Constructing it.
To construct an Optimizer you have to give it an iterable containing the
parameters (all should be Variable s) to optimize. Then, you can specify
optimizer-specific options such as the learning rate, weight decay, etc.
If you need to move a model to GPU via .cuda(), please do so before
constructing optimizers for it. Parameters of a model after .cuda()
will be different objects with those before the call.
In general, you should make sure that optimized parameters live
in consistent locations when optimizers are constructed and used.
- 首先,构造优化器时需要给定待优化的参数,另外还有诸如学习率、权重衰减策略之类的参数;其次,如果模型需要
G
P
U
\rm GPU
GPU 加速,移动到
G
P
U
\rm GPU
GPU 上保存,那么
.
c
u
d
a
(
)
\rm.cuda()
.cuda() 方法的调用必须在
o
p
t
i
m
.
x
x
x
(
)
\rm optim.xxx()
optim.xxx() 构造优化器之前。
Taking an optimization step.
1: optimizer.step().
This is a simplified version supported by most optimizers. The function can be
called once the gradients are computed using e.g. backward().
- 在计算出损失函数并且反向传播
l
o
s
s
.
b
a
c
k
w
a
r
d
(
)
\rm loss.backward()
loss.backward() 后调用
o
p
t
i
m
i
z
e
r
.
s
t
e
p
(
)
.
\rm optimizer.step().
optimizer.step().
for input, target in dataset:
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(input)
loss = loss_fn(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
2: optimizer.step(closure).
Some optimization algorithms such as Conjugate Gradient and LBFGS need to
reevaluate the function multiple times, so you have to pass in a closure
that allows them to recompute your model. The closure should clear the
gradients, compute the loss, and return it.
- 一些特殊的优化算法例如
C
o
n
j
u
g
a
t
e
?
G
r
a
d
i
e
n
t
\rm Conjugate~Gradient
Conjugate?Gradient 共轭梯度法以及
L
B
F
G
S
\rm LBFGS
LBFGS 需要多次评估函数,因此会给
o
p
t
i
m
i
z
e
r
.
s
t
e
p
(
)
\rm optimizer.step()
optimizer.step() 传入一个函数
c
l
o
s
u
r
e
\rm closure
closure 作为参数,该函数中需要完成梯度清理、损失计算并返回损失值。另外在
P
y
T
o
r
c
h
.
o
p
t
i
m
\rm PyTorch.optim
PyTorch.optim 实现的优化器中,只有
L
B
F
G
S
.
s
t
e
p
(
c
l
o
s
u
r
e
)
\rm LBFGS.step(closure)
LBFGS.step(closure) 中是必须有参数的,其他优化器均为可选参数。
for input, target in dataset:
def closure():
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(input)
loss = loss_fn(output, target)
loss.backward()
return loss
optimizer.step(closure)
RoitSky:
When shall I use ‘optimizer.step(closure)’ instead of ‘optimizer.step()’ ?
I have read the PyTorch Docs, however i’m not aware of its description.
"Some optimization algorithms such as Conjugate Gradient and LBFGS need to reevaluate
the function multiple times, so you have to pass in a closure that allows them to
recompute your model. The closure should clear the gradients, compute the loss, and
return it."
What does ‘reevaluate the function multiple times’ mean ? What does the ‘function’ refer to ?
googlebot:
‘function’ is a callable that returns a differentiable loss (i.e. main
nn.Module with attached loss function), these algorithms have an [inner] training loop
inside optimizer.step, hence this ‘closure’ is mostly a boilerplate to have a loop
turned inside out (i.e. a delegate allowing nested forward+backward+change_params
iterations)
RoitSky:
But why PyTorch Docs emphasizes that ‘Some optimization algorithms such as Conjugate
Gradient and LBFGS…’. When i create a SGD or an Adam optimizer, i just code in
‘optimizer.step()’.
googlebot:
BFGS & co are batch (whole dataset) optimizers, they do multiple steps on same inputs.
Though docs illustrate them with an outer loop (mini-batches), that’s a bit unusual
use, I think. Anyway, the inner loop enabled by ‘closure’ does parameter search with
inputs fixed, it is not a stochastic gradient loop you do with SGD or Adam.
Per-parameter options.
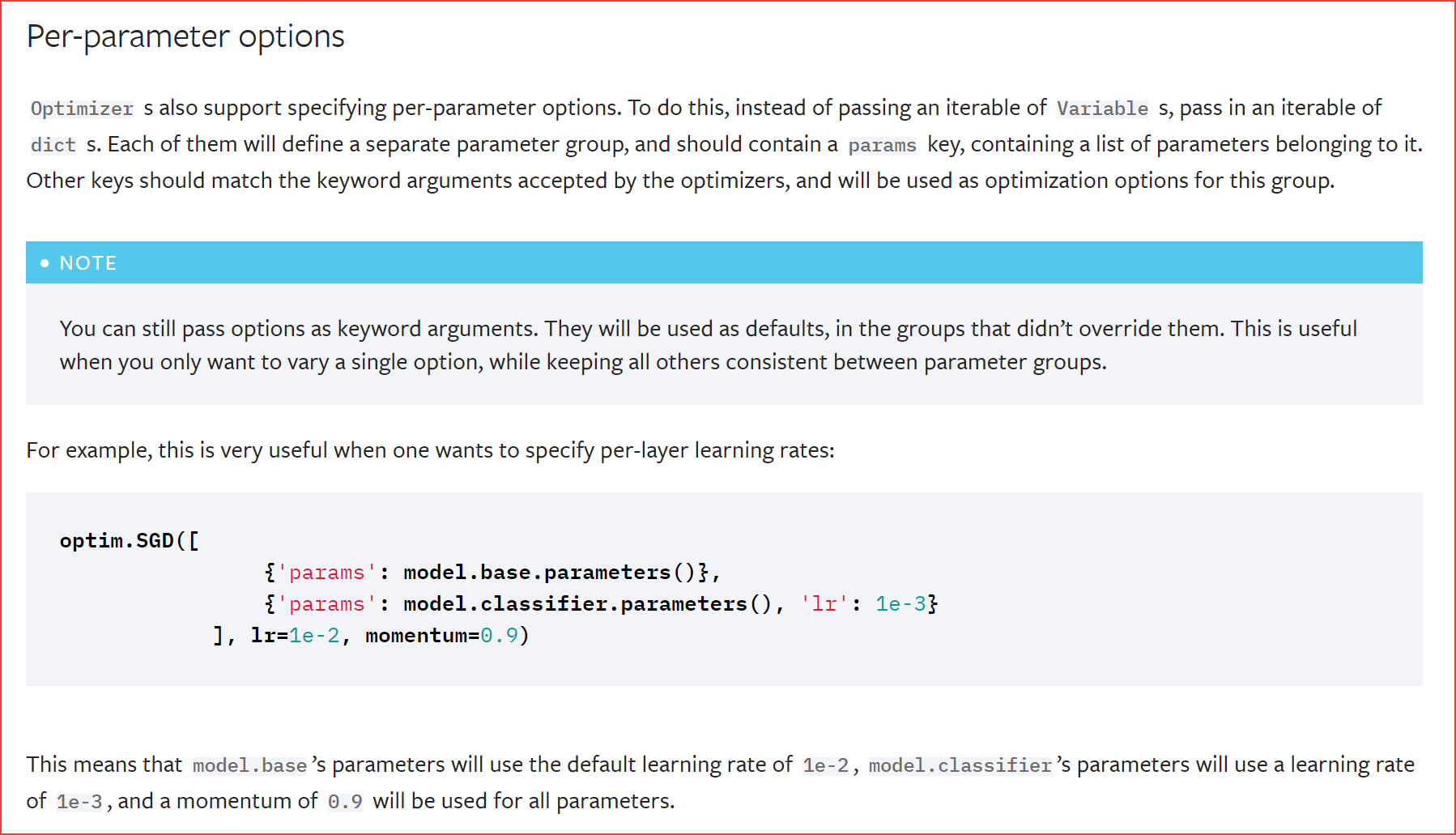
optim.SGD([
{'params': model.base.parameters()},
{'params': model.classifier.parameters(), 'lr': 1e-3}
], lr=1e-2, momentum=0.9)
| 