1.认识
? ? ? ?感知器算法是神经网络算法中结构最简单的模型,它可以对两种类型进行线性分类。
2.单层感知器通用模型示意图
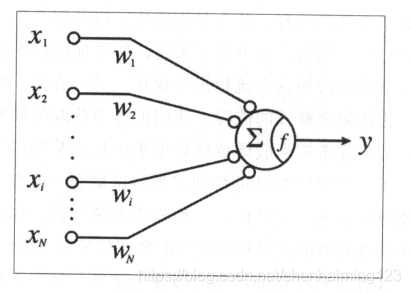
? ? ? ? 这幅图中的 xi 表示输入信号, Wi表示每一种输入信号对应的权重, y 表示输出信号?。 f是激活函数。 实际上,累加符号表示的是对所有输入数据的求和计算。 请牢记,xi是依据预先定义的特征工程以非线性转换,所以 X i?是工程化的特征。
3、设计思想
? ? ? 3.1、感知器返回的输出是每个特征乘以其对应权重,然后求和,再将所求和作为阶跃函数的激活输入。 其输出结果就是感知器的判断结果 。
4.架构设计
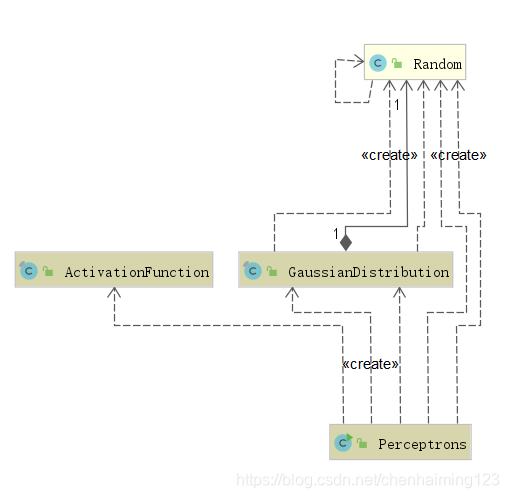
5.类设计
Perceptrons类:
package DLWJ.SingleLayerNeuralNetworks;
import java.util.Random;
import DLWJ.util.GaussianDistribution;
import static DLWJ.util.ActivationFunction.step;
//单层感知器
public class Perceptrons {
public int nIn; // dimensions of input data 输入数据的维度
public double[] w; // weight vector of perceptrons 感知器的权重向量
//这个感知器模型中只有网络的权重w,非常检查
public Perceptrons(int nIn) {
this.nIn = nIn;
w = new double[nIn];
}
//在train方法中使用帝都下降算法--这里的网络参数w已经更新了
public int train(double[] x, int t, double learningRate) {
int classified = 0;
double c = 0.;
// check if the data is classified correctly 检查数据是否正确分类
for (int i = 0; i < nIn; i++) {
c += w[i] * x[i] * t;
}
// apply steepest descent method if the data is wrongly classified 如果数据分类错误,则应用最速下降法
if (c > 0) {
classified = 1;//分类重新设置
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < nIn; i++) {
w[i] += learningRate * x[i] * t;
}
}
return classified;
}
//predict只是简单地通过网络激活了输入,这里的阶跃函数定义在ActivationFunction.java中
public int predict (double[] x) {
double preActivation = 0.;
for (int i = 0; i < nIn; i++) {
preActivation += w[i] * x[i];//权重乘以测试集合的数组,然后累加--P37页的公式
}
return step(preActivation);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
// Declare (Prepare) variables and constants for perceptrons 为感知器声明(准备)变量和常量
//
final int train_N = 1000; // number of training data训练数据的数量
final int test_N = 200; // number of test data测试数据数量
final int nIn = 2; // dimensions of input data 输入数据的维度--我们设置了学习数据的维度为2维,即平面型数据--输入层中的单元数-决定了模型的轮廓
double[][] train_X = new double[train_N][nIn]; // input data for training训练输入数据
int[] train_T = new int[train_N]; // output data (label) for training用于训练的输出数据(标签)
double[][] test_X = new double[test_N][nIn]; // input data for test测试输入数据
int[] test_T = new int[test_N]; // label of inputs 用于测试的数据的实际标记
int[] predicted_T = new int[test_N]; // output data predicted by the model模型预测的输出数据
final int epochs = 2000; // maximum training epochs 最大训练时期--最大迭代次数
final double learningRate = 1.; // learning rate can be 1 in perceptrons 感知器中的学习率可以是 1
//
// Create training data and test data for demo.为演示创建训练数据和测试数据。
//
// Let training data set for each class follow Normal (Gaussian) distribution here: 让每个类的训练数据集遵循正态(高斯)分布:
// class 1 : x1 ~ N( -2.0, 1.0 ), y1 ~ N( +2.0, 1.0 )
// class 2 : x2 ~ N( +2.0, 1.0 ), y2 ~ N( -2.0, 1.0 )
//
final Random rng = new Random(1234); // seed random 随机种子
GaussianDistribution g1 = new GaussianDistribution(-2.0, 1.0, rng);//实例1 //均值mean为-2.0,var方差1.0
GaussianDistribution g2 = new GaussianDistribution(2.0, 1.0, rng);//实例2
// data set in class 1---得到一组正太分布的数值--在类1中可以生成500个数据属性--类1中的数据都标记为1--最终结果训练数据在区间-2.0到2.0
for (int i = 0; i < train_N/2 - 1; i++) {
train_X[i][0] = g1.random();//均值-2.0,方差1.0-- train_X[i][0]产生例如-1.4157的数
train_X[i][1] = g2.random();//均值2.0,方差1.0
train_T[i] = 1;// 用于测试的数据的实际标记为1
}
for (int i = 0; i < test_N/2 - 1; i++) {//得到一组测试数据
test_X[i][0] = g1.random();
test_X[i][1] = g2.random();
test_T[i] = 1;
}
// data set in class 2 生成另外500个数据属性---------类2的每个数据都标记为-1---最终结果在区间2.0到-2.0--java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException : Invalid array index: 501
for (int i = train_N/2; i < train_N; i++) {//异常-todo--边界异常
train_X[i][0] = g2.random();
train_X[i][1] = g1.random();
train_T[i] = -1;
}
for (int i = test_N/2; i < test_N; i++) {
test_X[i][0] = g2.random();
test_X[i][1] = g1.random();
test_T[i] = -1;
}
//
// Build SingleLayerNeuralNetworks model 构建单层神经网络模型
//
int epoch = 0; // training epochs
// construct perceptrons 构建感知器---nIn的维度决定模型的轮廓
Perceptrons classifier = new Perceptrons(nIn);
// train models 最后一步,学习迭代会一直持续,直到学习集达到预设的数值。或正确分类所有训练数据
while (true) {//最大训练时期--最大迭代次数2000
int classified_ = 0;
for (int i=0; i < train_N; i++) {//训练数据的数量,得到类型为0的集合的总数
classified_ += classifier.train(train_X[i], train_T[i], learningRate);
}
if (classified_ == train_N) {
break;
} // when all data classified correctly 当所有数据正确分类时
epoch++;
if (epoch > epochs){
break;
}
}
// test ---一旦你对足够的数据完成了学习并构建好模型,下一步就可以测试了。首先使用训练好的模型检查测试数据的分类属于哪一类
for (int i = 0; i < test_N; i++) {
predicted_T[i] = classifier.predict(test_X[i]);//得到预测为1的分类
}
//
// Evaluate the model 评估模型;
//
int[][] confusionMatrix = new int[2][2];//混淆矩阵
double accuracy = 0.;//正确率
double precision = 0.;//精确度
double recall = 0.;//召回率
for (int i = 0; i < test_N; i++) {
if (predicted_T[i] > 0) {
if (test_T[i] > 0) {
accuracy += 1;//正确率
precision += 1;//精确度
recall += 1;//召回率
confusionMatrix[0][0] += 1;
} else {
confusionMatrix[1][0] += 1;
}
} else {
if (test_T[i] > 0) {
confusionMatrix[0][1] += 1;
} else {
accuracy += 1;//正确率
confusionMatrix[1][1] += 1;
}
}
}
accuracy /= test_N;//准确性=正确/总数
precision /= confusionMatrix[0][0] + confusionMatrix[1][0];//精确度=正确/(正确预测到正例+把负例预测到正例)
recall /= confusionMatrix[0][0] + confusionMatrix[0][1];//召回率=正确/(正确预测到正例+把正例预测到负例)=1
System.out.println("-------------感知器模型评估---------------");
System.out.println("Perceptrons model evaluation");
System.out.println("----------------------------");
System.out.printf("Accuracy: %.1f %%\n", accuracy * 100);
System.out.printf("Precision: %.1f %%\n", precision * 100);
System.out.printf("Recall: %.1f %%\n", recall * 100);
}
}
ActivationFunction类:package DLWJ.util;
//激活函数;---阶跃函数
public final class ActivationFunction {
public static int step(double x) {
if (x >= 0) {
return 1;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
public static double sigmoid(double x) {
return 1. / (1. + Math.pow(Math.E, -x));
}
//sigmoid函数求导
public static double dsigmoid(double y) {
return y * (1. - y);
}
//双曲正切---Sigmoid tanh : 核函数--Hyperbolic Tangent--双曲正切函数
public static double tanh(double x) {
return Math.tanh(x);
}
//双曲正切函数求导
public static double dtanh(double y) {
return 1. - y * y;
}
//分类器---回归--该方法返回一个数组,该数组显示了当前样本属于每个类别的概率,因此,你只需要找出数组中具有最高概率的元素索引,该索引代表预测的类
public static double[] softmax(double[] x, int n) {
double[] y = new double[n];
double max = 0.;
double sum = 0.;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (max < x[i]) {
max = x[i]; // to prevent overflow 为了防止溢出;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
y[i] = Math.exp( x[i] - max );
sum += y[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
y[i] /= sum;
}
return y;
}
}
GaussianDistribution类:package DLWJ.util;
import java.util.Random;
//高斯分布---正太分布---返回某个值
public final class GaussianDistribution {
private final double mean;//均值
private final double var;
private final Random rng;
//均值、方差、随机数种子
public GaussianDistribution(double mean, double var, Random rng) {
if (var < 0.0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Variance must be non-negative value.");//方差必须是非负值
}
this.mean = mean;
this.var = var;
if (rng == null) {
rng = new Random();
}
this.rng = rng;
}
//随机数范围
public double random() {
double r = 0.0;
while (r == 0.0) {
r = rng.nextDouble();//得到一个均匀分布的随机数范围在0.0到1.0之间
}
double c = Math.sqrt( -2.0 * Math.log(r) );//此方法返回一个正平方根.Math.log() 方法用于返回参数的自然数底数的对数值
if (rng.nextDouble() < 0.5) {//如果均匀分布的随机数小于0.5
return c * Math.sin( 2.0 * Math.PI * rng.nextDouble() ) * var + mean;//重置返回一个:均值(训练1设置为-2)+方差+c+正弦函数值sin(圆周长)
}
return c * Math.cos( 2.0 * Math.PI * rng.nextDouble() ) * var + mean;//返回一个正态分布的数
}
}
6、总结
? ? ? ? ?该例子需要逐步调试来验证原理。
本文资料来自《深度学习-Java语音实现》-【日】Yusuke Sugomori 著