前言
本文是训练多层感知机的代码实现,具体原理及推导请看BP神经网络原理(详细推导)。
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
第一步.读取数据
import os
import struct
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def getMNIST(kind = 'train'):
#获得当前路径
path = os.getcwd()
#获得标签文件路径
labels_path = os.path.join(path,'%s-labels-idx1-ubyte' % kind)
#获得图片路径
images_path = os.path.join(path,'%s-images-idx3-ubyte' % kind)
with open(labels_path,'rb') as lbpath:
magic, n = struct.unpack('>II',
lbpath.read(8))
labels = np.fromfile(lbpath,dtype = np.uint8)
with open(images_path,'rb') as imgpath:
magic, num, rows, cols = struct.unpack('>IIII',
imgpath.read(16))
images = np.fromfile(imgpath,dtype = np.uint8).reshape(len(labels),rows*cols)
#像素归一化
images = ((images/255)-0.5)*2
return images,labels
#MNIST 数据集 : 60000,60000*784,10000,10000*784 respectly.
X_train,y_train = getMNIST(kind = 'train')
X_test,y_test = getMNIST(kind = 't10k')
第二步.搭建多层感知机
class MutiLayerNeuralNetWork(object):
def __init__(self,
l2 = 0.01,
eta = 0.001,
epochs = 10,
shuffle = True,
Random_seed = 1,
hidden_unit = 100,
minibatch_size = 200,):
self.l2 = l2
self.eta = eta
self.epochs = epochs
self.shuffle = shuffle
self.hidden_unit = hidden_unit
self.minibatch_size = minibatch_size
self.random = np.random.RandomState(Random_seed)
self.cost = {'Cost': []}
def ReadData(self,X_train,y_train,X_test,y_test):
self.X_train = X_train
self.y_train = y_train
self.X_trian = X_test
self.y_test = y_test
return self
def OneHot(self,y):
#此函数用于独热编码,将原数据的每一个样本的y值变成一个向量的形式,其对应的位置元素为1,其余的元素为0
num_samples = y.shape[0]
num_classes = np.unique(y).shape[0]
y_onehot = np.zeros((num_samples,num_classes))
for i,j in enumerate(y):
y_onehot[i,j]= 1
return y_onehot
def Initialization(self,X,y):
##############################
#此函数用于初始化权重矩阵和偏置向量#
##############################
#第一步:初始化指向隐藏层的权重矩阵,其大小为:样本的特征数*隐藏层的单元数
num_feature = X.shape[1]
num_hidden = self.hidden_unit
self.weight_hidden = np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=(num_feature,num_hidden))
#第二步:初始化隐藏层的偏置向量(这里用偏置向量取代偏置单元,二者等价),其大小为:1*隐藏层的单元数,并将其初始化的值定位0
self.bias_hidden = np.zeros(shape = (1,num_hidden))
#第三步:初始化指向输出层的权重矩阵,其大小为:隐藏层的单元数*样本的结果种类数目(MNIST数据结果为0-9:所以此处为10)
num_hidden = self.hidden_unit
num_output = np.unique(y).shape[0]
self.weight_output = np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=(num_hidden,num_output))
#第四步:初始化输出层的偏置向量(这里用偏置向量取代偏置单元,二者等价),其大小为:1*输出层的单元数,并将其初始化的值定位0
self.bias_output = np.zeros(shape = (1,num_output))
return self
def Sigmoid(self,z):
######################
#此函数用于激活净输入变量z
#####################
#同时利用了np.clip设置了z阙值在(-200,200),防止数据溢出
return 1./(1+np.exp(-np.clip(z,-200,200)))
def SigmoidDerivative(self,z):
######################
#此函数为Sigmoid函数的导数
######################
return self.Sigmoid(z)*(1-self.Sigmoid(z))
def ComputeCost(self, y_enc, output):
L2_term = (self.l2 *
(np.sum(self.weight_hidden ** 2.) +
np.sum(self.weight_output ** 2.)))
term1 = -y_enc * (np.log(output))
term2 = (1. - y_enc) * np.log(1. - output)
cost = np.sum(term1 - term2) + L2_term
return cost
def ForwardPropagation(self,X):
##################
#此函数实现向前传播#
#################
#第一步:获得隐藏层的净输入矩阵,其值为输入值矩阵和指向隐藏层的权重矩阵做乘积
z_hidden = np.dot(X,self.weight_hidden) + self.bias_hidden
#第二步:利用sigmoid函数对隐藏层的净输入矩阵进行激活
a_hidden = self.Sigmoid(z_hidden)
#第三步:获得输出层的净输入矩阵,其值为激活的隐藏层的净输入矩阵和指向输出层的权重矩阵做乘积
z_output = np.dot(a_hidden,self.weight_output) + self.bias_output
#第四步:利用sigmoid函数对输出层的净输入矩阵进行激活
a_output = self.Sigmoid(z_output)
#第五步:返回上面的求解的各个矩阵,其目的是为了下面求解梯度
return z_hidden,a_hidden,z_output,a_output
def BackPropagation(self,X,y):
####################
#此函数实现误差反向传播
####################
#首先将输入的y进行独热编码
y_enc = self.OneHot(y)
for epoch in range(self.epochs):
indices = np.arange(X.shape[0])
#洗牌
if self.shuffle:
np.random.shuffle(indices)
#以self.minibatch_size为单位,实现小批量实现梯度下降
for start_indx in range(0,X.shape[0] + 1 - self.minibatch_size,self.minibatch_size):
minibatch_indx = indices[start_indx : start_indx+self.minibatch_size + 1]
minibatch_X = X[minibatch_indx]
minibatch_y_enc = y_enc[minibatch_indx]
z_hidden,a_hidden,z_output,a_output = self.ForwardPropagation(minibatch_X)
#########
#计算误差
########
#输出层误差
Sigmoid_prime_output = self.SigmoidDerivative(z_output)
#delta_output为输出层的误差
# delta_output = (a_output - minibatch_y_enc) * Sigmoid_prime_output 错误!!!
delta_output = (a_output - minibatch_y_enc)
#隐藏层误差
Sigmoid_prime_hidden = self.SigmoidDerivative(z_hidden)
#delta_hidden为隐藏层的误差
delta_hidden = np.dot(delta_output,self.weight_output.T) * Sigmoid_prime_hidden
#########
#计算梯度
########
#指向输出层权重矩阵梯度
gradient_output = np.dot(a_hidden.T,delta_output)
#输出层偏置向量梯度
gradient_bias_output = np.sum(delta_output,axis = 0)
#指向隐藏层权重矩阵梯度
gradient_hidden = np.dot(minibatch_X.T,delta_hidden)
#隐藏层偏置向量梯度
gradient_bias_hidden = np.sum(delta_hidden,axis = 0)
############
#输出层梯度下降
############
#由于正则化,实际的梯度为梯度+正则化项
Datla_output = gradient_output + self.l2 * self.weight_output
#偏置向量不进行正则化
Delta_bias_output = gradient_bias_output
self.weight_output -= self.eta*Datla_output
self.bias_output -= self.eta*Delta_bias_output
############
#隐藏层梯度下降
############
#由于正则化,实际的梯度为梯度+正则化项
Datla_hidden = gradient_hidden + self.l2 * self.weight_hidden
#偏置向量不进行正则化
Delta_bias_hidden = gradient_bias_hidden
self.weight_hidden -= self.eta*Datla_hidden
self.bias_hidden -= self.eta*Delta_bias_hidden
z_hidden,a_hidden,z_output,a_output = self.ForwardPropagation(X)
cost = self.ComputeCost(y_enc, a_output)
#存储每次训练的误差函数的大小
self.cost['Cost'].append(cost)
return self
第三步.训练
if __name__ == "__main__":
MLP = MutiLayerNeuralNetWork(
l2 = 0.01,
eta = 0.001,
epochs = 50,
shuffle = True,
Random_seed = 1,
hidden_unit = 100,
minibatch_size = 200,)
MLP.ReadData(X_train,y_train,X_test,y_test)
MLP.Initialization(X_train,y_train)
MLP.BackPropagation(X_train,y_train)
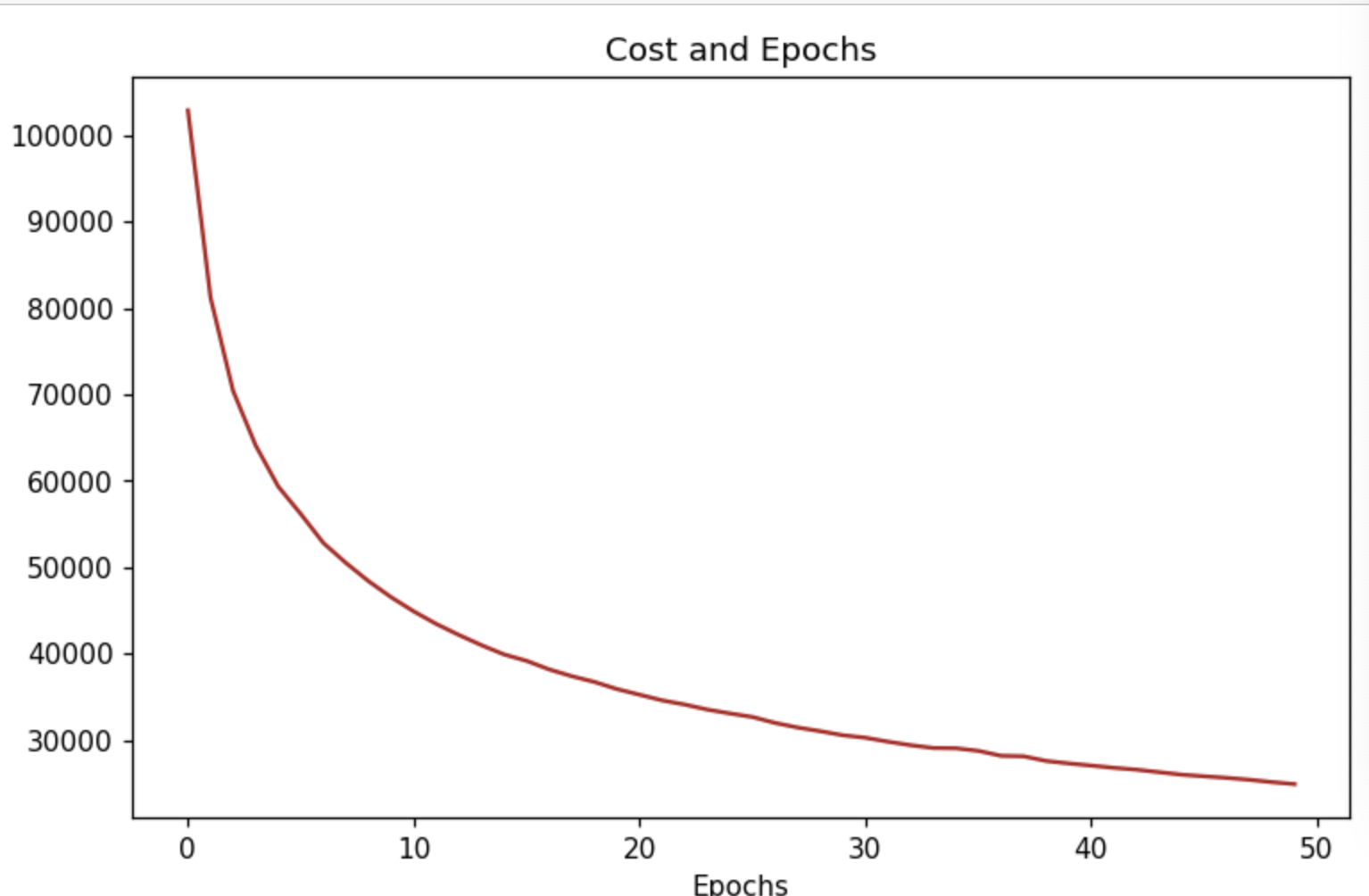
第四步.可视化误差函数
plt.figure(figsize=(8,5),dpi=110)
plt.plot(range(MLP.epochs), MLP.cost['Cost'],color = 'firebrick')
plt.title('Cost and Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Cost')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.show()
总结
本文的数据集来自MNIST,读者可以从我的GitHub上下载(另其他机器学习模型的代码):Sunsky的Github。