事件驱动
使用Tempotron进行MNIST分类
我们关注event_driven/examples/tempotron_mnist.py,只有一个main函数,原注释如下
def main():
'''
:return: None
使用高斯调谐曲线编码器编码图像为脉冲,单层Tempotron进行MNIST识别。运行示例:
.. code-block:: python
>>> import spikingjelly.event_driven.examples.tempotron_mnist as tempotron_mnist
>>> tempotron_mnist.main()
输入运行的设备,例如“cpu”或“cuda:0”
input device, e.g., "cpu" or "cuda:0": cuda:15
输入保存MNIST数据集的位置,例如“./”
input root directory for saving MNIST dataset, e.g., "./": ./mnist
输入batch_size,例如“64”
input batch_size, e.g., "64": 64
输入学习率,例如“1e-3”
input learning rate, e.g., "1e-3": 1e-3
输入仿真时长,例如“100”
input simulating steps, e.g., "100": 100
输入训练轮数,即遍历训练集的次数,例如“100”
input training epochs, e.g., "100": 10
输入使用高斯调谐曲线编码每个像素点使用的神经元数量,例如“16”
input neuron number for encoding a piexl in GaussianTuning encoder, e.g., "16": 16
输入保存tensorboard日志文件的位置,例如“./”
input root directory for saving tensorboard logs, e.g., "./": ./logs_tempotron_mnist
cuda:15 ./mnist 64 0.001 100 100 16 ./logs_tempotron_mnist
train_acc 0.09375 0
cuda:15 ./mnist 64 0.001 100 100 16 ./logs_tempotron_mnist
train_acc 0.78125 512
...
'''
a. 网络结构
单层的Tempotron网络结构如下
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, m, T):
# m是高斯调谐曲线编码器编码一个像素点所使用的神经元数量
super().__init__()
self.tempotron = neuron.Tempotron(784*m, 10, T)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):
# 返回的是输出层10个Tempotron在仿真时长内的电压峰值
return self.tempotron(x, 'v_max')
Tempotron的膜电位定义为:
V
(
t
)
=
∑
i
w
i
∑
t
i
K
(
t
?
t
i
)
+
V
reset?
(1)
V(t)=\sum_{i} w_{i} \sum_{t_{i}} K\left(t-t_{i}\right)+V_{\text {reset }} \tag{1}
V(t)=i∑?wi?ti?∑?K(t?ti?)+Vreset??(1)
其中
w
i
w_{i}
wi? 是第
i
i
i 个输入的权重, 也可以看作是所连接的突触的权重;
t
i
t_{i}
ti? 是第
i
i
i 个输入的脉冲发放时
刻,
K
(
t
?
t
i
)
K\left(t-t_{i}\right)
K(t?ti?) 是甴于输入脉冲引发的突触后膜电位(postsynaptic potentials, PSPs);
V
reset?
V_{\text {reset }}
Vreset?? 是 Tempotron的重置电位,或者叫静息电位。
K
(
t
?
t
i
)
K\left(t-t_{i}\right)
K(t?ti?) 是一个关于
t
i
t_{i}
ti? 的函数(PSP Kernel), 1 中使用的函数形式如下:
K
(
t
?
t
i
)
=
{
V
0
(
exp
?
(
?
t
?
t
i
τ
)
?
exp
?
(
?
t
?
t
i
τ
s
)
)
,
t
≥
t
i
0
,
t
<
t
i
(2)
K\left(t-t_{i}\right)= \begin{cases}V_{0}\left(\exp \left(-\frac{t-t_{i}}{\tau}\right)-\exp \left(-\frac{t-t_{i}}{\tau_{s}}\right)\right), & t \geq t_{i} \\ 0, & t<t_{i}\end{cases} \tag{2}
K(t?ti?)={V0?(exp(?τt?ti??)?exp(?τs?t?ti??)),0,?t≥ti?t<ti??(2)
其中
V
0
V_{0}
V0? 是归一化系数,使得函数的最大值为1;
τ
\tau
τ 是膜电位时间常数,可以看出输入的脉冲在 Tempotron上会引起瞬时的点位激增, 但之后会指数衰减;
τ
s
\tau_{s}
τs? 则是突触电流的时间常数,这一项的 存在表示突触上传导的电流也会随着时间衰减。
单个的Tempotron可以作为一个二分类器, 分类结果的判别, 是看Tempotron的膜电位在仿真周期 内是否过阈值:
y
=
{
1
,
V
t
m
x
≥
V
threshold?
0
,
V
t
m
x
<
V
threshold?
(3)
y= \begin{cases}1, & V_{t_{m x}} \geq V_{\text {threshold }} \\ 0, & V_{t_{m x}}<V_{\text {threshold }}\end{cases} \tag{3}
y={1,0,?Vtmx??≥Vthreshold??Vtmx??<Vthreshold???(3)
其中
t
max
?
=
argmax
?
{
V
t
}
t_{\max }=\operatorname{argmax}\left\{V_{t}\right\}
tmax?=argmax{Vt?}。 从Tempotron的输出结果也能看出, Tempotron只能发放不超过1个脉冲。单个Tempotron只能做二分类,但多个Tempotron就可以做多分类。
class Tempotron(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, T, tau=15.0, tau_s=15.0 / 4, v_threshold=1.0):
'''
:param in_features: 输入数量,含义与nn.Linear的in_features参数相同
:param out_features: 输出数量,含义与nn.Linear的out_features参数相同
:param T: 仿真周期
:param tau: LIF神经元的积分时间常数
:param tau_s: 突触上的电流的衰减时间常数
:param v_threshold: 阈值电压
Gutig R, Sompolinsky H. The tempotron: a neuron that learns spike timing–based decisions[J]. Nature \
Neuroscience, 2006, 9(3): 420-428. 中提出的Tempotron模型
'''
super().__init__()
self.tau = tau
self.tau_s = tau_s
self.T = T
self.v_threshold = v_threshold
self.fc = nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias=False)
# v0要求使psp_kernel的最大值为v_threshold,通过求极值点,计算出最值
t_max = (tau * tau_s * math.log(tau / tau_s)) / (tau - tau_s)
self.v0 = self.v_threshold / (math.exp(-t_max / tau) - math.exp(-t_max / tau_s))
前向传播过程是将输入图片经过高斯协调曲线编码后的脉冲发放时刻,送入膜电位公式(1)中,得到out_features个Tempotron神经元在仿真时长T内的电压(或者峰值电压)
@staticmethod
def psp_kernel(t: torch.Tensor, tau, tau_s):
'''
:param t: 表示时刻的tensor
:param tau: LIF神经元的积分时间常数
:param tau_s: 突触上的电流的衰减时间常数
:return: t时刻突触后的LIF神经元的电压值
'''
# 指数衰减的脉冲输入
return (torch.exp(-t / tau) - torch.exp(-t / tau_s)) * (t >= 0).float()
def forward(self, in_spikes: torch.Tensor, ret_type):
'''
:param in_spikes: shape=[batch_size, in_features]
in_spikes[:, i]表示第i个输入脉冲的脉冲发放时刻,介于0到T之间,T是仿真时长
in_spikes[:, i] < 0则表示无脉冲发放
:param ret_type: 返回值的类项,可以为'v','v_max','spikes'
:return:
ret_type == 'v': 返回一个shape=[batch_size, out_features, T]的tensor,表示out_features个Tempotron神经元在仿真时长T\
内的电压值
ret_type == 'v_max': 返回一个shape=[batch_size, out_features]的tensor,表示out_features个Tempotron神经元在仿真时长T\
内的峰值电压
ret_type == 'spikes': 返回一个out_spikes,shape=[batch_size, out_features]的tensor,表示out_features个Tempotron神\
经元的脉冲发放时刻,out_spikes[:, i]表示第i个输出脉冲的脉冲发放时刻,介于0到T之间,T是仿真时长。out_spikes[:, i] < 0\
表示无脉冲发放
'''
t = torch.arange(0, self.T).to(in_spikes.device) # t = [0, 1, 2, ..., T-1] shape=[T]
t = t.view(1, 1, t.shape[0]).repeat(in_spikes.shape[0], in_spikes.shape[1], 1) # shape=[batch_size, in_features, T]
in_spikes = in_spikes.unsqueeze(-1).repeat(1, 1, self.T) # shape=[batch_size, in_features, T]
v_in = self.v0 * self.psp_kernel(t - in_spikes, self.tau, self.tau_s) * (in_spikes >= 0).float() # in_spikes[:, i] < 0的位置,输入电压也为0
v_out = self.fc(v_in.permute(0, 2, 1)).permute(0, 2, 1) # shape=[batch_size, out_features, T]
if ret_type == 'v':
return v_out
elif ret_type == 'v_max':
return F.max_pool1d(v_out, kernel_size=self.T).squeeze()
elif ret_type == 'spikes':
max_index = v_out.argmax(dim=2) # shape=[batch_size, out_features]
# 用soft arg max的方法,将tempotron扩展到多层
t = torch.arange(0, self.T).to(in_spikes.device) # t = [0, 1, 2, ..., T-1] shape=[T]
t = t.view(1, 1, t.shape[0]).repeat(in_spikes.shape[0], v_out.shape[1], 1) # shape=[batch_size, out_features, T]
max_index_soft = (F.softmax(v_out * self.T, dim=2) * t).sum(dim=2) # shape=[batch_size, out_features]
v_max = F.max_pool1d(v_out, kernel_size=self.T).squeeze()
mask = (v_max >= self.v_threshold).float() * 2 - 1
# mask_soft = torch.tanh(v_max - self.v_threshold)
# mask中的元素均为±1,表示峰值电压是否过阈值
max_index = max_index * mask
# max_index_soft = max_index_soft * mask_soft
max_index_soft = max_index_soft * mask
# print('max_index\n', max_index, '\nmax_index_soft\n', max_index_soft)
return max_index_soft + (max_index - max_index_soft).detach()
else:
raise ValueError
代码实现中,原来公式中 V t h r e s h o l d 为 1 , V r e s e t 为 0 V_{threshold}为1,V_{reset} 为0 Vthreshold?为1,Vreset?为0,用fc实现了膜电位的forward过程。
b. 高斯调谐曲线编码
源程序对输入图像的每个像素点用m个神经元来编码,这里编码的数据即MNIST图像,因其是单通道图像,可以认为只有1个特征。取值范围是[0, 1]
encoder = encoding.GaussianTuning(n=1, m=m, x_min=torch.zeros(size=[1]).to(device), x_max=torch.ones(size=[1]).to(device))
对第
i
i
i个特征
X
i
X^i
Xi,它的取值范围是
X
m
i
n
i
≤
X
i
≤
X
m
a
x
i
X_{min}^i \le X^i \le X_{max}^i
Xmini?≤Xi≤Xmaxi?,计算m条高斯曲线
g
j
i
g_j^i
gji?的均值和方差:
μ
j
i
=
x
min
?
i
+
2
j
?
3
2
x
max
?
i
?
x
min
?
i
m
?
2
,
j
=
1
,
2
,
…
,
m
σ
j
i
=
1
β
x
max
?
i
?
x
min
?
i
m
?
2
(4)
\begin{aligned} \mu_{j}^{i} &=x_{\min }^{i}+\frac{2 j-3}{2} \frac{x_{\max }^{i}-x_{\min }^{i}}{m-2}, j=1,2, \ldots, m \\ \sigma_{j}^{i} &=\frac{1}{\beta} \frac{x_{\max }^{i}-x_{\min }^{i}}{m-2} \end{aligned} \tag{4}
μji?σji??=xmini?+22j?3?m?2xmaxi??xmini??,j=1,2,…,m=β1?m?2xmaxi??xmini???(4)
其中
β
\beta
β通常取值为1.5。可以看出,这
m
m
m条高斯曲线的形状完全相同,只是对称轴所在的位置不同。
对于要编码的数据
x
∈
X
i
x \in X^{i}
x∈Xi, 首先计算出
x
x
x 对应的高斯函数值
g
j
i
(
x
)
g_{j}^{i}(x)
gji?(x), 这些函数值全部介于
[
0
,
1
]
[0,1]
[0,1] 之 间。接下来, 将函数值线性地转换到
[
0
,
T
]
[0, T]
[0,T] 之间的脉冲发放时刻,其中
T
T
T 是编码周期, 或者说是仿真时长:
t
j
=
Round
?
(
(
1
?
g
j
i
(
x
)
)
T
)
(5)
t_{j}=\operatorname{Round}\left(\left(1-g_{j}^{i}(x)\right) T\right) \tag{5}
tj?=Round((1?gji?(x))T)(5)
其中 Round 取整函数。此外, 对于发放时刻太晩的脉冲, 例如发放时刻为
T
T
T, 则直接将发放时刻设置为
?
1
-1
?1, 表示没有脉冲发放。
class GaussianTuning:
def __init__(self, n, m, x_min: torch.Tensor, x_max: torch.Tensor):
'''
:param n: 特征的数量,int
:param m: 编码一个特征所使用的神经元数量,int
:param x_min: n个特征的最小值,shape=[n]的tensor
:param x_max: n个特征的最大值,shape=[n]的tensor
Bohte S M, Kok J N, La Poutre J A, et al. Error-backpropagation in temporally encoded networks of spiking \
neurons[J]. Neurocomputing, 2002, 48(1): 17-37. 中提出的高斯调谐曲线编码方式
编码器所使用的变量所在的device与x_min.device一致
'''
assert m > 2
self.m = m
self.n = n
i = torch.arange(1, m+1).unsqueeze(0).repeat(n, 1).float().to(x_min.device) # shape=[n, m]
self.mu = x_min.unsqueeze(-1).repeat(1, m) + \
(2 * i - 3) / 2 * \
(x_max.unsqueeze(-1).repeat(1, m) - x_min.unsqueeze(-1).repeat(1, m)) / (m - 2) # shape=[n, m]
self.sigma2 = (1 / 1.5 * (x_max - x_min) / (m - 2)).unsqueeze(-1).square().repeat(1, m) # shape=[n, m]
# print('mu\n', self.mu)
# print('sigma2\n', self.sigma2)
def encode(self, x: torch.Tensor, max_spike_time=50):
'''
:param x: shape=[batch_size, n, k],batch_size个数据,每个数据含有n个特征,每个特征中有k个数据
:param max_spike_time: 最大(最晚)脉冲发放时间,也可以称为编码时间窗口的长度
:return: out_spikes, shape=[batch_size, n, k, m],将每个数据编码成了m个神经元的脉冲发放时间
'''
x_shape = x.shape
# shape: [batch_size, n, k] -> [batch_size, k, n]
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1)
x = x.contiguous().view(-1, x.shape[2]) # shape=[batch_size * k, n]
x = x.unsqueeze(-1).repeat(1, 1, self.m) # shape=[batch_size * k, n, m]
# 计算x对应的m个高斯函数值
y = torch.exp(- (x - self.mu).square() / 2 / self.sigma2) # shape=[batch_size * k, n, m]
out_spikes = (max_spike_time * (1 - y)).round()
out_spikes[out_spikes >= max_spike_time] = -1 # -1表示无脉冲发放
# shape: [batch_size * k, n, m] -> [batch_size, k, n, m]
out_spikes = out_spikes.view(x_shape[0], x_shape[2], out_spikes.shape[1], out_spikes.shape[2])
out_spikes = out_spikes.permute(0, 2, 1, 3) # shape: [batch_size, k, n, m] -> [batch_size, n, k, m]
return out_spikes
c. 损失函数、训练
对于分类错误的神经元,误差为其峰值电压与阈值电压之差的平方。
@staticmethod
def mse_loss(v_max, v_threshold, label, num_classes):
'''
:param v_max: Tempotron神经元在仿真周期内输出的最大电压值,与forward函数在ret_type == 'v_max'时的返回值相\
同。shape=[batch_size, out_features]的tensor
:param v_threshold: Tempotron的阈值电压,float或shape=[batch_size, out_features]的tensor
:param label: 样本的真实标签,shape=[batch_size]的tensor
:param num_classes: 样本的类别总数,int
:return: 分类错误的神经元的电压,与阈值电压之差的均方误差
'''
wrong_mask = ((v_max >= v_threshold).float() != F.one_hot(label, num_classes)).float()
return torch.sum(torch.pow((v_max - v_threshold) * wrong_mask, 2)) / label.shape[0]
训练仍然是forward、backward、optimize三个过程
for epoch in range(train_epoch):
net.train()
for img, label in train_data_loader:
img = img.view(img.shape[0], -1).unsqueeze(1) # [batch_size, 1, 784]
in_spikes = encoder.encode(img.to(device), T) # [batch_size, 1, 784, m]
in_spikes = in_spikes.view(in_spikes.shape[0], -1) # [batch_size, 784*m]
v_max = net(in_spikes)
train_acc = (v_max.argmax(dim=1) == label.to(device)).float().mean().item()
if train_times % 256 == 0:
writer.add_scalar('train_acc', train_acc, train_times)
if train_times % 512 == 0:
print(device, dataset_dir, batch_size, learning_rate, T, train_epoch, m, log_dir)
print('train_acc', train_acc, train_times)
loss = neuron.Tempotron.mse_loss(v_max, net.tempotron.v_threshold, label.to(device), 10)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_times += 1
d. 结果、分析
不同于时钟驱动的每次epoch都进行T个仿真步长,事件驱动神经元的状态更新由事件触发,例如产生脉冲或接受输入脉冲,因而不同神经元的活动可以异步计算,不需要在时钟上保持同步。
训练100个epoch后结果如下:
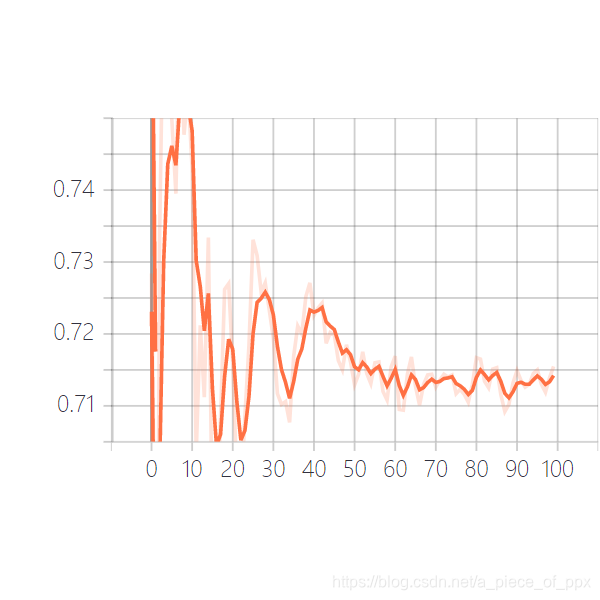
随着训练的进行,测试集正确率不断下降,过拟合比较严重。
tempotron也不适合使用大量数据集的训练:参考SNN-Tempotron.
原文教程:事件驱动