该文主要介绍OpenCV中XML文件的读写。大部分代码来自于OpenCV官方文档。
一、向XML文件中写入数据
1.1 打开文件
首先以写得方式打开一个xml文件。
//以写得方式打开一个xml文件
string filename = "123.xml";
FileStorage fs(filename, FileStorage::WRITE);
//filename:为文件的路径
//注:如果文件不存在则创建文件,如果文件存在会将文件中已有的内容清空。
1.2向文件中写入数据
通过不同的写入方式可以向文件中写入不同形式的数据,以下将一一介绍。
写入方式一:
向文件中写入一个节点和一个值,在xml中的形式如下:
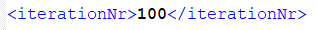
写入如上形式的xml数据的代码如下:
//1、节点名和节点值一一对应,
//2、不能连续在一个节点名后面跟两个值(如:fs << "iterationNr" << 100 << 20;这种是错误的)。
//3、节点名必须是字符串类型。
fs << "iterationNr" << 100;
写入方式二:
向一个节点中写入多个值,这时需要使用中括号,在xml文件中该节点的值用空格间隔。在xml中的形式如下:

写入如上形式的xml数据的代码如下:
//写入的这多个值要放在中括号中
string a = "node1";
fs << a << "[" << 30;
fs << 20 << "]" ;
写入方式三:
创建多级节点,创建多级节点需要使用大括号。在xml中的形式如下:
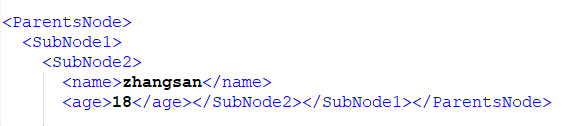
写入如上形式的xml数据的代码如下:
fs << "ParentsNode" << "{" << "SubNode1";
fs << "{" << "SubNode2" << "{";
fs << "name" << "zhangsan" << "age" << 18 << "}" << "}" << "}";
写入方式四:
向XML文件中写入OpenCV中的Mat对象,在xml中的形式如下:

写入如上形式的xml数据的代码如下:
Mat F3 = Mat_<Vec3f>::eye(3, 3);
fs << "F3" << F3;
code
xml文件的写入的测试代码如下:
string filename = "123.xml";
Mat R = Mat_<uchar>::eye(3, 3);
Mat T = Mat_<double>::zeros(3, 1);
FileStorage fs(filename, FileStorage::WRITE);
fs << "iterationNr" << 100;
string a = "node1";
fs << a << "[" << 30;
fs << 20 << "]" ;
fs << "strings" << "["
<< "image1.jpg" << "Awesomeness" << "../data/baboon.jpg";
fs << "]";
fs << "ParentsNode" << "{" << "SubNode1";
fs << "{" << "SubNode2" << "{";
fs << "name" << "zhangsan" << "age" << 18 << "}" << "}" << "}";
fs << "Mapping";
fs << "{" << "One" << 1;
fs << "Two" << 2 << "}";
Mat R3 = Mat_<Vec3b>::eye(3, 3);
Mat F3 = Mat_<Vec3f>::eye(3, 3);
fs << "R3" << R3;
fs << "F3" << F3;
fs << "R" << R;
fs << "T" << T;
fs.release();
cout << "Write Done." << endl;
通过代码写入后xml的文件形式如下:

二、从XML文件中读取数据
在OpenCV中读取xml文件中的数据有如下几种方式。
方式一:
读取如下形式的数据:
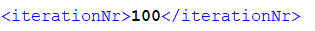
读取代码为:
//读取方法一:
int itNr;
itNr = (int)fs["iterationNr"];
cout << itNr << endl;
//读取方法二:
FileNode nod = fs["iterationNr"];
for (FileNodeIterator it = nod.begin(), it_end = nod.end(); it != it_end; it++)
{
cout << (int)*it << endl;
}
方式二:
读取如下形式的数据:

读取代码为:
FileNode n = fs["strings"];
if (n.type() != FileNode::SEQ)
{
cerr << "strings is not a sequence! FAIL" << endl;
return 1;
}
FileNodeIterator it = n.begin(), it_end = n.end();
for (; it != it_end; ++it)
cout << (string)*it << endl;
方式三:
读取如下形式的数据:
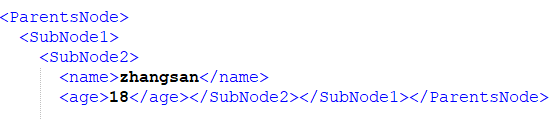
读取代码为:
FileNode n3 = fs["ParentsNode"];
FileNode n4 = n3["SubNode1"];
FileNode n5 = n4["SubNode2"];
cout << n5.name() << endl;
cout << "name = " << (string)(n5["name"]) << endl;
cout << "age = " << (int)(n5["age"]) << endl;
方式四:
读取如下形式的数据:

读取代码为:
//矩阵的读取方式
Mat F3;
fs["F3"] >> F3;
cout << "F3 = " << F3 << endl;
code
xml文件数据的读取的测试代码如下:
cout << "endl" << "Reading: " << endl;
string filename = "123.xml";
FileStorage fs;
fs.open(filename, FileStorage::READ);
if (!fs.isOpened())
{
cerr << "Failed to open " << filename << endl;
return 1;
}
int itNr;
itNr = (int)fs["iterationNr"];
cout << itNr << endl;
FileNode nod = fs["iterationNr"];
for (FileNodeIterator it = nod.begin(), it_end = nod.end(); it != it_end; it++)
{
cout << (int)*it << endl;
}
string n2 = (string)fs["strings"];
cout << "n2 = " << n2 << endl;
FileNode n = fs["strings"];
if (n.type() != FileNode::SEQ)
{
cerr << "strings is not a sequence! FAIL" << endl;
return 1;
}
FileNodeIterator it = n.begin(), it_end = n.end();
for (; it != it_end; ++it)
cout << (string)*it << endl;
FileNode n3 = fs["ParentsNode"];
FileNode n4 = n3["SubNode1"];
FileNode n5 = n4["SubNode2"];
cout << n5.name() << endl;
cout << "name = " << (string)(n5["name"]) << endl;
cout << "age = " << (int)(n5["age"]) << endl;
//矩阵的读取方式
Mat F3;
fs["F3"] >> F3;
cout << "F3 = " << F3 << endl;
fs.release();