文章目录
一、数据预处理transforms模块机制
??torchvision.transforms模块包含了很多图像预处理方法:
- 数据中心化
- 数据标准化
- 缩放
- 裁剪
- 旋转
- 翻转
- 填充
- 噪声添加
- 灰度变换
- 线性变换
- 仿射变换
- 亮度、饱和度及对比度变换
这个模块可以进行数据增强与数据预处理,增强模型的泛化能力。数据预处理transforms在数据读取过程中,最后生成数据预处理完的batch data。
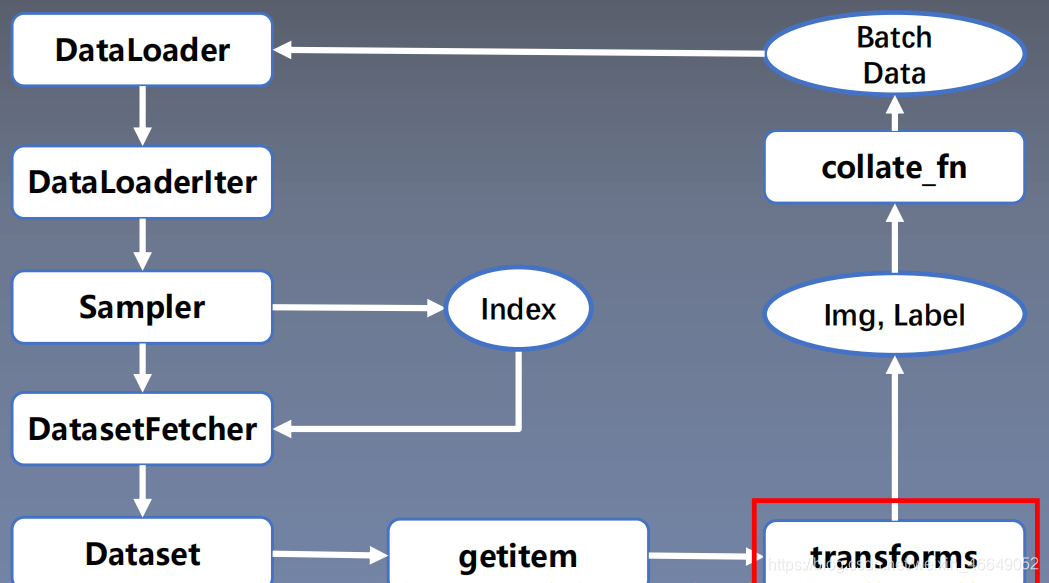
class RMBDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data_dir, transform=None):
"""
rmb面额分类任务的Dataset
:param data_dir: str, 数据集所在路径
:param transform: torch.transform,数据预处理
"""
self.label_name = {"1": 0, "100": 1}
self.data_info = self.get_img_info(data_dir) # data_info存储所有图片路径和标签,在DataLoader中通过index读取样本
self.transform = transform
def __getitem__(self, index):
path_img, label = self.data_info[index]
img = Image.open(path_img).convert('RGB') # 0~255
# 在数据读取的这个节点开始调用transform,迭代使用多种tansform方法
if self.transform is not None:
img = self.transform(img) # 在这里做transform,转为tensor等等
return img, label
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data_info)
@staticmethod
def get_img_info(data_dir):
data_info = list()
for root, dirs, _ in os.walk(data_dir):
# 遍历类别
for sub_dir in dirs:
img_names = os.listdir(os.path.join(root, sub_dir))
img_names = list(filter(lambda x: x.endswith('.jpg'), img_names))
# 遍历图片
for i in range(len(img_names)):
img_name = img_names[i]
path_img = os.path.join(root, sub_dir, img_name)
label = rmb_label[sub_dir]
data_info.append((path_img, int(label)))
return data_info
二、二十二种transforms数据预处理方法
2.裁剪
??transforms.CenterCrop
功能:从图像中心裁剪图片
- size:所需裁剪图片尺寸
??transforms.RandomCrop
transforms.RandomCrop(size,
padding=None,
pad_if_needed=False,fill=6,
padding_mode= 'constant ' )
功能:从图片中随机裁剪出尺寸为size的图片
- size:所需裁剪图片尺寸
- padding:设置填充大小
当为a时,上下左右均填充a个像素
当为(a, b)时,上下填充b个像素,左右填充a个像素
当为(a,b,c,d)时,左,上,右,下分别填充a, b,c, d - pad_if_need:若图像小于设定size,则填充
- padding_mode:填充模式,有4种模式
1、constant:像素值由filI设定
2、edge:像素值由图像边缘像素决定
3、reflect:镜像填充,最后一个像素不镜像,eg:[1,2,3.4] →[3,2,1,2,3,4,3,2]
4、symmetric:镜像填充,最后一个像素镜像,eg:[1,2,3,4]→[2,1,1,2,3,4,4,3]. - fill: constant时,设置填充的像素值
??transforms.RandomResizedCrop
RandomResizedCrop(size,
scale=(0.08,1.0),
ratio=(3/4,4/3),interpolation)
功能:随机大小、长宽比裁剪图片
- size:所需裁剪图片尺寸
- scale :随机裁剪面积比例,默认(0.08,1)
- ratio:随机长宽比,默认(3/4,4/3)
- interpolation:插值方法
PIL.lmage.NEAREST
PIL.lmage.BILINEAR
PIL.lmage.BICUBIC
??transforms.FiveCrop
transforms .FiveCrop(size)
功能:在图像的上下左右以及中心裁剪出尺寸为size的5张图片
# 将tuple格式转换为Tensor格式
transforms.FiveCrop(112),
transforms.Lambda(lambda crops: torch.stack([(transforms.ToTensor()(crop)) for crop in crops]))
??transforms.TenCrop
功能:TenCrop对这5张图片进行水平或者垂直镜像获得10张图片
- size :所需裁剪图片尺寸
- vertical_flip :是否垂直翻转
transforms.TenCrop(112, vertical_flip=False),
transforms.Lambda(lambda crops: torch.stack([(transforms.ToTensor()(crop)) for crop in crops]))
3. 翻转与旋转
??transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5)
功能:依概率水平(左右)翻转图片
- p:翻转概率
??transforms.RandomVerticalFlip
transforms.RandomVerticalFlip(p=0.5)
功能:依概率垂直(上下)翻转图片
- p:翻转概率
??transforms.RandomRotation
RandomRotation(degrees,
resample=False,expand=False,
center=None)
功能:随机旋转图片
- degrees :旋转角度
当为a时,在(-a,a)之间选择旋转角度
当为(a,b)时,在(a,b)之间选择旋转角度 - resample :重采样方法
- expand :是否扩大图片,以保持原图信息
4.图像变换
??transforms.Pad
transforms.Pad(padding,
fill=0,
padding_mode= ' constant ' )
功能:对图片边缘进行填充
- padding:设置填充大小
当为a时,上下左右均填充a个像素
当为(a, b)时,上下填充b个像素,左右填充a个像素
当为(a,b,c,d)时,左,上,右,下分别填充a,b,c,d - padding_mode:填充模式,有4种模式,
constant、edge、reflect和symmetric - fill:constant时,设置填充的像素值,(R,G,B)or(Gray)
??transforms.colorjitter
transforms.colorJitter(brightness=0,
contrast=0,
saturation=0,
hue=0)
功能:调整亮度、对比度、饱和度和色相
- brightness:亮度调整因子
当为a时,从[max(0,1-a),1+a]中随机选择
当为(a,b)时,从[a,b]中随机选择 - contrast :对比度参数,同brightness
- saturation:饱和度参数,同brightness
- hue:色相参数,
当为a时,从[-a,a]中选择参数,
注:0<= a <= 0.5
当为(a,b)时:,从[a,b]中选择参数
注:-0.5<=a<=b<=0.5
??transforms.Grayscale
Grayscale(num_output_channels)
功能:将图片转换为灰度图
- num_ouput_channels:输出通道数 只能设1或3
??transforms.RandomGrayscale
功能:依概率将图片转换为灰度图
- num_ouput_channels:输出通道数 只能设1或3
- p︰概率值,图像被转换为灰度图的概率
??transforms.RandomAffine
transforms.RandomAffine(degrees,
translate=None,scale=None,
shear=None ,resample=False,fillcolor=)
功能:对图像进行仿射变换,仿射变换是二维的线性变换,由五种基本原子变换构成,分别是旋转、平移、缩放、错切和翻转
- degrees:旋转角度设置
- translate:平移区间设置
如(a,b),a设置宽(width),b设置高(height)图像在宽维度平移的区间为
-img_width * a < dx < img_width * a - scale:缩放比例(以面积为单位)
- fill_color:填充颜色设置
- shear:错切角度设置,有水平错切和垂直错切
若为a,则仅在x轴错切,错切角度在(-a, a)之间
若为(a, b),则a设置x轴角度,b设置y的角度
若为(a, b,c,d),则a, b设置x轴角度,c,d设置y轴角度 - resample:重采样方式,有NEAREST 、BILINEAR、BICUBIC
??transforms.RandomErasing
transforms.RandomErasing(p=0.5,
scale=(0.02,0.33),
ratio=(0.3,3.3),value=0,
inplace=False)
功能:对图像进行随机遮挡
- p:概率值,执行该操作的概率
- scale:遮挡区域的面积
- ratio:遮挡区域长宽比
- value:设置遮挡区域的像素值,(R,G,B) or (Gray)
??transforms.Lambda(lambd)
功能:用户自定义lambda方法
- lambd : lambda匿名函数
lambda [arg1 [,arg2, … , argn]] : expression
eg:
transforms. Lambda(lambda crops: torch.stack([transforms. Totensor()(crop) for crop in crops]))
5.transforms方法的选择操作
??transforms.RandomChoice
功能:从一系列transforms方法中随机挑选一个
transforms. RandomChoice([transforms1,transforms2,transforms3])
??transforms.RandomApply
功能:依据概率执行一组transforms操作
transforms.RandomApply([transforms1,transforms2,transforms3], p=0.5)
??transforms.RandomOrder
功能:对一组transforms操作打乱顺序
transforms. Randomorder([transforms1,transforms2,transforms3])
??transforms.Resize
功能:调整图片的大小
??transforms.Totensor
功能:将之前的数据结构转换为张量
??transforms.Normalize
transforms.Normalize(mean,
std,
inplace=False)
功能:逐channel的对图像进行标准化(变换后的数据均值为0,标准差为1),标准化的优点是加快模型的收敛。
o
u
t
p
u
t
=
(
i
n
p
u
t
?
m
e
a
n
)
/
s
t
d
output = (input - mean) / std
output=(input?mean)/std
- mean :各通道的均值
- std:各通道的标准差
- inplace :是否原地操作
源码如下:
def normalize(tensor, mean, std, inplace=False):
"""Normalize a tensor image with mean and standard deviation.
.. note::
This transform acts out of place by default, i.e., it does not mutates the input tensor.
See :class:`~torchvision.transforms.Normalize` for more details.
Args:
tensor (Tensor): Tensor image of size (C, H, W) to be normalized.
mean (sequence): Sequence of means for each channel.
std (sequence): Sequence of standard deviations for each channel.
inplace(bool,optional): Bool to make this operation inplace.
Returns:
Tensor: Normalized Tensor image.
"""
# 输入的合法性判断-是否为Tensor
if not _is_tensor_image(tensor):
raise TypeError('tensor is not a torch image.')
# 是否原地操作,如果不是原地操作,需要将张量克隆一份
if not inplace:
tensor = tensor.clone()
dtype = tensor.dtype
# 将均值与方差转化为张量
mean = torch.as_tensor(mean, dtype=dtype, device=tensor.device)
std = torch.as_tensor(std, dtype=dtype, device=tensor.device)
# sub_:下划线表示原地操作;(input - mean) / std
tensor.sub_(mean[:, None, None]).div_(std[:, None, None])
# 返回变换后的张量
return tensor
6.自定义transfroms方法
??transforms方法是在Compose类中通过__call__方法调用的。
class Compose(object):
"""Composes several transforms together.
Args:
transforms (list of ``Transform`` objects): list of transforms to compose.
Example:
>>> transforms.Compose([
>>> transforms.CenterCrop(10),
>>> transforms.ToTensor(),
>>> ])
"""
def __init__(self, transforms):
self.transforms = transforms
def __call__(self, img):
# 循环执行transforms方法
for t in self.transforms:
img = t(img)
return img
def __repr__(self):
format_string = self.__class__.__name__ + '('
for t in self.transforms:
format_string += '\n'
format_string += ' {0}'.format(t)
format_string += '\n)'
return format_string
我们可以发现调用transforms时有如下特点:
- 仅接收一个参数,返回一个参数
- 注意上下游的输出与输入
??下面我们自定义transforms,它的基本结构为:
class YourTransforms(object) :
def __init_(self, ...):
...
def __cal1__(self, img):
...
return img
??椒盐噪声又称为脉冲噪声,是一种随机出现的白点或者黑点,白点称为盐噪声,黑色为椒噪声。信噪比(Signal-Noise Rate,SNR)是衡量噪声的比例,图像中为图像像素的占比。我们以椒盐噪声为例来自定义transforms方法。
class AddPepperNoise(object):
"""增加椒盐噪声
Args:
snr (float): Signal Noise Rate
p (float): 概率值,依概率执行该操作
"""
def __init__(self, snr, p=0.9):
assert isinstance(snr, float) and (isinstance(p, float)) # 2020 07 26 or --> and
# 信号百分比
self.snr = snr
# 概率
self.p = p
def __call__(self, img):
"""
Args:
img (PIL Image): PIL Image
Returns:
PIL Image: PIL image.
"""
# 概率的判断
if random.uniform(0, 1) < self.p:
# 数据格式转换到ndarray
img_ = np.array(img).copy()
# 高,宽,通道数
h, w, c = img_.shape
# 获取信号百分比
signal_pct = self.snr
# 噪声百分比
noise_pct = (1 - self.snr)
# 依概率选取3个mask
mask = np.random.choice((0, 1, 2), size=(h, w, 1), p=[signal_pct, noise_pct/2., noise_pct/2.])
mask = np.repeat(mask, c, axis=2)
img_[mask == 1] = 255 # 盐噪声
img_[mask == 2] = 0 # 椒噪声
return Image.fromarray(img_.astype('uint8')).convert('RGB')
else:
return img
如果对您有帮助,麻烦点赞关注,这真的对我很重要!!!如果需要互关,请评论或者私信!
