之前一直和Tensorflow、PyToch一些框架进行纠缠。现在显然幡然醒悟,这样是不对的,我们不是去学怎么搭别人的顺风车,我们要做的是自己造轮子造车。
任何课程评价都可以说是对这一门五星级课程的亵渎了。
概念
讲述了机器学习的几种模式,包括了监督学习、无监督学习、半监督学习等。
监督学习就是我们知道了输入与输出的关系,比如等会作业里要做的假设了一个代价函数,而我们的目标就是不断去缩小这个损失。
其他的先不说,这一章主要讲的就是监督学习下的回归问题,而且是线性回归,也就是Linear regression。
代价函数
代价函数其实就是我们的损失函数。
我们在框架内应该用过许多“XXXLoss”,吴老师这里着重讲了个BCELoss。
也就是我们的均值平方差?
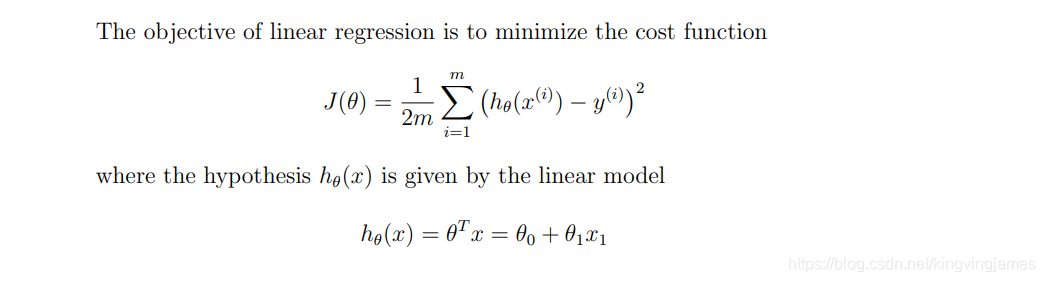
上述两个公式就是这章的重点了。
一个就是我们的模型预测函数h(x)。
我们要做的就是不断去迭代更新两个theta的值以做到让这个均值平方差(损失)最小,最后就是去拿这一对最优解去进行后续的预测。
梯度下降法
我们在上面提到了迭代更新,吴老师在视频中讲述了ML的第一个算法,梯度下降法。梯度就是slope,其实简而言之就是我们的导数。我们知道沿导数方向可以做到最快的下降。
这里还有几个注意点
1.梯度下降法有时候会陷入局部最优解从而漏掉全局最优解。
2.从不同位置进行梯度下降法可能得到的解不同。但是!基于我们优化的代价函数是convex凸函数,总是可以得到最优解。
求导,不具体推导了,同济大学的绿不拉机的书伺候。
其实就是换元咯,把(h(x) - y)视为t, 最后就是2t × h(x)对theta求偏导。
这里的alpha我们称之为学习率。
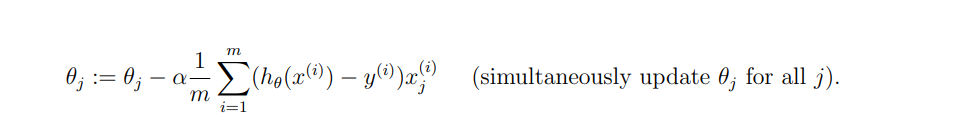
学习率太小则需要多轮迭代。
学习率太大则有可能错过最优解,甚至离其越来越远。
线性代数
矩阵与向量。
矩阵向量乘法。
矩阵乘法。
矩阵的转置和逆。
课后作业
作业自己得去网上找资源哈,git上有,我忘了链接了。。。。
1.了解一些基本的编程语法。跳过具体步骤,以创建一个对角1矩阵为例。
这里换成numpy来生成也可以。
def function1():
# helps you be familiar with the python syntax
x = torch.eye(5, dtype=torch.int)
print(x)
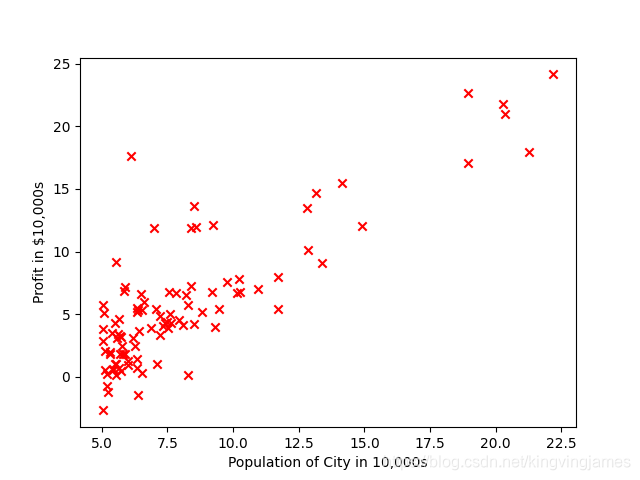
2.从ex1的txt文件中读取数据,并画出散点图。
def function2():
# linear regression with only one Variable
# you will be demand to predict the profit for a food truck and the dataset is in 'ex1.txt'
# first you should plot a scatter picture
file = pd.read_csv("./ex1data1.txt", header=None, names=["Population", "Profit"])
# print(file)
x_set = file["Population"]
y_set = file["Profit"]
plt.scatter(x_set, y_set, marker='x', c='red')
plt.ylabel("Profit in $10,000s", loc="center")
plt.xlabel("Population of City in 10,000s", loc="center")
plt.show()
对csv文件理解还是要深刻一些,它其实是逗号分割符文件。这样一来用pandas读再转array会很方便。比直接用open配合readline来实现要好很多。
结果图:
3.完成损失函数的设计,然后进行梯度下降法的实现。
打印每一轮的损失值,最后实现可视化。
注意:题目中吴老师要求我们做两个变量的梯度下降,他题目中补充的一种思路就是在原先的Populations前边加上一列全1用以代表theta0相乘的值,也就是视为
hx = theta0 × 1 + theta1 × X。
我们的file变量是一个Dataframe,样子如下:
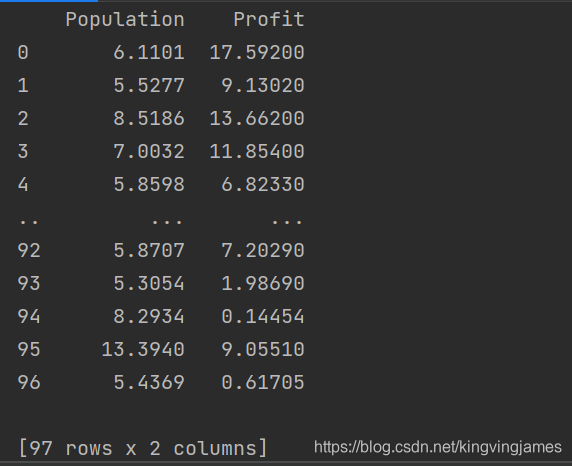
我们对下面的代码略微解读:
theta0就是我们的全一列,我们用colomn_stack来进行堆叠。就是按列堆叠,简单理解就是把theta0这个全一视为一列堆到M矩阵的左边去。
这个M就是我们直接由file利用numpy转换过来的一个array类型。
numpy实际上还有matrix矩阵类型可以用,用在这里实际上会更加方便。
因为我们知道矩阵相称的规则就是做矩阵的列数要和右矩阵的行数相等。
这里sub变量就是中间的差值,可以看到我们需要用dot函数才可以对array类型进行矩阵一样的运算。而如果这里面的变量都是matrix的话,直接用乘号即可。
最后就是里面众多的reshape(-1,1)就是转化为[N,1]的矩阵。否则单取一列的话你的shape是(N, )第二个维度是空的说明这个实际上是一个向量。这样在进行运算时会有很多bug出现。
以上是我觉得一些困难的点,具体的就由自己下载好作业文件,把txt复制到和你的python同一目录下,然后debug执行。
多看看array的shape,你就会明白代码里一些看似多余的操作。你可以删去你认为的多余的操作看看有什么exception出现。
def function3():
"""
In this part, you will fit the linear regression parameters θ to our dataset
using gradient descent.
"""
file = pd.read_csv("./ex1data1.txt", header=None, names=["Population", "Profit"])
# print(file)
M = np.array(file)
length = len(M[:, 1])
theta0 = np.ones((length, 1))
M = np.column_stack((theta0, M))
theta = np.zeros((2, 1))
# print(theta)
iterations = 1500
learning_rate = 0.01
reals = M[:, 2].reshape(-1, 1) # 扩维 否则只是一个向量没法计算
x_coef = M[:, 1].reshape(-1, 1)
# print(theta[0, 0], theta[1, 0])
for i in range(iterations):
loss = 0
sub = np.dot(M[:, :-1], theta) - reals
loss += np.sum(np.power(sub, 2) / (2 * length))
print("loss is %f" % loss)
temp = theta
for j in range(2):
yy = sub * M[:, j].reshape(-1, 1)
temp[j, 0] = theta[j, 0] - learning_rate * 1 / length * np.sum(yy)
theta = temp
x_set = np.array(file["Population"])
y_set = np.array(file["Profit"])
predicts = np.dot(M[:, :-1], theta)
plt.plot(x_set, predicts, color="blue")
plt.scatter(x_set, y_set, marker='x', c='red')
plt.ylabel("Profit in $10,000s", loc="center")
plt.xlabel("Population of City in 10,000s", loc="center")
plt.show()
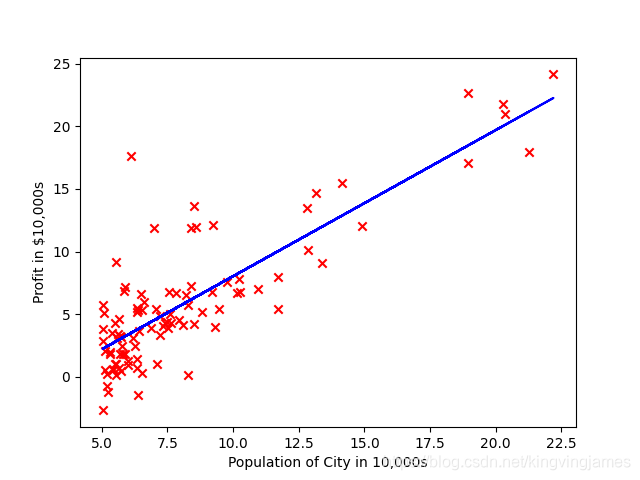
最后的拟合结果图。
完整代码:
import torch
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
'''
In this exercise, you will implement linear regression and get to see it work
on data. Before starting on this programming exercise, we strongly
recommend watching the video lectures and completing the review questions for
the associated topics.
'''
def function1():
# helps you be familiar with the python syntax
x = torch.eye(5, dtype=torch.int)
print(x)
def function2():
# linear regression with only one Variable
# you will be demand to predict the profit for a food truck and the dataset is in 'ex1.txt'
# first you should plot a scatter picture
file = pd.read_csv("./ex1data1.txt", header=None, names=["Population", "Profit"])
print(file)
x_set = file["Population"]
y_set = file["Profit"]
plt.scatter(x_set, y_set, marker='x', c='red')
plt.ylabel("Profit in $10,000s", loc="center")
plt.xlabel("Population of City in 10,000s", loc="center")
plt.show()
def function3():
"""
In this part, you will fit the linear regression parameters θ to our dataset
using gradient descent.
"""
file = pd.read_csv("./ex1data1.txt", header=None, names=["Population", "Profit"])
# print(file)
M = np.array(file)
length = len(M[:, 1])
theta0 = np.ones((length, 1))
M = np.column_stack((theta0, M))
theta = np.zeros((2, 1))
# print(theta)
iterations = 1500
learning_rate = 0.01
reals = M[:, 2].reshape(-1, 1) # 扩维 否则只是一个向量没法计算
x_coef = M[:, 1].reshape(-1, 1)
# print(theta[0, 0], theta[1, 0])
for i in range(iterations):
loss = 0
sub = np.dot(M[:, :-1], theta) - reals
loss += np.sum(np.power(sub, 2) / (2 * length))
print("loss is %f" % loss)
temp = theta
for j in range(2):
yy = sub * M[:, j].reshape(-1, 1)
temp[j, 0] = theta[j, 0] - learning_rate * 1 / length * np.sum(yy)
theta = temp
x_set = np.array(file["Population"])
y_set = np.array(file["Profit"])
predicts = np.dot(M[:, :-1], theta)
plt.plot(x_set, predicts, color="blue")
plt.scatter(x_set, y_set, marker='x', c='red')
plt.ylabel("Profit in $10,000s", loc="center")
plt.xlabel("Population of City in 10,000s", loc="center")
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
function1()
function2()
function3()