
背景知识
内容概要
针对的问题 or 出发点: 人工标注成本大。 还是为了解决小样本问题。
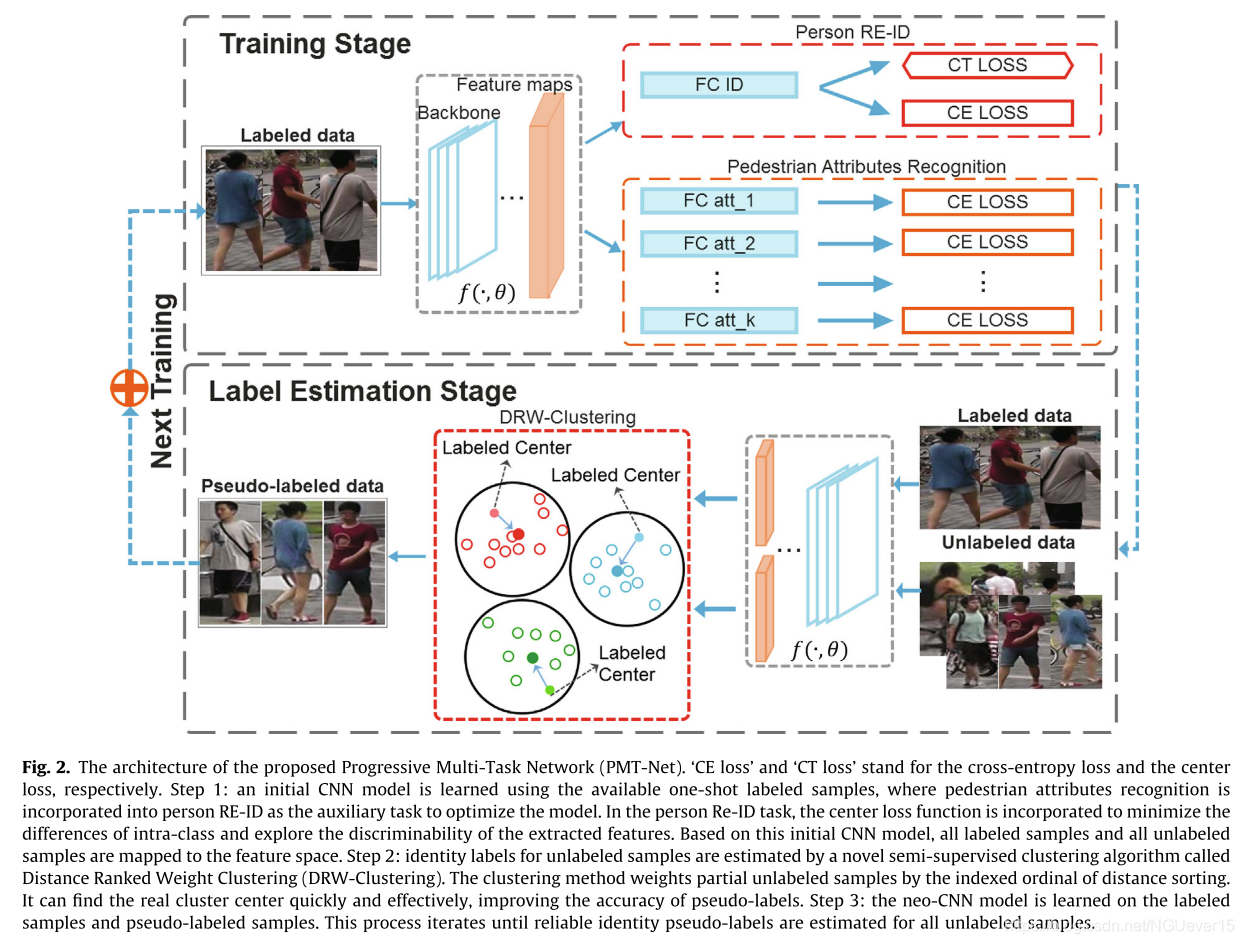
提出了渐进的多任务网络 (PMT-net): 用one-shot初始化模型,然后迭代优化(秉承EUG一脉)
- 首先,行人的属性识别作为辅助任务。 (参照了APR那篇文章,也是EUG同作者的文章)
- 基于学到的特征,根据特征空间中的距离估计身份标签。
- 此外,为了提高对未标记样本的标签估计的准确性,设计了一种半监督聚类方法——距离加权聚类(Distance Ranked Weight clustering, DRW-Clustering)。 聚类方法根据距离排序的索引顺序对部分未标记样本进行加权,从而能够快速有效地找到真实的聚类中心。
实验结果表明,所提出的方法在one-shot person reid 中达到了与现有方法相当或更好的性能。
相关工作
- Person RE-ID method
- Multi-task learning
- Progressive algorithms
- Semi-supervised clustering
数据集
- Market1501
- DukeMTMC-reID
方法提要
方法框架
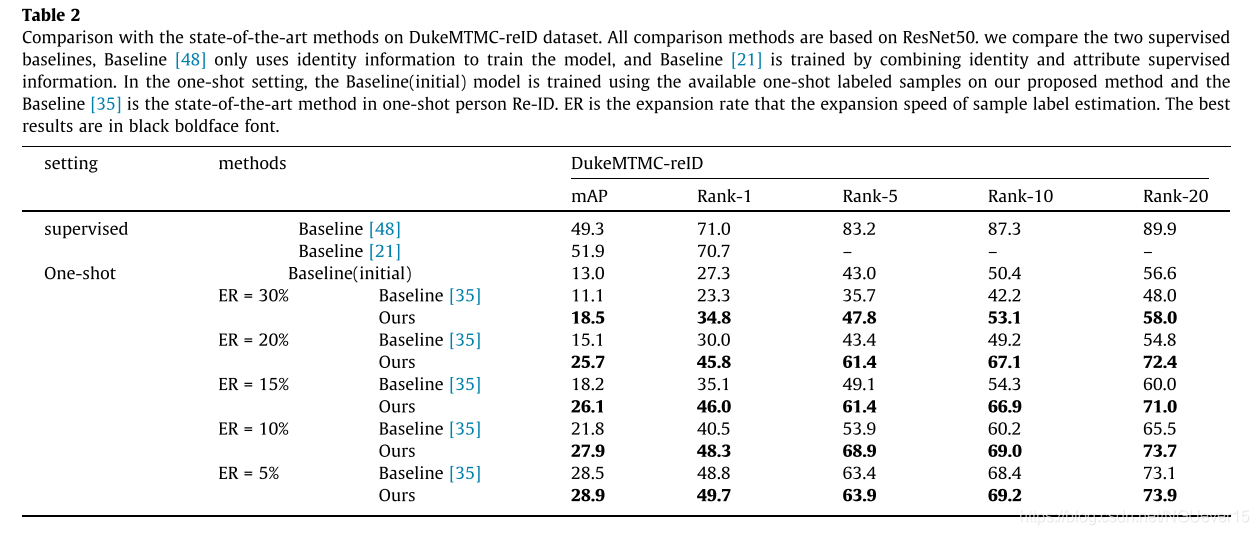
实验结果
方法详解
参考文献
[1] C. Gao, Y. Chen, J.-G. Yu, N. Sang, Pose-guided spatiotemporal alignment for video-based person re-identification, Information Sciences 527 (2020)
176–190.
[2] L. An, X. Chen, S. Yang, B. Bhanu, Sparse representation matching for person re-identification, Information Sciences 355 (2016) 74–89.
[3] S. Basu, A. Banerjee, R.J. Mooney, Semi-supervised clustering by seeding, 2002, pp. 27–34…
[4] G. Bender, P.-J. Kindermans, B. Zoph, V. Vasudevan, Q. Le, Understanding and simplifying one-shot architecture search, in: International Conference on
Machine Learning, 2018, pp. 549–558.
[5] Y. Bengio, J. Louradour, R. Collobert, J. Weston, Curriculum learning, 2009, pp. 41–48.
[6] F. Chen, N. Wang, J. Tang, D. Liang, A negative transfer approach to person re-identification via domain augmentation, Information Sciences 549, 1–12…
[7] D. Cheng, Y. Gong, X. Chang, W. Shi, A. Hauptmann, N. Zheng, Deep feature learning via structured graph laplacian embedding for person reidentification, Pattern Recognition 82 (2018) 94–104.
[8] H. Fan, L. Zheng, C. Yan, Y. Yang, Unsupervised person re-identification: clustering and fine-tuning, ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing,
Communications, and Applications (TOMM) 14 (4) (2018) 83.
[9] D. Figueira, L. Bazzani, H.Q. Minh, M. Cristani, A. Bernardino, V. Murino, Semi-supervised multi-feature learning for person re-identification (2013)
111–116…
[10] K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, J. Sun, Deep residual learning for image recognition, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern
Recognition, 2016, pp. 770–778.
[11] S. Ioffe, C. Szegedy, Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift, 2015, arXiv preprint
arXiv:1502.03167…
[12] A.K. Jain, Data clustering: 50 years beyond k-means 31 (8) (2010) 651–666.
[13] L. Jiang, D. Meng, S. Yu, Z. Lan, S. Shan, A.G. Hauptmann, Self-paced learning with diversity (2014) 2078–2086…
[14] M.M. Kalayeh, E. Basaran, M. G?kmen, M.E. Kamasak, M. Shah, Human semantic parsing for person re-identification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018, pp. 1062–1071.
[15] A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, G.E. Hinton, Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks, in: Advances in Neural Information
Processing Systems, 2012, pp. 1097–1105…
[16] M.P. Kumar, B. Packer, D. Koller, Self-paced learning for latent variable models, 2010, pp. 1189–1197.
[17] Y.J. Lee, K. Grauman, Learning the easy things first: Self-paced visual category discovery, 2011, pp. 1721–1728.
[18] H. Li, J. Xu, J. Zhu, D. Tao, Z. Yu, Top distance regularized projection and dictionary learning for person re-identification, Information Sciences (2019).
[19] H. Li, J. Xu, J. Zhu, D. Tao, Z. Yu, Top distance regularized projection and dictionary learning for person re-identification, Information Sciences 502
(2019) 472–491.
[20] J. Li, A.J. Ma, P.C. Yuen, Semi-supervised region metric learning for person re-identification, International Journal of Computer Vision 126 (8) (2018)
855–874.
[21] Y. Lin, L. Zheng, Z. Zheng, Y. Wu, Z. Hu, C. Yan, Y. Yang, Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity learning, Pattern Recognition
(2019).
[22] X. Liu, W. Liu, T. Mei, H. Ma, Provid: Progressive and multimodal vehicle reidentification for large-scale urban surveillance, IEEE Transactions on
Multimedia 20 (3) (2017) 645–658.
[23] Z. Liu, D. Wang, H. Lu, Stepwise metric promotion for unsupervised video person re-identification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference
on Computer Vision, 2017, pp. 2429–2438.
[24] Z. Lu, T.K. Leen, Semi-supervised learning with penalized probabilistic clustering, in: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2005, pp.
849–856…
[25] X. Ma, X. Zhu, S. Gong, X. Xie, J. Hu, K.-M. Lam, Y. Zhong, Person re-identification by unsupervised video matching, Pattern Recognition 65 (2017) 197–
210.
[26] E. Ristani, F. Solera, R. Zou, R. Cucchiara, C. Tomasi, Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking, in: European
Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, 2016, pp. 17–35.
[27] E. Ristani, C. Tomasi, Features for multi-target multi-camera tracking and re-identification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition, 2018, pp. 6036–6046.
[28] J. Si, H. Zhang, C.-G. Li, J. Kuen, X. Kong, A.C. Kot, G. Wang, Dual attention matching network for context-aware feature sequence based person reidentification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018, pp. 5363–5372.
[29] Y. Suh, J. Wang, S. Tang, T. Mei, K. Mu Lee, Part-aligned bilinear representations for person re-identification, in: Proceedings of the European Conference
on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2018, pp. 402–419.
[30] J.S. Supancic, D. Ramanan, Self-paced learning for long-term tracking (2013) 2379–2386…
[31] J. Wang, X. Zhu, S. Gong, W. Li, Transferable joint attribute-identity deep learning for unsupervised person re-identification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018, pp. 2275–2284.
[32] L. Wei, S. Zhang, H. Yao, W. Gao, Q. Tian, Glad: Global-local-alignment descriptor for pedestrian retrieval, in: Proceedings of the 25th ACM International
Conference on Multimedia, ACM, 2017, pp. 420–428.
[33] Y. Wen, K. Zhang, Z. Li, Y. Qiao, A discriminative feature learning approach for deep face recognition, in: European Conference on Computer Vision,
Springer, 2016, pp. 499–515.
[34] A. Wu, W.-S. Zheng, X. Guo, J.-H. Lai, Distilled person re-identification: towards a more scalable system, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019, pp. 1187–1196.
[35] Y. Wu, Y. Lin, X. Dong, Y. Yan, W. Bian, Y. Yang, Progressive learning for person re-identification with one example, IEEE Transactions on Image
Processing 28 (6) (2019) 2872–2881.
[36] Y. Wu, Y. Lin, X. Dong, Y. Yan, W. Ouyang, Y. Yang, Exploit the unknown gradually: one-shot video-based person re-identification by stepwise learning,
in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018, pp. 5177–5186.
[37] J. Xu, R. Zhao, F. Zhu, H. Wang, W. Ouyang, Attention-aware compositional network for person re-identification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference
on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018, pp. 2119–2128.
[38] X. Yang, M. Wang, R. Hong, Q. Tian, Y. Rui, Enhancing person re-identification in a self-trained subspace, ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing,
Communications, and Applications (TOMM) 13 (3) (2017) 27.
[39] Y. Yang, L. Wen, S. Lyu, S.Z. Li, Unsupervised learning of multi-level descriptors for person re-identification, in: Thirty-First AAAI Conference on
Artificial Intelligence, 2017.
[40] M. Ye, A.J. Ma, L. Zheng, J. Li, P.C. Yuen, Dynamic label graph matching for unsupervised video re-identification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE International
Conference on Computer Vision, 2017, pp. 5142–5150.
[41] H.-X. Yu, W.-S. Zheng, A. Wu, X. Guo, S. Gong, J.-H. Lai, Unsupervised person re-identification by soft multilabel learning, in: Proceedings of the IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019, pp. 2148–2157.
[42] D. Zhang, D. Meng, J. Han, Co-saliency detection via a self-paced multiple-instance learning framework, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence 39 (5) (2017) 865–878.
[43] Z. Zhang, C. Lan, W. Zeng, Z. Chen, Densely semantically aligned person re-identification (2019) 667–676…
[44] H. Zhao, M. Tian, S. Sun, J. Shao, J. Yan, S. Yi, X. Wang, X. Tang, Spindle net: Person re-identification with human body region guided feature
decomposition and fusion, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017, pp. 1077–1085.
[45] L. Zheng, L. Shen, L. Tian, S. Wang, J. Wang, Q. Tian, Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark, in: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference
on Computer Vision, 2015, pp. 1116–1124.
[46] Z. Zheng, X. Yang, Z. Yu, L. Zheng, Y. Yang, J. Kautz, Joint discriminative and generative learning for person re-identification, in: Proceedings of the IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019, pp. 2138–2147.
[47] Z. Zheng, L. Zheng, Y. Yang, Pedestrian alignment network for large-scale person re-identification, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video
Technology (2018).
[48] Z. Zhong, L. Zheng, D. Cao, S. Li, Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding, in: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer
Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017, pp. 1318–1327.
[49] S. Zhou, J. Wang, D. Meng, X. Xin, Y. Li, Y. Gong, N. Zheng, Deep self-paced learning for person re-identification, Pattern Recognition 76 (2018) 739–751.