主要内容是A与A*算法
湖南大学 从自然世界到智能时代
进化计算
进化计算是以达尔文的进化论、孟德尔的遗传学作为基础的智能方法。现实中生物进化包括:繁殖、基因重组、基因变异、个体竞争、自然选择,进化计算主要包括:选择、重组、变异。
进化计算方法:遗传算法、协同进化、进化策略、进化规划、遗传编程
遗传算法
一种随机搜索方法,不需要数学的求导
选择:
交叉:概率选择交叉点
变异:概率选择变异点
适应度比例法、适应度排序法
随机选择一位按概率变异,每位都按概率变异
协同进化
种群与种群间,三种算法:基于竞争机制(大象与狮子)、基于共生机制(鳄鱼与燕千鸟)、基于捕食-猎物机制(老鹰与兔子)
将一个问题分解为若干子问题,每个子问题对应一个种群,每个种群用独立的算法求解。
进化策略
模拟自然界生物进化概率解决参数优化问题的方法
1+1进化策略:种群只有一个个体,只使用变异操作,变异后的个体与变异前的个体中选择较好的一个,变异算子基于生态分布
μ+1进化策略:种群有μ个个体,随机选择一个变异,然后选择出μ个中最差的一个,用变异个体代替
μ+λ进化策略:种群有μ个个体,随机选择λ个变异,然后选择出μ个中最差的λ个,用变异个体代替
μ,λ进化策略:产生的新个体数λ大于原个体数μ,取新个体中最优的μ个作为下一代
遗传编程
种群大小与基因大小是变化的
选择、交叉、变异:针对运算符,数值,函数进行,比如sin变异为cos,+变异为*,而之前的遗传算法只是对数值的变异
群体优化
粒子群(鸟群与鱼群)
通过个体极值与全局极值来更新个体速度与位置
当前速度=保持自身状态(惯性)+个体认识(自己之前所达到的最好位置)+全局认识(所有人中达到的最好位置)
当前位置=之前位置+当前速度
蜂群
artificial bee colony algorithm (ABC)
蜜源
侦察蜂:侦察到蜜源,当侦察到蜜源后,一轮搜索结束回到舞蹈区,有三个选择:1、放弃蜜源,再去侦察,2、放弃蜜源,跟着引领蜂去采蜜,自己就变成了跟随蜂,3、自己作为引领蜂,带着其他蜂去之前观察到的蜜源采蜜;当没有侦察到时,有两个选择:1、再去侦察,2、跟着引领蜂去采蜜,自己就变成了跟随蜂。
跟随蜂:当自己没有或者蜜源小于其他蜂,跟着引领蜂去采蜜
雇佣蜂(引领蜂):当自己蜜源最大,带着其他蜂去采蜜
舞蹈区:侦察到蜜源后,在舞蹈区招募没有蜜源或比自己蜜源小的蜜蜂
蚁群
ant colony optimization algorithm (ACO)

信息素浓度消散规则:
τ
x
y
(
t
)
=
ρ
τ
x
y
(
t
)
+
δ
τ
x
y
(
t
)
\tau_{xy}(t)=\rho\tau_{xy}(t)+\delta\tau_{xy}(t)
τxy?(t)=ρτxy?(t)+δτxy?(t),根据
δ
τ
x
y
(
t
)
\delta\tau_{xy}(t)
δτxy?(t)更新信息素
根据更新规则不同分为:蚂蚁圈系统、蚂蚁数量系统、蚂蚁密度系统
蚁群算法(Ant Colony Optimization) https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/137408401
浙江工业大学 人工智能导论
搜索求解策略
问题怎么表示,如何求解
搜索方法分类1:数据驱动、目的驱动,同时驱动
搜索方法分类2:盲目搜索、启发式搜索
状态空间:状态集合S,操作算子集合O,初始状态S0,结束状态G
S
0
→
O
1
S
1
→
O
2
S
2
→
O
3
S
3
.
.
.
→
O
n
G
S_0 \rightarrow^{O_1} S_1 \rightarrow^{O_2} S_2 \rightarrow^{O_3} S_3... \rightarrow^{O_n} G
S0?→O1?S1?→O2?S2?→O3?S3?...→On?G
组合优化:规模增加一点,计算量是非线性增加。
启发信息:用来简化搜索过程有关具体问题领域的特性的信息
启发搜索策略:A算法,A*算法
估价函数
f
(
n
)
=
g
(
n
)
+
h
(
n
)
f(n)=g(n)+h(n)
f(n)=g(n)+h(n),g(n)为初始节点到n节点的实际代价,h(n)为n节点到目标节点的估计代价
h(n) 比重大:降低搜索工作量,但可能导致找不到最优解;
h(n) 比重小:一般导致工作量加大,极限情况下变为盲目搜索,但可能可以找到最优解。
A与A*搜索算法
两种算法区别
https://cs.stackexchange.com/questions/50722/algorithm-a-vs-algorithm-a-whats-the-difference
https://blog.csdn.net/znr1995/article/details/62235481
A算法和A*算法的区别是什么? - OKWeCool的回答 - 知乎 https://www.zhihu.com/question/361118402/answer/940876304
A* Search Algorithm
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/a-search-algorithm/
A* 代码
https://rosettacode.org/wiki/A*_search_algorithm#Python
https://www.redblobgames.com/pathfinding/a-star/implementation.html#python-astar
https://towardsdatascience.com/a-star-a-search-algorithm-eb495fb156bb
内置方法进阶 __eq__ https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42233629/article/details/82353806
A算法:best-first search 加 heuristic evaluation,
f
(
n
)
=
g
(
n
)
+
h
(
n
)
f(n)=g(n)+h(n)
f(n)=g(n)+h(n)
A算法:best-first search 加 heuristic evaluation,
f
(
n
)
=
g
?
(
n
)
+
h
?
(
n
)
,
g
?
(
n
)
≤
g
(
n
)
,
h
(
n
)
≤
h
?
(
n
)
f(n)=g^*(n)+h^*(n), g^*(n)\leq g(n), h(n)\leq h*(n)
f(n)=g?(n)+h?(n),g?(n)≤g(n),h(n)≤h?(n)
A 算法是在 A 算法的基础上,每一次都选择最佳节点产生后继,并且人为的规定最小费用的估计始终满足 h ≤ h*,防止搜索过程中偏离期望的最佳路径。
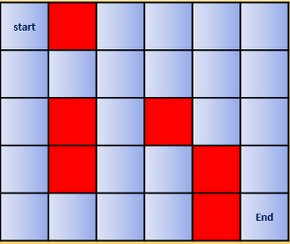
example——迷宫问题
红色方块不允许移动,移动方向:上下左右,每次移动一步,得出从start方块到达end方块的最优路径
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@time: 2021-08-09 下午 12:13
@author: leslie lee
"""
import numpy as np
class Node:
"""
A node class for A* Pathfinding
parent is parent of the current Node
position is current position of the Node in the maze
g is cost from start to current Node
h is heuristic based estimated cost for current Node to end Node
f is total cost of present node i.e. : f = g + h
"""
def __init__(self, parent=None, position=None):
self.parent = parent
self.position = position
self.g = 0
self.h = 0
self.f = 0
def __eq__(self, other):
return self.position == other.position
# This function return the path of the search
def return_path(current_node, maze):
path = []
no_rows, no_columns = np.shape(maze)
# here we create the initialized result maze with -1 in every position
result = [[-1 for i in range(no_columns)] for j in range(no_rows)] # 列表解析
current = current_node
while current is not None:
path.append(current.position)
current = current.parent
# Return reversed path as we need to show from start to end path
path = path[::-1] # 翻转
start_value = 0
# we update the path of start to end found by A-star serch with every step incremented by 1
for i in range(len(path)):
result[path[i][0]][path[i][1]] = start_value
start_value += 1
return result
def search(maze, cost, start, end):
"""
Returns a list of tuples as a path from the given start to the given end in the given maze
:param maze: 迷宫
:param cost: 每次移动步长
:param start: 开始位置
:param end: 目的位置
:return: 返回最优路径
"""
# Create start and end node with initized values for g, h and f
start_node = Node(None, tuple(start)) # 无父节点
start_node.g = start_node.h = start_node.f = 0
end_node = Node(None, tuple(end)) # 无父节点
end_node.g = end_node.h = end_node.f = 0
# Initialize both yet_to_visit and visited list
# in this list we will put all node that are yet_to_visit for exploration.
# From here we will find the lowest cost node to expand next
yet_to_visit_list = [] # 尚未访问的节点
# in this list we will put all node those already explored so that we don't explore it again
visited_list = [] # 已访问的节点
# Add the start node
yet_to_visit_list.append(start_node)
# Adding a stop condition. This is to avoid any infinite loop and stop
# execution after some reasonable number of steps
outer_iterations = 0
max_iterations = (len(maze) // 2) ** 10
# what squares do we search . serarch movement is left-right-top-bottom
# (4 movements) from every positon
move = [[-1, 0], # go up
[0, -1], # go left
[1, 0], # go down
[0, 1]] # go right
"""
1) We first get the current node by comparing all f cost and selecting the lowest cost node for further expansion
2) Check max iteration reached or not . Set a message and stop execution
3) Remove the selected node from yet_to_visit list and add this node to visited list
4) Perofmr Goal test and return the path else perform below steps
5) For selected node find out all children (use move to find children)
a) get the current postion for the selected node (this becomes parent node for the children)
b) check if a valid position exist (boundary will make few nodes invalid)
c) if any node is a wall then ignore that
d) add to valid children node list for the selected parent
For all the children node
a) if child in visited list then ignore it and try next node
b) calculate child node g, h and f values
c) if child in yet_to_visit list then ignore it
d) else move the child to yet_to_visit list
"""
# find maze has got how many rows and columns
no_rows, no_columns = np.shape(maze)
# 不断更新yet_to_visit_list
# Loop until you find the end
while len(yet_to_visit_list) > 0:
# Every time any node is referred from yet_to_visit list, counter of limit operation incremented
outer_iterations += 1
# Get the current node
current_node = yet_to_visit_list[0]
current_index = 0
for index, item in enumerate(yet_to_visit_list):
if item.f < current_node.f:
current_node = item
current_index = index
# if we hit this point return the path such as it may be no solution or
# computation cost is too high
if outer_iterations > max_iterations:
print("giving up on pathfinding too many iterations")
return return_path(current_node, maze)
# Pop current node out off yet_to_visit list, add to visited list
yet_to_visit_list.pop(current_index)
visited_list.append(current_node)
# test if goal is reached or not, if yes then return the path
if current_node == end_node:
return return_path(current_node, maze)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 获取当前节点的下一个节点,一个节点有四个子节点,如果子结点中有红方块或靠近边界则需去除其中几个子节点
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Generate children from all adjacent squares
children = []
for new_position in move:
# Get node position
node_position = (current_node.position[0] + new_position[0], current_node.position[1] + new_position[1])
# 排除边界
# Make sure within range (check if within maze boundary)
if (node_position[0] > (no_rows - 1) or
node_position[0] < 0 or
node_position[1] > (no_columns - 1) or
node_position[1] < 0):
continue
# 排除红方块
# Make sure walkable terrain
if maze[node_position[0]][node_position[1]] != 0:
continue
# 不是边界也不是红方块那么将其作为子节点
# Create new node
new_node = Node(current_node, node_position)
# Append
children.append(new_node)
# --------------------------------------------------------------
# 遍历当前节点所有的下一个节点, 取其中g最小的节点加入yet_to_visit_list
# --------------------------------------------------------------
# Loop through children
for child in children:
# 如果子节点已经访问过了 跳过本次循环
# Child is on the visited list (search entire visited list)
if len([visited_child for visited_child in visited_list if visited_child == child]) > 0:
continue
# Create the f, g, and h values
child.g = current_node.g + cost
# 欧氏距离
# Heuristic costs calculated here, this is using eucledian distance
child.h = (((child.position[0] - end_node.position[0]) ** 2) +
((child.position[1] - end_node.position[1]) ** 2))
child.f = child.g + child.h
# Child is already in the yet_to_visit list and g cost is already lower
if len([i for i in yet_to_visit_list if child == i and child.g > i.g]) > 0:
continue
# Add the child to the yet_to_visit list
yet_to_visit_list.append(child)
if __name__ == '__main__':
maze = [[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0]]
start = [0, 0] # starting position
end = [4, 5] # ending position
cost = 1 # cost per movement
path = search(maze, cost, start, end)
print('\n'.join(["".join(["{:"">3d}".format(item) for item in row])
for row in path]))
模拟退火算法
模拟退火算法和遗传算法 https://www.cnblogs.com/houqingying/p/12743159.html
其他知识
PCA主成分分析
ICA独立成分分析
blind signal separation 盲信号分离