在目标检测的后处理阶段我们需要用到NMS算法。
而在NMS算法里有一个步是需要计算当前score最大的框和其他框的IoU大小的。
针对这一步,我们可以进行优化,改变IoU的计算方式。
目前经典的IoU计算方式有GIoU,DIoU和CIoU。我们可以在传统的NMS算法中进行修改实现
CIoU NMS,DIoU NMS和GIoU NMS。
先看下传统的NMS算法的代码:
def ori_nms(self, scores, boxes, iou_thres):
if boxes.shape[0] == 0:
return torch.zeros(0,device=boxes.device).long()
x1,y1,x2,y2 = boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 2], boxes[:,3]
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
order = torch.sort(scores, descending=True)[1] #(?,)
keep =[]
while order.numel() > 0:
if order.numel() == 1:
keep.append(order.item())
break
else:
i = order[0].item()
keep.append(i)
xmin = torch.clamp(x1[order[1:]], min = float(x1[i]))
ymin = torch.clamp(y1[order[1:]], min = float(y1[i]))
xmax = torch.clamp(x2[order[1:]], max = float(x2[i]))
ymax = torch.clamp(y2[order[1:]], max = float(y2[i]))
inter_area = torch.clamp(xmax - xmin, min=0.0) * torch.clamp(ymax - ymin, min=0.0)
iou = inter_area / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter_area + 1e-16)
mask_ind = (iou <= iou_thres).nonzero().squeeze()
if mask_ind.numel() == 0:
break
order = order[mask_ind + 1]
return torch.LongTensor(keep)
传统的NMS算法网上解读很多了,简单来说,就是先挑一个最大score的框,和剩下的做IoU计算,如果低于iou_thres就舍弃掉。接着在剩下的再选score最大的框,依次循环,直到结束。
接着我们使用DIoU改造NMS算法。
# wzf add diou nms
def diou_box_nms(self, scores, boxes, iou_thres):
if boxes.shape[0] == 0:
return torch.zeros(0,device=boxes.device).long()
x1,y1,x2,y2 = boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 2], boxes[:,3]
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
order = torch.sort(scores, descending=True)[1] #(?,)
keep =[]
while order.numel() > 0:
if order.numel() == 1:
keep.append(order.item())
break
else:
i = order[0].item()
keep.append(i)
xmin = torch.clamp(x1[order[1:]], min = float(x1[i]))
ymin = torch.clamp(y1[order[1:]], min = float(y1[i]))
xmax = torch.clamp(x2[order[1:]], max = float(x2[i]))
ymax = torch.clamp(y2[order[1:]], max = float(y2[i]))
inter_area = torch.clamp(xmax - xmin, min=0.0) * torch.clamp(ymax - ymin, min=0.0)
iou = inter_area / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter_area + 1e-16)
# diou add center
# inter_diag
cxpreds = (x2[i] + x1[i]) / 2
cypreds = (y2[i] + y1[i]) / 2
cxbbox = (x2[order[1:]] + x1[order[1:]]) / 2
cybbox = (y1[order[1:]] + y2[order[1:]]) / 2
inter_diag = (cxbbox - cxpreds) ** 2 + (cybbox - cypreds) ** 2
# outer_diag
ox1 = torch.min(x1[order[1:]], x1[i])
oy1 = torch.min(y1[order[1:]], y1[i])
ox2 = torch.max(x2[order[1:]], x2[i])
oy2 = torch.max(y2[order[1:]], y2[i])
outer_diag = (ox1 - ox2) ** 2 + (oy1 - oy2) ** 2
diou = iou - inter_diag / outer_diag
diou = torch.clamp(diou, min=-1.0, max=1.0)
# mask_ind = (iou <= iou_thres).nonzero().squeeze()
mask_ind = (diou <= iou_thres).nonzero().squeeze()
if mask_ind.numel() == 0:
break
order = order[mask_ind + 1]
return torch.LongTensor(keep)
关于DIoU,D是Distance的意思,也就是下面这张图。
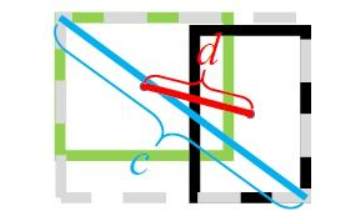
DIoU Loss
图片是讲DIoU Loss,但是也可以帮助我们理解DIoU的计算方式。
其实从代码角度,我们可以发现,就是乘了一个系数。
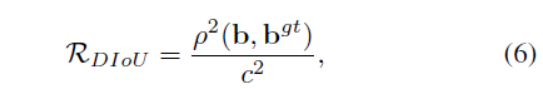
接下来我们看GIoU。
其实GIoU是更早的论文了,先于DIoU和CIoU。
直接看下代码吧!~
# wzf add ciou
def ciou_box_nms(self, scores, boxes, iou_thres):
if boxes.shape[0] == 0:
return torch.zeros(0,device=boxes.device).long()
x1,y1,x2,y2 = boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 2], boxes[:,3]
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
order = torch.sort(scores, descending=True)[1] #(?,)
keep =[]
while order.numel() > 0:
if order.numel() == 1:
keep.append(order.item())
break
else:
i = order[0].item()
keep.append(i)
xmin = torch.clamp(x1[order[1:]], min = float(x1[i]))
ymin = torch.clamp(y1[order[1:]], min = float(y1[i]))
xmax = torch.clamp(x2[order[1:]], max = float(x2[i]))
ymax = torch.clamp(y2[order[1:]], max = float(y2[i]))
inter_area = torch.clamp(xmax - xmin, min=0.0) * torch.clamp(ymax - ymin, min=0.0)
iou = inter_area / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter_area + 1e-16)
# ciou add center
# inter_diag
cxpreds = (x2[i] + x1[i]) / 2
cypreds = (y2[i] + y1[i]) / 2
cxbbox = (x2[order[1:]] + x1[order[1:]]) / 2
cybbox = (y1[order[1:]] + y2[order[1:]]) / 2
inter_diag = (cxbbox - cxpreds) ** 2 + (cybbox - cypreds) ** 2
# outer_diag
ox1 = torch.min(x1[order[1:]], x1[i])
oy1 = torch.min(y1[order[1:]], y1[i])
ox2 = torch.max(x2[order[1:]], x2[i])
oy2 = torch.max(y2[order[1:]], y2[i])
outer_diag = (ox1 - ox2) ** 2 + (oy1 - oy2) ** 2
# ciou
u = (inter_diag) / outer_diag
w1 = x2[i] - x1[i]
h1 = y2[i] - y1[i]
w2 = x2[order[1:]] - x1[order[1:]]
h2 = y2[order[1:]] - y1[order[1:]]
with torch.no_grad():
arctan = torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1)
v = (4 / (math.pi ** 2)) * torch.pow((torch.atan(w2 / h2) - torch.atan(w1 / h1)), 2)
S = 1 - iou
alpha = v / (S + v)
ciou = iou - (u + alpha * v)
# end
# mask_ind = (iou <= iou_thres).nonzero().squeeze()
mask_ind = (ciou <= iou_thres).nonzero().squeeze()
if mask_ind.numel() == 0:
break
order = order[mask_ind + 1]
return torch.LongTensor(keep)
CIoU,中的C就是Completely的意思,也就是考虑的东西更多也更加复杂。而且和DIoU是同一篇论文!
后续:关于NMS的改进里还有Soft-NMS,其中也是有IoU的计算的,我们也是可以进行修改得到Soft CIoU-NMS,Soft DIoU-NMS和Soft GIoU-NMS。
参考:
1、paper:Generalized Intersection over Union: A Metric and A Loss for Bounding Box Regression
2、paper:Distance-IoU Loss: Faster and Better Learning for Bounding Box Regression