文章目录
教程
环境配置
安装Windows CPU版本tensorflow
参考链接:
打开cmd,运行以下语句:
- pip install tensorflow
- 进入python,运行import tensorflow as tf
错误:
2021-09-06 21:51:38.471339: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'cudart64_110.dll'; dlerror: cudart64_110.dll not found
2021-09-06 21:51:38.472290: I tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cudart_stub.cc:29] Ignore above cudart dlerror if you do not have a GPU set up on your machine.
- 打开链接下载cudart64_110.dll下载 CUDART64_110.DLL
- 复制文件dll进路径C:\Windows\System32
- 重新运行import tensorflow as tf不报错
参考链接:
出现Could not load dynamic library ‘cudart64_110.dll‘; dlerror: cudart64_110.dll not found解决办法
但复制文件的路径有变化
注意:
运行程序可以出现结果,但同时会出现:
2021-09-07 16:33:57.746978: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'cublas64_11.dll'; dlerror: cublas64_11.dll not found
2021-09-07 16:33:57.749512: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'cublasLt64_11.dll'; dlerror: cublasLt64_11.dll not found
2021-09-07 16:33:57.751775: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'cufft64_10.dll'; dlerror: cufft64_10.dll not found
2021-09-07 16:33:57.753878: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'curand64_10.dll'; dlerror: curand64_10.dll not found
2021-09-07 16:33:57.756025: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'cusolver64_11.dll'; dlerror: cusolver64_11.dll not found
2021-09-07 16:33:57.758276: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'cusparse64_11.dll'; dlerror: cusparse64_11.dll not found
2021-09-07 16:33:57.761254: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'cudnn64_8.dll'; dlerror: cudnn64_8.dll not found
2021-09-07 16:33:57.762224: W tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1835] Cannot dlopen some GPU libraries. Please make sure the missing libraries mentioned above are installed properly if you would like to use GPU. Follow the guide at https://www.tensorflow.org/install/gpu for how to download and setup the required libraries for your platform.
Skipping registering GPU devices...
2021-09-07 16:33:57.763272: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:142] This TensorFlow binary is optimized with oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library (oneDNN) to use the following CPU instructions in performance-critical operations: AVX AVX2
To enable them in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.
原因是没有装上GPU版本的
CUDA
cuDNN
安装CUDA、cuDNN
参考链接:
- 在Windows下安装TensorFlow GPU版本教程(超级详细哦)
C:\Windows\System32\cuda\bin - 在安装cuDNN时:下载dudnn之后,复制cuDNN里的三个文件夹到C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.4
安装Windows GPU版本tensorflow
- pip install tensorflow-gpu
报错:
ERROR: Could not install packages due to an OSError: [WinError 5] 拒绝访问。: 'c:\\users\\22164\\appdata\\local\\programs\\python\\python39\\Lib\\site-packages\\tensorflow\\lite\\experimental\\microfrontend\\python\\ops\\_audio_microfrontend_op.so'
Consider using the `--user` option or check the permissions.
- pip install --user tensorflow-gpu
警告;
WARNING: The scripts estimator_ckpt_converter.exe, import_pb_to_tensorboard.exe, saved_model_cli.exe, tensorboard.exe, tf_upgrade_v2.exe, tflite_convert.exe, toco.exe and toco_from_protos.exe are installed in 'C:\Users\22164\AppData\Roaming\Python\Python39\Scripts' which is not on PATH.
Consider adding this directory to PATH or, if you prefer to suppress this warning, use --no-warn-script-location.
将C:\Users\22164\AppData\Roaming\Python\Python39\Scripts加入path环境变量
查看使用的是CPU还是GPU
- 使用以下代码:
from tensorflow.python.client import device_lib
print(device_lib.list_local_devices())
可以查看挂载的设备有哪些
print(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU'))
print(tf.config.list_physical_devices('CPU'))
可以查看挂载的CPU/GPU设备有哪些
- 使用以下代码可以启用/禁用GPU
import os
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "-1" # 禁用GPU,使用CPU
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "0" # 使用GPU:0
- 使用以下代码:
with tf.device('/gpu:0'):
使用指定设备运行代码段
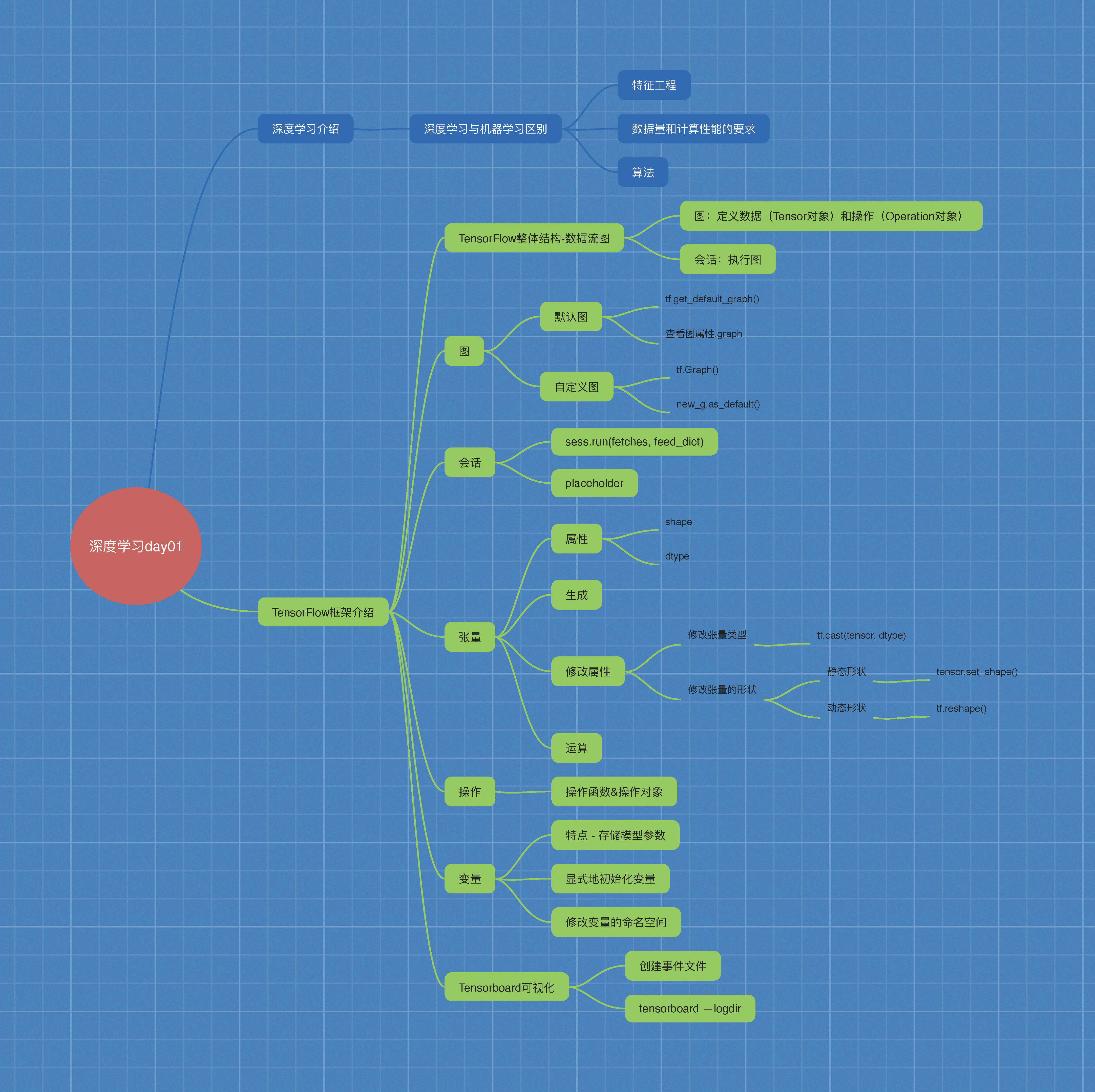
深度学习介绍
1.1 深度学习与机器学习的区别
机器学习是实现人工智能的一种途径,深度学习是机器学习的一个子集,也就是说深度学习是实现机器学习的一种方法。
1.1.1 特征提取方面
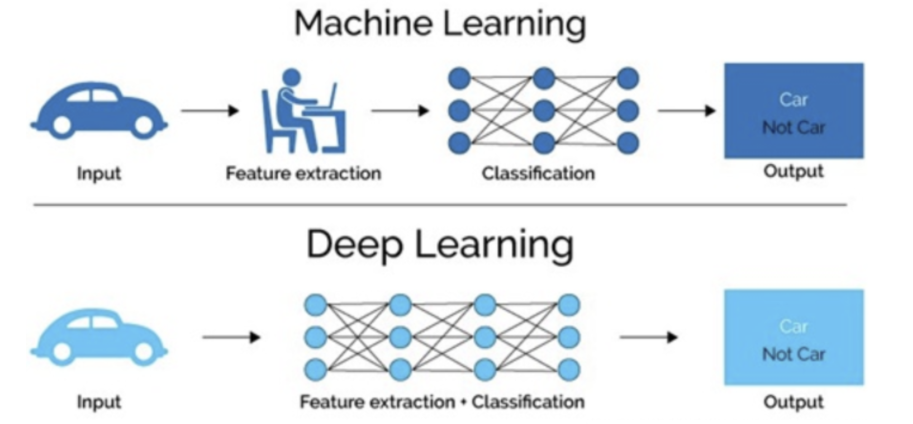
- 机器学习的特征工程步是要手动究成的,而且需要大量领域专业知识
- 深度学习通常由多个层组成,它们通常将更简单的模型组合在一起,将数据从层传选到另一层来构建更复杂的模型,通过训练大量数据自动得出模型,不需要人工特征提取环节。
深度学习算法试图从数据中学习高级功能,这是深度学习的一个非常独特的部分。因此,减少了为每个问题开发新特征提取器的任务。适合用在难提取特征的图像、语音、自然语言处理领域。
1.1.2 数据量和计算性能要求

第一、深度学习需要大量的训练数据集
第二、训练深度神经网络需要大量的算力
可能要花费数天、甚至数周的时间,才能使用数百万张图像的数据集训练出一个深度网络。所以深度学习通常
- 需要强大的GPU服务器来进行计算
- 全面管理的分布式训练与预测服务ー一比如谷歌 Tensorflow云机器学习平台
1.1.3 算法代表
- 机器学习
朴素贝叶斯、决策树等 - 深度学习
神经网络
1.2 深度学习的应用场景
- 图像识别
物体识别
场景识别
车型识别
人脸检测跟踪
人脸关键点定位
人脸身份认证 - 自然语言处理技术
机器翻译
文本识别
聊天对话 - 语音技术
语音识别
1.3 深度学习框架介绍
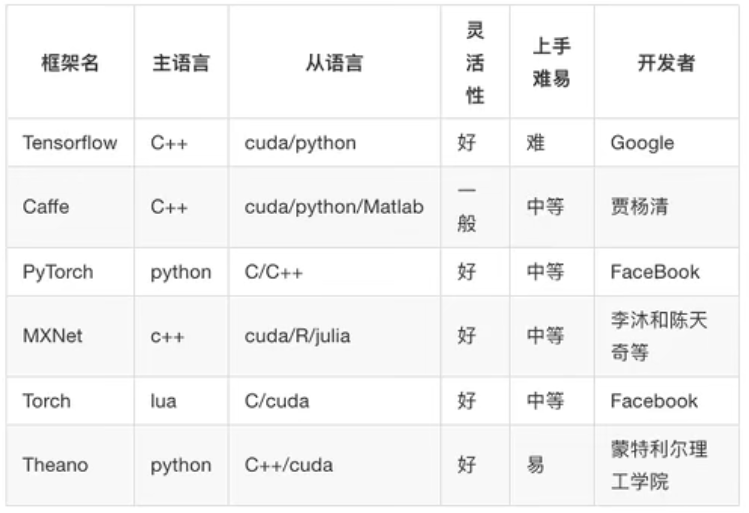
1.3.1 常见深度学习框架对比
总结
- 最常用的框架当 Tensorflow和 Pytorch,而Cafe和Cafe2次之。
- Pytorch和Toch更适用于学术研究( (research); Tensorflow,Cafe
Cafe2更适用于工业界的生产环境部署( (industrial production) - Caffe适用于处理静态图像( static graph); Torch和 Pytorch更适用于动
态图像( dynamic graph); Tensorflow在两种情况下都很实用。 - Tensorflow和Cafe2可在移动端使用。
1.3.2 TensorFlow的特点
- 高度灵活( Deep Flexibility)
它不仅可来做神经网络算法研究,也可以用来做普通的机器学习算法,
甚至是只要把计算表示成数据流图,都可以用 Tensorflow - 语言多样( Language Options)
Tensorflom使用C+实现的,然后用 Python封装。谷歌号召社区通过SWG
开发更多的语言接口来支持 Tensorflow - 设备支持
Tensorflow可以运行在各种硬件上,同时根据计算的需要,合理将运算分配
到相应的设备,比如卷积就分配到GPU上,也允许在CPU和GPU上的计算
分布,甚至支持使用gRPC进行水平扩展 - Tensorboard可视化
Tensorboard是 Tensorflow的一组Web应用,用来监控 Tensorflow运行过程,或可视化 Computation Graph. Tensorboard日前支持5种可视化:标量scalars)、图片( Images)、音频( audio)、直方图( histograms)和计算图( Computation Graph). Tensorboardp的 Events Dashboard可以用来持地监控运行时的关键指标,比如loss、学习速率( ( learning rate)或是验证集上的准确率( accuracy)
1.3.3 TensorFlow的安装
-
1 CPU版本
-
2 GPU版本
注:
- CPU:诸葛亮
综合能力比较强
核芯的数量更少
更适用于处理连续性(sequential)任务。 - GPU:臭皮匠
专做某一个事情很好
核芯的数量更多
更适用于并行(parallel)任务
TensorFlow框架的使用
2.0 兼容性问题
2.0版本的tensorflow与1.8的有很多不一样的地方。当出现模块找不到的情况(大部分情况)可以使用兼容性运行的办法解决。
用法:
指令中间加入compat.v1
例如:
- 1.8版本:tf.disable_eager_execution()
- 2.0版本:tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution()
2.1 TF数据流图
2.1.1 案例:TensorFlow实现一个加法运算
import tensorflow as tf
a_t = tf.constant(2)
b_t = tf.constant(3)
c_t = a_t + b_t
print("tensorflow加法运算的结果:\n", c_t)
with tf.Session() as sess
c_t_value = sess.run(c_t)
print("c_t_value:\n", c_t_value)
错误:找不到Session()
原因:2.0版本的tensorflow已经没有Session()模块
方案:改用以下语句
import tensorflow as tf
tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution()
a_t = tf.constant(2)
b_t = tf.constant(3)
c_t = a_t + b_t
print("tensorflow加法运算的结果:\n", c_t)
sess = tf.compat.v1.Session()
c_t_value = sess.run(c_t)
sess = tf.compat.v1.Session()
TensorFlow结构分析
-
一个构建图阶段
流程图:定义数据(张量Tensor)和操作(节点Operation) -
一个执行图阶段
调用各方资源,将定义好的数据和操作运行起来 -
图和会话:
- 图:这是 Tensorflow将计算表示为指令之间的依赖关系的一种表示法
- 会话: Tensorflow跨一个或多个本地或远程设备运行数据流图的机制
-
张量: Tensorflow中的基本数据对象
-
节点:提供图当中执行的操作
2.1.2 数据流图介绍
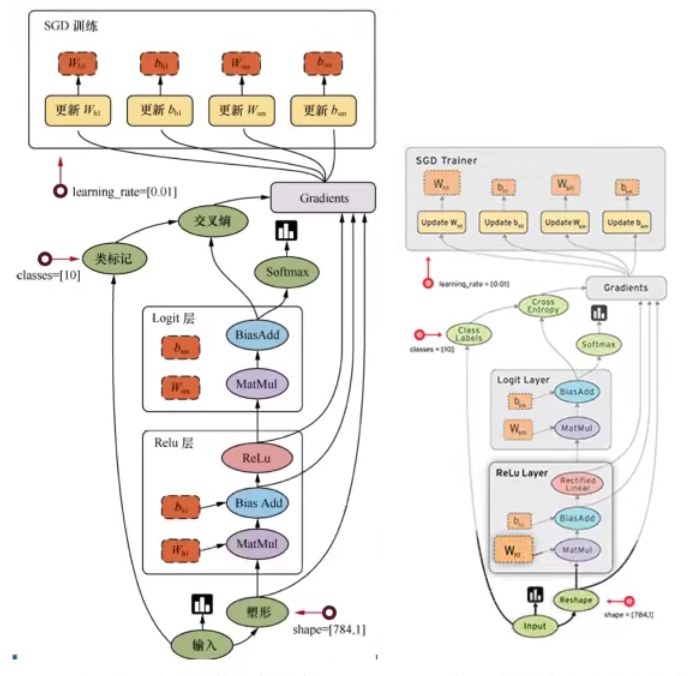
Tensor - 张量 - 数据
Flow - 流动
Tensorflow是一个采用数据流图( data flow graphs),用于数值计算的开源框架。
节点( Operation)在图中表示数学操作,线( edges)则表示在节点间相互联系的多维数据数组,即张量( tensor)
2.2 图与TensorBoard
2.2.1 什么是图结构
图包含了一组tf.Operation代表的计算单元对象和tf.Tensor代表的计算单元之间流动的数据。
图结构:
数据(Tensor) + 操作(Operation)
2.2.2 图相关操作
1 默认图
通常 Tensorflow会默认帮我们创建一张图。
查看默认图的方法
- 1)调用方法
用tf.get_default_graph()访问,要将操作添加到默认图形中,直接创建OP即可
2.0版本改用:tf.compat.v1.get_default_graph() - 2)查看属性
op、sess都含有graph属性,默认都在一张图中
.graph
2 创建图
new_g = tf.Graph()
with new_g.as_default():
定义数据和操作
示例
图的演示
def graph_show():
"""
图的演示
:return:
"""
# tensorflow加法运算
a_t = tf.constant(2)
b_t = tf.constant(3)
c_t = a_t + b_t
print("tensorflow加法运算的结果:\n", c_t)
# 查看默认图
# 方法1:调用方法
# default_g = tf.get_default_graph() # 2.0版本没有get_default_graph()
default_g = tf.compat.v1.get_default_graph()
print("default_g:\n", default_g)
# 方法2:查看属性
print("a_t的图属性:\n", a_t.graph)
print("c_t的图属性:\n", c_t.graph)
# 自定义图
new_g = tf.Graph()
# 在自己的图中定义数据和操作
with new_g.as_default():
a_new = tf.constant(20)
b_new = tf.constant(30)
c_new = a_new + b_new
print("c_new:\n", c_new)
# print(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU'))
# print(tf.config.list_physical_devices('CPU'))
# 开启会话
# with tf.Session() as sess # 2.0版本没有Session模块
# with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess: # 使用这个
sess = tf.compat.v1.Session() # 或者使用这个
c_t_value = sess.run(c_t)
print("c_t_value:\n", c_t_value)
print("sess的图属性:\n", sess.graph)
# 尝试运行自定义图中的数据、操作(会报错,因为这个数据在自定义的图中)
# c_new_value = sess.run(c_new)
# print("c_new_value:\n", c_new_value)
# 开启new_g的会话
new_sess = tf.compat.v1.Session(graph=new_g)
c_new_value = new_sess.run(c_new)
print("c_new_value:\n", c_new_value)
print("new_sess的图属性:\n", new_sess.graph)
结果:
tensorflow加法运算的结果:
Tensor("add:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
default_g:
<tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x00000143571916A0>
a_t的图属性:
<tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x00000143571916A0>
c_t的图属性:
<tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x00000143571916A0>
c_new:
Tensor("add:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
2021-09-08 10:25:14.248406: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:142] This TensorFlow binary is optimized with oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library (oneDNN) to use the following CPU instructions in performance-critical operations: AVX AVX2
To enable them in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.
2021-09-08 10:25:14.896050: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0 with 2778 MB memory: -> device: 0, name: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1050 Ti, pci bus id: 0000:01:00.0, compute capability: 6.1
c_t_value:
5
sess的图属性:
<tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x00000143571916A0>
c_new_value:
50
new_sess的图属性:
<tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Graph object at 0x000001436BE9BC40>
2021-09-08 10:25:14.944687: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0 with 2778 MB memory: -> device: 0, name: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1050 Ti, pci bus id: 0000:01:00.0, compute capability: 6.1
2.2.3 TensorBoard:可视化学习
- 1 数据序列化-events文件
tf.summary.FileWriter(path, graph=sess.graph)
2.0版本改用:tf.compat.v1.summary.FileWriter("…/events", graph=sess.graph) - 2 启动tensorboard
tensorboard --logdir="./events"
注意: - 引号里的路径到events文件所在的文件夹
- =前后不要有空格
示例
(接前面代码)
将图写入本地生成events文件
# 开启会话
# with tf.Session() as sess # 2.0版本没有Session模块
# with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess: # 使用这个
sess = tf.compat.v1.Session() # 或者使用这个
c_t_value = sess.run(c_t)
print("c_t_value:\n", c_t_value)
print("sess的图属性:\n", sess.graph)
# 尝试运行自定义图中的数据、操作(会报错,因为这个数据在自定义的图中)
# c_new_value = sess.run(c_new)
# print("c_new_value:\n", c_new_value)
# 1)将图写入本地生成events文件
# tf.summary.FileWriter("../events", graph=sess.graph) # 2.0没有
tf.compat.v1.summary.FileWriter("../events", graph=sess.graph)
结果:
会生成一个文件:events.out.tfevents.{timestamp} . {hostname}
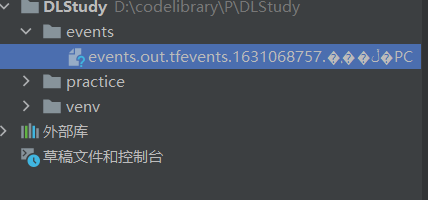
在终端输入命令:tensorboard --logdir="./events"
D:\codelibrary\P\DLStudy> tensorboard --logdir="./events"
结果:
出现一个网页,Ctrl+鼠标左键点击可以访问

进入网页后可以看到
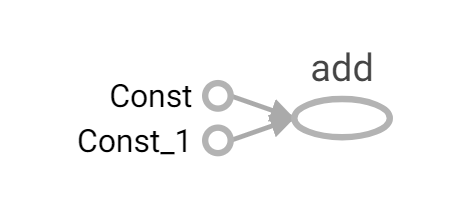
注意:
- 不知道是不是版本的问题,一开始显示的图箭头很大,需要点击add,点击add to main graph才能显示正常。
- 定义变量时可以重命名,例如:a_t = tf.constant(2, name=“a_t”)。方便看张量图。
2.2.4 OP
数据:Tensor对象
操作:Operation对象 - Op
1 常见OP
| 类型 | 实例 |
|---|---|
| 标量运算 | add,sub, mul, div, exp, log, greater, less, equal |
| 向量运算 | concat, slice, splot, constant, rank, shape, shuffle |
| 矩阵运算 | matmul,matrixinverse, matrixdateminant |
| 带状态的运算 | Variable, assgin, assginadd |
| 神经网络组件 | softmax,sigmoid, relu,convolution,max_pool |
| 存储,恢复 | Save, Restroe |
| 队列及同步运算 | Enqueue, Dequeue,MutexAcquire,MutexRelease |
| 控制流 | Merge,Switch, Enter,Leave,Nextlteration |
tf.constant()就是一个操作函数,传入参数运行以后会产生一个张量Const,就是操作对象。
| 操作函数 | 操作对象 |
|---|---|
| tf.constant(Tensor对象) | 输入Tensor对象 - Const-输出 Tensor对象 |
| tf.add(Tensor对象1, Tensor对象2) | 输入Tensor对象1, Tensor对象2 - Add对象 - 输出 Tensor对象3 |
一个操作对象(Operation)是 Tensorflow图中的一个节点,可以接收0个或者多个输入Tensor,并且可以输出0个或者多个Tensor, Operation对象是通过op构造函数(如tf.matui())创建的。
例如:c= tf.matmul(a,b)创建了ー个 Operation对象,类型为Matmul类型,它将张量a,b作为输入,c作为输出,并且输出数据,打印的时候也是打印的数
据。其中计tf.matmul()是函数,在执行matmul函数的过程中会通过Matmul类创建一个与之对应的对象。
打印con_a
Tensor("Const: 0", shape=(), dtype=float32)
打印con_b:
Tensor("Const_1: 0, shape=(), dtype=f Loat32
打印sum_C:
Tensor("Add: 0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
注意:
- 打印出来的是张量值,可以理解成OP当中包含了这个值。并且每一个OP指令都对应一个唯一的名称,如上面的 Const:0,这个在 Tensor Board上面也可以显示
- tf Tensor对象以输出该张量的tf.Operation明确命名。张量名称的形式为
“< OP NAME >:< i >”, 其中:- "< OP NAME>"是生成该张量的指令的名称
- "< i >"是一个整数它表示该张量在指令的输出中的索引
2 指令名称
一张图一个命名空间
tf.Graph对象为其包含的 tf.Operation对象定义的一个命名空间。TensorFlow 会自动为图中的每个指令选择一个唯一名称,用户也可以指定描述性名称,使程序阅读起来更轻松。我们可以以以下方式改写指令名称:
- 每个创建新的tf.Operation或返回新的tf.Tensor的 API函数可以接受可选的name 参数。
例如,tf.constant(42.0, name=“answer”)创建了一个名为““answer”的新tf.Operation并返回一个名为“answer:O”的tf.Tensor。如果默认图已包含名为"answer”的指令,则TensorFlow 会在名称上附加“1”、""2”等字符,以便让名称具有唯一性。
- 当修改好之后,我们在Tensorboard显示的名字也会被修改。
2.3 会话
2.3.1 创建会话
一个运行TensorFlow operation的类。会话包含以下两种开启方式
- tf.Session:用于完整的程序当中
- tf.InteractiveSession:用于交互式上下文中的TensorFlow ,例如shell
- TensorFlow使用tf.Session类来表示客户端程序(通常为Python程序,但也提供了使用其他语言的类似接口)与C++运行时之间的连接
- tf.Session对象使用分布式TensorFlow运行时提供对本地计算机中的设备和远程设备的访问权限
示例
tf.InteractiveSession的使用
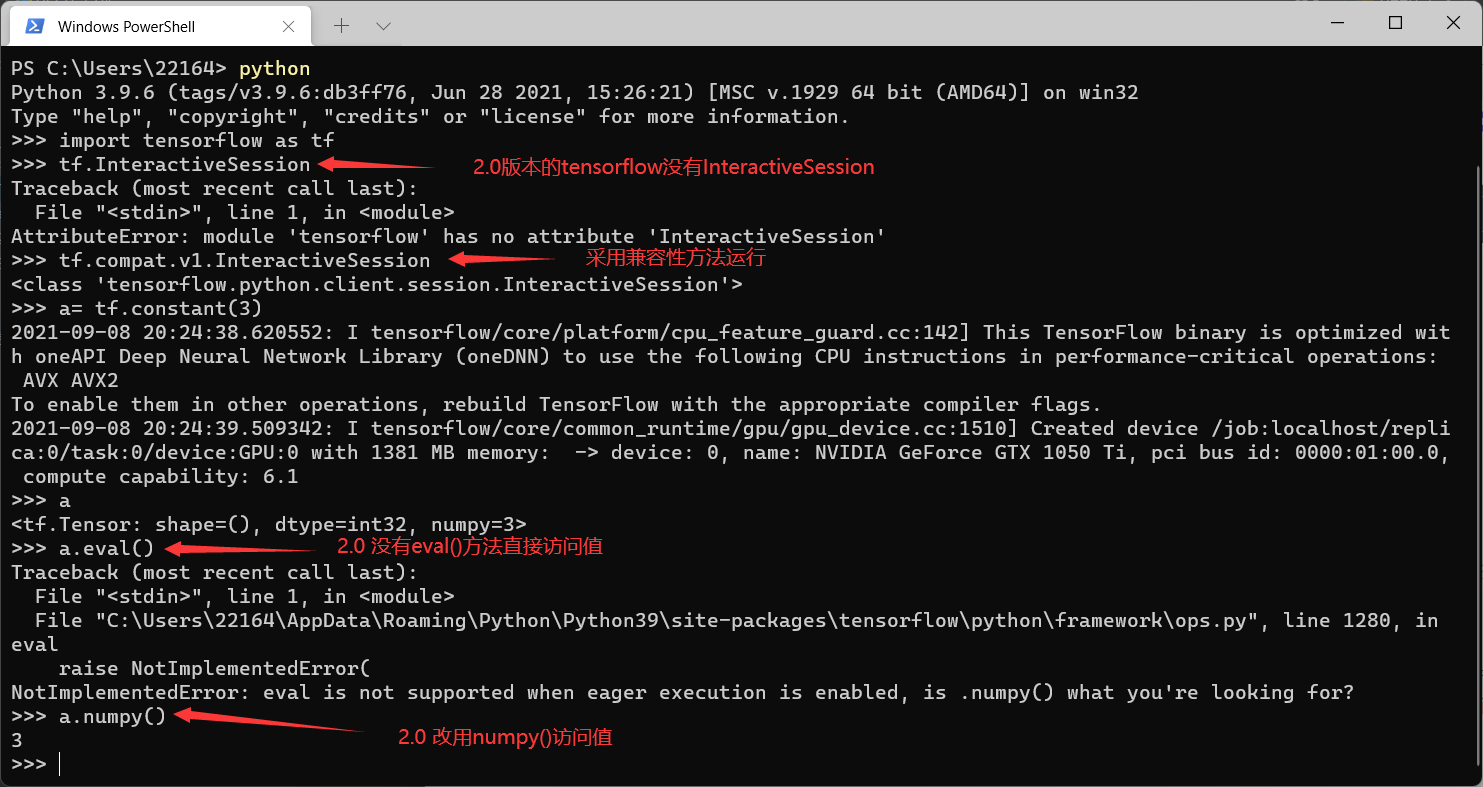
注意: 2.0版本的InteractiveSession里的eval()改用numpy()
2.3.1.1 会话掌握资源,用完要回收 - 上下文管理器
init(target=", graph=None, config=None)
会话可能拥有的资源,如tf.Variable,tf.QueueBase和tf.ReaderBase。当这些资源不再需要时,释放这些资源非常重要。因此,需要调tf.Sessioh.close会话中的方法,或将会话用作上下文管理器。以下两个例子作用是一样的(直白一点就是打开会话用完必须要关闭,就像文件读写那样):
def session_demo():
"""
会话演示
:return:
"""
a_t = tf.constant(10)
b_t = tf.constant(20)
# 不提倡直接用+ - 符号直接运算
# 推荐用tensorflow 提供的函数进行运算
# c_t = a_t + b_t
c_t = tf.add(a_t, b_t)
print("tensorflow实现加法运算:\n", c_t)
# 开启会话
# 传统的定义会话
sess = tf.Session()
sum_t = sess.run(c_t)
print("sum_t:\n", sum_t)
sess.close()
# 用上下文管理开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 同时执行多个tensor
print(sess.run([a_t, b_t, c_t]))
# 也可以用eval 查看值
print('用eval查看计算的值', a_t.eval())
print('会话的属性:\n', sess.graph)
2.3.1.2 初始化会话对象时的参数
- target:如果将此参数留空(默认设置),会话将仅使用本地计算机中的设备。可以指定grpc:/l网址,以便指定TensorFlow服务器的地址,这使得会话可以访问该服务器控制的计算机上的所有设备。
- graph:默认情况下,新的tf.Session将绑定到当前的默认图。
- config:此参数允许您指定一个tf.ConfigProto 以便控制会话的行为。例如,ConfigProto协议用于打印设备使用信息
示例
创建会话时使用config参数,用ConfigProto协议用于打印设备使用信息
def tensorflow_test():
"""
Tensorflow的基本结构
:return:
"""
# tensorflow加法运算
a_t = tf.constant(2)
b_t = tf.constant(3)
c_t = a_t + b_t
print("a_t:\n", a_t)
print("tensorflow加法运算的结果:\n", c_t)
# 开启会话
# with tf.Session() as sess # 2.0版本没有Session模块
# with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess: # 使用这个
# sess = tf.compat.v1.Session() # 或者使用这个
# 使用config参数,ConfigProto协议用于打印设备使用信息
with tf.compat.v1.Session(config=tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True,
log_device_placement=True)) as sess:
c_t_value = sess.run(c_t)
print("c_t_value:\n", c_t_value)
a_t:
Tensor("Const:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
tensorflow加法运算的结果:
Tensor("add:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
2021-09-08 20:58:45.944506: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:142] This TensorFlow binary is optimized with oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library (oneDNN) to use the following CPU instructions in performance-critical operations: AVX AVX2
To enable them in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.
2021-09-08 20:58:46.743283: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0 with 2778 MB memory: -> device: 0, name: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1050 Ti, pci bus id: 0000:01:00.0, compute capability: 6.1
2021-09-08 20:58:46.745709: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/direct_session.cc:361] Device mapping:
/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0 -> device: 0, name: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1050 Ti, pci bus id: 0000:01:00.0, compute capability: 6.1
2021-09-08 20:58:46.748970: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/placer.cc:114] add: (AddV2): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
2021-09-08 20:58:46.749642: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/placer.cc:114] Const: (Const): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
2021-09-08 20:58:46.750346: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/placer.cc:114] Const_1: (Const): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
add: (AddV2): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
Const: (Const): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
Const_1: (Const): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
c_t_value:
5
2.3.2 会话的run()
run(fetches, feed_dict=None, options=None, run_metadata=None)
- 通过使用 sess. run()来运行 operation
- fetches:单一的 operation,或者列表、元组(其它不属于tensorflow的类型不行)
- feed_dict:参数允许调用者覆盖图中张量的值,运行时赋值
- 与 tf.placeholder搭配使用,则会检查值的形状是否与占位符兼容。
使用tf.operation.eval()也可运行operation,但要在会话中运行
示例
同时打印a_t,b_t,c_t
def tensorflow_test():
"""
Tensorflow的基本结构
:return:
"""
# tensorflow加法运算
a_t = tf.constant(2)
b_t = tf.constant(3)
c_t = a_t + b_t
print("a_t:\n", a_t)
print("tensorflow加法运算的结果:\n", c_t)
# 开启会话
# with tf.Session() as sess # 2.0版本没有Session模块
# with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess: # 使用这个
# sess = tf.compat.v1.Session() # 或者使用这个
# 使用config参数,ConfigProto协议用于打印设备使用信息
with tf.compat.v1.Session(config=tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True,
log_device_placement=True)) as sess:
# c_t_value = sess.run(c_t)
# print("c_t_value:\n", c_t_value)
# 同时查看a_t,b_t,c_t
abc = sess.run([a_t, b_t, c_t])
print("abc:\n", abc)
结果:
a_t:
Tensor("Const:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
tensorflow加法运算的结果:
Tensor("add:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
2021-09-08 21:09:55.825888: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:142] This TensorFlow binary is optimized with oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library (oneDNN) to use the following CPU instructions in performance-critical operations: AVX AVX2
To enable them in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.
2021-09-08 21:09:56.792615: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1510] Created device /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0 with 1467 MB memory: -> device: 0, name: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1050 Ti, pci bus id: 0000:01:00.0, compute capability: 6.1
2021-09-08 21:09:56.795448: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/direct_session.cc:361] Device mapping:
/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0 -> device: 0, name: NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1050 Ti, pci bus id: 0000:01:00.0, compute capability: 6.1
2021-09-08 21:09:56.798106: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/placer.cc:114] add: (AddV2): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
2021-09-08 21:09:56.798696: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/placer.cc:114] Const: (Const): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
2021-09-08 21:09:56.799291: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/placer.cc:114] Const_1: (Const): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
add: (AddV2): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
Const: (Const): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
Const_1: (Const): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
abc:
[2, 3, 5]
2.3.3 feed操作
placeholder提供占位符,run时候通过feed_dict指定参数
可以理解为先声明一个变量,然后后面再赋值
placeholder提供占位符,run时候通过feed_dict指定参数
示例
feed操作
def session_run_demo():
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
sum_ab = tf.add(a, b)
print("sum_ab:", sum_ab)
# 开启会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
print('占位符结果:', sess.run(sum_ab, feed_dict={a: 3.0, b: 4.0}))
注意: 请注意运行时候报的错误eror
- Runtimeerror:如果这 Session是无效状态(例如已关闭)
- Typeerror:如果 fetches或者feed_d1ct键的类型不合适
- Valueerror:如果 fetches或feed_dict键无效或引用 Tensor不存在的键
2.4 张量Tensor
print()
ndarray
2.4.1 张量(Tensor)
标量:一个数字 0阶张量
向量:一维数组 [2, 3, 4] 1阶张量
矩阵:二维数组 [[2, 3, 4], [2, 3, 4]] 2阶张量
……
张量:n维数组 n阶张量
2.4.1.1 张量的类型
| 数据类型 | Python 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| DT_FLOAT | tf.float32 | 32 位浮点数. |
| DT_DOUBLE | tf.float64 | 64 位浮点数. |
| DT_INT64 | tf.int64 | 64 位有符号整型. |
| DT_INT32 | tf.int32 | 32 位有符号整型. |
| DT_INT16 | tf.int16 | 16 位有符号整型. |
| DT_INT8 | tf.int8 | 8 位有符号整型. |
| DT_UINT8 | tf.uint8 | 8 位无符号整型. |
| DT_STRING | tf.string | 可变长度的字节数组.每一个张量元素都是一个字节数组. |
| DT_BOOL | tf.bool | 布尔型. |
| DT_COMPLEX64 | tf.complex64 | 由两个32位浮点数组成的复数:实数和虚数. |
| DT_QINT32 | tf.qint32 | 用于量化Ops的32位有符号整型. |
| DT_QINT8 | tf.qint8 | 用于量化Ops的8位有符号整型. |
| DT_QUINT8 | tf.quint8 | 用于量化Ops的8位无符号整型. |
2.4.1.2 张量的阶
| 阶 | 数学实例 | python | 例子 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 纯量 | 只有大小 | s=123 |
| 1 | 向量 | 大小和方向 | v = [1,2] |
| 2 | 矩阵 | 数据表 | m= [[1,2],[3,4],[5,6]] |
| 3 | 3阶张量 | 数据立体 | … |
| n | n阶 |
示例
def tensor_demo():
"""
张量的演示
:return:
"""
tensor1 = tf.compat.v1.constant(4.0)
tensor2 = tf.compat.v1.constant([1, 2, 3, 4])
linear_squares = tf.constant([[4], [9], [16], [25]], dtype=tf.int32)
print("tensor1:\n", tensor1)
print("tensor2:\n", tensor2)
print("linear_squares_before:\n", linear_squares)
结果;
tensor1:
Tensor("Const:0", shape=(), dtype=float32)
tensor2:
Tensor("Const_1:0", shape=(4,), dtype=int32)
linear_squares_before:
Tensor("Const_2:0", shape=(4, 1), dtype=int32)
创建张量的时候
- 如果不指定类型,默认 tf.float32
- 整型 tf.int32
- 浮点型 tf.float32
2.4.2 创建张量的指令
2.4.2.1. 固定值张量
tf.zeros(shape, dtype=tf.float32, name=None)
创建所有元素设置为零的张量。此操作返回一个dtype具有形状shape和所有元素设置为零的类型的张量。
tf.zeros_like(tensor, dtype=None, name=None)
给tensor定单张量(),此操作返回tensor与所有元素设置为零相同的类型和形状的张量。
tf.ones(shape, dtype=tf.float32, name=None)
创建一个所有元素设置为1的张量。此操作返回一个类型的张量,dtype形状shape和所有元素设置为1。
tf.ones_like(tensor, dtype=None, name=None)
给tensor定单张量(),此操作返回tensor与所有元素设置为1相同的类型和形状的张量。
tf.fill(dims, value, name=None)
创建一个填充了标量值的张量。此操作创建一个张量的形状dims并填充它value。
tf.constant(value, dtype=None, shape=None, name=‘Const’)
创建一个常数张量。
2.4.2.2. 随机值张量
一般我们经常使用的随机数函数Math.random() 产生的是服从均匀分布的随机数,能够模拟等概率出现的况,例如扔一个骰子,1到6点的概率应该相等,但现实生活中更多的随机现象是符合正态分布的,例如20岁成年人的体重分布等。
假如我们在制作一个游戏,要随机设定许许多多NPC的身高,如果还用Math.random(),生成从140到22之间的数字,就会发现每个身高段的人数是一样多的,这是比较无趣的,这样的世界也与我们习惯不同,玛实应该是特别高和特别矮的都很少,处于中间的人数最多,这就要求随机函数符合正态分布。
tf.truncated_normal[shape, mean=0.0, stddev=1.0, ctype=tf.float32, seed=None, name=None)
从截断的正态分布中输出随机值,和 tf.random_normal)一样,但是所有数字都不超过两个标准差
tf.random_normal(shape, mean=0.0, stddev=1.0, dtype=tf.float32,seed=None, name=None)
从正态分布中输出随机值,由随机正态分布的数字组成的矩阵
其它特殊的创建张量的op
- tf.Variable
- tf.placeholder
2.4.3 张量的变换
- ndarray属性的修改
类型的修改- 1)ndarray.astype(type)
tf.cast(tensor, dtype)
不会改变原始的tensor
返回新的改变类型后的tensor - 2)ndarray.tostring()
- 1)ndarray.astype(type)
- 形状的修改
- 1)ndarray.reshape(shape)
- -1 自动计算形状
- 2)ndarray.resize(shape)
- 1)ndarray.reshape(shape)
2.4.3.1 类型改变
改变张量中数值类型的函数:
- tf.string_to_number(string_tensor, out_type=None, name=None)
- tf.to_double(x, name=‘ToDouble’)
- tf.to_float(x, name=‘ToFloat’)
- tf.to_bfloat16(x, name=‘ToBFloat16’)
- tf.to_int32(x, name=‘Tolnt32’)
- tf.to_int64(x, name=‘Tolnt64’)
- tf.cast(x, dtype, name=None)
2.4.3.2 形状改变
TensorFlow的张量具有两种形状变换,动态形状和静态形状
- tf.reshape
- tf.set_shape
静态形状——初始创建张量时的形状
关于动态形状和静态形状必须符合以下规则
-
静态形状
转换静态形状的时候,1-D到1-D,2-D到2-D,不能跨阶数改变形状(比如原来形状是[None,None],可以改成[3,4],不能改成[2,2,2])
对于已经固定的张量的静态形状的张量,不能再次设置静态形状 -
动态形状
tf.reshape()动态创建新张量时,张量的元素个数必须匹配 -
1)如何改变静态形状
tensor.set_shape(shape)
只有在形状没有完全固定下来的情况下才可以改变/更新静态形状 -
2)如何改变动态形状
tf.reshape(tensor, shape)
不会改变原始的tensor
返回新的改变形状后的tensor
动态创建新张量时,张量的元素个数必须匹配
示例
- 修改张量静态形状
def tensor_demo():
"""
张量的演示
:return:
"""
tensor1 = tf.compat.v1.constant(4.0)
tensor2 = tf.compat.v1.constant([1, 2, 3, 4])
linear_squares = tf.constant([[4], [9], [16], [25]], dtype=tf.int32)
# print("tensor1:\n", tensor1)
# print("tensor2:\n", tensor2)
# print("linear_squares_before:\n", linear_squares)
# 张量类型的修改
l_cast = tf.cast(linear_squares, dtype=tf.float32)
print("linear_squares:\n", linear_squares)
print("l_cast:\n", l_cast)
# 更新/改变静态形状
# 定义占位符
# 没有完全固定下来的静态形状
a_p = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, None])
b_p = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, 10])
# 已经固定的静态形状
c_p = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[3, 2])
print('a_p静态形状:', a_p.get_shape())
print('b_p静态形状:', b_p.get_shape())
print('c_p静态形状:', c_p.get_shape())
# 形状更新
a_p.set_shape([2, 3])
# 静态形状已经固定部分就不能修改了
b_p.set_shape([3, 10])
print('a_p修改后的静态形状:', a_p.get_shape())
print('b_p修改后的静态形状:', b_p.get_shape())
# 已经固定部分就不能修改
# c_p.set_shape([2, 3]) # 会报错
# print('c_p修改后的静态形状:', c_p.get_shape()) # 会报错
- 修改张量动态形状
c_p = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[3, 2, 3])
print('c_p静态形状:', c_p.get_shape())
# 形状更新
new_c_p = tf.reshape(c_p, shape=[3, 3, 2])
print('c_p更新后的静态形状:', c_p.get_shape())
print('new_c_p的静态形状:', new_c_p.get_shape())
2.4.4 张量的数学运算
- 算术运算符
- 基本数学函数
- 矩阵运算
- reduce操作
- 序列索引操作
详细请参考: TensorFlow Core v2.6.0
这些API使用,我们在使用的时候介绍,具体参考文档
2.5 变量OP
TensorFlow变量是表示程序处理的共享持久状态的最佳方法。变量通过tf.VariableOP类进行操作。变量的特点∶
- 存储持久化
- 可修改值
- 可指定被训练
变量用来保存深度学习的模型参数
2.5.1 创建变量
tf.Variable(initial_value=None,trainable=True,collections=None,name=None)
- initial_value:初始化的值
- trainable:是否被训练
- collections:新变量将添加到列出的图的集合中collections,默认为[GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES],如果trainable是True变量也被添加到图形集合GraphKeys.TRA INABLE_VARIABLES
- 变量需要显式初始化,才能运行值
示例
def varibal_demo():
"""
变量的演示
:return:
"""
# 创建变量
a = tf.Variable(initial_value=50)
b = tf.Variable(initial_value=40)
c = tf.add(a, b)
print("a:\n", a)
print("b:\n", b)
print("c:\n", c)
# 初始化变量
init = tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer() # 变量需要显式初始化,才能运行值
with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
# 运行初始化
sess.run(init)
a_value, b_value, c_value = sess.run([a, b, c])
print("a_value:\n", a_value)
print("b_value:\n", b_value)
print("c_value:\n", c_value)
2.5.2 使用tf.variable_scope()修改变量的命名空间
会在OP的名字前面增加命名空间的指定名字,使得结构更加清晰
示例
创建一个命名空间
# 创建变量
with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("my_scope"): # 创建一个命名空间
a = tf.Variable(initial_value=50)
b = tf.Variable(initial_value=40)
c = tf.add(a, b)
print("a:\n", a)
print("b:\n", b)
print("c:\n", c)
结果:
原来

现在

2.6 API
关于 Tensorflow的API图示
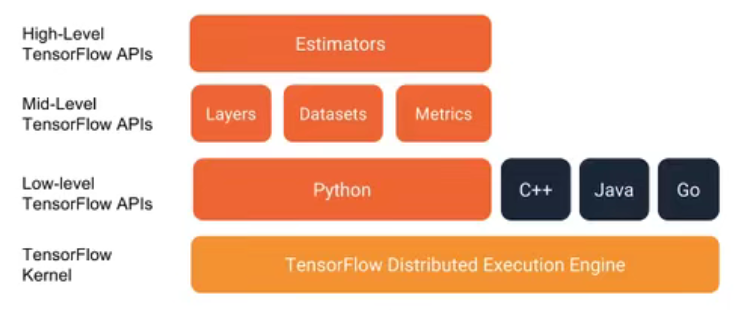
2.6.1 基础API
tf.app
这个模块相当于为TensorFlow进行的脚本提供一个main 函数入口,可以定义脚本运行的 flags。
tf.image
TensorFlow的图像处理操作。主要是一些颜色变换、变形和图像的编码和解码。
tf.gfile
提供文件操作模块
tf.summary
用来生成TensorBoard可用的统计日志,目前Summary主要提供了4种类型;audio、image、histogram.scalar
tf.python_io
用来读写TFRecords文件
tf.train
这个模块提供了一些训练器,与tf.nn组合起来,实现一些网络的优化计算。 tf.nn
这个模块提供了一些构建神经网络的底层函数。TensorFlow构建网络的核心模块。其中包含了添加各种层的函数,比如添加卷积层、池化层等。
2.6.2 高级API
tf.keras
Keras本来是一个独立的深度学习库,tensorflow将其学习过来,增加这部分模块在于快速构建模型。
tf.layers
高级API,以更高级的概念层来定义一个模型。尖似tf.Keras
tf.contrib
tf.contrib.layers提供够将计算图中的网络层、正则化、摘要操作、是构建计算图的高级操作,但是tf.contrib包含不稳定和实验代码,有可能以后API会改变。
tf.estimator
一个Estimator相当于Model + Training + Evaluate 的合体。在模块中,已经实现了几种简单的分类器和回归器,包括:Baseline,Learning 和 DNN。这里的 DNN的网络,只是全连接网络,没有提供卷积之类的。
2.7 案例:实现线性回归
2.7.1 线性回归原理复习
- 1)构建模型
y = w 1 x 1 + w 2 x 2 + … … + w n x n + b y = w_1x_1 + w_2x_2 + …… + w_nx_n + b y=w1?x1?+w2?x2?+……+wn?xn?+b - 2)构造损失函数
均方误差 - 3)优化损失
梯度下降
2.7.2 案例:实现线性回归的训练
案例确定
- 准备真实数据
100样本
x 特征值 形状 (100, 1)
y_true 目标值 (100, 1)
y_true = 0.8x + 0.7 - 假定x 和 y 之间的关系 满足
y = kx + b
k ≈ 0.8 b ≈ 0.7
API
运算
- 矩阵运算
tf.matmul(x, w) - 平方
tf.square(error) - 均值
tf.reduce_mean(error)
梯度下降优化
- tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate)
梯度下降优化 - learning_rate:学习率,一般为0~1之间比较小的值
- method:
- minimize(loss)
- return:梯度下降op
流程分析
(
100
,
1
)
?
(
1
,
1
)
=
(
100
,
1
)
(100, 1) * (1, 1) = (100, 1)
(100,1)?(1,1)=(100,1)
y
_
p
r
e
d
i
c
t
=
x
?
w
e
i
g
h
t
s
(
1
,
1
)
+
b
i
a
s
(
1
,
1
)
y\_predict = x * weights(1, 1) + bias(1, 1)
y_predict=x?weights(1,1)+bias(1,1)
- 1)构建模型
y_predict = tf.matmul(x, weights) + bias
- 2)构造损失函数
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict - y_true))
- 3)优化损失
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(error)
5 学习率的设置、步数的设置与梯度爆炸
示例
自实现一个线性回归
def linear_regression():
"""
自实现一个线性回归
:return:
"""
# 1.准备数据
x = tf.compat.v1.random_normal(shape=[100, 1])
y_true = tf.matmul(x, [[0.8]]) + 0.7
# 2.构造模型
# 定义模型参数用变量
weight = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.compat.v1.random_normal(shape=[1, 1])) # 先使用随机值对weight进行初始化
bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.compat.v1.random_normal(shape=[1, 1])) # 先使用随机值对bias进行初始化
y_predict = tf.matmul(x, weight) + bias
# 3.构造损失函数
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict - y_true))
# 4.优化损失
optimizer = tf.compat.v1.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(error)
# 显式地初始化变量
init = tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()
# 开启会话
with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
# 初始化变量
sess.run(init)
# 查看初始化模型参数之后的值
print("训练前模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失%f" % (weight.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
# 开始训练
for i in range(1000):
sess.run(fetches=optimizer)
print("第%d次训练后模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失%f" % (i+1, weight.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
# 查看初始化模型参数之后的值
print("训练后模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失%f" % (weight.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
结果:
训练前模型参数为:权重-1.970245,偏置-1.167298,损失12.787583
第1次训练后模型参数为:权重-1.900054,偏置-1.120071,损失8.568954
第2次训练后模型参数为:权重-1.845930,偏置-1.085134,损失10.069593
第3次训练后模型参数为:权重-1.801681,偏置-1.054058,损失8.939274
第4次训练后模型参数为:权重-1.734405,偏置-1.007101,损失11.473066
第5次训练后模型参数为:权重-1.679682,偏置-0.980237,损失9.313668
第6次训练后模型参数为:权重-1.619766,偏置-0.943636,损失8.337710
第7次训练后模型参数为:权重-1.570481,偏置-0.905890,损失9.915030
第8次训练后模型参数为:权重-1.524673,偏置-0.874753,损失8.296886
第9次训练后模型参数为:权重-1.477295,偏置-0.834806,损失7.259823
第10次训练后模型参数为:权重-1.422785,偏置-0.804612,损失7.320126
......
第1000次训练后模型参数为:权重0.799999,偏置0.699999,损失0.000000
训练后模型参数为:权重0.799999,偏置0.699999,损失0.000000
学习率的设置、步数的设置与梯度爆炸
学习率越大,训练到较好结果的步数越小;学习率越小,训练到较好结果的步数越大。
但是学习过大会出现梯度爆炸现象。关于梯度爆炸/梯度消失?
在极情况下,权重的值变得非常大,以至于滋出,导致NaN值
如何解决梯度爆炸问题(深度神经网络当中更容易出现)
- 重新设计网络
- 调整学习率
- 使用梯度載断(在训练过程中检查和限制度的大小
- 使用激活函数
变量的 trainable设置观察
trainable的参数作用,指定是否训练
weights = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal(shape=[1, 1]), name='weight',trainable=False)
2.7.3 增加其他功能
- 变量Tensorboard显示
- 增加命名空间
- 模型保存和加载
- 命令行参数设置
2.7.3.1 增加变量显示
目的:在TensorBoard当中观察模型的参数、损失值等变量值的变化。
- 收集变量
- tf.summary.scalar(name=",tensor)收集对于损失函数和准确率等单值变量,name为变量的名字,tensor为值
- tf.summary.histogram(name=",tensor)收集高维度的变量参数
tf.summary.image(name=",tensor)收集输入的图片张量能显示图片
- 合并变量写入事件文件
- merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
- 运行合并: summary = sess.run(merged),每次迭代都需运行
- 添加:FileWriter.add_summary(summary,i),i表示第几次的值
增加变量显示具体步骤:
1)创建事件文件
2)收集变量
3)合并变量
4)每次送代运行一次合并变量
5)每次送代将 summary:对象写入事件文件
示例
增加了变量显示
def linear_regression():
"""
自实现一个线性回归
:return:
"""
# 1.准备数据
x = tf.compat.v1.random_normal(shape=[100, 1])
y_true = tf.matmul(x, [[0.8]]) + 0.7
# 2.构造模型
# 定义模型参数用变量
weight = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.compat.v1.random_normal(shape=[1, 1])) # 先使用随机值对weight进行初始化
bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.compat.v1.random_normal(shape=[1, 1])) # 先使用随机值对bias进行初始化
y_predict = tf.matmul(x, weight) + bias
# 3.构造损失函数
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict - y_true))
# 4.优化损失
optimizer = tf.compat.v1.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(error)
# 2_收集变量
tf.compat.v1.summary.scalar("error", error)
tf.compat.v1.summary.histogram("weight", weight)
tf.compat.v1.summary.histogram("bias", bias)
# 3_合并变量
merged = tf.compat.v1.summary.merge_all()
# 显式地初始化变量
init = tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()
# 开启会话
with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
# 初始化变量
sess.run(init)
# 1_创建事件文件
file_writer = tf.compat.v1.summary.FileWriter("../linear", graph=sess.graph)
# 查看初始化模型参数之后的值
print("训练前模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失%f" % (weight.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
# 开始训练
for i in range(1000):
sess.run(fetches=optimizer)
print("第%d次训练后模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失%f" % (i+1, weight.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
# 运行合并变量操作
summary = sess.run(merged)
# 将每次迭代后的变量写入事件文件
file_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
# 查看初始化模型参数之后的值
print("训练后模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失%f" % (weight.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
结果:
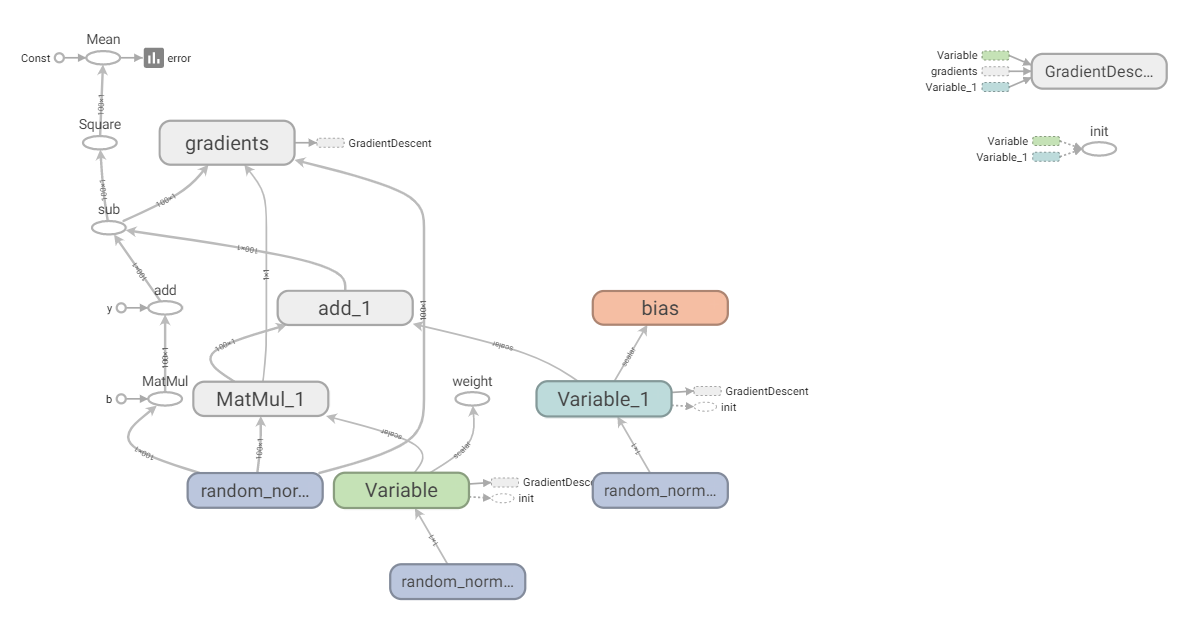
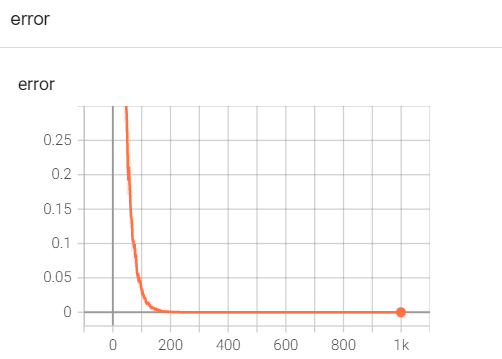
注意:
- 2.0版本的虽然tf有summar.scalar方法,但是与tf.compat.v1.summary.scalar(“error”, error)的参数类型不一样。按照上面示例来写会出现TypeError: Fetch argument None has invalid type <class ‘NoneType’>。
2.7.3.2 增加命名空间
使代码结构更加清晰,Tensorboard图结构清楚
例如:with tf.variable_scope( “lr_model”" ):
增加命名空间具体步骤:
1)实例化Saver
2)保存
saver.save(sess, path)
3)加载
saver.restore(sess, path)
示例
增加命名空间
def linear_regression():
"""
自实现一个线性回归
:return:
"""
with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("prepare_data"):
# 1.准备数据
x = tf.compat.v1.random_normal(shape=[100, 1])
y_true = tf.matmul(x, [[0.8]]) + 0.7
with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("creat_model"):
# 2.构造模型
# 定义模型参数用变量
weight = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.compat.v1.random_normal(shape=[1, 1])) # 先使用随机值对weight进行初始化
bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.compat.v1.random_normal(shape=[1, 1])) # 先使用随机值对bias进行初始化
y_predict = tf.matmul(x, weight) + bias
with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("loss_function"):
# 3.构造损失函数
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_predict - y_true))
with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("optimizer"):
# 4.优化损失
optimizer = tf.compat.v1.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(error)
# 2_收集变量
tf.compat.v1.summary.scalar("error", error)
tf.compat.v1.summary.histogram("weight", weight)
tf.compat.v1.summary.histogram("bias", bias)
# 3_合并变量
merged = tf.compat.v1.summary.merge_all()
# 显式地初始化变量
init = tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()
# 开启会话
with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
# 初始化变量
sess.run(init)
# 1_创建事件文件
file_writer = tf.compat.v1.summary.FileWriter("../linear", graph=sess.graph)
# 查看初始化模型参数之后的值
print("训练前模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失%f" % (weight.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
# 开始训练
for i in range(1000):
sess.run(fetches=optimizer)
print("第%d次训练后模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失%f" % (i+1, weight.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))
# 运行合并变量操作
summary = sess.run(merged)
# 将每次迭代后的变量写入事件文件
file_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
# 查看初始化模型参数之后的值
print("训练后模型参数为:权重%f,偏置%f,损失%f" % (weight.eval(), bias.eval(), error.eval()))

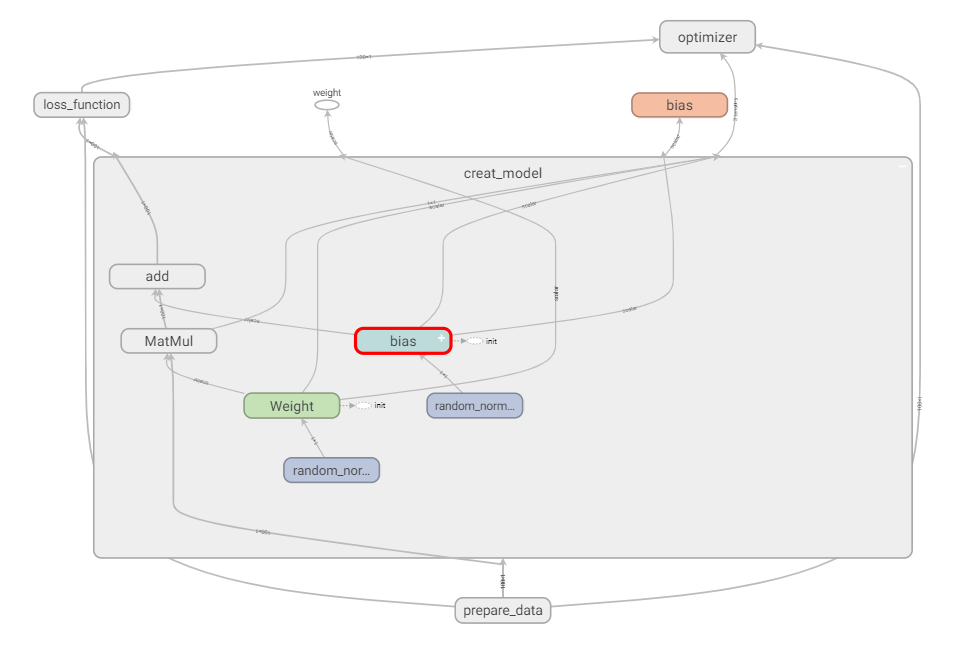
修改指令名称
with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("prepare_data"):
# 1.准备数据
x = tf.compat.v1.random_normal(shape=[100, 1], name="feature")
y_true = tf.matmul(x, [[0.8]]) + 0.7
with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("creat_model"):
# 2.构造模型
# 定义模型参数用变量
weight = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.compat.v1.random_normal(shape=[1, 1]), name="Weight") # 先使用随机值对weight进行初始化
bias = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.compat.v1.random_normal(shape=[1, 1]), name="bias") # 先使用随机值对bias进行初始化
y_predict = tf.matmul(x, weight) + bias
图结构变得更清晰
2.7.3.3 模型的保存与加载
tf.train.Saver(var_list=None,max_to_keep=5)
保存和加载模型(保存文件格式: checkpoint文件)
- var_list:指定将要保存和还原的变量。它可以作为一个dict或一个列表传递.
- max_to_keep:指示要保留的最近检查点文件的最大数量。创建新文件时,会删除较旧的文件。如果无或0,则保留所有检查点文件。默认为 5(即保留最新的5个检查点文件。)
例如:
保存与加载(指定目录+模型名字)
saver.save(sess,' /tmp/ckpt/test/myregression.ckpt ')
saver.restore(sess,'/tmp/ckpt/test/myregression.ckpt ' )
如要判断模型是否存在,直接指定目录
checkpoint =tf.train.latest_checkpoint("/tmp/model/")
saver.restore(sess, checkpoint)
模型的保存与加载具体步骤:
1)实例化Saver
2)保存
saver.save(sess, path)
3)加载
saver.restore(sess, path)
示例
在会话中保存模型
# 保存模型
if i % 10 == 0:
saver.save(sess, "../model/my_linear.ckpt")
加载模型
# 加载模型
if os.path.exists("../model/checkpoint"): # 确定文件是否存在
saver.restore(sess, "../model/my_linear.ckpt")
2.7.3.4 命令行参数使用
-
tf.app.flags,它支持应用从命令行接受参数,可以用来指定集群配置等。在tf.app.flags下面有各种定义参数的类型
- DEFINE_string(flag_name, default_value, docstring)
- DEFINE_integer(flag_name, default_value, docstring)
- DEFINE_boolean(flag_name, default_value, docstring)
- DEFINE_float(flag_name, default_value,docstring)
-
tf.app.flags,在flags有一个FLAGS标志,它在程序中可以调用到我们前面定义的flag_name
-
通过tf.app.run() 启动main 函数。
示例
import tensorflow as tf
# 1)定义命令行参数
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer("max_step", 100, "训练模型的步数")
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string("model_dir", "Unknown", "模型保存的路径+模型名字")
# 2)简化变量名
FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS
def command_demo():
"""
命令行参数演示
:return:
"""
print("max_step:\n", FLAGS.max_step)
print("model_dir:\n", FLAGS.model_dir)
return None
def main(argv):
print(argv)
if __name__ == '__main__':
command_demo()
tf.app.run() # 会调用main函数,argv 为本文件的路径
命令行里执行
python 03-命令行参数.py --max_step=3 --model-dir=hello
结果:
max_step:
3
model_dir:
hello
['03-命令行参数.py']
注意:
- 通过tf.app.run()*启动main 函数时,main函数里要写参数argv。argv实际上就是.py文件的路径。
TensorFlow框架的使用总结
数据读取、神经网络
有三种获取数据到TensorFlow程序的方法:
- QueueRunner:基于队列的输入管道从TensorFlow图形开头的文件中读取数据。
- Feeding:运行每一步时,Python代码提供数据。
- 预加载数据:TensorFlow图中的张量包含所有数据(对于小数据集)。
3.1 文件读取流程
多线程 + 队列
3.1.1 文件读取流程

- 第一阶段:构造文件名队列
- 第二阶段:读取与解码
- 第三阶段:批处理
- 注:这些操作需要启动运行这些队列操作的线程,以便我们在进行文件读取的过程中能够顺利进行入队出队操作。
3.1.1.1 构造文件名队列
file_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(string_tensor,shuffle=True)
3.1.1.2 读取与解码
文本:
读取:tf.TextLineReader()
解码:tf.decode_csv()
图片:
读取:tf.WholeFileReader()
解码:
tf.image.decode_jpeg(contents)
tf.image.decode_png(contents)
二进制:
读取:tf.FixedLengthRecordReader(record_bytes)
解码:tf.decode_raw()
TFRecords
读取:tf.TFRecordReader()
key, value = 读取器.read(file_queue)
key:文件名
value:一个样本
3.1.1.3 批处理队列
tf.train.batch(tensors, batch_size, num_threads = 1, capacity = 32, name=None)
手动开启线程
tf.train.QueueRunner()
开启会话:
tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=None, coord=None)
3.2 图片数据
3.2.1 图像基本知识
文本 特征词 -> 二维数组
字典 one-hot -> 二维数组
图片 像素值
1 图片三要素
黑白图、灰度图
一个通道
黑[0, 255]白
彩色图
三个通道
一个像素点 三个通道值构成
R [0, 255]
G [0, 255]
B [0, 255]
2 TensorFlow中表示图片
Tensor对象
指令名称、形状、类型
shape = [height, width, channel]
3 图片特征值处理
[samples, features]
为什么要缩放图片到统一大小?
1)每一个样本特征数量要一样多
2)缩小图片的大小
tf.image.resize_images(images, size)
4 数据格式
存储:uint8
训练:float32
3.2.4 案例:狗图片读取
1)构造文件名队列
file_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(string_tensor,shuffle=True)
2)读取与解码
读取:
reader = tf.WholeFileReader()
key, value = reader.read(file_queue)
解码:
image_decoded = tf.image.decode_jpeg(value)
3)批处理队列
image_decoded = tf.train.batch([image_decoded], 100, num_threads = 2, capacity=100)
手动开启线程
3.3 二进制数据
tensor对象
shape:[height, width, channel] -> [32, 32, 3] [0, 1, 2] -> []
[[32 * 32的二维数组],
[32 * 32的二维数组],
[32 * 32的二维数组]]
--> [3, 32, 32] [channel, height, width] 三维数组的转置 [0, 1, 2] -> [1, 2, 0]
[3, 2] -转置-> [2, 3]
1)NHWC与NCHW
T = transpose 转置
3.3.2 CIFAR10 二进制数据读取
流程分析:
1)构造文件名队列
2)读取与解码
3)批处理队列
开启会话
手动开启线程
3.4 TFRecords
3.4.1 什么是TFRecords文件
3.4.2 Example结构解析
cifar10
特征值 - image - 3072个字节
目标值 - label - 1个字节
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
"image":tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train. BytesList(value=[image])
"label":tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train. Int64List(value=[label]))
}))
example.SerializeToString()
3.4.3 案例:CIFAR10数据存入TFRecords文件
流程分析
3.4.4 读取TFRecords文件API
1)构造文件名队列
2)读取和解码
读取
解析example
feature = tf.parse_single_example(value, features={
"image":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
"label":tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64)
})
image = feature["image"]
label = feature["label"]
解码
tf.decode_raw()
3)构造批处理队列
3.5 神经网络基础
3.5.1 神经网络
输入层
特征值和权重 线性加权
y = w1x1 + w2x2 + …… + wnxn + b
细胞核-激活函数
sigmoid
sign
隐藏层
输出层
单个神经元 - 感知机
感知机(PLA: Perceptron Learning Algorithm))
x1, x2
w1x1 + w2x2 + b = 常数
w2x2 = -w1x1 - b + 常数
x2 = kx1 + b
x2 = kx1 + b
x1 x2
与问题
0 0 0
0 1 0
1 0 0
1 1 1
异或问题
0 0 0
0 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 0
单个神经元不能解决一些复杂问题
1)多层神经元
2)增加激活函数
3.6 神经网络原理
逻辑回归
y = w1x1 + w2x2 + …… + wnxn + b
sigmoid -> [0, 1] -> 二分类问题
损失函数:对数似然损失
用神经网络进行分类
假设函数
y_predict =
softmax - 多分类问题
构造损失函数
loss = 交叉熵损失
优化损失
梯度下降
3.6.1 softmax回归 - 多分类问题
假设要进行三分类
2.3, 4.1, 5.6
3.6.2 交叉熵损失
3.7 案例:Mnist手写数字识别
3.7.1 数据集介绍
1 特征值
[None, 784] * W[784, 10] + Bias = [None, 10]
构建全连接层:
y_predict = tf.matmul(x, W) + Bias
构造损失:
loss = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_true, logits=y_predict,name=None)
如何计算准确率?
np.argmax(y_predict, axis=1)
tf.argmax(y_true, axis=1)
y_predict [None, 10]
y_true [None, 10]
tf.equal()
如何提高准确率?
1)增加训练次数
2)调节学习率
3)调节权重系数的初始化值
4)改变优化器