1.实现效果
使用DCGAN训练MINIST数据集,最终实现生成手写数字
2.环境配置
2.1Python
Python版本为3.7
2.2Pytorch、CUDA
在这里不详细介绍了,网上有很多的安装教程,小伙伴们自行查找吧!
2.3Python IDE
Pycharm
3.具体实现
整体分为4个文件:data.py、model.py、net.py、main.py
3.1数据预处理(data.py)
(1)导入包
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import utils, datasets, transforms
(2)定义数据类
class ReadData():
def __init__(self,data_path,image_size=64):
self.root=data_path
self.image_size=image_size
self.dataset=self.getdataset()
def getdataset(self):
#3.dataset
dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=self.root,
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(self.image_size),
transforms.CenterCrop(self.image_size),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)),
]))
# Create the dataloader
print(f'Total Size of Dataset: {len(dataset)}')
return dataset
def getdataloader(self,batch_size=128):
dataloader = DataLoader(
self.dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=0)
return dataloader
3.2模型Generator,Discriminator,权重初始化(model.py)
(1)导入包
import torch.nn as nn
(2)Generator
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nz,ngf,nc):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
self.nz = nz
self.ngf = ngf
self.nc=nc
self.main = nn.Sequential(
# input is Z, going into a convolution
nn.ConvTranspose2d(self.nz, self.ngf * 8, 4, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(self.ngf * 8),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf*8) x 4 x 4
nn.ConvTranspose2d(self.ngf * 8, self.ngf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(self.ngf * 4),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf*4) x 8 x 8
nn.ConvTranspose2d(self.ngf * 4, self.ngf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(self.ngf * 2),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf*2) x 16 x 16
nn.ConvTranspose2d(self.ngf * 2, self.ngf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(self.ngf),
nn.ReLU(True),
# state size. (ngf) x 32 x 32
nn.ConvTranspose2d(self.ngf, self.nc, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.Tanh()
# state size. (nc) x 64 x 64
)
def forward(self, input):
return self.main(input)
(3)Discriminator
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ndf,nc):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
self.ndf=ndf
self.nc=nc
self.main = nn.Sequential(
# input is (nc) x 64 x 64
nn.Conv2d(self.nc, self.ndf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf) x 32 x 32
nn.Conv2d(self.ndf, self.ndf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(self.ndf * 2),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf*2) x 16 x 16
nn.Conv2d(self.ndf * 2, self.ndf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(self.ndf * 4),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf*4) x 8 x 8
nn.Conv2d(self.ndf * 4, self.ndf * 8, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(self.ndf * 8),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# state size. (ndf*8) x 4 x 4
nn.Conv2d(self.ndf * 8, 1, 4, 1, 0, bias=False),
# state size. (1) x 1 x 1
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, input):
return self.main(input)
(4)权重初始化
def weights_init(m):
classname = m.__class__.__name__
if classname.find('Conv') != -1:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 0.0, 0.02)
elif classname.find('BatchNorm') != -1:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 1.0, 0.02)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0)
3.3网络训练(net.py)
(1)导入包
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import utils, datasets, transforms
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation as animation
from IPython.display import HTML
(2)创建类
class DCGAN():
def __init__(self,nz, lr,beta1,device, model_save_path,figure_save_path,generator, discriminator, data_loader,):
self.nz=nz
self.real_label=1
self.fake_label=0
self.device = device
self.model_save_path=model_save_path
self.figure_save_path=figure_save_path
self.G = generator.to(device)
self.D = discriminator.to(device)
self.opt_G=torch.optim.Adam(self.G.parameters(), lr=lr, betas=(beta1, 0.999))
self.opt_D = torch.optim.Adam(self.D.parameters(), lr=lr, betas=(beta1, 0.999))
self.criterion = nn.BCELoss().to(device)
self.dataloader=data_loader
self.fixed_noise = torch.randn(100, nz, 1, 1, device=device)
self.img_list = []
self.G_loss_list = []
self.D_loss_list = []
self.D_x_list = []
self.D_z_list = []
def train(self,num_epochs):
loss_tep = 10
G_loss=0
D_loss=0
print("Starting Training Loop...")
# For each epoch
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
#**********计时*********************
beg_time = time.time()
# For each batch in the dataloader
for i, data in enumerate(self.dataloader):
############################
# (1) Update D network: maximize log(D(x)) + log(1 - D(G(z)))
###########################
x = data[0].to(self.device)
b_size = x.size(0)
lbx = torch.full((b_size,), self.real_label, dtype=torch.float, device=self.device)
D_x = self.D(x).view(-1)
LossD_x = self.criterion(D_x, lbx)
D_x_item = D_x.mean().item()
# print("log(D(x))")
z = torch.randn(b_size, self.nz, 1, 1, device=self.device)
gz = self.G(z)
lbz1 = torch.full((b_size,), self.fake_label, dtype=torch.float, device=self.device)
D_gz1 = self.D(gz.detach()).view(-1)
LossD_gz1 = self.criterion(D_gz1, lbz1)
D_gz1_item = D_gz1.mean().item()
# print("log(1 - D(G(z)))")
LossD = LossD_x + LossD_gz1
# print("log(D(x)) + log(1 - D(G(z)))")
self.opt_D.zero_grad()
LossD.backward()
self.opt_D.step()
# print("update LossD")
D_loss+=LossD
############################
# (2) Update G network: maximize log(D(G(z)))
###########################
lbz2 = torch.full((b_size,), self.real_label, dtype=torch.float, device=self.device) # fake labels are real for generator cost
D_gz2 = self.D(gz).view(-1)
D_gz2_item = D_gz2.mean().item()
LossG = self.criterion(D_gz2, lbz2)
# print("log(D(G(z)))")
self.opt_G.zero_grad()
LossG.backward()
self.opt_G.step()
# print("update LossG")
G_loss+=LossG
end_time = time.time()
# **********计时*********************
run_time = round(end_time - beg_time)
# print('lalala')
print(
f'Epoch: [{epoch + 1:0>{len(str(num_epochs))}}/{num_epochs}]',
f'Step: [{i + 1:0>{len(str(len(self.dataloader)))}}/{len(self.dataloader)}]',
f'Loss-D: {LossD.item():.4f}',
f'Loss-G: {LossG.item():.4f}',
f'D(x): {D_x_item:.4f}',
f'D(G(z)): [{D_gz1_item:.4f}/{D_gz2_item:.4f}]',
f'Time: {run_time}s',
end='\r\n'
)
# print("lalalal2")
# Save Losses for plotting later
self.G_loss_list.append(LossG.item())
self.D_loss_list.append(LossD.item())
# Save D(X) and D(G(z)) for plotting later
self.D_x_list.append(D_x_item)
self.D_z_list.append(D_gz2_item)
# # Save the Best Model
# if LossG < loss_tep:
# torch.save(self.G.state_dict(), 'model.pt')
# loss_tep = LossG
torch.save(self.D.state_dict(), self.model_save_path + 'disc_{}.pth'.format(epoch))
torch.save(self.G.state_dict(), self.model_save_path + 'gen_{}.pth'.format(epoch))
# Check how the generator is doing by saving G's output on fixed_noise
with torch.no_grad():
fake = self.G(self.fixed_noise).detach().cpu()
self.img_list.append(utils.make_grid(fake * 0.5 + 0.5, nrow=10))
print()
#绘图
plt.figure(1,figsize=(8, 4))
plt.title("Generator and Discriminator Loss During Training")
plt.plot(self.G_loss_list[::100], label="G")
plt.plot(self.D_loss_list[::100], label="D")
plt.xlabel("iterations")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.axhline(y=0, label="0", c="g") # asymptote
plt.legend()
plt.savefig(self.figure_save_path + str(num_epochs) + 'epochs_' + 'loss.jpg', bbox_inches='tight')
plt.figure(2,figsize=(8, 4))
plt.title("D(x) and D(G(z)) During Training")
plt.plot(self.D_x_list[::100], label="D(x)")
plt.plot(self.D_z_list[::100], label="D(G(z))")
plt.xlabel("iterations")
plt.ylabel("Probability")
plt.axhline(y=0.5, label="0.5", c="g") # asymptote
plt.legend()
plt.savefig(self.figure_save_path + str(num_epochs) + 'epochs_' + 'D(x)D(G(z)).jpg', bbox_inches='tight')
fig = plt.figure(3,figsize=(5, 5))
plt.axis("off")
ims = [[plt.imshow(item.permute(1, 2, 0), animated=True)] for item in self.img_list]
ani = animation.ArtistAnimation(fig, ims, interval=1000, repeat_delay=1000, blit=True)
HTML(ani.to_jshtml())
# ani.to_html5_video()
ani.save(self.figure_save_path + str(num_epochs) + 'epochs_' + 'generation.gif')
plt.figure(4,figsize=(8, 4))
# Plot the real images
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("Real Images")
real = next(iter(self.dataloader)) # real[0]image,real[1]label
plt.imshow(utils.make_grid(real[0][:100] * 0.5 + 0.5, nrow=10).permute(1, 2, 0))
# Load the Best Generative Model
# self.G.load_state_dict(
# torch.load(self.model_save_path + 'disc_{}.pth'.format(epoch), map_location=torch.device(self.device)))
self.G.eval()
# Generate the Fake Images
with torch.no_grad():
fake = self.G(self.fixed_noise).to('cpu')
# Plot the fake images
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("Fake Images")
fake = utils.make_grid(fake[:100] * 0.5 + 0.5, nrow=10)
plt.imshow(fake.permute(1, 2, 0))
# Save the comparation result
plt.savefig(self.figure_save_path + str(num_epochs) + 'epochs_' + 'result.jpg', bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
def test(self,epoch):
# Size of the Figure
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))
# Plot the real images
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("Real Images")
real = next(iter(self.dataloader))#real[0]image,real[1]label
plt.imshow(utils.make_grid(real[0][:100] * 0.5 + 0.5, nrow=10).permute(1, 2, 0))
# Load the Best Generative Model
self.G.load_state_dict(torch.load(self.model_save_path + 'disc_{}.pth'.format(epoch), map_location=torch.device(self.device)))
self.G.eval()
# Generate the Fake Images
with torch.no_grad():
fake = self.G(self.fixed_noise.to(self.device))
# Plot the fake images
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.axis("off")
plt.title("Fake Images")
fake = utils.make_grid(fake * 0.5 + 0.5, nrow=10)
plt.imshow(fake.permute(1, 2, 0))
# Save the comparation result
plt.savefig(self.figure_save_path+'result.jpg', bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
3.4 主函数(main.py)
(1)导入文件
from data import ReadData
from model import Discriminator, Generator, weights_init
from net import DCGAN
import torch
(2)定义超参数
ngpu=1
ngf=64
ndf=64
nc=1
nz=100
lr=0.003
beta1=0.5
datapath="./data"
batchsize=100
model_save_path="./models/"
figure_save_path="./figures/"
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if (torch.cuda.is_available() and ngpu > 0) else 'cpu')
(3)实例化
dataset=ReadData(datapath)
dataloader=dataset.getdataloader(batch_size=batchsize)
G = Generator(nz,ngf,nc).apply(weights_init)
D = Discriminator(ndf,nc).apply(weights_init)
dcgan=DCGAN(nz, lr,beta1,device, model_save_path,figure_save_path,G, D, dataloader)
(4)进行训练
dcgan.train(num_epochs=5)
4.训练过程
4.1 Generator和Discriminator的Loss损失曲线图
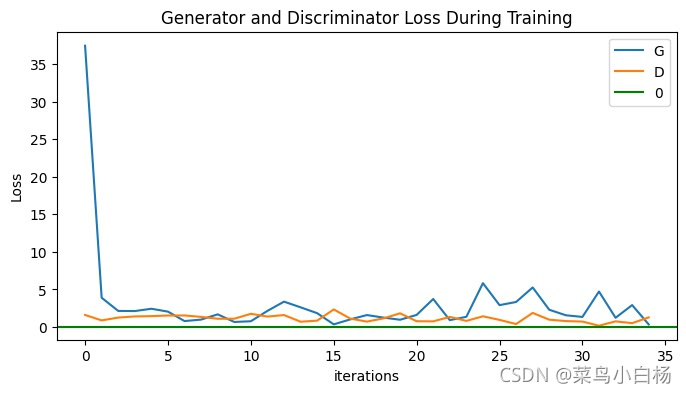
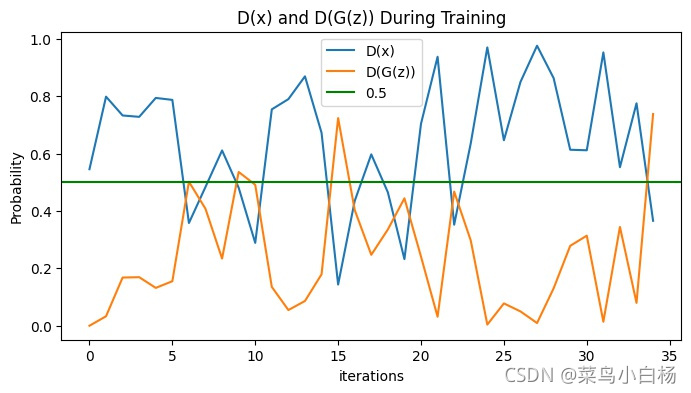
4.2 D(x)和D(G(z))曲线图
训练过程中Discriminator输出(以5个epoch为例):
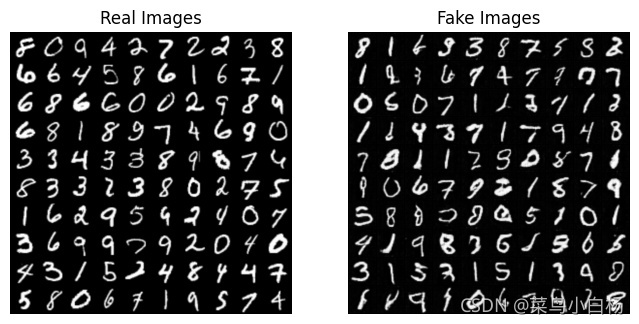
4.3最终生成结果图
训练结束后生成图片(以5个epoch为例):
4.4 训练过程的生成结果动图
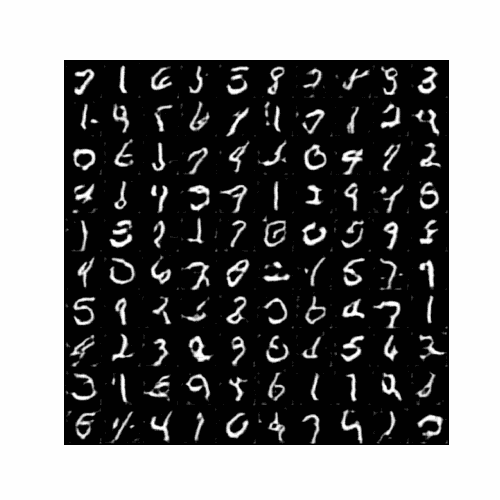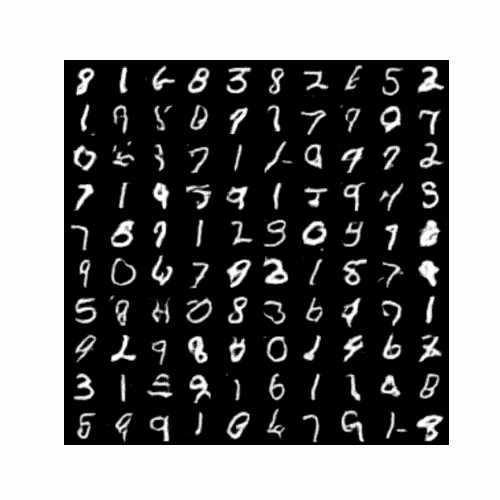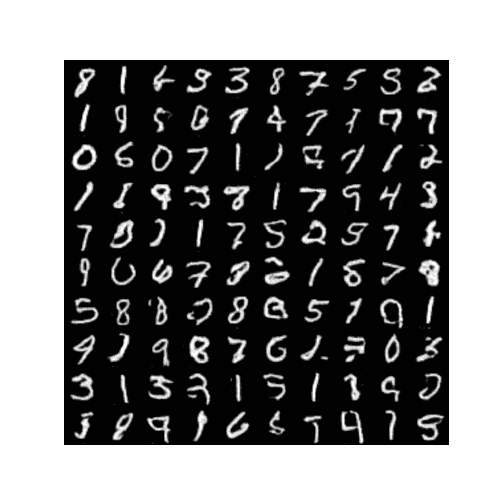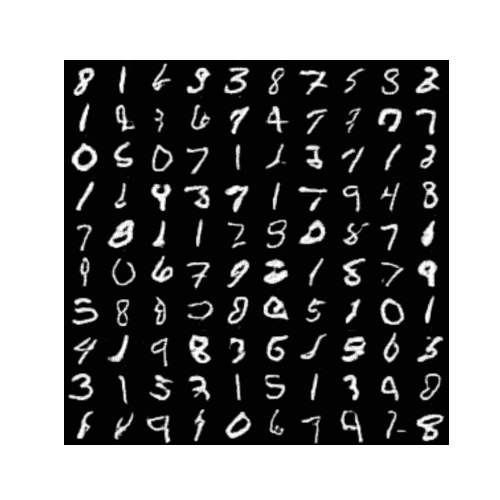
5.完整代码
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1suzA3-F2FYem99Gch8hnig
提取码:DGAN
6.引用参考
7.问题反馈
如果运行有问题,欢迎给我私信留言!