车辆目标检测模型测试记录
文章目录
前言
首先自己标注了2006张线上数据,制作成了测试数据集test1(1000张)、test2(1006张),其中test1是随机选取的线上模型检测出车辆图片,test2是随机选取的线上模型未检测出车辆图片。数据标注全部使用Labelme软件,生成格式为.json文件,bbox格式为:<left> <top> <right> <bottom>。标注过程test1以露出完整车辆外观三分之一为准,test2以人眼能识别出车辆为准,以下测试均使用test1与test2数据集。
一、YOLOv5系列模型测试记录
官方github:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
1. 环境配置
yolov5要求:Python>=3.6.0、PyTorch>=1.7,建立conda虚拟环境之后安装各依赖库:
$ git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
$ cd yolov5
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
2. 数据集的制作
官方提供的数据集的tree:
mytrain
├── mycoco
│ ├── images
│ │ ├── train
│ │ └── val
│ └── labels
│ ├── train
│ └── val
└── yolov5
针对测试任务、无需建立train文件夹,我建立的数据集结构如下:
home
├── car
│ ├── test1.txt
│ ├── test2.txt
│ ├── test1
│ └── test2
└── yolov5
其中test1和test2中存储图片文件与对应的label文件,命名规则例如:
img1.jpg img1.txt img2.jpg img2.txt ...
test1.txt与test2.txt中存放完整文件列表,例如:
./test1/img1.jpg
./test1/img2.jpg
...
建立好文件目录之后我们可以生成相应的文件了,由于我们直接使用Labelme软件进行标注,生成.json格式的label文件,例如:
{
"version": "4.5.7",
"flags": {},
"shapes": [
{
"label": "2",
"points": [
[
5.543307086614163,
333.8582677165354
],
[
352.7874015748032,
555.1181102362204
]
],
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {}
}
],
"imagePath": "1623513693636_file.jpg",
"imageData": null,
"imageHeight": 800,
"imageWidth": 370
}
由于标注完成后可能出现imagePath字段与文件真实名称不一致的情况,所以我仍使用图片文件真实的文件名。同理,imageHeight与imageWidth也通过读入图片进行获取。
为了方便与COCO数据集结合,我在标注时把所有的车辆的label都标注为2。
points格式为:<left> <top> <right> <bottom>,注意,有时由于标注点的顺序,可能为<right> <bottom> <left> <top>,所以要取最大最小值处理。
YOLOv5要求训练或测试的输入格式为每张图片的label为一个.txt文件,并且文件名与图片文件名一致,文件内容例如:
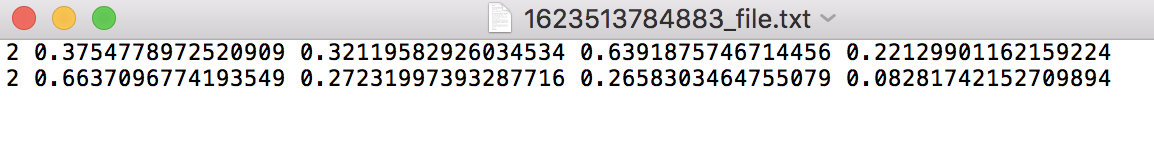
其中每行是对应的一个label,后四个值分别为标注矩形框的中心点x,y坐标与框宽,框高归一化之后的值。遂编写了脚本,实现了由标注.json文件生成YOLOv5要求的.txt,labelme_to_yolov5.py:
import argparse
import os
import numpy as np
import json
from glob import glob
import cv2
from os import getcwd
from tqdm import tqdm
def get_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--input', default='LabelmeData/')
parser.add_argument('--out_dir', default='tmp/')
return parser.parse_args()
# 根据xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax返回当前矩形的中心点坐标与长宽
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / (size[0])
dh = 1. / (size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
def Change2Yolo5(json_files, task="test"):
if not os.path.isdir(get_args().out_dir):
os.makedirs(get_args().out_dir)
# 创建当前数据集的txt文件,例 test.txt
list_file = open('tmp/%s.txt' % (task), 'w')
for json_name in tqdm(json_files, ncols=100, unit='B', unit_scale=True):
jsonPath = get_args().input + json_name + ".json"
imagePath = get_args().input + json_name + ".jpg"
# 写入一行图片路径
list_file.write('%s/%s\n' % (getcwd(), imagePath))
# 创建当前图片的标签txt文件
label_file = open('%s/%s.txt' % (get_args().input, json_name), 'w')
json_file = json.load(open(jsonPath, "r", encoding="utf-8"))
print(json_file)
height, width, channels = cv2.imread(get_args().input + json_name + ".jpg").shape
#print(cv2.imread(get_args().input + json_name + ".jpg").shape)
for multi in json_file["shapes"]:
points = np.array(multi["points"])
f = lambda x: x if x >= 0 else 0
xmin = f(min(points[:, 0]))
xmax = f(max(points[:, 0]))
ymin = f(min(points[:, 1]))
ymax = f(max(points[:, 1]))
if not xmax >= xmin or ymax >=ymin:
cls_id = multi["label"]
b = (float(xmin), float(xmax), float(ymin), float(ymax))
bb = convert((width, height), b)
label_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
#print(jsonPath, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, cls_id)
def main(args):
files = glob(args.input + "*.json")
files = [i.split("/")[-1].split(".json")[0] for i in files]
# print(files)
# trainval_files = files
test_files = files
Change2Yolo5(test_files,"test")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(get_args())
运行完成后会在对应图片文件与.json文件目录生成对应的.txt文件以及文件列表文件,将文件按之前的文件树组织即可。
3. 模型的准备
完成了数据集的组织后我们可以开始我们的测试或训练了,YOLOv5的模型包括如下几种:
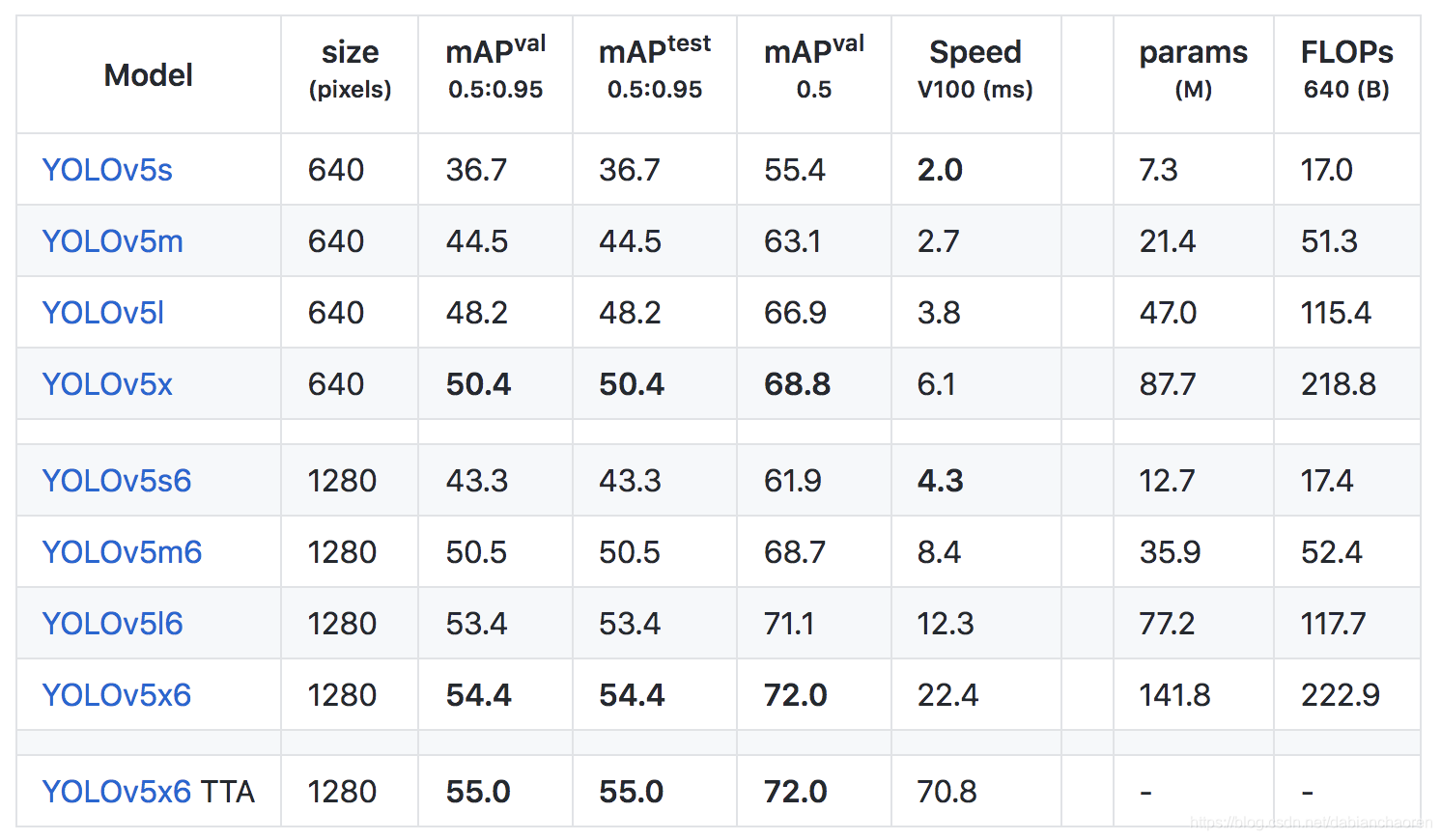
本文我主要针对前四个模型进行了测试,我直接使用了YOLOv5官方提供的用COCO2017数据集训练完成的模型,下载链接请移步:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases
下载后将其放入yolov5主目录下,模型就准备就绪了。
4. .yaml文件的编写
在./yolov5/data/目录下自己新建一个car1.yaml,代码如下:
# train and val data as 1) directory: path/images/, 2) file: path/images.txt, or 3) list: [path1/images/, path2/images/]
train: ../car/test1.txt # 118287 images
val: ../car/test1.txt # 5000 images
test: ../car/test1.txt # 20288 of 40670 images, submit to https://competitions.codalab.org/competitions/20794
# number of classes
nc: 80
# class names
names: [ 'person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light',
'fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow',
'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee',
'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard',
'tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple',
'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch',
'potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone',
'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear',
'hair drier', 'toothbrush' ]
同理,新建一个car2.yaml,代码如下:
# train and val data as 1) directory: path/images/, 2) file: path/images.txt, or 3) list: [path1/images/, path2/images/]
train: ../car/test2.txt # 118287 images
val: ../car/test2.txt # 5000 images
test: ../car/test2.txt # 20288 of 40670 images, submit to https://competitions.codalab.org/competitions/20794
# number of classes
nc: 80
# class names
names: [ 'person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light',
'fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow',
'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee',
'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard',
'tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple',
'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch',
'potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone',
'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear',
'hair drier', 'toothbrush' ]
5. 开始测试
使用如下指令即可开始测试:
$ python val.py --task study --data car1.yaml --iou 0.5 --weights yolov5s.pt yolov5m.pt yolov5l.pt yolov5x.pt
几个常用参数的重点说明:
--task study是指针对该模型对其在不同分辨率下进行测试,所花费的时间较长,但可以看到模型对数据集在不同分辨率的效果;当然还可以指定--task val这时可以同时指定需要测试的分辨率--img 640,分辨率默认为640;
--data car_test1.yaml是指使用的数据集的.yaml文件;
--iou 0.5可以根据需求设置具体的iou,这里测试时统一设置为0.5
--weights yolov5s.pt yolov5m.pt yolov5l.pt yolov5x.pt可以指定使用的模型,一个多个均可;
--save-txt默认为False,如果需要保存测试结果文件可以指定。
其他参数可以参考官方的代码:
parser.add_argument('--data', type=str, default='data/coco128.yaml', help='dataset.yaml path')
parser.add_argument('--weights', nargs='+', type=str, default='yolov5s.pt', help='model.pt path(s)')
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=32, help='batch size')
parser.add_argument('--imgsz', '--img', '--img-size', type=int, default=640, help='inference size (pixels)')
parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.001, help='confidence threshold')
parser.add_argument('--iou-thres', type=float, default=0.6, help='NMS IoU threshold')
parser.add_argument('--task', default='val', help='train, val, test, speed or study')
parser.add_argument('--device', default='', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu')
parser.add_argument('--single-cls', action='store_true', help='treat as single-class dataset')
parser.add_argument('--augment', action='store_true', help='augmented inference')
parser.add_argument('--verbose', action='store_true', help='report mAP by class')
parser.add_argument('--save-txt', action='store_true', help='save results to *.txt')
parser.add_argument('--save-hybrid', action='store_true', help='save label+prediction hybrid results to *.txt')
parser.add_argument('--save-conf', action='store_true', help='save confidences in --save-txt labels')
parser.add_argument('--save-json', action='store_true', help='save a COCO-JSON results file')
parser.add_argument('--project', default='runs/val', help='save to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--name', default='exp', help='save to project/name')
parser.add_argument('--exist-ok', action='store_true', help='existing project/name ok, do not increment')
parser.add_argument('--half', action='store_true', help='use FP16 half-precision inference')
测试完成后可自动输出模型的mAP等指标,(mAP@0.5:0.95指的是我们常说的mmAP)
6. 绘制可视化图片
由上一步生成的测试结果文件出发,将YOLOv5的数据格式再转换回方便我们绘制的<left> <top> <right> <bottom>格式,之后使用cv库对图片进行绘制并保存。
代码如下:
import argparse
import os
import numpy as np
import json
from glob import glob
import cv2
from os import getcwd
from tqdm import tqdm
def get_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--input', default='test1_datection_fasterrcnn/')
parser.add_argument('--out_dir', default='cls2/')
return parser.parse_args()
def main(args):
files = glob(args.input + "*.txt")
files_name = [i.split("/")[-1].split(".txt")[0] for i in files]
# print(files)
# trainval_files = files
for file_name in tqdm(files_name, ncols=100, unit='word(s)', unit_scale=True):
file = open(get_args().input + file_name + '.txt').read()
for i in range(0, 3): # 遍历每行
cls = file.splitlines()[i].split(' ', 1)[0]
if cls in ['2', '5', '6', '7']:
yolo_datas = file.splitlines()[i].split(' ', 1)
print(yolo_datas)
# print(file.splitlines()[i].split(' ', 1)[0])
yolo_datas = file.splitlines()[i].split(' ', 1)
yolo_datas = yolo_datas[1]
yolo_datas = yolo_datas.split(' ')
image = cv2.imread('yolo_detection_test1/img/' + file_name + '.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
img_h, img_w, channels = image.shape
center_x = round(float(str(yolo_datas[0]).strip()) * img_w)
center_y = round(float(str(yolo_datas[1]).strip()) * img_h)
bbox_width = round(float(str(yolo_datas[2]).strip()) * img_w)
bbox_height = round(float(str(yolo_datas[3]).strip()) * img_h)
xmin = str(int(center_x - bbox_width / 2))
ymin = str(int(center_y - bbox_height / 2))
xmax = str(int(center_x + bbox_width / 2))
ymax = str(int(center_y + bbox_height / 2))
cv2.rectangle(image, (int(xmin), int(ymin)), (int(xmax), int(ymax)),
(255, 0, 0), thickness=3)
cv2.imwrite('yolo_detection_test1/img2/' + file_name + '.jpg', image)
break
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(get_args())
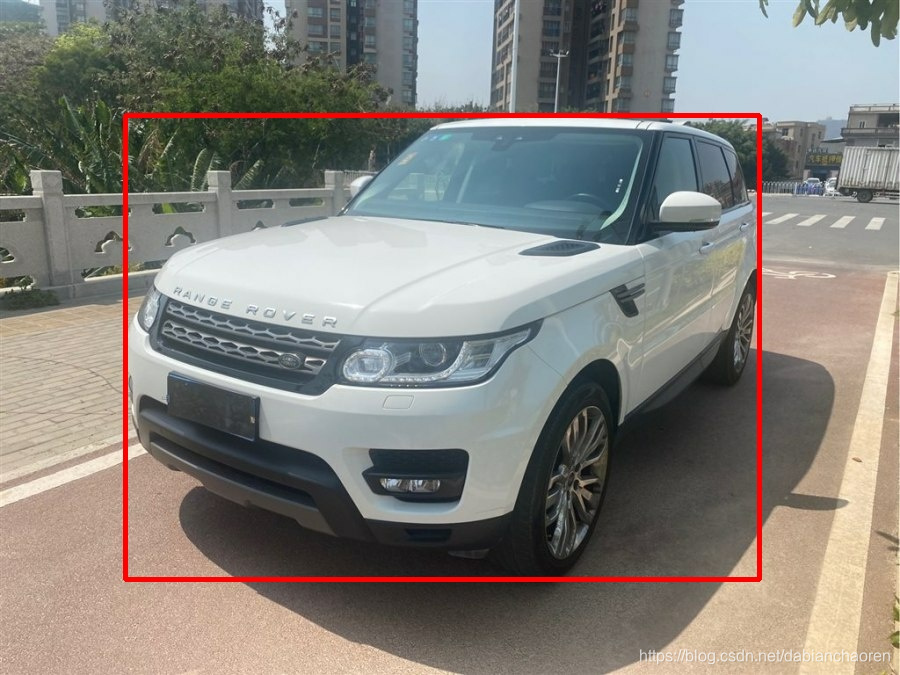

7. 筛选出识别为相似类别的图片
编写了脚本实现了筛选出了被识别为相似类别的图片,并输出到特定文件夹,文件夹为car、train、bus。
import argparse
import os
import numpy as np
import json
from glob import glob
import cv2
from os import getcwd
from tqdm import tqdm
def get_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--input', default='test1_datection_fasterrcnn/')
parser.add_argument('--out_dir', default='cls2/')
return parser.parse_args()
def main(args):
files = glob(args.input + "*.txt")
files_name = [i.split("/")[-1].split(".txt")[0] for i in files]
# print(files)
# trainval_files = files
for file_name in tqdm(files_name, ncols=100, unit='word(s)', unit_scale=True):
file = open(get_args().input + file_name + '.txt').read()
for i in range(0, 3): # 遍历每行
cls = file.splitlines()[i].split(' ', 1)[0]
if cls in ['2', '5', '6', '7']:
if not os.path.isdir('cls2/' + cls):
os.makedirs('cls2/' + cls)
f_copy = open('cls2/' + cls +'/'+ file_name + '.jpg', 'wb')
# 将原图片内容通过二进制形式写入新的图片文件
f_copy.write(content)
f_src.close()
f_copy.close()
break
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(get_args())
二、Faster R-CNN模型测试记录
直接使用了Torchvision中提供的训练好的Faster R-CNN模型,通过模型detect生成对应的label与bbox,并存于txt方便进行计算与绘图。
结果输出为.txt文件,具体内容为每个label一行,每行的字段分别代表对象、置信度、bbox,例如: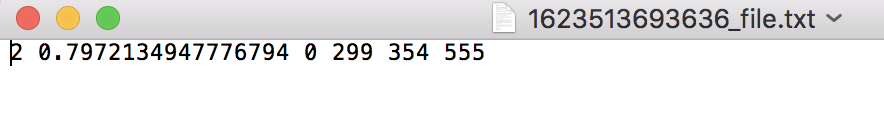
为了方便测试,我把标注的文件也转换成类似的格式,脚本如下:
import argparse
import os
import numpy as np
import json
from glob import glob
import cv2
from os import getcwd
from tqdm import tqdm
def get_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--input', default='car/test2/')
parser.add_argument('--out_dir', default='FRCNNtest/test2_label/')
return parser.parse_args()
def labelme2test(json_files, task="test"):
if not os.path.isdir(get_args().out_dir):
os.makedirs(get_args().out_dir)
# 创建当前数据集的txt文件,例 test.txt
list_file = open('FRCNNtest/%s.txt' % (task), 'w')
for json_name in tqdm(json_files, ncols=100, unit='B', unit_scale=True):
jsonPath = get_args().input + json_name + ".json"
imagePath = get_args().input + json_name + ".jpg"
# 写入一行图片路径
list_file.write('%s/%s\n' % (getcwd(), imagePath))
# 创建当前图片的标签txt文件
label_file = open('%s/%s.txt' % (get_args().out_dir, json_name), 'w')
json_file = json.load(open(jsonPath, "r", encoding="utf-8"))
#print(json_file)
height, width, channels = cv2.imread(get_args().input + json_name + ".jpg").shape
#print(cv2.imread(get_args().input + json_name + ".jpg").shape)
for multi in json_file["shapes"]:
points = np.array(multi["points"])
f = lambda x: x if x >= 0 else 0
xmin = f(min(points[:, 0]))
xmax = f(max(points[:, 0]))
ymin = f(min(points[:, 1]))
ymax = f(max(points[:, 1]))
if not xmax >= xmin or ymax >=ymin:
cls_id = 2 #multi["label"]
b = (float(xmin), float(ymin), float(xmax), float(ymax))
# b = (float(xmin), float(xmax), float(ymin), float(ymax))
# bb = convert((width, height), b)
label_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in b]) + '\n')
#print(jsonPath, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, cls_id)
def main(args):
files = glob(args.input+ "*.json")
files = [i.split("/")[-1].split(".json")[0] for i in files]
#print(files)
# trainval_files = files
test_files = files
labelme2test(test_files,"test")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(get_args())
数据都具备之后可以计算mAP了,这里采用VOC2012的计算方法,但是又有VOC2012采用MATLAB编码,于是调研了一个基于Python的项目(github:https://github.com/Cartucho/mAP),该项目将VOC的MATLAB代码转换成了Python的代码,我基于该项目代码进行了相应的修改:
import glob
import json
import os
import shutil
import operator
import sys
import argparse
import math
import numpy as np
MINOVERLAP = 0.5
def get_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--input', default='input/')
parser.add_argument('--output', default='output/')
return parser.parse_args()
GT_PATH = get_args().input + 'ground-truth'
DR_PATH = get_args().input + 'detection-results'
def log_average_miss_rate(prec, rec, num_images):
# if there were no detections of that class
if prec.size == 0:
lamr = 0
mr = 1
fppi = 0
return lamr, mr, fppi
fppi = (1 - prec)
mr = (1 - rec)
fppi_tmp = np.insert(fppi, 0, -1.0)
mr_tmp = np.insert(mr, 0, 1.0)
# Use 9 evenly spaced reference points in log-space
ref = np.logspace(-2.0, 0.0, num = 9)
for i, ref_i in enumerate(ref):
# np.where() will always find at least 1 index, since min(ref) = 0.01 and min(fppi_tmp) = -1.0
j = np.where(fppi_tmp <= ref_i)[-1][-1]
ref[i] = mr_tmp[j]
# log(0) is undefined, so we use the np.maximum(1e-10, ref)
lamr = math.exp(np.mean(np.log(np.maximum(1e-10, ref))))
return lamr, mr, fppi
"""
throw error and exit
"""
def error(msg):
print(msg)
sys.exit(0)
"""
check if the number is a float between 0.0 and 1.0
"""
def is_float_between_0_and_1(value):
try:
val = float(value)
if val > 0.0 and val < 1.0:
return True
else:
return False
except ValueError:
return False
"""
Calculate the AP given the recall and precision array
1st) We compute a version of the measured precision/recall curve with
precision monotonically decreasing
2nd) We compute the AP as the area under this curve by numerical integration.
"""
def voc_ap(rec, prec):
"""
--- Official matlab code VOC2012---
mrec=[0 ; rec ; 1];
mpre=[0 ; prec ; 0];
for i=numel(mpre)-1:-1:1
mpre(i)=max(mpre(i),mpre(i+1));
end
i=find(mrec(2:end)~=mrec(1:end-1))+1;
ap=sum((mrec(i)-mrec(i-1)).*mpre(i));
"""
rec.insert(0, 0.0) # insert 0.0 at begining of list
rec.append(1.0) # insert 1.0 at end of list
mrec = rec[:]
prec.insert(0, 0.0) # insert 0.0 at begining of list
prec.append(0.0) # insert 0.0 at end of list
mpre = prec[:]
"""
This part makes the precision monotonically decreasing
(goes from the end to the beginning)
matlab: for i=numel(mpre)-1:-1:1
mpre(i)=max(mpre(i),mpre(i+1));
"""
# matlab indexes start in 1 but python in 0, so I have to do:
# range(start=(len(mpre) - 2), end=0, step=-1)
# also the python function range excludes the end, resulting in:
# range(start=(len(mpre) - 2), end=-1, step=-1)
for i in range(len(mpre)-2, -1, -1):
mpre[i] = max(mpre[i], mpre[i+1])
"""
This part creates a list of indexes where the recall changes
matlab: i=find(mrec(2:end)~=mrec(1:end-1))+1;
"""
i_list = []
for i in range(1, len(mrec)):
if mrec[i] != mrec[i-1]:
i_list.append(i) # if it was matlab would be i + 1
"""
The Average Precision (AP) is the area under the curve
(numerical integration)
matlab: ap=sum((mrec(i)-mrec(i-1)).*mpre(i));
"""
ap = 0.0
for i in i_list:
ap += ((mrec[i]-mrec[i-1])*mpre[i])
return ap, mrec, mpre
"""
Convert the lines of a file to a list
"""
def file_lines_to_list(path):
# open txt file lines to a list
with open(path) as f:
content = f.readlines()
# remove whitespace characters like `\n` at the end of each line
content = [x.strip() for x in content]
return content
"""
Create a ".temp_files/" and "output/" directory
"""
TEMP_FILES_PATH = ".temp_files"
if not os.path.exists(TEMP_FILES_PATH): # if it doesn't exist already
os.makedirs(TEMP_FILES_PATH)
output_files_path = "output"
if os.path.exists(output_files_path): # if it exist already
# reset the output directory
shutil.rmtree(output_files_path)
"""
ground-truth
Load each of the ground-truth files into a temporary ".json" file.
Create a list of all the class names present in the ground-truth (gt_classes).
"""
# get a list with the ground-truth files
ground_truth_files_list = glob.glob(GT_PATH + '/*.txt')
if len(ground_truth_files_list) == 0:
error("Error: No ground-truth files found!")
ground_truth_files_list.sort()
# dictionary with counter per class
gt_counter_per_class = {}
counter_images_per_class = {}
gt_files = []
for txt_file in ground_truth_files_list:
#print(txt_file)
file_id = txt_file.split(".txt", 1)[0]
file_id = os.path.basename(os.path.normpath(file_id))
# check if there is a correspondent detection-results file
temp_path = os.path.join(DR_PATH, (file_id + ".txt"))
if not os.path.exists(temp_path):
error_msg = "Error. File not found: {}\n".format(temp_path)
error_msg += "(You can avoid this error message by running extra/intersect-gt-and-dr.py)"
error(error_msg)
lines_list = file_lines_to_list(txt_file)
# create ground-truth dictionary
bounding_boxes = []
is_difficult = False
already_seen_classes = []
for line in lines_list:
try:
if "difficult" in line:
class_name, left, top, right, bottom, _difficult = line.split()
is_difficult = True
else:
class_name, left, top, right, bottom = line.split()
except ValueError:
error_msg = "Error: File " + txt_file + " in the wrong format.\n"
error_msg += " Expected: <class_name> <left> <top> <right> <bottom> ['difficult']\n"
error_msg += " Received: " + line
error_msg += "\n\nIf you have a <class_name> with spaces between words you should remove them\n"
error_msg += "by running the script \"remove_space.py\" or \"rename_class.py\" in the \"extra/\" folder."
error(error_msg)
bbox = left + " " + top + " " + right + " " +bottom
if is_difficult:
bounding_boxes.append({"class_name":class_name, "bbox":bbox, "used":False, "difficult":True})
is_difficult = False
else:
bounding_boxes.append({"class_name":class_name, "bbox":bbox, "used":False})
# count that object
if class_name in gt_counter_per_class:
gt_counter_per_class[class_name] += 1
else:
# if class didn't exist yet
gt_counter_per_class[class_name] = 1
if class_name not in already_seen_classes:
if class_name in counter_images_per_class:
counter_images_per_class[class_name] += 1
else:
# if class didn't exist yet
counter_images_per_class[class_name] = 1
already_seen_classes.append(class_name)
# dump bounding_boxes into a ".json" file
new_temp_file = TEMP_FILES_PATH + "/" + file_id + "_ground_truth.json"
gt_files.append(new_temp_file)
with open(new_temp_file, 'w') as outfile:
json.dump(bounding_boxes, outfile)
gt_classes = list(gt_counter_per_class.keys())
# let's sort the classes alphabetically
gt_classes = sorted(gt_classes)
n_classes = len(gt_classes)
#print(gt_classes)
#print(gt_counter_per_class)
"""
detection-results
Load each of the detection-results files into a temporary ".json" file.
"""
# get a list with the detection-results files
dr_files_list = glob.glob(DR_PATH + '/*.txt')
dr_files_list.sort()
for class_index, class_name in enumerate(gt_classes):
bounding_boxes = []
for txt_file in dr_files_list:
#print(txt_file)
# the first time it checks if all the corresponding ground-truth files exist
file_id = txt_file.split(".txt",1)[0]
file_id = os.path.basename(os.path.normpath(file_id))
temp_path = os.path.join(GT_PATH, (file_id + ".txt"))
if class_index == 0:
if not os.path.exists(temp_path):
error_msg = "Error. File not found: {}\n".format(temp_path)
error_msg += "(You can avoid this error message by running extra/intersect-gt-and-dr.py)"
error(error_msg)
lines = file_lines_to_list(txt_file)
for line in lines:
try:
tmp_class_name, confidence, left, top, right, bottom = line.split()
except ValueError:
error_msg = "Error: File " + txt_file + " in the wrong format.\n"
error_msg += " Expected: <class_name> <confidence> <left> <top> <right> <bottom>\n"
error_msg += " Received: " + line
error(error_msg)
if tmp_class_name == class_name:
#print("match")
bbox = left + " " + top + " " + right + " " +bottom
bounding_boxes.append({"confidence":confidence, "file_id":file_id, "bbox":bbox})
#print(bounding_boxes)
# sort detection-results by decreasing confidence
bounding_boxes.sort(key=lambda x:float(x['confidence']), reverse=True)
with open(TEMP_FILES_PATH + "/" + class_name + "_dr.json", 'w') as outfile:
json.dump(bounding_boxes, outfile)
"""
Calculate the AP for each class
"""
sum_AP = 0.0
# open file to store the output
if not os.path.isdir(output_files_path + "/"):
os.makedirs(output_files_path + "/")
with open(output_files_path + "/output.txt", 'w') as output_file:
output_file.write("# AP and precision/recall per class\n")
count_true_positives = {}
for class_index, class_name in enumerate(gt_classes):
count_true_positives[class_name] = 0
"""
Load detection-results of that class
"""
dr_file = TEMP_FILES_PATH + "/" + class_name + "_dr.json"
dr_data = json.load(open(dr_file))
"""
Assign detection-results to ground-truth objects
"""
nd = len(dr_data)
tp = [0] * nd # creates an array of zeros of size nd
fp = [0] * nd
for idx, detection in enumerate(dr_data):
file_id = detection["file_id"]
# assign detection-results to ground truth object if any
# open ground-truth with that file_id
gt_file = TEMP_FILES_PATH + "/" + file_id + "_ground_truth.json"
ground_truth_data = json.load(open(gt_file))
ovmax = -1
gt_match = -1
# load detected object bounding-box
bb = [ float(x) for x in detection["bbox"].split() ]
for obj in ground_truth_data:
# look for a class_name match
if obj["class_name"] == class_name:
bbgt = [ float(x) for x in obj["bbox"].split() ]
bi = [max(bb[0],bbgt[0]), max(bb[1],bbgt[1]), min(bb[2],bbgt[2]), min(bb[3],bbgt[3])]
iw = bi[2] - bi[0] + 1
ih = bi[3] - bi[1] + 1
if iw > 0 and ih > 0:
# compute overlap (IoU) = area of intersection / area of union
ua = (bb[2] - bb[0] + 1) * (bb[3] - bb[1] + 1) + (bbgt[2] - bbgt[0]
+ 1) * (bbgt[3] - bbgt[1] + 1) - iw * ih
ov = iw * ih / ua
if ov > ovmax:
ovmax = ov
gt_match = obj
# set minimum overlap
min_overlap = MINOVERLAP
if ovmax >= min_overlap:
if "difficult" not in gt_match:
if not bool(gt_match["used"]):
# true positive
tp[idx] = 1
gt_match["used"] = True
count_true_positives[class_name] += 1
# update the ".json" file
with open(gt_file, 'w') as f:
f.write(json.dumps(ground_truth_data))
else:
# false positive (multiple detection)
fp[idx] = 1
else:
# false positive
fp[idx] = 1
if ovmax > 0:
status = "INSUFFICIENT OVERLAP"
"""
Draw image to show animation
"""
#print(tp)
# compute precision/recall
cumsum = 0
for idx, val in enumerate(fp):
fp[idx] += cumsum
cumsum += val
cumsum = 0
for idx, val in enumerate(tp):
tp[idx] += cumsum
cumsum += val
#print(tp)
rec = tp[:]
for idx, val in enumerate(tp):
rec[idx] = float(tp[idx]) / gt_counter_per_class[class_name]
#print(rec)
prec = tp[:]
for idx, val in enumerate(tp):
prec[idx] = float(tp[idx]) / (fp[idx] + tp[idx])
#print(prec)
ap, mrec, mprec = voc_ap(rec[:], prec[:])
sum_AP += ap
text = "{0:.2f}%".format(ap*100) + " = " + class_name + " AP " #class_name + " AP = {0:.2f}%".format(ap*100)
"""
Write to output.txt
"""
rounded_prec = [ '%.2f' % elem for elem in prec ]
rounded_rec = [ '%.2f' % elem for elem in rec ]
output_file.write(text + "\n Precision: " + str(rounded_prec) + "\n Recall :" + str(rounded_rec) + "\n\n")
print(text)
output_file.write("\n# mAP of all classes\n")
mAP = sum_AP / n_classes
text = "mAP = {0:.2f}%".format(mAP*100)
output_file.write(text + "\n")
print(text)
# remove the temp_files directory
shutil.rmtree(TEMP_FILES_PATH)
"""
Count total of detection-results
"""
# iterate through all the files
det_counter_per_class = {}
for txt_file in dr_files_list:
# get lines to list
lines_list = file_lines_to_list(txt_file)
for line in lines_list:
class_name = line.split()[0]
# count that object
if class_name in det_counter_per_class:
det_counter_per_class[class_name] += 1
else:
# if class didn't exist yet
det_counter_per_class[class_name] = 1
#print(det_counter_per_class)
dr_classes = list(det_counter_per_class.keys())
"""
Write number of ground-truth objects per class to results.txt
"""
with open(output_files_path + "/output.txt", 'a') as output_file:
output_file.write("\n# Number of ground-truth objects per class\n")
for class_name in sorted(gt_counter_per_class):
output_file.write(class_name + ": " + str(gt_counter_per_class[class_name]) + "\n")
"""
Finish counting true positives
"""
for class_name in dr_classes:
# if class exists in detection-result but not in ground-truth then there are no true positives in that class
if class_name not in gt_classes:
count_true_positives[class_name] = 0
#print(count_true_positives)
"""
Write number of detected objects per class to output.txt
"""
with open(output_files_path + "/output.txt", 'a') as output_file:
output_file.write("\n# Number of detected objects per class\n")
for class_name in sorted(dr_classes):
n_det = det_counter_per_class[class_name]
text = class_name + ": " + str(n_det)
text += " (tp:" + str(count_true_positives[class_name]) + ""
text += ", fp:" + str(n_det - count_true_positives[class_name]) + ")\n"
output_file.write(text)
在项目根目录下新建input与output文件夹,input文件夹中新建detection-result1用于存放模型预测得到的.txt文件,ground-truth用于存放标注得到的.txt,运行该项目即可得到对应的mAP。