七、反向传播算法
内容参考来自https://github.com/dragen1860/Deep-Learning-with-TensorFlow-book开源书籍《TensorFlow2深度学习》,这只是我做的简单的学习笔记,方便以后复习。
1.激活函数导数
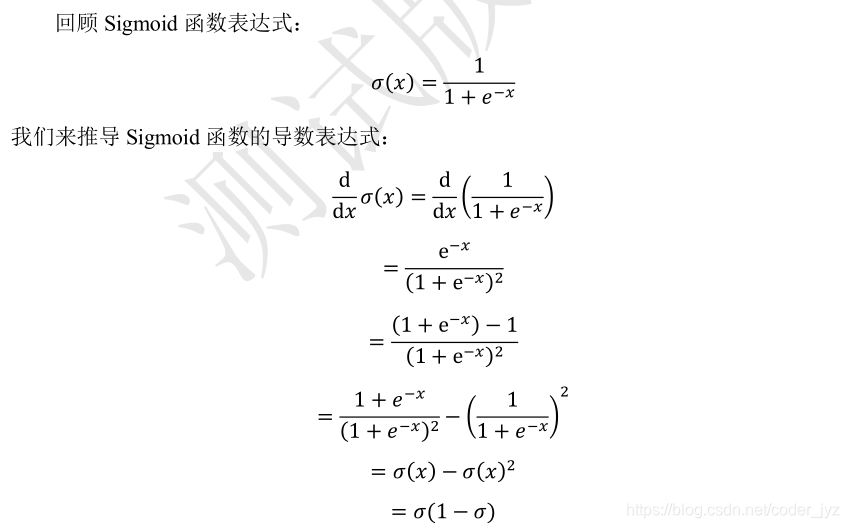
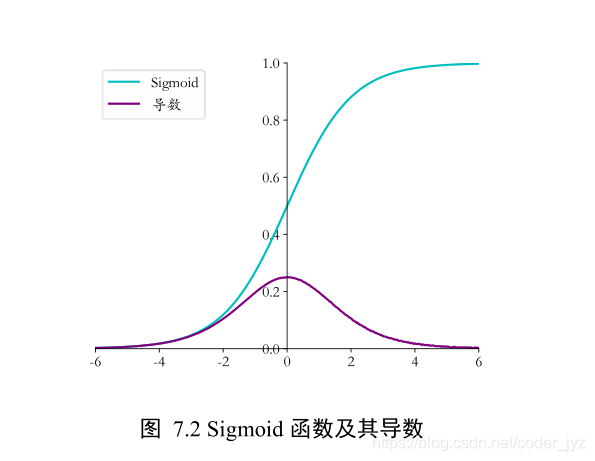
1.1Sigmoid 函数导数
import numpy as np # 导入 numpy 库
def sigmoid(x): # 实现 sigmoid 函数
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def derivative(x): # sigmoid 导数的计算
# sigmoid 函数的表达式由手动推导而得
return sigmoid(x)*(1-sigmoid(x))
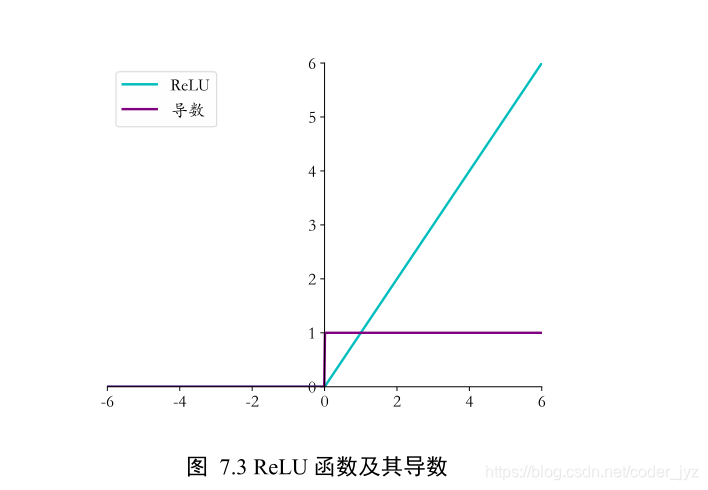
1.2ReLU函数导数

def derivative(x): # ReLU 函数的导数
d = np.array(x, copy=True) # 用于保存梯度的张量
d[x < 0] = 0 # 元素为负的导数为 0
d[x >= 0] = 1 # 元素为正的导数为 1
return d
1.3LeakyReLU 函数导数
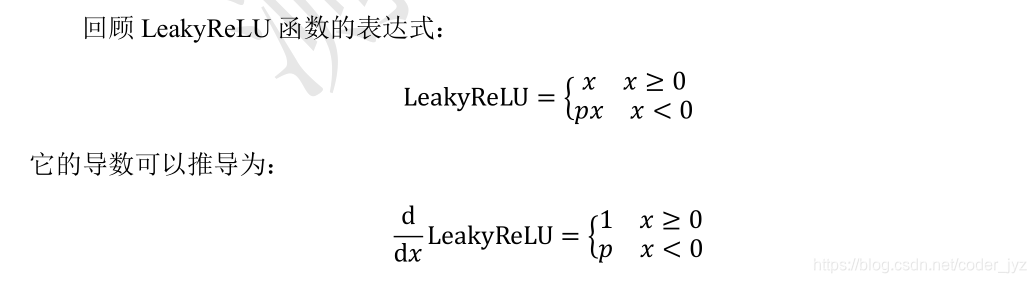
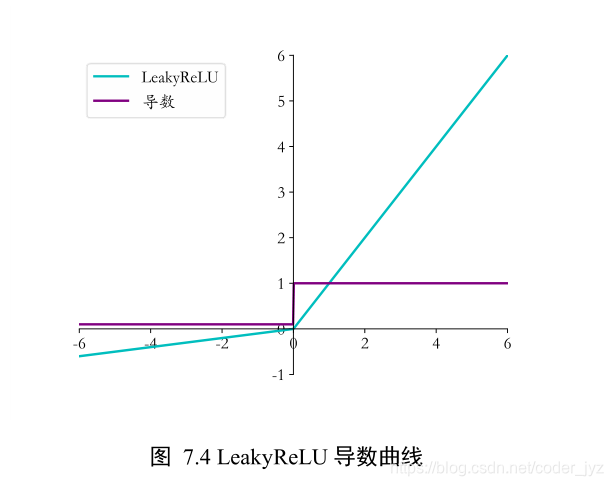
# 其中 p 为 LeakyReLU 的负半段斜率,为超参数
def derivative(x, p):
dx = np.ones_like(x) # 创建梯度张量,全部初始化为 1
dx[x < 0] = p # 元素为负的导数为 p
return dx
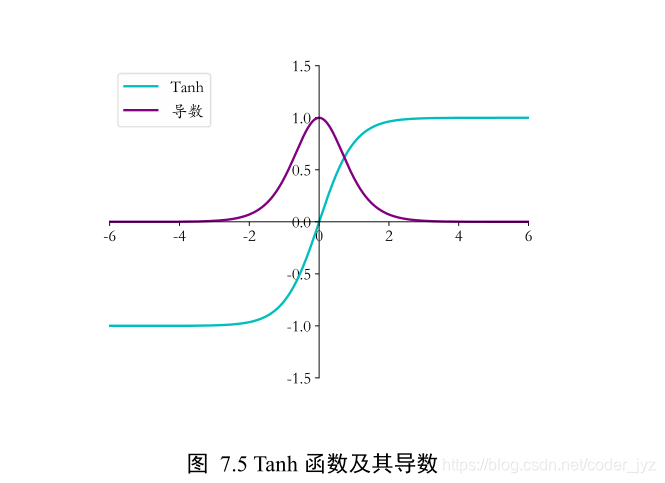
1.4Tanh 函数梯度
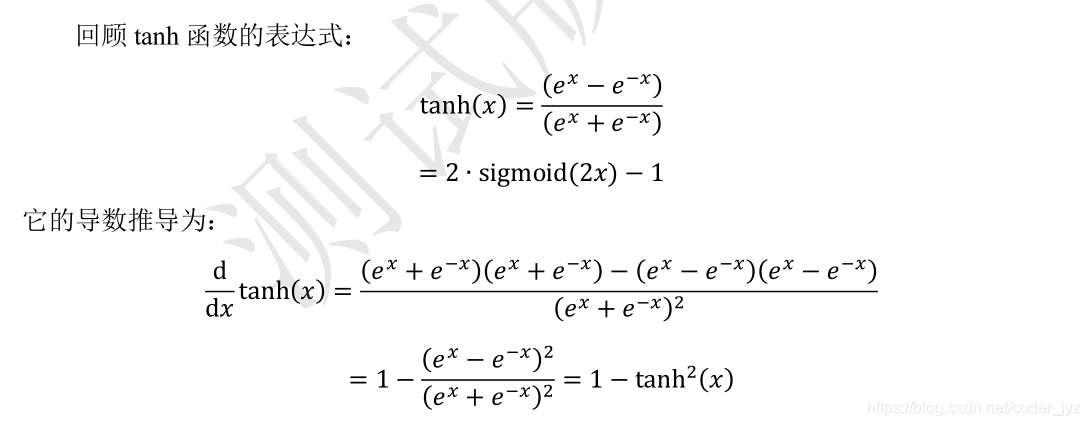
def sigmoid(x): # sigmoid 函数实现
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def tanh(x): # tanh 函数实现
return 2*sigmoid(2*x) - 1
def derivative(x): # tanh 导数实现
return 1-tanh(x)**2
2.链式法则
import tensorflow as tf
# 构建待优化变量
x = tf.constant(1.)
w1 = tf.constant(2.)
b1 = tf.constant(1.)
w2 = tf.constant(2.)
b2 = tf.constant(1.)
with tf.GradientTape(persistent=True) as tape:
# 非tf.Variable类型的张量需要人为设置记录梯度信息
tape.watch([w1, b1, w2, b2])
# 构建2层网络
y1 = x * w1 + b1
y2 = y1 * w2 + b2
# 独立求解出各个导数
dy2_dy1 = tape.gradient(y2, [y1])[0]
dy1_dw1 = tape.gradient(y1, [w1])[0]
dy2_dw1 = tape.gradient(y2, [w1])[0]
# 验证链式法则
print(dy2_dy1 * dy1_dw1)
print(dy2_dw1)
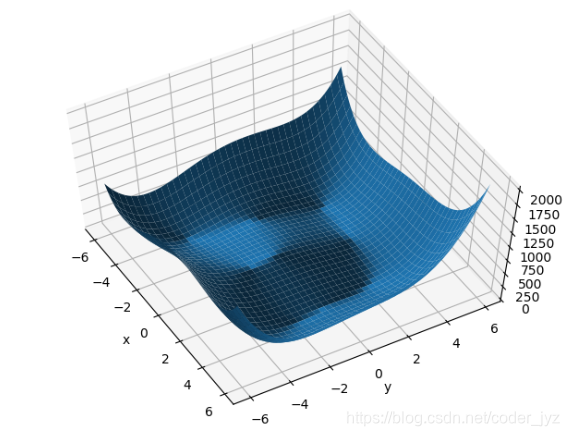
3.Himmelblau 函数优化实战
Himmelblau 函数是用来测试优化算法的常用样例函数之一,它包含了两个自变量𝑦和𝑧,数学表达式是
f ( x , y ) = ( x 2 + y ? 11 ) 2 + ( x + y 2 ? 7 ) 2 f(x,y)=(x^2+y-11)^2+(x+y^2-7)^2 f(x,y)=(x2+y?11)2+(x+y2?7)2
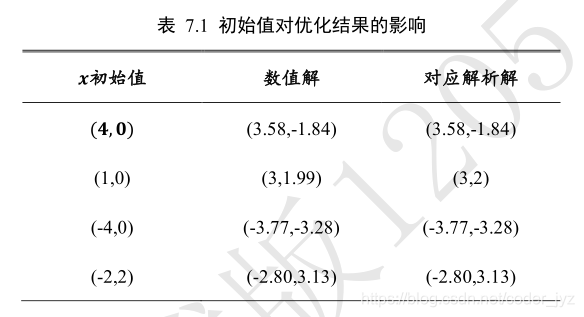
Himmelblau 函数的等高线图,大致可以看出,它共有 4 个局部极小值点,并且局部极小值都是 0,所以这 4 个局部极小值也是全局最小值。我们可以通过解析的方法计算出局部极小值的精确坐标,它们分别是:(3,2),(?2 805,3 131),(?3 779,?3 283),(3 584,?1 848)
import numpy as np
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
def himmelblau(x):
# himmelblau函数实现
return (x[0] ** 2 + x[1] - 11) ** 2 + (x[0] + x[1] ** 2 - 7) ** 2
x = np.arange(-6, 6, 0.1)
y = np.arange(-6, 6, 0.1)
print('x,y range:', x.shape, y.shape)
# 生成x-y平面采样网格点,方便可视化
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
print('X,Y maps:', X.shape, Y.shape)
Z = himmelblau([X, Y]) # 计算网格点上的函数值
# 绘制himmelblau函数曲面
fig = plt.figure('himmelblau')
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)
ax.view_init(60, -30)
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
plt.show()
# 参数的初始化值对优化的影响不容忽视,可以通过尝试不同的初始化值,
# 检验函数优化的极小值情况
# [1., 0.], [-4, 0.], [4, 0.]
# x = tf.constant([4., 0.])
# x = tf.constant([1., 0.])
# x = tf.constant([-4., 0.])
x = tf.constant([-2., 2.])
for step in range(200):# 循环优化
with tf.GradientTape() as tape: #梯度跟踪
tape.watch([x]) # 记录梯度
y = himmelblau(x) # 前向传播
# 反向传播
grads = tape.gradient(y, [x])[0]
# 更新参数,0.01为学习率
x -= 0.01*grads
# 打印优化的极小值
if step % 20 == 19:
print ('step {}: x = {}, f(x) = {}'
.format(step, x.numpy(), y.numpy()))
4.反向传播算法实战
#!/usr/bin/env python
# encoding: utf-8
"""
@author: HuRuiFeng
@file: 7.9-backward-prop.py
@time: 2020/2/24 17:32
@desc: 7.9 反向传播算法实战的代码
"""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.datasets import make_moons
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
plt.rcParams['font.size'] = 16
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = ['STKaiti']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
def load_dataset():
# 采样点数
N_SAMPLES = 2000
# 测试数量比率
TEST_SIZE = 0.3
# 利用工具函数直接生成数据集
X, y = make_moons(n_samples=N_SAMPLES, noise=0.2, random_state=100)
# 将 2000 个点按着 7:3 分割为训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=TEST_SIZE, random_state=42)
return X, y, X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
def make_plot(X, y, plot_name, XX=None, YY=None, preds=None, dark=False):
# 绘制数据集的分布, X 为 2D 坐标, y 为数据点的标签
if (dark):
plt.style.use('dark_background')
else:
sns.set_style("whitegrid")
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 12))
axes = plt.gca()
axes.set(xlabel="$x_1$", ylabel="$x_2$")
plt.title(plot_name, fontsize=30)
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.20)
plt.subplots_adjust(right=0.80)
if XX is not None and YY is not None and preds is not None:
plt.contourf(XX, YY, preds.reshape(XX.shape), 25, alpha=1, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral)
plt.contour(XX, YY, preds.reshape(XX.shape), levels=[.5], cmap="Greys", vmin=0, vmax=.6)
# 绘制散点图,根据标签区分颜色
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y.ravel(), s=40, cmap=plt.cm.Spectral, edgecolors='none')
plt.savefig('数据集分布.svg')
plt.close()
class Layer:
# 全连接网络层
def __init__(self, n_input, n_neurons, activation=None, weights=None,
bias=None):
"""
:param int n_input: 输入节点数
:param int n_neurons: 输出节点数
:param str activation: 激活函数类型
:param weights: 权值张量,默认类内部生成
:param bias: 偏置,默认类内部生成
"""
# 通过正态分布初始化网络权值,初始化非常重要,不合适的初始化将导致网络不收敛
self.weights = weights if weights is not None else np.random.randn(n_input, n_neurons) * np.sqrt(1 / n_neurons)
self.bias = bias if bias is not None else np.random.rand(n_neurons) * 0.1
self.activation = activation # 激活函数类型,如’sigmoid’
self.last_activation = None # 激活函数的输出值o
self.error = None # 用于计算当前层的delta 变量的中间变量
self.delta = None # 记录当前层的delta 变量,用于计算梯度
# 网络层的前向传播函数实现如下,其中last_activation 变量用于保存当前层的输出值:
def activate(self, x):
# 前向传播函数
r = np.dot(x, self.weights) + self.bias # X@W+b
# 通过激活函数,得到全连接层的输出o
self.last_activation = self._apply_activation(r)
return self.last_activation
# 上述代码中的self._apply_activation 函数实现了不同类型的激活函数的前向计算过程,
# 尽管此处我们只使用Sigmoid 激活函数一种。代码如下:
def _apply_activation(self, r):
# 计算激活函数的输出
if self.activation is None:
return r # 无激活函数,直接返回
# ReLU 激活函数
elif self.activation == 'relu':
return np.maximum(r, 0)
# tanh 激活函数
elif self.activation == 'tanh':
return np.tanh(r)
# sigmoid 激活函数
elif self.activation == 'sigmoid':
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-r))
return r
# 针对于不同类型的激活函数,它们的导数计算实现如下:
def apply_activation_derivative(self, r):
# 计算激活函数的导数
# 无激活函数,导数为1
if self.activation is None:
return np.ones_like(r)
# ReLU 函数的导数实现
elif self.activation == 'relu':
grad = np.array(r, copy=True)
grad[r > 0] = 1.
grad[r <= 0] = 0.
return grad
# tanh 函数的导数实现
elif self.activation == 'tanh':
return 1 - r ** 2
# Sigmoid 函数的导数实现
elif self.activation == 'sigmoid':
return r * (1 - r)
return r
# 神经网络模型
class NeuralNetwork:
def __init__(self):
self._layers = [] # 网络层对象列表
def add_layer(self, layer):
# 追加网络层
self._layers.append(layer)
# 网络的前向传播只需要循环调各个网络层对象的前向计算函数即可,代码如下:
# 前向传播
def feed_forward(self, X):
for layer in self._layers:
# 依次通过各个网络层
X = layer.activate(X)
return X
def backpropagation(self, X, y, learning_rate):
# 反向传播算法实现
# 前向计算,得到输出值
output = self.feed_forward(X)
for i in reversed(range(len(self._layers))): # 反向循环
layer = self._layers[i] # 得到当前层对象
# 如果是输出层
if layer == self._layers[-1]: # 对于输出层
layer.error = y - output # 计算2 分类任务的均方差的导数
# 关键步骤:计算最后一层的delta,参考输出层的梯度公式
layer.delta = layer.error * layer.apply_activation_derivative(output)
else: # 如果是隐藏层
next_layer = self._layers[i + 1] # 得到下一层对象
layer.error = np.dot(next_layer.weights, next_layer.delta)
# 关键步骤:计算隐藏层的delta,参考隐藏层的梯度公式
layer.delta = layer.error * layer.apply_activation_derivative(layer.last_activation)
# 循环更新权值
for i in range(len(self._layers)):
layer = self._layers[i]
# o_i 为上一网络层的输出
o_i = np.atleast_2d(X if i == 0 else self._layers[i - 1].last_activation)
# 梯度下降算法,delta 是公式中的负数,故这里用加号
layer.weights += layer.delta * o_i.T * learning_rate
def train(self, X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test, learning_rate, max_epochs):
# 网络训练函数
# one-hot 编码
y_onehot = np.zeros((y_train.shape[0], 2))
y_onehot[np.arange(y_train.shape[0]), y_train] = 1
# 将One-hot 编码后的真实标签与网络的输出计算均方误差,并调用反向传播函数更新网络参数,循环迭代训练集1000 遍即可
mses = []
accuracys = []
for i in range(max_epochs + 1): # 训练1000 个epoch
for j in range(len(X_train)): # 一次训练一个样本
self.backpropagation(X_train[j], y_onehot[j], learning_rate)
if i % 10 == 0:
# 打印出MSE Loss
mse = np.mean(np.square(y_onehot - self.feed_forward(X_train)))
mses.append(mse)
accuracy = self.accuracy(self.predict(X_test), y_test.flatten())
accuracys.append(accuracy)
print('Epoch: #%s, MSE: %f' % (i, float(mse)))
# 统计并打印准确率
print('Accuracy: %.2f%%' % (accuracy * 100))
return mses, accuracys
def predict(self, X):
return self.feed_forward(X)
def accuracy(self, X, y):
return np.sum(np.equal(np.argmax(X, axis=1), y)) / y.shape[0]
def main():
X, y, X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = load_dataset()
# 调用 make_plot 函数绘制数据的分布,其中 X 为 2D 坐标, y 为标签
make_plot(X, y, "Classification Dataset Visualization ")
plt.show()
nn = NeuralNetwork() # 实例化网络类
nn.add_layer(Layer(2, 25, 'sigmoid')) # 隐藏层 1, 2=>25
nn.add_layer(Layer(25, 50, 'sigmoid')) # 隐藏层 2, 25=>50
nn.add_layer(Layer(50, 25, 'sigmoid')) # 隐藏层 3, 50=>25
nn.add_layer(Layer(25, 2, 'sigmoid')) # 输出层, 25=>2
mses, accuracys = nn.train(X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test, 0.01, 1000)
x = [i for i in range(0, 101, 10)]
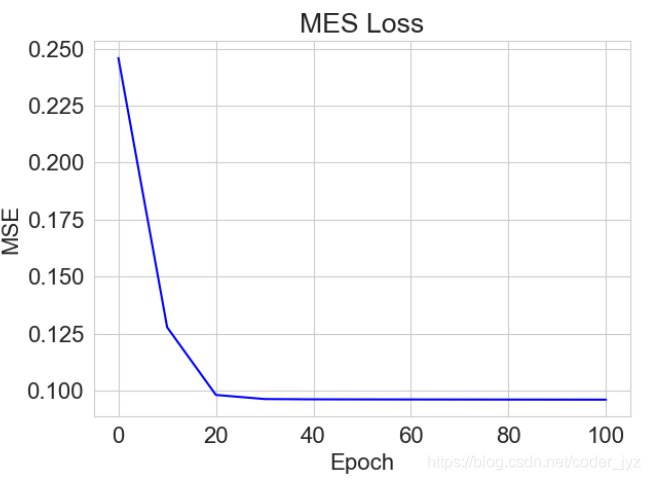
# 绘制MES曲线
plt.title("MES Loss")
plt.plot(x, mses[:11], color='blue')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('MSE')
plt.savefig('训练误差曲线.svg')
plt.close()
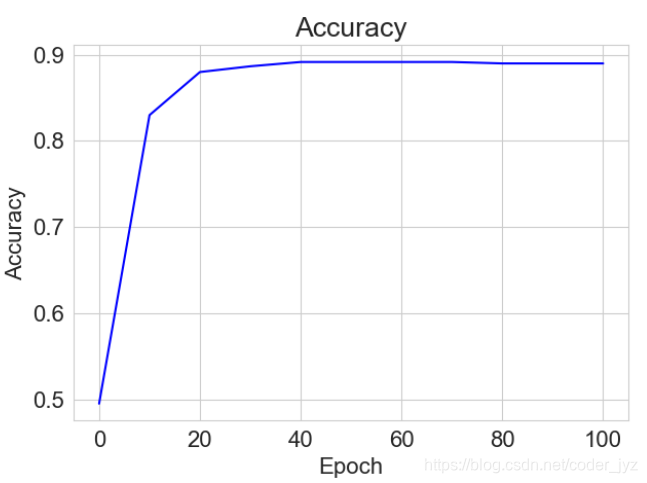
# 绘制Accuracy曲线
plt.title("Accuracy")
plt.plot(x, accuracys[:11], color='blue')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.savefig('网络测试准确率.svg')
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
5.题外话
这章相对于书的内容我减少了很多,感觉好多都是常识性东西,还有就是比较难做笔记,就懒得弄了。我还是太懒了…
我的微信公众号,同步更新,求关注,嘻嘻
