yolo v1
yolo v1的模型训练过程。
- 首先要做标签的变换,因为yolo v1生成的 embedding 是 b a t c h ? s i z e × S × S × 30 batch-size \times S \times S \times 30 batch?size×S×S×30的维度,所以首先要把每张图像的标签也转换成相同的 S × S × 30 S \times S \times 30 S×S×30的维度。标签转换的具体流程如下:
def encoder(self, boxes, labels): //这里的boxes是voc2007.txt中的bounding box
"""
boxes (tensor) [[x1,y1,x2,y2],[]]
labels (tensor) [...]
return 14x14x30 //这里的 S = 14 B = 2
"""
grid_num = 14
target = torch.zeros((grid_num, grid_num, 30)) //每张图片都要根据voc2007.txt中的标签编码成[S, S, 30]的向量
cell_size = 1./grid_num # 归一化后每个网格的大小
wh = boxes[:, 2:] - boxes[:, :2] # 读出每个bounding box的宽高
cxcy = (boxes[:, 2:] + boxes[:, :2]) / 2 # 读出每个bounding box的中心点
for i in range(cxcy.size()[0]): # 有几个obj就是[n, n]
cxcy_sample = cxcy[i] # 第 i 个obj的bounding box 的归一化中心点
ij = (cxcy_sample/cell_size).ceil()-1 # 找到该obj的bounding box的中心的索引,也就是看它属于那个网格
target[int(ij[1]), int(ij[0]), 4] = 1 # 将target中box设为1
target[int(ij[1]), int(ij[0]), 9] = 1 # 将target中box设为1
target[int(ij[1]), int(ij[0]), int(labels[i])+9] = 1 # 将target中class设为1
xy = ij*cell_size # 匹配到网格的左上角相对坐标
delta_xy = (cxcy_sample - xy)/cell_size
target[int(ij[1]), int(ij[0]), 2:4] = wh[i] # 每个bounding box的归一化宽高
target[int(ij[1]), int(ij[0]), :2] = delta_xy # 相对中心点的偏移量
target[int(ij[1]), int(ij[0]), 7:9] = wh[i]
target[int(ij[1]), int(ij[0]), 5:7] = delta_xy
return target
标签转换的过程就是将图片编码成一个[S,S,30]维的向量,也就是将
S
×
S
S \times S
S×S个patch每个都encode为30维的向量,如果这个patch 中存在object,则将该patch的30维的向量的第 5 个, 第 10 个位置(即是置信度,代表有 obj 的位置)置 1,另外将 20 个类别的相应类别位置置 1,注意前 4 个位置是经过转换后的,(x, y, w, h --> x y 代表相对中心点的偏移量,w h–>代表 每个bounding box的归一化宽高),因为该obj的框是唯一的,所以第1-4 个和 5-8个位置的数都相同。
2. yolo 的训练流程:先将整张图片分成
S
×
S
S \times S
S×S 个patch,然后每个 patch 负责预测两个 bounding box,如果 图片分成了
14
×
14
14 \times 14
14×14个patch,那么就将有
14
×
14
×
2
14 \times 14 \times 2
14×14×2个bounding box,然后通过计算 IoU来选择出最好的那个 bounding box作为最终的bounding box。
- 损失的计算
yolo v1的损失包括 5 个部分。
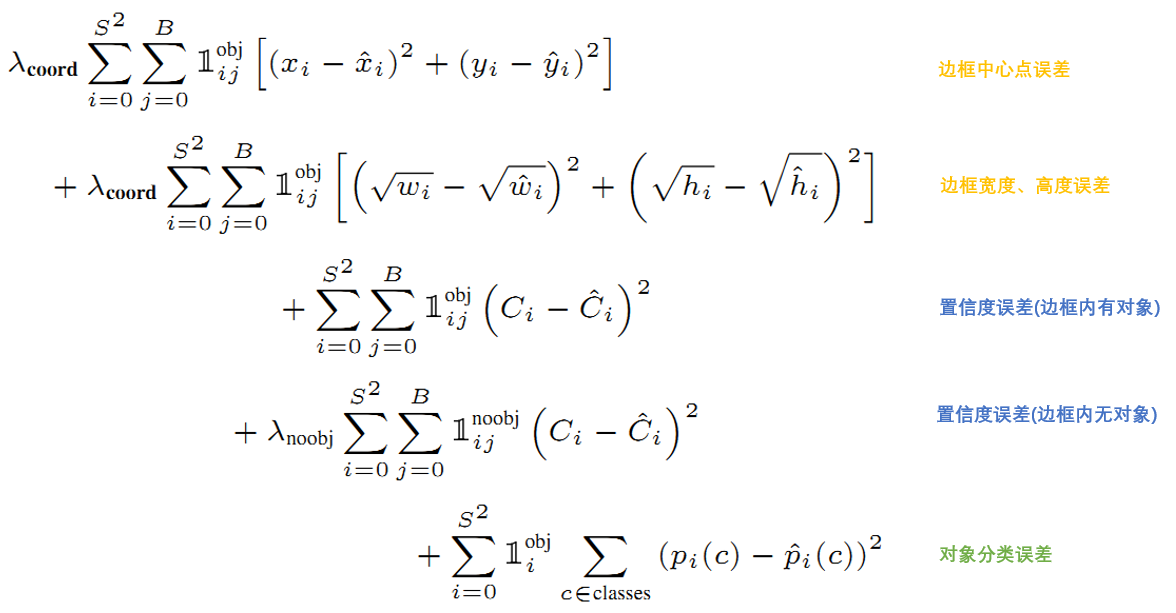
- IoU的计算
注意:在训练过程中没有用到 NMS
模型的预测过程(指预测图片)
这个过程和训练过程不同的是采用了 NMS 方法来产生 预测窗口。
NMS方法原理
yolo v1的注意点
1、每个网格只预测一个类别(也即一个类别的边界框),而且最后只取置信度最大的那个边界框。这就导致如果多个不同物体(或者同类物体的不同实体)的中心落在同一个网格中,会造成漏检。
2、yolo对相互靠的很近的物体,还有很小的群体检测效果不好,这是因为一个网格中只预测了两个框,并且只属于一类。
3、位置精准性差,召回率低。由于损失函数的问题,定位误差是影响检测效果的主要原因。尤其是大小物体的处理上,还有待加强
4、对测试图像中,同一类物体出现的新的不常见的长宽比和其他情况时。泛化能力偏弱
