请参考Dual-Path-RNN-Pytorch的网络架构图。 这里我们单独把Segmentation部分拿来分析。 (文件:model_rnn.py)
到达Segmentation时,输入的张量维度为[B,N,L], 其中B为Batch Size, N为特征维度, L为特征长度。
主体函数
函数主体如下,输入首先做padding
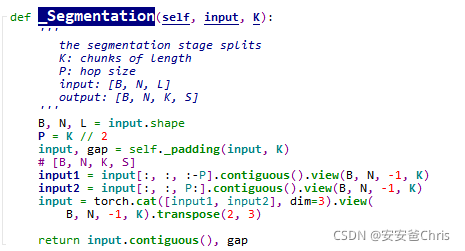
padding
padding函数如下:
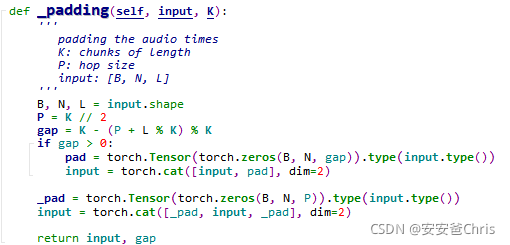
该函数主要做两件事
- 将最后一维(特征长度)对齐,即如果长度要与P(hop size)的整数倍对齐
- 将对齐后张量前后各补长度为P的0
其中gap = K - (P + L % K) % K看着有点云里雾里,它的作用就是计算L的长度与P的奇数倍的差距(gap);如果有gap,就在最后补上,这样做的好处在下一小节再说。
假设输入长度(改为1维图像便于理解)为深蓝色,那么蓝色部分即为补全的gap;对齐后整个长度为**(2n+1)K**,然后两边各有长度为P的padding

Segmentation
padding后的输入张量最后一维是 (2n+3)P,
然后对该张量分别取input[:, :, 😛]和input[:, :, P:],这样每个分割出来的最后一维长度都是 (2n+2)P即 (n+1)K,
这样将K再单独抽取一维出来,令l=n+1,
i
n
p
u
t
1.
s
h
a
p
e
=
[
B
,
N
,
l
,
K
]
i
n
p
u
t
2.
s
h
a
p
e
=
[
B
,
N
,
l
,
K
]
input1.shape=[B,N,l,K] \newline input2.shape=[B,N,l,K]
input1.shape=[B,N,l,K]input2.shape=[B,N,l,K]
这样抽取是什么意义?

根据paper中的介绍,这里是分离出chunk,每一个K长度为一个chunk;
再将两部分chunk做合并,即==[B,N,2l,K] ==,这又是什么意思?
原因是这两部分的chunk是差了P取的,所以合并的时候每个chunk变成了2l,但是前后保持了P的hopping。
转置
最后将最后两维转置,目的应该是方便后续的处理.即[B,N,K,2l]
将S=2l,
shape = ==[B,N,K,S] ==
源码部分
下面把源码部分抽取出来,单独测试,
def padding(input, K):
'''
padding the audio times
K: chunks of length
P: hop size
input: [B, N, L]
'''
B, N, L = input.shape
P = K // 2
gap = K - (P + L % K) % K
print(f'gap={K} - ({P}+{L}%{K})%{K}={gap}')
if gap > 0:
pad = torch.Tensor(torch.zeros(B, N, gap)).type(input.type())
input = torch.cat([input, pad], dim=2)
_pad = torch.Tensor(torch.zeros(B, N, P)).type(input.type())
input = torch.cat([_pad, input, _pad], dim=2)
return input, gap
def Segmentation(input, K):
'''
the segmentation stage splits
K: chunks of length
P: hop size
input: [B, N, L]
output: [B, N, K, S]
'''
B, N, L = input.shape
P = K // 2
input, gap = padding(input, K)
print('after padding: input.shape ',input.shape)
# [B, N, K, S]
input1 = input[:, :, :-P].contiguous().view(B, N, -1, K)
print('input[:, :, :-P] shape ', input[:, :, :-P].shape)
print('input1.shape ',input1.shape)
input2 = input[:, :, P:].contiguous().view(B, N, -1, K)
print('input[:, :, P:] shape ', input[:, :, P:].shape)
print('input2.shape ',input2.shape)
input = torch.cat([input1, input2], dim=3).view(
B, N, -1, K).transpose(2, 3)
print()
return input.contiguous(), gap
input = torch.linspace(1, 800, 1200).view(1, 10, 120)
K = 200
output, gap = Segmentation(input, K)
print(output.shape, gap)
