深度学习中的固定学习率衰减策略总结
深层神经网络的参数学习主要是通过梯度下降方法来寻找一组可以最小化结构风险的参数。 在梯度下降中学习率的取值非常关键,如果过大可能不会收敛,过小则收敛速度太慢。
通常的策略的在一开始采用大的学习率保证收敛,在收敛到最优点附近时要小些以避免来回震荡。因此,比较简单直接的学习率 调整可以通过学习率衰减(Learning Rate Decay)的方式来实现。
学习率衰减策略可以分为两种:固定策略的学习率衰减和自适应学习率衰减,其中固定学习率衰减包括分段衰减、逆时衰减、指数衰减等,自适应学习率衰减包括AdaGrad、 RMSprop、 AdaDelta等。一般情况,两种策略会结合使用。
本文主要基于tensorflow,对一些常见的固定策略衰减策略进行总结,包括基本的衰减策略、循环学习率衰减和单循环学习率衰减。
基本学习率衰减
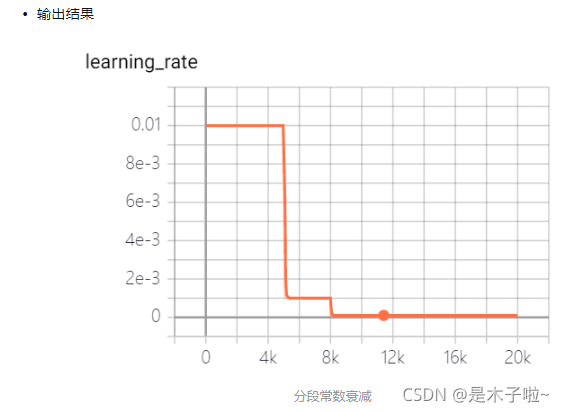
piecewise decay
分段常数衰减, 在训练过程中不同阶段设置不同的学习率,便于更精细的调参。在目标检测任务如Faster RCNN 和 SSD 的训练中都采用分段常数衰减策略,调整学习率。
方法接口
tf.train.piecewise_constant_decay
boundaries:学习率衰减边界;values:不同阶段对应学习率。
注意由于boundaries忽略了初始边界0,因此values的长度会比boundaries多1。
验证代码
import os
import tensorflow as tf
summary_path = './summary'
method = 'piecewise_decay'
max_step = 20000
base_learning_rate = 0.01
decay_boundaries = [5000, 8000]
learning_rate_value = [base_learning_rate, base_learning_rate/10., base_learning_rate/100.]
summary_step = 10
def main():
global_step_op = tf.train.get_or_create_global_step()
# x = tf.get_variable(shape=[1], initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(), name="x")
learning_rate = tf.train.piecewise_constant_decay(global_step_op,
boundaries=decay_boundaries,
values=learning_rate_value)
tf.summary.scalar("learning_rate", learning_rate)
summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all()
init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(),
tf.local_variables_initializer())
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
summary_write = tf.summary.FileWriter(os.path.join(summary_path, method))
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess, coord)
try:
if not coord.should_stop():
for step in range(max_step):
if step % summary_step == 0:
summary, global_step = sess.run([summary_op, global_step_op], feed_dict={global_step_op:step})
summary_write.add_summary(summary, global_step=global_step)
summary_write.flush()
summary, global_step = sess.run([summary_op, global_step_op], feed_dict={global_step_op:step})
except Exception as e:
# Report exceptions to the coordinator.
coord.request_stop(e)
finally:
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
print('all threads are asked to stop!')
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
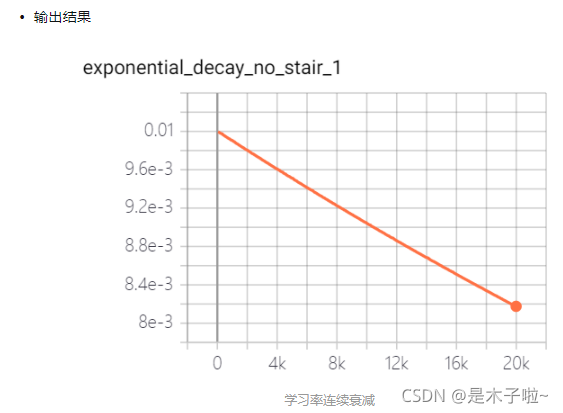
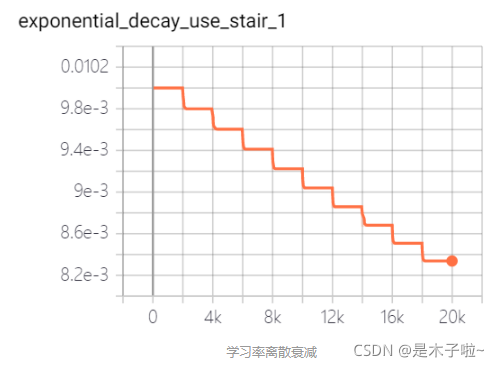
exponential decay
指数衰减:学习率以指数的形式进行衰减,其中指数函数的底为decay_rate, 指数为 global_step / decay_steps
函数接口
tf.train.exponential_decay
learning_rate: 基学习率;decay_rate: 衰减率;decay_steps: 衰减步数(周期)
staircase: 是否以离散的时间间隔衰减学习率
验证代码
import os
import tensorflow as tf
summary_path = './summary'
method = 'exponential_decay'
max_step = 20000
base_learning_rate = 0.01
decay_rate = 0.98
decay_steps = 2000
summary_step = 10
def main():
global_step_op = tf.train.get_or_create_global_step()
# decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate * decay_rate ^ (global_step / decay_steps)
learning_rate_no_stair = tf.train.exponential_decay(learning_rate=base_learning_rate,
decay_rate=decay_rate,
decay_steps=decay_steps,
staircase=False,
global_step=global_step_op,
name="exponential_decay_no_stair")
tf.summary.scalar("exponential_decay_no_stair", learning_rate_no_stair)
learning_rate_no_stair = tf.train.exponential_decay(learning_rate=base_learning_rate,
decay_rate=decay_rate,
decay_steps=decay_steps,
staircase=True,
global_step=global_step_op,
name="exponential_decay_use_stair")
tf.summary.scalar("exponential_decay_use_stair", learning_rate_no_stair)
summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all()
init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(),
tf.local_variables_initializer())
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
summary_write = tf.summary.FileWriter(os.path.join(summary_path, method))
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess, coord)
try:
if not coord.should_stop():
for step in range(max_step):
if step % summary_step == 0:
summary, global_step = sess.run([summary_op, global_step_op], feed_dict={global_step_op:step})
summary_write.add_summary(summary, global_step=global_step)
summary_write.flush()
summary, global_step = sess.run([summary_op, global_step_op], feed_dict={global_step_op:step})
except Exception as e:
# Report exceptions to the coordinator.
coord.request_stop(e)
finally:
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
print('all threads are asked to stop!')
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
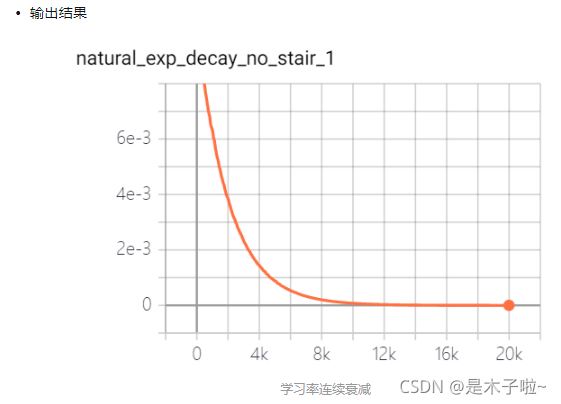
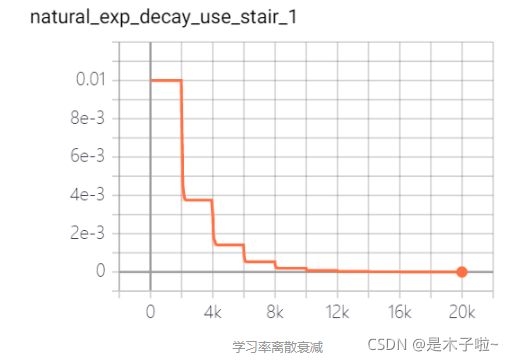
natural exponential decay
自然指数衰减:学习率以自然指数进行衰减,其中指数函数底为自然常数e, 指数为-decay_rate * global_step / decay_step, 相比指数衰减具有更快的衰减速度。
方法接口
tf.train.natural_exp_decay
learning_rate: 基学习率;decay_rate: 衰减率;decay_steps: 衰减步数/周期;staircase: 是否以离散的时间间隔衰减学习率
验证代码
import os
import tensorflow as tf
summary_path = './summary'
method = 'natural_exp_decay'
max_step = 20000
base_learning_rate = 0.01
decay_rate = 0.98
decay_steps = 2000
summary_step = 10
def main():
global_step_op = tf.train.get_or_create_global_step()
# decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate * exp(-decay_rate * global_step / decay_step)
learning_rate_no_stair = tf.train.natural_exp_decay(learning_rate=base_learning_rate,
decay_rate=decay_rate,
decay_steps=decay_steps,
staircase=False,
global_step=global_step_op,
name="natural_exp_decay_no_stair")
tf.summary.scalar("natural_exp_decay_no_stair", learning_rate_no_stair)
learning_rate_no_stair = tf.train.natural_exp_decay(learning_rate=base_learning_rate,
decay_rate=decay_rate,
decay_steps=decay_steps,
staircase=True,
global_step=global_step_op,
name="natural_exp_decay_use_stair")
tf.summary.scalar("natural_exp_decay_use_stair", learning_rate_no_stair)
summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all()
init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(),
tf.local_variables_initializer())
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
summary_write = tf.summary.FileWriter(os.path.join(summary_path, method))
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess, coord)
try:
if not coord.should_stop():
for step in range(max_step):
if step % summary_step == 0:
summary, global_step = sess.run([summary_op, global_step_op], feed_dict={global_step_op:step})
summary_write.add_summary(summary, global_step=global_step)
summary_write.flush()
summary, global_step = sess.run([summary_op, global_step_op], feed_dict={global_step_op:step})
except Exception as e:
# Report exceptions to the coordinator.
coord.request_stop(e)
finally:
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
print('all threads are asked to stop!')
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
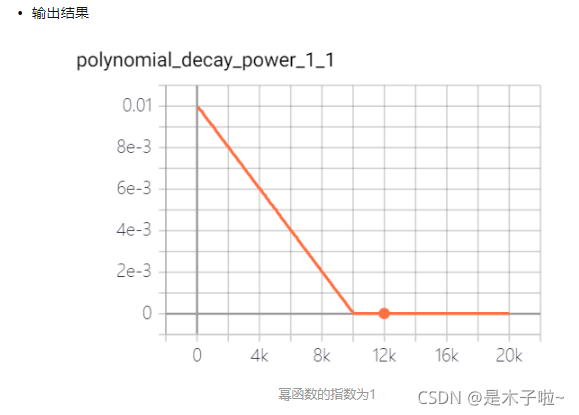
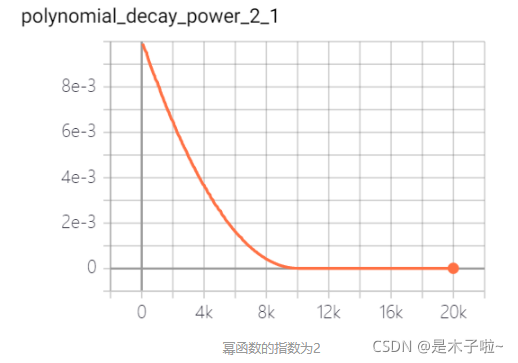
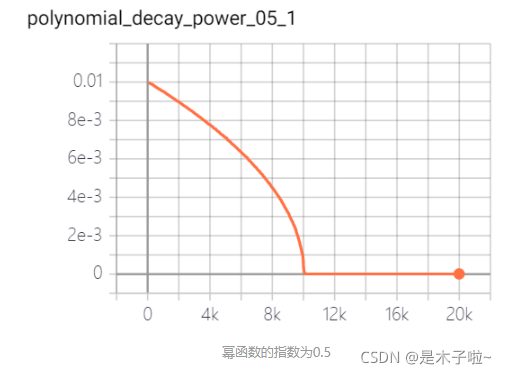
polynomial decay
多项式衰减:调整学习率的衰减轨迹以多项式对应的轨迹进行。其中(1 - global_step / decay_steps) 为幂函数的底; power为指数,控制衰减的轨迹。
方法接口
tf.train.polynomial_decay
learning_rate: 基学习率;decay_steps: 衰减率衰减步数;power: 多项式的幂;end_learning_rate:最小学习率
验证代码
import os
import tensorflow as tf
summary_path = './summary'
method = 'polynomial_decay'
max_step = 20000
base_learning_rate = 0.01
decay_steps = 10000
end_learning_rate = 0.00001
summary_step = 10
def main():
global_step_op = tf.train.get_or_create_global_step()
# global_step = min(global_step, decay_steps)
# decayed_learning_rate = (learning_rate - end_learning_rate) *
# (1 - global_step / decay_steps) ^ (power) + end_learning_rate
learning_rate_power_1 = tf.train.polynomial_decay(learning_rate=base_learning_rate,
decay_steps=decay_steps,
end_learning_rate = end_learning_rate,
power=1.,
global_step=global_step_op,
name="polynomial_decay_power_1")
tf.summary.scalar("polynomial_decay_power_1", learning_rate_power_1)
learning_rate_power_05 = tf.train.polynomial_decay(learning_rate=base_learning_rate,
decay_steps=decay_steps,
end_learning_rate=end_learning_rate,
power=0.5,
global_step=global_step_op,
name="polynomial_decay_power_05")
tf.summary.scalar("polynomial_decay_power_05", learning_rate_power_05)
learning_rate_power_2 = tf.train.polynomial_decay(learning_rate=base_learning_rate,
decay_steps=decay_steps,
end_learning_rate=end_learning_rate,
power=2,
global_step=global_step_op,
name="polynomial_decay_power_2")
tf.summary.scalar("polynomial_decay_power_2", learning_rate_power_2)
summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all()
init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(),
tf.local_variables_initializer())
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
summary_write = tf.summary.FileWriter(os.path.join(summary_path, method))
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess, coord)
try:
if not coord.should_stop():
for step in range(max_step):
if step % summary_step == 0:
summary, global_step = sess.run([summary_op, global_step_op], feed_dict={global_step_op:step})
summary_write.add_summary(summary, global_step=global_step)
summary_write.flush()
summary, global_step = sess.run([summary_op, global_step_op], feed_dict={global_step_op:step})
except Exception as e:
# Report exceptions to the coordinator.
coord.request_stop(e)
finally:
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
print('all threads are asked to stop!')
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
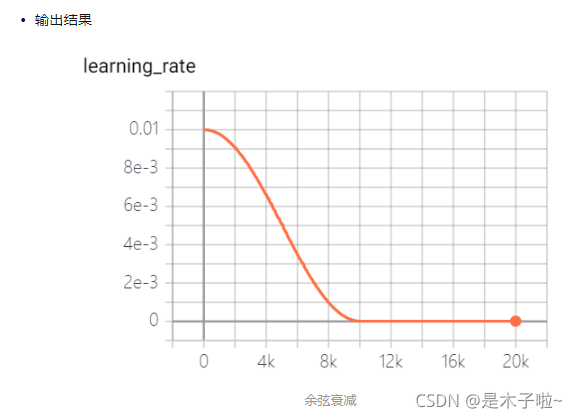
cosine decay
余弦衰减:学习率以cosine 函数曲线进行进行衰减, 其中余弦函数的周期为
![[公式]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9508666eab4c4be192357d04e345f2c7.png)
, 自变量为
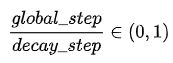
函数接口
tf.train.cosine_decay
learning_rate: 基学习率;decay_steps: 衰减率衰减步数;alpha: 最小学习率
代码验证
import os
import tensorflow as tf
summary_path = './summary'
method = 'cosine_decay'
max_step = 20000
base_learning_rate = 0.01
decay_steps = 10000
alpha = 0.001
summary_step = 10
def main():
global_step_op = tf.train.get_or_create_global_step()
# global_step = min(global_step, decay_steps)
# cosine_decay = 0.5 * (1 + cos(pi * global_step / decay_steps))
# decayed = (1 - alpha) * cosine_decay + alpha
# decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate * decayed
# update learning rate(decayed learning rate) just according to decayed parameter and learning no change
learning_rate = tf.train.cosine_decay(learning_rate=base_learning_rate,
decay_steps=decay_steps,
alpha=alpha,
global_step=global_step_op,
name="cosine_decay")
tf.summary.scalar("learning_rate", learning_rate)
summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all()
init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(),
tf.local_variables_initializer())
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
summary_write = tf.summary.FileWriter(os.path.join(summary_path, method))
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess, coord)
try:
if not coord.should_stop():
for step in range(max_step):
if step % summary_step == 0:
summary, global_step = sess.run([summary_op, global_step_op], feed_dict={global_step_op:step})
summary_write.add_summary(summary, global_step=global_step)
summary_write.flush()
summary, global_step = sess.run([summary_op, global_step_op], feed_dict={global_step_op:step})
except Exception as e:
# Report exceptions to the coordinator.
coord.request_stop(e)
finally:
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
print('all threads are asked to stop!')
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
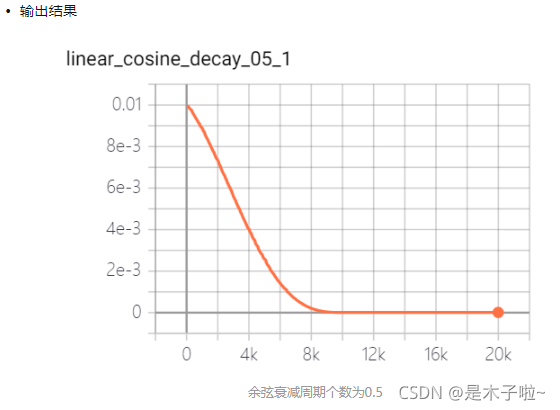
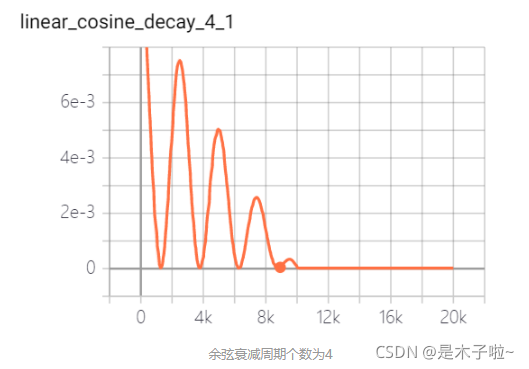
linear cosine decay
线性余弦衰减:动机式在开始的几个周期,执行warm up 操作,线性余弦衰减比余弦衰减更具aggressive,通常可以使用更大的初始学习速率。其中余弦函数的周期 为
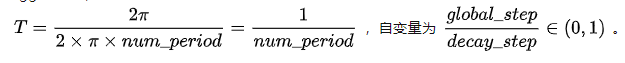
函数接口
tf.train.linear_cosine_decay
learning_rate: 基学习率;decay_steps: 衰减率衰减步数;alpha: 调节学习率衰减系数;
beta: 最小学习率;num_periods:余弦衰减部分周期数
代码验证
import os
import tensorflow as tf
summary_path = './summary'
method = 'linear_cosine_decay'
max_step = 20000
base_learning_rate = 0.01
decay_steps = 10000
num_periods_05= 0.5
num_periods_4 = 4
alpha = 0.001
beta = 0.001
summary_step = 10
def main():
global_step_op = tf.train.get_or_create_global_step()
# global_step = min(global_step, decay_steps)
# linear_decay = (decay_steps - global_step) / decay_steps)
# cosine_decay = 0.5 * (
# 1 + cos(pi * 2 * num_periods * global_step / decay_steps))
# decayed = (alpha + linear_decay + eps_t) * cosine_decay + beta
# decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate * decayed
linear_cosine_decay_05 = tf.train.linear_cosine_decay(learning_rate=base_learning_rate,
decay_steps=decay_steps,
num_periods=num_periods_05,
alpha=alpha,
beta=beta,
global_step=global_step_op,
name="linear_cosine_decay_05")
tf.summary.scalar("linear_cosine_decay_05", linear_cosine_decay_05)
linear_cosine_decay_4 = tf.train.linear_cosine_decay(learning_rate=base_learning_rate,
decay_steps=decay_steps,
num_periods=num_periods_4,
alpha=alpha,
beta = beta,
global_step=global_step_op,
name="linear_cosine_decay_4")
tf.summary.scalar("linear_cosine_decay_4", linear_cosine_decay_4)
summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all()
init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(),
tf.local_variables_initializer())
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
summary_write = tf.summary.FileWriter(os.path.join(summary_path, method))
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess, coord)
try:
if not coord.should_stop():
for step in range(max_step):
if step % summary_step == 0:
summary, global_step = sess.run([summary_op, global_step_op], feed_dict={global_step_op:step})
summary_write.add_summary(summary, global_step=global_step)
summary_write.flush()
summary, global_step = sess.run([summary_op, global_step_op], feed_dict={global_step_op:step})
except Exception as e:
# Report exceptions to the coordinator.
coord.request_stop(e)
finally:
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
print('all threads are asked to stop!')
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
参考资料
https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/v1.13.0/official/resnet/resnet_run_loop.py#L225
https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/object_detection/utils/learning_schedules.py
https://www.zhihu.com/question/338066667/answer/771252708