- 比赛名称:中文成语填空挑战赛算法挑战大赛
- 比赛链接:https://challenge.xfyun.cn/topic/info?type=chinese-idioms
- 关注“ChallengeHub”回复“成语填空”获取完整baseline
一、赛事背景
中国文化博大精深源远流长,其中成语更是中国文化的精华。成语大多由四个字组成,一般都有典故或出处。有些成语从字面上不难理解,如“小题大做”、“后来居上”等。有些成语必须知道来源或典故才能懂得意思,如“朝三暮四”、“杯弓蛇影”等。
成语学习是小学语文和初中重要的学习内容,如何在语句中选择合适的成语?本次赛题中希望选手构建模型能理解中文成语。
二、赛事任务
给定一个中文句子的情况下,需要选手在给定上下文的情况下从待选的成语中选择最为合适的成语。即给定句子的上下文,完成合适的成语填入对应位置。
赛题训练集案例如下:
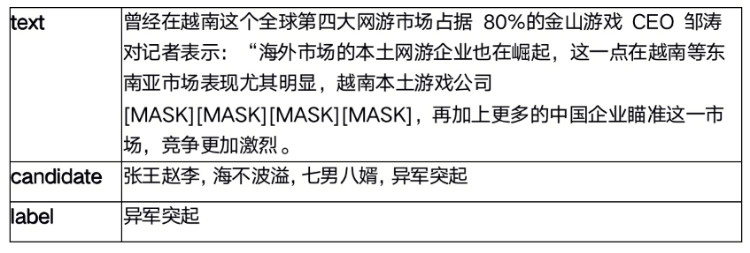
训练集5w条数据,测试集1w条数据。测试集中label字段为空,需要选手预测。
三、评审规则
1. 数据说明
赛题数据由训练集和测试集组成,训练集5w条数据,测试集1w条数据,均为csv格式,列使用\t分割。测试集提交案例见sample_submit.csv文件,不需要表头,直接按照顺序按行写入1w条成语即可。
2. 评估指标
本次竞赛的评价标准采用分类准确率,最高分为1。评估代码参考:
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
y_pred = [0, 2, 1, 3]
y_true = [0, 1, 2, 3]
accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred)
3. 评测及排行
1、赛事提供下载数据,选手在本地进行算法调试,在比赛页面提交结果。
2、每支团队每天最多提交3次。
3、排行按照得分从高到低排序,排行榜将选择团队的历史最优成绩进行排名。
四、作品提交要求
文件格式:预测结果文件按照csv格式提交
文件大小:无要求
提交次数限制:每支队伍每天最多3次
预测结果文件详细说明:
-
以csv格式提交,编码为UTF-8
-
提交前请确保预测结果的格式与sample_submit.csv中的格式一致。具体格式如下:
label
津津乐道
息息相关
必经之路
顾名思义
痛快淋漓
名列前茅
无所事事
如火如荼
夜以继日
紧锣密鼓
源源不断
五、赛程规则
正式赛
8月16日——9月15日
-
初赛截止成绩以团队在初赛时间段内最优成绩为准(不含测试排名)。
-
初赛作品提交截止日期为9月15日17:00;正式赛名次公布日期为8月16日10:00。
长期赛
9月16日——10月24日
因赛事以学习实践为主,正式赛将转变为长期赛,供开发者学习实践。本阶段提交后,系统会根据成绩持续更新榜单,但该阶段榜单不再进行公示和奖励。
六、奖项设置
本赛题设立一、二、三等奖各一名,具体详情如下:
-
一等奖:1支队伍,周赛一等奖证书,奖金:1000元
-
二等奖:1支队伍,周赛二等奖证书,奖金:800元
-
三等奖:1支队伍,周赛三等奖证书,奖金:500元
七、baseline思路
- 按照NLP中阅读理解题目处理比赛数据格式,具体内容可以参考swag格式
- 构建描述文本
text和选项‘choice’,以及候选答案:四个候选‘成语’ - 输入‘AutoModelForMultipleChoice’模型进行训练和预测
构建训练集和测试集
import re
import pandas as pd
from tqdm import tqdm
train = pd.read_csv('data/train.csv', sep='\t')
test = pd.read_csv('data/test.csv', sep='\t')
print(train)
print(test)
def process_text(text):
return re.sub(' +', ' ', text).strip()
def get_question(text):
"""
根据[MASK][MASK][MASK][MASK]获取问题
:param text:
:return:
"""
sentences = re.split('(。|!|\!|\.|?|\?)', text) # 保留分割符
for sent in sentences:
if '[MASK][MASK][MASK][MASK]' in sent:
return sent
return text
cols = [
"Unnamed: 0",
"video-id",
"fold-ind", # q_id
"startphrase",
"sent1", # content
"sent2", # question
"gold-source",
"ending0", "ending1", "ending2", "ending3", # choice
"label"]
# ======================================================
# 生成训练集
# ======================================================
res = []
for idx, row in tqdm(train.iterrows()):
q_id = f'train_{idx}'
content = row['text']
content = process_text(content)
question = get_question(content)
modified_choices = eval(row['candidate'])
label = modified_choices.index(row['label'])
## Hard-code for swag format!
res.append(("",
"",
q_id,
"",
content,
question,
"",
modified_choices[0],
modified_choices[1],
modified_choices[2],
modified_choices[3],
label))
df = pd.DataFrame(res, columns=cols)
模型训练
数据处理函数
@dataclass
class DataCollatorForMultipleChoice:
"""
Data collator that will dynamically pad the inputs for multiple choice received.
Args:
tokenizer (:class:`~transformers.PreTrainedTokenizer` or :class:`~transformers.PreTrainedTokenizerFast`):
The tokenizer used for encoding the data.
padding (:obj:`bool`, :obj:`str` or :class:`~transformers.tokenization_utils_base.PaddingStrategy`, `optional`, defaults to :obj:`True`):
Select a strategy to pad the returned sequences (according to the model's padding side and padding index)
among:
* :obj:`True` or :obj:`'longest'`: Pad to the longest sequence in the batch (or no padding if only a single
sequence if provided).
* :obj:`'max_length'`: Pad to a maximum length specified with the argument :obj:`max_length` or to the
maximum acceptable input length for the model if that argument is not provided.
* :obj:`False` or :obj:`'do_not_pad'` (default): No padding (i.e., can output a batch with sequences of
different lengths).
max_length (:obj:`int`, `optional`):
Maximum length of the returned list and optionally padding length (see above).
pad_to_multiple_of (:obj:`int`, `optional`):
If set will pad the sequence to a multiple of the provided value.
This is especially useful to enable the use of Tensor Cores on NVIDIA hardware with compute capability >=
7.5 (Volta).
"""
tokenizer: PreTrainedTokenizerBase
padding: Union[bool, str, PaddingStrategy] = True
max_length: Optional[int] = None
pad_to_multiple_of: Optional[int] = None
def __call__(self, features):
label_name = "label" if "label" in features[0].keys() else "labels"
labels = [feature.pop(label_name) for feature in features]
batch_size = len(features)
num_choices = len(features[0]["input_ids"])
flattened_features = [
[{k: v[i] for k, v in feature.items()} for i in range(num_choices)] for feature in features
]
flattened_features = sum(flattened_features, [])
batch = self.tokenizer.pad(
flattened_features,
padding=self.padding,
max_length=self.max_length,
pad_to_multiple_of=self.pad_to_multiple_of,
return_tensors="pt",
)
# Un-flatten
batch = {k: v.view(batch_size, num_choices, -1) for k, v in batch.items()}
# Add back labels
batch["labels"] = torch.tensor(labels, dtype=torch.int64)
return batch
模型训练
# Metric
def compute_metrics(eval_predictions):
predictions, label_ids = eval_predictions
preds = np.argmax(predictions, axis=1)
return {"accuracy": (preds == label_ids).astype(np.float32).mean().item()}
# Initialize our Trainer
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=tokenized_datasets["train"] if training_args.do_train else None,
eval_dataset=tokenized_datasets["validation"] if training_args.do_eval else None,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
data_collator=data_collator,
compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
)
# Training
if training_args.do_train:
if last_checkpoint is not None:
checkpoint = last_checkpoint
elif os.path.isdir(model_args.model_name_or_path):
checkpoint = model_args.model_name_or_path
else:
checkpoint = None
train_result = trainer.train(resume_from_checkpoint=checkpoint)
trainer.save_model() # Saves the tokenizer too for easy upload
output_train_file = os.path.join(training_args.output_dir, "train_results.txt")
if trainer.is_world_process_zero():
with open(output_train_file, "w") as writer:
logger.info("***** Train results *****")
for key, value in sorted(train_result.metrics.items()):
logger.info(f" {key} = {value}")
writer.write(f"{key} = {value}\n")
# Need to save the state, since Trainer.save_model saves only the tokenizer with the model
trainer.state.save_to_json(os.path.join(training_args.output_dir, "trainer_state.json"))
模型参数设置
预训练模型选择hfl/chinese-xlnet-base,大约需要训练1个小时左右。
#!/bin/bash
python -u baseline.py \
--model_name_or_path 'hfl/chinese-xlnet-base' \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--do_predict \
--logging_steps=100 \
--max_seq_length 200 \
--train_file data/new_train.csv \
--validation_file data/new_valid.csv \
--test_file data/new_test.csv \
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
--num_train_epochs 2 \
--output_dir 'models/xlnet' \
--gradient_accumulation_steps 4 \
--per_device_eval_batch_size 16 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 16 \
--overwrite_output
八、提升思路
- 参数调整:学习率、最大长度,Batch Size
- 交叉验证,多种子融合
- 模型投票融合
- 尝试多种预训练模型