?数据链接和代码:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/19Rj_kP2iJ0szS6l2IWg6FQ?
提取码:ezbd
1、数据分析
数据集divorce.xlsx,我们先来看一下数据说明。简单来说,每一个维度对应一个调查问卷的问题。如图

需要引入的库:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns # 用这个库绘制数据分布特征图比较方便,pip install seaborn 就行了
%matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['KaiTi'] # 指定默认字体
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score # k折交叉验证
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # 导入自动生成训练集和测试集的模块
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report # 导入预测结果评估模块
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression # 逻辑回归
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix # 混淆矩阵
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier # 随机森林分类
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier # 决策树
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier # KNN
from sklearn import svm # 支持向量机?读入数据
data_train = pd.read_excel('divorce.xlsx')
# 让pandas自己先告诉我们一些信息,发现没有缺失值,因此不用进行缺失值的填充
data_train.info()
print(data_train)
data_train.describe()<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 170 entries, 0 to 169
Data columns (total 55 columns):
Atr1 170 non-null int64
Atr2 170 non-null int64
Atr3 170 non-null int64
Atr4 170 non-null int64
Atr5 170 non-null int64
Atr6 170 non-null int64
Atr7 170 non-null int64
Atr8 170 non-null int64
Atr9 170 non-null int64
Atr10 170 non-null int64
Atr11 170 non-null int64
Atr12 170 non-null int64
Atr13 170 non-null int64
Atr14 170 non-null int64
Atr15 170 non-null int64
Atr16 170 non-null int64
Atr17 170 non-null int64
Atr18 170 non-null int64
Atr19 170 non-null int64
Atr20 170 non-null int64
Atr21 170 non-null int64
Atr22 170 non-null int64
Atr23 170 non-null int64
Atr24 170 non-null int64
Atr25 170 non-null int64
Atr26 170 non-null int64
Atr27 170 non-null int64
Atr28 170 non-null int64
Atr29 170 non-null int64
Atr30 170 non-null int64
Atr31 170 non-null int64
Atr32 170 non-null int64
Atr33 170 non-null int64
Atr34 170 non-null int64
Atr35 170 non-null int64
Atr36 170 non-null int64
Atr37 170 non-null int64
Atr38 170 non-null int64
Atr39 170 non-null int64
Atr40 170 non-null int64
Atr41 170 non-null int64
Atr42 170 non-null int64
Atr43 170 non-null int64
Atr44 170 non-null int64
Atr45 170 non-null int64
Atr46 170 non-null int64
Atr47 170 non-null int64
Atr48 170 non-null int64
Atr49 170 non-null int64
Atr50 170 non-null int64
Atr51 170 non-null int64
Atr52 170 non-null int64
Atr53 170 non-null int64
Atr54 170 non-null int64
Class 170 non-null int64
dtypes: int64(55)
memory usage: 73.2 KB
Atr1 Atr2 Atr3 Atr4 Atr5 Atr6 Atr7 Atr8 Atr9 Atr10 ... Atr46 \
0 2 2 4 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 2
1 4 4 4 4 4 0 0 4 4 4 ... 2
2 2 2 2 2 1 3 2 1 1 2 ... 3
3 3 2 3 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 ... 2
4 2 2 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 ... 2
.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
165 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 1
166 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 4
167 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 ... 3
168 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 3
169 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 ... 3
Atr47 Atr48 Atr49 Atr50 Atr51 Atr52 Atr53 Atr54 Class
0 1 3 3 3 2 3 2 1 1
1 2 3 4 4 4 4 2 2 1
2 2 3 1 1 1 2 2 2 1
3 2 3 3 3 3 2 2 2 1
4 1 2 3 2 2 2 1 0 1
.. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
165 0 4 1 1 4 2 2 2 0
166 1 2 2 2 2 3 2 2 0
167 0 2 0 1 1 3 0 0 0
168 3 2 2 3 2 4 3 1 0
169 4 4 0 1 3 3 3 1 0
[170 rows x 55 columns]
Out[23]:
| Atr1 | Atr2 | Atr3 | Atr4 | Atr5 | Atr6 | Atr7 | Atr8 | Atr9 | Atr10 | ... | Atr46 | Atr47 | Atr48 | Atr49 | Atr50 | Atr51 | Atr52 | Atr53 | Atr54 | Class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | ... | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 | 170.000000 |
| mean | 1.776471 | 1.652941 | 1.764706 | 1.482353 | 1.541176 | 0.747059 | 0.494118 | 1.452941 | 1.458824 | 1.576471 | ... | 2.552941 | 2.270588 | 2.741176 | 2.382353 | 2.429412 | 2.476471 | 2.517647 | 2.241176 | 2.011765 | 0.494118 |
| std | 1.627257 | 1.468654 | 1.415444 | 1.504327 | 1.632169 | 0.904046 | 0.898698 | 1.546371 | 1.557976 | 1.421529 | ... | 1.371786 | 1.586841 | 1.137348 | 1.511587 | 1.405090 | 1.260238 | 1.476537 | 1.505634 | 1.667611 | 0.501442 |
| min | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | ... | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 25% | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | ... | 2.000000 | 1.000000 | 2.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 2.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 50% | 2.000000 | 2.000000 | 2.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 2.000000 | ... | 3.000000 | 2.000000 | 3.000000 | 3.000000 | 2.000000 | 3.000000 | 3.000000 | 2.000000 | 2.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 75% | 3.000000 | 3.000000 | 3.000000 | 3.000000 | 3.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 3.000000 | 3.000000 | 3.000000 | ... | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 1.000000 |
| max | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | ... | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 4.000000 | 1.000000 |
8 rows × 55 columns
发现没有缺失值,
看一下数据中离婚和没有离婚的人数。
# 看一下数据中离婚和没有离婚的人数
data_train['Class'].value_counts().plot(kind='bar')
plt.title(u"离婚情况 (1为离婚)") # puts a title on our graph
plt.ylabel(u"人数")
'''我们发现正负样本个数基本持平Text(0, 0.5, '人数')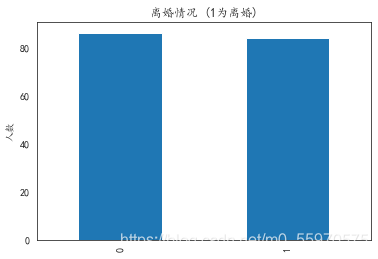
查看数据的相关性
# 由于一共有50多维的特征,对应50几个问题的不同回答,可以有些特征的重要程度不是那么大
# 各特征向量相关性
print(data_train.corr())
# 作出相关性矩阵
plt.figure(figsize=(48, 36))
sns.set_style("whitegrid")
sns.heatmap(data_train.corr(),annot=True, cmap='Blues', vmin = 0.0, vmax = 1 ,linewidths=1)
'''发现很多数据都具有比较强的相关性'''
再看一下方差
# 协方差矩阵
print(data_train.cov())
xfc = data_train.cov()
cov = []
for i in range(data_train.shape[1]-1):
cov.append(xfc.iloc[i, i])
plt.bar(data_train.columns[:-1], np.array(cov))
plt.title(u"各特征方差")
plt.xlabel("特征")
plt.ylabel(u"方差")
plt.show()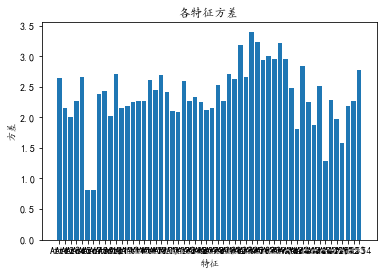
?总的来说数据还是很完美的,没有缺失值,因此不需要填充缺失值。由于每个数据都是0~4的数字,代表着对问题的不同程度的回答,因此不必要对数据进行归一化与标准化,也不需要进行one-hot操作。某些特征之间的相关性比较高,可以考虑一下降维操作,但基于此问题每一个属性对应一个调查问题这一特殊性质, PCA、SVD等降维方法降维后的得到的数据的每一行可以看成是原来m条数据在新的k个维度上的投影坐标,这改变了每一个特征对应一个调查问题这一特殊性质,而我们希望的是从这些问题中挑选出一些重要的问题来简化模型,因此不适合用PCA、SVD等降维方法来进行降维操作。因此需要用特征选择(feature selection)的方法来简化模型。
先之间用模型试试,这里都试一下。
# 逻辑回归,采用10折交叉验证,用准确率来评估,发现曲线在C=0.4时收敛。
C_params = np.linspace(0.01, 1, 100)
test_scores = []
for c in C_params:
clf = LogisticRegression(C=c, penalty='l2', tol=1e-6)
test_score = cross_val_score(clf, train_X, train_y, cv=10, scoring='accuracy')
test_scores.append(np.mean(test_score))
plt.plot(C_params, test_scores)
plt.title("调整LR的惩罚系数c")
plt.xlabel('惩罚系数C')
plt.ylabel('10折交叉验证的准确率')
plt.show()
得到最优参数 C=0.4,准确率0.982
# 预测评估、绘制混淆矩阵
# 将数据集37分,7份训练,3份预测
clf = LogisticRegression(C=0.4, penalty='l2', tol=1e-6)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(train_X, train_y, test_size=0.3)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("预测评估结果如下:\n", classification_report(y_test, clf.predict(X_test)))预测评估结果如下:
precision recall f1-score support
0 0.97 1.00 0.98 28
1 1.00 0.96 0.98 23
accuracy 0.98 51
macro avg 0.98 0.98 0.98 51
weighted avg 0.98 0.98 0.98 51from sklearn import svm # 支持向量机
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV # 网格搜索调参
# SVM 的网格搜索 调参
param = {'kernel': ['rbf', 'poly'], 'C': np.linspace(1, 100, 100)}
grid = GridSearchCV(svm.SVC(), param_grid=param, cv=10)
grid.fit(train_X, train_y)
print('best params:', grid.best_params_,'best score:', grid.best_score_) # 得到最优的参数和分值
means = grid.cv_results_['mean_test_score']
params = grid.cv_results_['params']
hhhh = pd.concat([pd.DataFrame(params), pd.DataFrame({'score': means})], axis=1)
hhhh
# for mean, param in zip(means, params):
# print("参数:{} \t test_score:{}\t".format(param, mean))best params: {'C': 2.0, 'kernel': 'rbf'} best score: 0.9823529411764707特征选择
具体请参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/stevenlk/p/6543628.html
这里借鉴了这链接里的内容。
在数据分析阶段已经分析过,离婚预测问题的每一个属性对应一个调查问题, PCA、SVD等降维方法降维会改变这一特殊性质。为了从这些问题中挑选出一些重要的问题来简化和优化模型,因而需要做特征选择(feature selection)。
特征选择主要有两个目的,一是减少特征数量、降维,使模型泛化能力更强,减少过拟合;二是增强对特征和特征值之间的理解。根据特征选择的形式可以将特征选择方法分为如下3种:
- Filter:过滤法,按照发散性或者相关性对各个特征进行评分,设定阈值或者待选择阈值的个数,选择特征。
- Wrapper:包装法,根据目标函数(通常是预测效果评分),每次选择若干特征,或者排除若干特征。使用一个基础模型来进行多轮训练,每轮训练后,移除若干权值系数的特征,再基于新的特征集进行下一轮训练。
- Embedded:嵌入法,先使用某些机器学习的算法和模型进行训练,得到各个特征的权值系数,根据系数从大到小选择特征。类似于Filter方法,但是是通过训练来确定特征的优劣。
由数据分析阶段的图3可知,各个维度的方差都较大,因而数据比较发散,不适合用Filter方法对低方差数据进行过滤。若采用Wrapper通过递归的方式来进行特征选择,本例中是一个数量为54的特征的集合,共有254-1个非空子集,因此时间复杂度和计算量巨大,也不适合本例。
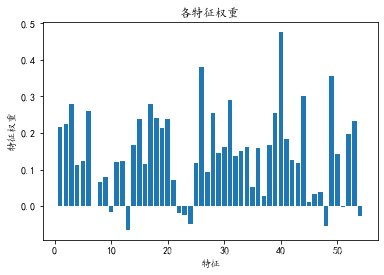
由于逻辑回归这一模型本身就包含了各个特征的权重W1~Wn,因而符合Embedded方法的特点。以已调好的逻辑回归模型参数为基础模型,通过Embedded方法进行特征选择
# 找到权重最大的6个特征,其下标分别是2 30 43 48 25 39
clf = LogisticRegression(C=0.4, penalty='l2', tol=1e-6)
clf.fit(train_X, train_y)
weight_arr = np.array(clf.coef_).reshape(-1)
print('重最大的10个特征下标:', weight_arr.argsort()[-10:])
print('各个特征的权重', clf.coef_)
plt.bar(range(1, train_X.shape[1]+1), weight_arr)
plt.title(u"各特征权重")
plt.xlabel("特征")
plt.ylabel(u"特征权重")
plt.show()重最大的6个特征下标: [38 27 5 16 2 30 43 48 25 39]
各个特征的权重 [[ 2.17720972e-01 2.24766611e-01 2.80719097e-01 1.13008502e-01
1.22699281e-01 2.60222839e-01 -2.21849802e-04 6.48332841e-02
7.97345462e-02 -1.58821783e-02 1.20942969e-01 1.24425583e-01
-6.46131183e-02 1.67072655e-01 2.37785099e-01 1.14999839e-01
2.78684197e-01 2.41468503e-01 2.14227280e-01 2.39629025e-01
7.05548979e-02 -2.00206891e-02 -2.57268937e-02 -4.95804574e-02
1.18052477e-01 3.81350374e-01 9.34487757e-02 2.55759482e-01
1.44724330e-01 1.62397921e-01 2.90033904e-01 1.38180436e-01
1.50782978e-01 1.61433520e-01 5.26107564e-02 1.58250954e-01
2.66690085e-02 1.65857456e-01 2.54333885e-01 4.76657143e-01
1.84107213e-01 1.26628270e-01 1.17035298e-01 3.02576017e-01
1.21383739e-02 3.40128328e-02 3.84344718e-02 -5.41742213e-02
3.56737710e-01 1.42873105e-01 -3.61608478e-03 1.97740815e-01
2.31508643e-01 -2.79129682e-02]]
# 接下来我们迭代寻优,权重最大的n个特征为纵坐标,10折交叉验证的准确率为横坐标,找到具体几个参数的时候准确率最高
# 发现特征个数为10个时,准确率最高,0.994,这10个特征的下标分别是38 27 5 16 2 30 43 48 25 39
clf = LogisticRegression(C=0.4, penalty='l2', tol=1e-6)
clf.fit(train_X, train_y)
weight_arr = np.array(clf.coef_).reshape(-1)
weight_arr_arg = weight_arr.argsort()
test_scores = []
for i in range(3, 20):
clf = LogisticRegression(C=0.4, penalty='l2', tol=1e-6)
test_score = cross_val_score(clf, train_X[:, weight_arr_arg[-i:]], train_y, cv=10, scoring='accuracy')
test_scores.append(np.mean(test_score))
plt.plot(range(3, 20), test_scores)
plt.title("特征个数——准确率 图")
plt.xlabel("选择权重最大的前n个特征数")
plt.ylabel("10折交叉验证的准确率")
plt.show()
?当只选择权重最大的前4~6个特征时,交叉验证的准确率从原来的0.982提升到了0.988,当选择权重最大的前10个特征时,交叉验证的准确率提升到了最高——0.994。
这10个特征对应的问题如下:
| question | feature | 权值 |
| We're just starting a discussion before I know what's going on | 40 | 0.47665714 |
| I know my spouse's basic anxieties. | 26 | 0.38135037 |
| I have nothing to do with what I've been accused of. | 49 | 0.35673771 |
| Sometimes I think it's good for me to leave home for a while. | 44 | 0.30257602 |
| I feel aggressive when I argue with my spouse. | 31 | 0.2900339 |
| When we need it, we can take our discussions with my spouse from the beginning and correct it.? | 3 | 0.2807191 |
| We share the same views about being happy in our life with my spouse | 17 | 0.2786842 |
| We don't have time at home as partners. | 6 | 0.26022284 |
| I know my spouse's hopes and wishes. | 28 | 0.25575948 |
| Our discussions often occur suddenly. | 39 | 0.25433389 |
6特征模型的准确率和f1-score到达0.98,和之前用全部特征进行训练的模型效果相差无几,大大降低了训练模型的数据维数,也就是说减少了这个模型在实际应用过程中的被调查者所需填写的问题个数,从原来的54个问题降低到了6个或10个问题,这便于模型的实际应用。
?最后得到训练好的模型,并将其保存为? ?离婚LR.pkl? 文件
from sklearn.externals import joblib # 保存模型
train_X = train_X[:, [2, 30, 43, 48, 25, 39]]
clf = LogisticRegression(C=0.4, penalty='l2', tol=1e-6)
test_score = cross_val_score(clf, train_X, train_y, cv=10, scoring='accuracy')
print('accuracy:', np.mean(test_score))
clf.fit(train_X, train_y)
# 保存模型
joblib.dump(clf, '离婚LR.pkl')?最后做了个GUI界面(虽然样子不太好看,懒得打磨了),方便使用。
兄弟们可以留着以后必要的时候用哈哈哈。
import pyefun.wxefun as wx # GUI设计的库,这个库还蛮方便使用的,pip install pyefun
from sklearn.externals import joblib # 保存模型
class 窗口1(wx.窗口):
def __init__(self):
self.初始化界面()
self.clf = joblib.load('离婚LR.pkl')
self.dic = {'从不': 0, '很少': 1, '有时': 2, '经常': 3, '总是': 4}
self.result_dic = {0: '不会离婚', 1: '离婚'}
print("加载模型完毕")
def 初始化界面(self):
#########以下是创建的组件代码#########
wx.窗口.__init__(self, None, title='离婚测试系统 by阿豪', size=(742, 532), name='frame', style=541072896)
self.容器 = wx.容器(self)
self.Centre()
self.窗口1 = self
self.标签1 = wx.标签(self.容器, size=(582, 47), pos=(23, 22), label='此系统仅试用于已婚人士!', name='staticText', style=2321)
self.标签1.字体 = wx.Font(22, 74, 90, 400, False, 'Microsoft YaHei UI', 28)
self.标签2 = wx.标签(self.容器, size=(479, 37), pos=(17, 91), label="必要时,我可以从一开始就和我的配偶讨论问题并纠正它。", name='staticText', style=2321)
self.标签2.字体 = wx.Font(12, 74, 90, 400, False, 'Microsoft YaHei UI', -1)
self.组合框1 = wx.组合框(self.容器, value='', pos=(535, 91), name='comboBox', choices=[], style=16)
self.组合框1.SetSize((60, 37))
self.组合框1.字体 = wx.Font(12, 74, 90, 400, False, 'Microsoft YaHei UI', -1)
self.组合框1.背景颜色 = (255, 255, 255, 255)
self.组合框1.加入项目(['从不', '很少', '有时', '经常', '总是'])
self.标签3 = wx.标签(self.容器, size=(479, 37), pos=(17, 141), label="当我和配偶争吵时,我觉得自己很有攻击性。", name='staticText', style=2321)
self.标签3.字体 = wx.Font(12, 74, 90, 400, False, 'Microsoft YaHei UI', -1)
self.组合框3 = wx.组合框(self.容器, value='', pos=(535, 141), name='comboBox', choices=[], style=16)
self.组合框3.SetSize((60, 37))
self.组合框3.字体 = wx.Font(12, 74, 90, 400, False, 'Microsoft YaHei UI', -1)
self.组合框3.背景颜色 = (255, 255, 255, 255)
self.组合框3.加入项目(['从不', '很少', '有时', '经常', '总是'])
self.标签4 = wx.标签(self.容器, size=(479, 37), pos=(17, 191), label='有时我觉得离开家一段时间对我有好处。', name='staticText', style=2321)
self.标签4.字体 = wx.Font(12, 74, 90, 400, False, 'Microsoft YaHei UI', -1)
self.组合框4 = wx.组合框(self.容器, value='', pos=(535, 191), name='comboBox', choices=[], style=16)
self.组合框4.SetSize((60, 37))
self.组合框4.字体 = wx.Font(12, 74, 90, 400, False, 'Microsoft YaHei UI', -1)
self.组合框4.背景颜色 = (255, 255, 255, 255)
self.组合框4.加入项目(['从不', '很少', '有时', '经常', '总是'])
self.标签5 = wx.标签(self.容器, size=(479, 37), pos=(17, 241), label="曾经被配偶指责过的地方,我没有想纠正它的想法", name='staticText', style=2321)
self.标签5.字体 = wx.Font(12, 74, 90, 400, False, 'Microsoft YaHei UI', -1)
self.组合框5 = wx.组合框(self.容器, value='', pos=(535, 241), name='comboBox', choices=[], style=16)
self.组合框5.SetSize((60, 37))
self.组合框5.字体 = wx.Font(12, 74, 90, 400, False, 'Microsoft YaHei UI', -1)
self.组合框5.背景颜色 = (255, 255, 255, 255)
self.组合框5.加入项目(['从不', '很少', '有时', '经常', '总是'])
self.标签6 = wx.标签(self.容器, size=(479, 37), pos=(17, 291), label='我知道我配偶的最基本的烦恼。', name='staticText', style=2321)
self.标签6.字体 = wx.Font(12, 74, 90, 400, False, 'Microsoft YaHei UI', -1)
self.组合框6 = wx.组合框(self.容器, value='', pos=(535, 291), name='comboBox', choices=[], style=16)
self.组合框6.SetSize((60, 37))
self.组合框6.字体 = wx.Font(12, 74, 90, 400, False, 'Microsoft YaHei UI', -1)
self.组合框6.背景颜色 = (255, 255, 255, 255)
self.组合框6.加入项目(['从不', '很少', '有时', '经常', '总是'])
self.标签7 = wx.标签(self.容器, size=(479, 37), pos=(17, 341), label="我们只是在我知道发生了什么之前开始讨论而已。", name='staticText', style=2321)
self.标签7.字体 = wx.Font(12, 74, 90, 400, False, 'Microsoft YaHei UI', -1)
self.组合框7 = wx.组合框(self.容器, value='', pos=(535, 341), name='comboBox', choices=[], style=16)
self.组合框7.SetSize((60, 37))
self.组合框7.字体 = wx.Font(12, 74, 90, 400, False, 'Microsoft YaHei UI', -1)
self.组合框7.背景颜色 = (255, 255, 255, 255)
self.组合框7.加入项目(['从不', '很少', '有时', '经常', '总是'])
self.按钮2 = wx.按钮(self.容器, size=(106, 35), pos=(105, 415), label='按钮', name='button')
self.按钮2.字体 = wx.Font(9, 70, 90, 400, False, 'Microsoft YaHei UI', -1)
self.按钮2.绑定事件(wx.事件.被单击, self.按钮2_被单击)
self.编辑框1 = wx.编辑框(self.容器, size=(149, 38), pos=(317, 418))
self.编辑框1.字体 = wx.Font(12, 74, 90, 400, False, 'Microsoft YaHei UI', -1)
self.编辑框1.背景颜色 = (255, 255, 255, 255)
self.编辑框1.禁止 = True
#########以上是创建的组件代码##########
#########以下是组件绑定的事件代码#########
def 按钮2_被单击(self,event):
print("按钮2_被单击")
d1 = self.组合框1.取选中项文本()
d2 = self.组合框3.取选中项文本()
d3 = self.组合框4.取选中项文本()
d4 = self.组合框5.取选中项文本()
d5 = self.组合框6.取选中项文本()
d6 = self.组合框7.取选中项文本()
ls = [[self.dic[d1], self.dic[d2], self.dic[d3], self.dic[d4], self.dic[d5], self.dic[d6]]]
jg = self.clf.predict(ls)[0]
self.编辑框1.内容 = self.result_dic[jg]
#########以上是组件绑定的事件代码#########
class 应用(wx.App):
def OnInit(self):
self.窗口1 = 窗口1()
self.窗口1.Show(True)
return True
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = 应用()
app.MainLoop()