循环神经网络
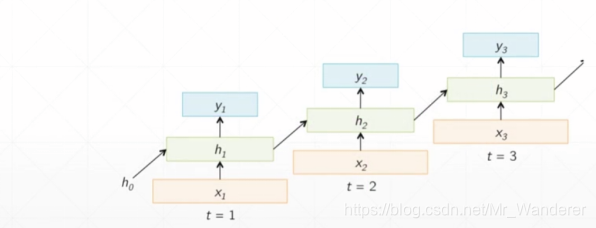
RNN单元会自我更新之后再输出,其前向传播函数如下:
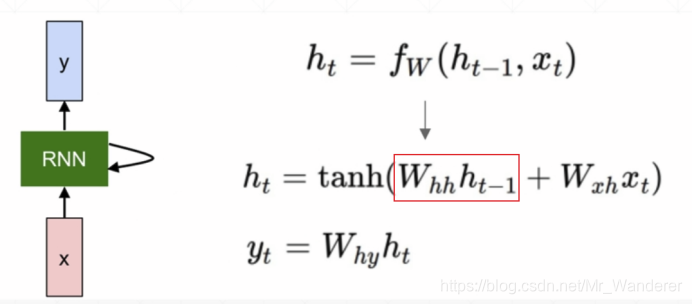
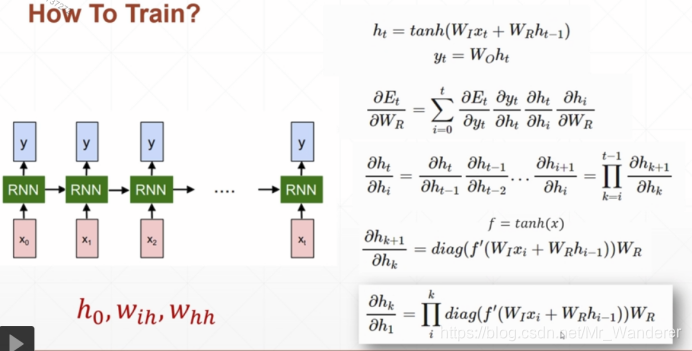
Pytorch实现RNN单元的两种方式
nn.RNN()
初始化:

使用:
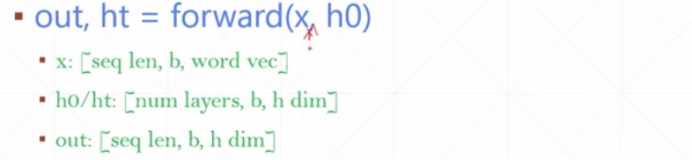
- x给的是x不是x(t),就是把x一次全部喂进去
X.shape:[seq_len, batch_size, input_size]
input_size就是word_vec - h0可以给也可以不给,不给的话就默认给0
- ht:最后一个时刻的所有层cnn的状态
h.shape:[num_layers, batch_size, h_dim]
h_dim就是hidden_len - out:所有时刻的最后一层cnn的状态
out_size:[seq_len, batch_size, h_dim]
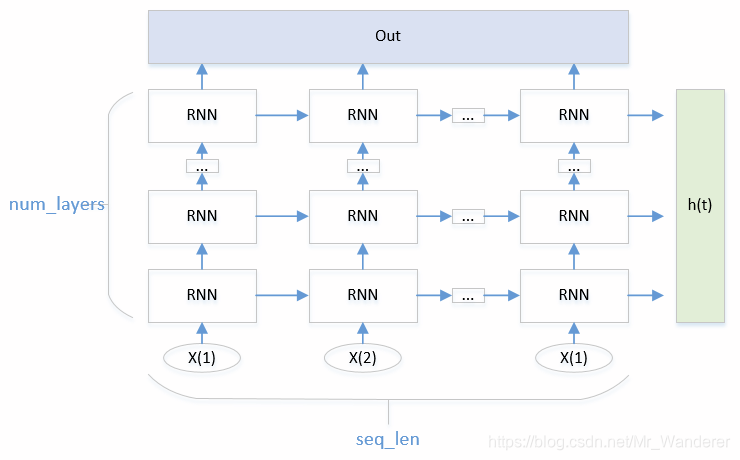
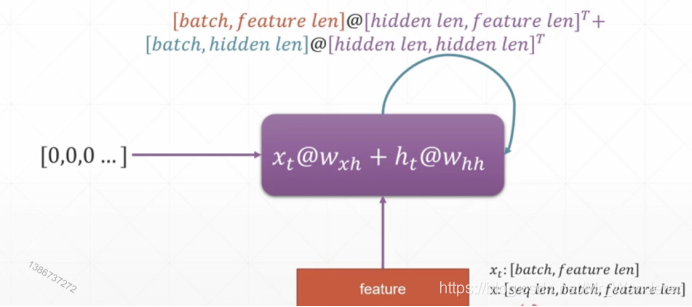
单层的RNN网络:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=100, hidden_size=20, num_layers=1)
print(rnn) # RNN(100, 20)
x = torch.randn(10, 3, 100) # [seq_length, b, input_size]
out, h = rnn(x, torch.zeros(1, 3, 20)) # [x, h0],不给h0参数也行
print(out.shape) # torch.Size([10, 3, 20]) 所有时间的状态
print(h.shape) # torch.Size([1, 3, 20]) 最后一个时刻的状态
多层RNN网络:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=100, hidden_size=20, num_layers=4)
print(rnn) # RNN(100, 20, num_layers=4)
x = torch.randn(10, 3, 100) # [seq_length, b, input_size]
out, h = rnn(x) # [x, h0],不给h0参数也行
print(out.shape) # torch.Size([10, 3, 20]) 所有时间戳上最后一层rnn的状态
print(h.shape) # torch.Size([4, 3, 20]) 最后时间戳上所有rnn层的状态
nn.RNNCell()

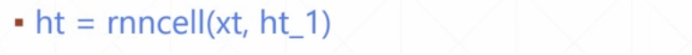
- x给的是x(t)。
x(t):[batch_size, input_size] - ht:t时刻某一层的状态
[batch_size, hidden_size]
单层RNN:
x = torch.randn(10, 3, 100) # [句子长度, b, 每个单词用几维向量表示]
cell1 = nn.RNNCell(100,20) # input_size, hidden_size, num_layer = 1
h1 = torch.zeros(3, 20) # batch_size, hidden_size
for xt in x:
h1 = cell1(xt,h1)
print(h1.shape) # torch.Size([3, 20])
双层RNN:
x = torch.randn(10, 3, 100) # [句子长度, b, 每个单词用几维向量表示]
cell1 = nn.RNNCell(100,30) # [input_size, hidden_size, num_layer = 1]
cell2 = nn.RNNCell(30,20)
h1 = torch.zeros(3, 30) # [batch_size, hidden_size]
h2 = torch.zeros(3, 20)
for xt in x:
h1 = cell1(xt,h1)
h2 = cell2(h1,h2)
print(h2.shape) # torch.Size([3, 20])
RNN预测正弦函数
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2021/7/31 21:18
# @Author : Liu Lihao
# @File : test.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import torch.optim as optim
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
'''超参数'''
num_time_steps = 50
input_size = 1
hidden_size = 16
output_size = 1
num_layers = 1
lr=0.01
'''定义网络结构'''
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.RNN(
input_size=input_size,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_layers=num_layers,
batch_first=True # [batch, seq, feature]
)
self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, x, hidden_prev): # x, h0
# x: [batch_size, seq_len, input_size]
# hidden_prev: [num_layers, batch_size, h_dim] h_dim就是hidden_size
out, hidden_prev = self.rnn(x, hidden_prev)
# out: [batch_size, seq_len, h_dim]
# hidden_prev: [num_layers, batch_size, h_dim]
# [batch, seq, hidden_size] => [batch * seq, hidden_size]
out = out.view(-1, hidden_size)
# [batch * seq_len, hidden_size] => [batch * seq_len, output_size]
out = self.linear(out)
# [batch * seq_len, output_size] => [1, batch * seq_len, output_size] 这里batch=1
out = out.unsqueeze(dim=0)
return out, hidden_prev
'''声明网络。loss,优化器'''
model = Net()
loss_function = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr)
hidden_prev = torch.zeros(num_layers, 1, hidden_size)
'''训练'''
for iter in range(6000):
start = np.random.randint(3, size=1)[0] # 开始的时刻,会在0-3之随机初始化。
time_steps = np.linspace(start, start + 10, num_time_steps) # 训练的数据:从start时刻到start+10时刻
data = np.sin(time_steps)
data = data.reshape(num_time_steps, 1)
# 只往后预测一个点
x = torch.tensor(data[:-1]).float().view(1, num_time_steps - 1, 1) # 去掉最后一个元素,作为输入
# x.shape: torch.Size([1, 49, 1]) [batch_size, seq_len, input_size]
y = torch.tensor(data[1:]).float().view(1, num_time_steps - 1, 1) # 去掉第一个元素,作为label
# y.shape: torch.Size([1, 49, 1])
# 神经网络前传
output, hidden_prev = model(x, hidden_prev)
hidden_prev = hidden_prev.detach() # 将variable参数从网络中隔离开,不参与参数更新。
loss = loss_function(output, y)
model.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if iter % 100 == 0:
print("Iteration: {} loss {}".format(iter, loss.item()))
'''测试'''
start = np.random.randint(3, size=1)[0]
time_steps = np.linspace(start, start + 10, num_time_steps)
data = np.sin(time_steps)
data = data.reshape(num_time_steps, 1)
x = torch.tensor(data[:-1]).float().view(1, num_time_steps - 1, 1)
y = torch.tensor(data[1:]).float().view(1, num_time_steps - 1, 1)
predictions = []
input = x[:, 0, :]
for _ in range(x.shape[1]):
input = input.view(1, 1, 1)
pred, hidden_prev = model(input, hidden_prev)
input = pred
predictions.append(pred.detach().numpy().ravel()[0])
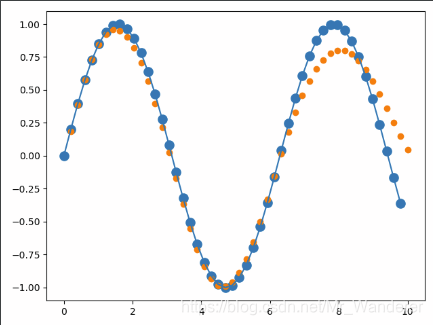
'''绘图'''
x = x.data.numpy().ravel()
y = y.data.numpy()
plt.scatter(time_steps[:-1], x.ravel(), s=90)
plt.plot(time_steps[:-1], x.ravel())
plt.scatter(time_steps[1:], predictions)
plt.show()