否需要梯度
??torch.full(),torch.full_like()
torch.full(size,
fill_value,out=None,dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:依input形状创建指定数据的张量
- size:张量的形状,如(3,3)
- fill_value:张量的值
t2 = torch.full((3, 3), fill_value=10)
print(t2)
#tensor([[10., 10., 10.],
# [10., 10., 10.],
# [10., 10., 10.]])
??torch.arange()
torch.arange(start=0,
end,step=1,
out=None,dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided ,device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:创建等差的1维张量
注意事项:数值区间为[start, end),start:数列起始值,end:数列“结束值”,step:数列公差,默认为1
t3 = torch.arange(2, 10, 2)
print(t3)
# tensor([2, 4, 6, 8])
??torch.linspace()
torch.linspace(start,
end,
steps=100,out=None,dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:创建均分的1维张量
注意事项:数值区间为[start, end],start:数列起始值,end :数列结束值,steps:数列长度
??torch.logspace()
torch. logspace(start,end,
steps=100,base=10.0,out=None,dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:创建对数均分的1维张量
注意事项:长度为steps,底为base;start:数列起始值,end :数列结束值,steps:数列长度,base :对数函数的底,默认为10
??torch.eye()
torch.eye(n,
m=None,out=None,dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:创建单位对角矩阵(2维张量)
注意事项:默认为方阵;n:矩阵行数,m:矩阵列数
2.3 依概率分布创建
??torch.normal()
torch.normal(mean,
std,
out=None)
功能:生成正态分布(高斯分布);mean :均值,std :标准差
四种模式:
- mean为标量,std为标量
- mean为标量,std为张量
- mean为张量, std为标量
- mean为张量,std为张量
# mean:张量 std: 张量
mean = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
std = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
t_normal = torch.normal(mean, std)
print("mean:{}\nstd:{}".format(mean, std))
print(t_normal)
# mean:标量 std: 标量
t_normal = torch.normal(0., 1., size=(4,))
print(t_normal)
# mean:张量 std: 标量
mean = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float)
std = 1
t_normal = torch.normal(mean, std)
print("mean:{}\nstd:{}".format(mean, std))
print(t_normal)
??torch.randn(),torch.randn_like()
torch.randn(*size,
out=None,dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:生成标准正态分布;size :张量的形状
??torch.rand(),torch.rand_like()
torch.rand(*size,
out=None,dtype=None,
layout=torch. strided ,device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:在区间[0,1)上,生成均匀分布
??torch.randint(),torch.randint_like()
torch.randint(low=0,
high,size,
out=None,dtype=None,
layout=torch.strided,device=None,
requires grad=False)
功能:区间[low,high)生成整数均匀分布; size :张量的形状
??torch.randperm()
torch.randperm(n,
out=None,
dtype=torch.int64,layout=torch.strided ,device=None,
requires_grad=False)
功能:生成从0到n-1的随机排列;n:张量的长度
??torch.bernoulli()
torch.bernoulli(input,
*,
generator=None,
out=None)
功能:以input为概率,生成伯努利分布(0-1分布,两点分布);input :概率值
3.张量的操作
??张量的操作这一部分包括张量的拼接、切分、索引、变换以及数学运算
3.1 张量的拼接
??张量的拼接有两个方法:torch.cat()与torch.stack(),cat方法不会拓展张量维度,而stack方法会拓展张量的维度。
torch.cat()
torch.cat(tensors,
dim=0,out=None)
功能:将张量按维度dim进行拼接
- tensors:张量序列
- dim :要拼接的维度
# torch.cat() t = torch.ones((2, 3)) t_1 = torch.cat((t, t), dim=0) t_2 = torch.cat((t, t), dim=1) print("t_1:{},\nt_1.shape:{}\nt_2:{},\nt_2.shape:{}".format(t_1, t_1.shape, t_2, t_2.shape))t_1:tensor([[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]]), t_1.shape:torch.Size([4, 3]) t_2:tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]]), t_2.shape:torch.Size([2, 6])
torch.stack()
torch.stack (tensors,
dim=0,out=None)
功能:在新创建的维度dim上进行拼接
-
tensors:张量序列
-
dim :要拼接的维度
t = torch.ones((2, 3)) t_stack = torch.stack((t, t), dim=2) print('t_stack:{},\nt_stack.shape:{}'.format(t_stack, t_stack.shape))t_stack:tensor([[[1., 1.], [1., 1.], [1., 1.]], [[1., 1.], [1., 1.], [1., 1.]]]), t_stack.shape:torch.Size([2, 3, 2])
3.2 张量的切分
??张量的切分有两个方法:torch.chunk()与torch.split()
torch.chunk()
torch.chunk (input,
chunks,dim=0)
功能:将张量按维度dim进行平均切分
返回值:张量列表
注意事项:若不能整除,最后一份张量小于其他张量
-
input:要切分的张量
-
chunks :要切分的份数
-
dim:要切分的维度
t = torch.ones((2, 5)) list_of_tensor = torch.chunk(t, dim=1, chunks=2) for idx, tensor in enumerate(list_of_tensor): print('第{}个张量:{},shape:{}'.format(idx, tensor, tensor.shape))第0个张量:tensor([[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]]),shape:torch.Size([2, 3]) 第1个张量:tensor([[1., 1.], [1., 1.]]),shape:torch.Size([2, 2])
torch.split()
torch.split(tensor,
split_size_or_sections,dim=0)
功能:将张量按维度dim进行切分
返回值:张量列表
-
tensor:要切分的张量
-
split_size_or_sections : 为int时,表示每一份的长度;为list时,按list元素切分
-
dim:要切分的维度
t = torch.ones((2, 5)) list_of_tensor = torch.split(t, [2, 1, 2], dim=1) for idx, tensor in enumerate(list_of_tensor): print('第{}个张量:{},shape:{}'.format(idx, tensor, tensor.shape))第0个张量:tensor([[1., 1.], [1., 1.]]),shape:torch.Size([2, 2]) 第1个张量:tensor([[1.], [1.]]),shape:torch.Size([2, 1]) 第2个张量:tensor([[1., 1.], [1., 1.]]),shape:torch.Size([2, 2])
3.3 张量的索引
??张量的索引有如下方法:torch.index_select() 与torch.masked_select()
torch.index_select()
torch.index_select(input,
dim,index,out=None)
功能:在维度dim上,按index索引数据
返回值:依index索引数据拼接的张量
-
input:要索引的张量
-
dim:要索引的维度
-
index:要索引数据的序号
# 3*3的均匀分布 t = torch.randint(0, 9, size=(3, 3)) # 生成索引序号-torch.long64位的整型 idx = torch.tensor([0, 2], dtype=torch.long) # 依据索引选择数据 t_select = torch.index_select(t, dim=1, index=idx) print('t:\n{}\nt_select:\n{}'.format(t, t_select))t: tensor([[8, 1, 2], [4, 2, 5], [3, 4, 7]]) t_select: tensor([[8, 2], [4, 5], [3, 7]])
torch.masked_select()
torch.masked_select(input,
mask,
out=None)
功能:按mask中的True进行索引
返回值:一维张量
-
input:要索引的张量
-
mask: 与input同形状的布尔类型张量
# 3*3的均匀分布 t = torch.randint(0, 9, size=(3, 3)) # ge:大于等于;gt:大于 mask = t.ge(5) t_select = torch.masked_select(t, mask) print('t:\n{}\nmask:\n{}\nt_select:\n{}'.format(t, mask, t_select))t: tensor([[0, 7, 7], [5, 6, 5], [6, 7, 1]]) mask: tensor([[False, True, True], [ True, True, True], [ True, True, False]]) t_select: tensor([7, 7, 5, 6, 5, 6, 7])
3.4 张量的变换
??张量的变换包括:torch.reshape() 与torch.transpose()与torch.t()与torch.squeeze()与torch.unsqueeze()
torch.reshape()
torch.reshape(input,
shape)
功能:变换张量形状
注意事项:当张量在内存中是连续时,新张量与input共享数据内存
如果两个变量之间共享内存,那么改变其中一个变量的同时,另一个变量也会改变
-
input:要变换的张量
-
shape:新张量的形状
# 生成随机排列 t = torch.randperm(8) t_reshape = torch.reshape(t, (2, 4)) print('t:\n{}\nt_reshape:\n{}'.format(t, t_reshape))t: tensor([1, 3, 5, 2, 7, 4, 0, 6]) t_reshape: tensor([[1, 3, 5, 2], [7, 4, 0, 6]])
torch.transpose()
torch.transpose(input,
dim0,dim1)
功能:交换张量的两个维度
-
input:要变换的张量
-
dim0:要交换的维度
-
dim1:要交换的维度
t = torch.rand((2, 3, 4)) t_transpose = torch.transpose(t, dim0=1, dim1=2) # c*h*w h*w*c print("t shape:{}\nt_transpose shape: {}".format(t.shape, t_transpose.shape))t shape:torch.Size([2, 3, 4]) t_transpose shape: torch.Size([2, 4, 3])
torch.t()
torch.t(input)
功能:2维张量转置,对矩阵而言,等价于torch.transpose(input,0,1)
torch.squeeze()
torch.squeeze(input,
dim=None,out=None)
功能∶压缩长度为1的维度(轴)
-
dim:若为None,移除所有长度为1的轴;若指定维度,当且仅当该轴长度为1时,可以被移除
t = torch.rand((1, 2, 3, 1)) # dim为None t_sq = torch.squeeze(t) # dim=0时长度为1 t_0 = torch.squeeze(t, dim=0) # dim=1时长度不为1 t_1 = torch.squeeze(t, dim=1) print(t.shape) print(t_sq.shape) print(t_0.shape) print(t_1.shape)torch.Size([1, 2, 3, 1]) torch.Size([2, 3]) torch.Size([2, 3, 1]) torch.Size([1, 2, 3, 1])
torch.unsqueeze()
torch.usqueeze( input,
dim,
out=None)
功能:依据dim扩展维度
-
dim:扩展的维度
t_unsq = torch.unsqueeze(t_sq, dim=0) print(t_sq.shape) print(t_unsq.shape)torch.Size([2, 3]) torch.Size([1, 2, 3])
3.5 张量的数学运算
??PyTorch中提供大量的数学运算,大致可以分为三类:
-
加减乘除
torch.add() torch.addcdiv() torch.addcmul() torch.sub() torch.div() torch.mu()torch.add()torch.add(input, alpha=1,other,out=None)功能:逐元素计算inputo+alpha ×other
input:第一个张量
alpha:乘项因子
other:第二个张量torch.addcmul()torch.addcmul(input, value=1,tensor1,tensor2,out=None)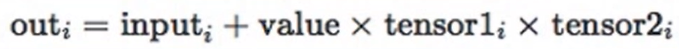
torch.addcdiv()
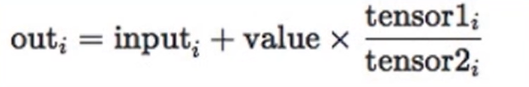
-
对数指数幂函数
torch.log(input,out=None) torch.log10(input, out=None) torch.log2(input, out=None) torch.exp(input,out=None) torch.pow() -
三角函数
torch.abs(input, out=None) torch.acos(input, out=None) torch.cosh(input, out=None) torch.cos(input, out=None) torch.asin(input, out=None) torch.atan(input, out=None) torch.atan2(input, other, out=None)
如果对您有帮助,麻烦点赞关注,这真的对我很重要!!!如果需要互关,请评论或者私信!
