一般来说,二维卷积nn.Conv2d用于图像数据,对宽度和高度都进行卷积
Conv2d 参数详解
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode=‘zeros’, device=None, dtype=None)
Parameters
in_channels (int) – Number of channels in the input image 输入通道 例如输入RGB图形 则为3
out_channels (int) – Number of channels produced by the convolution 输出通道,例如有6个卷积核,则输出为6
kernel_size (int or tuple) – Size of the convolving kernel 卷积核大小,例如(3,3)
stride (int or tuple, optional) – Stride of the convolution. Default: 1 步长
padding (int, tuple or str, optional) – Padding added to all four sides of the input. Default: 0 填充
padding_mode (string, optional) – 'zeros', 'reflect', 'replicate' or 'circular'. Default: 'zeros'
dilation (int or tuple, optional) – Spacing between kernel elements. Default: 1 膨化或者扩张
groups (int, optional) – Number of blocked connections from input channels to output channels. Default: 1
bias (bool, optional) – If True, adds a learnable bias to the output. Default: True
 MaxPool2d 参数详解
MaxPool2d 参数详解
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size, stride=None, padding=0, dilation=1, return_indices=False, ceil_mode=False)
Parameters
kernel_size – the size of the window to take a max over 池化窗口大小,如(2,2)
stride – the stride of the window. Default value is kernel_size 步长(默认与卷积步长一致)
padding – implicit zero padding to be added on both sides
dilation – a parameter that controls the stride of elements in the window
return_indices – if True, will return the max indices along with the outputs. Useful for torch.nn.MaxUnpool2d later
ceil_mode – when True, will use ceil instead of floor to compute the output shape
代码示例
假设现有大小为32 x 32的图片样本,输入样本的channels为1,该图片可能属于10个类中的某一类。CNN框架定义如下:
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
nn.Model.__init__(self)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5) # 输入通道数为1,输出通道数为6
# self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), dilation=1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5) # 输入通道数为6,输出通道数为16
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(5 * 5 * 16, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# 输入x -> conv1 -> relu -> 2x2窗口的最大池化
x = self.conv1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
# 输入x -> conv2 -> relu -> 2x2窗口的最大池化
x = self.conv2(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
# view函数将张量x变形成一维向量形式,总特征数不变,为全连接层做准备
x = x.view(x.size()[0], -1)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
网络整体结构:[conv + relu + pooling] * 2 + FC * 3
原始输入样本的大小:32 x 32 x 1
第一次卷积:使用6个大小为5 x 5的卷积核,故卷积核的规模为(5 x 5) x 6;卷积操作的stride参数默认值为1 x 1,32 - 5 + 1 = 28,并且使用ReLU对第一次卷积后的结果进行非线性处理,输出大小为28 x 28 x 6;
第一次卷积后池化:kernel_size为2 x 2,输出大小变为14 x 14 x 6;
第二次卷积:使用16个卷积核,故卷积核的规模为(5 x 5 x 6) x 16;使用ReLU对第二次卷积后的结果进行非线性处理,14 - 5 + 1 = 10,故输出大小为10 x 10 x 16;
第二次卷积后池化:kernel_size同样为2 x 2,输出大小变为5 x 5 x 16;
第一次全连接:将上一步得到的结果铺平成一维向量形式,5 x 5 x 16 = 400,即输入大小为400 x 1,W大小为120 x 400,输出大小为120 x 1;
第二次全连接,W大小为84 x 120,输入大小为120 x 1,输出大小为84 x 1;
第三次全连接:W大小为10 x 84,输入大小为84 x 1,输出大小为10 x 1,即分别预测为10类的概率值。
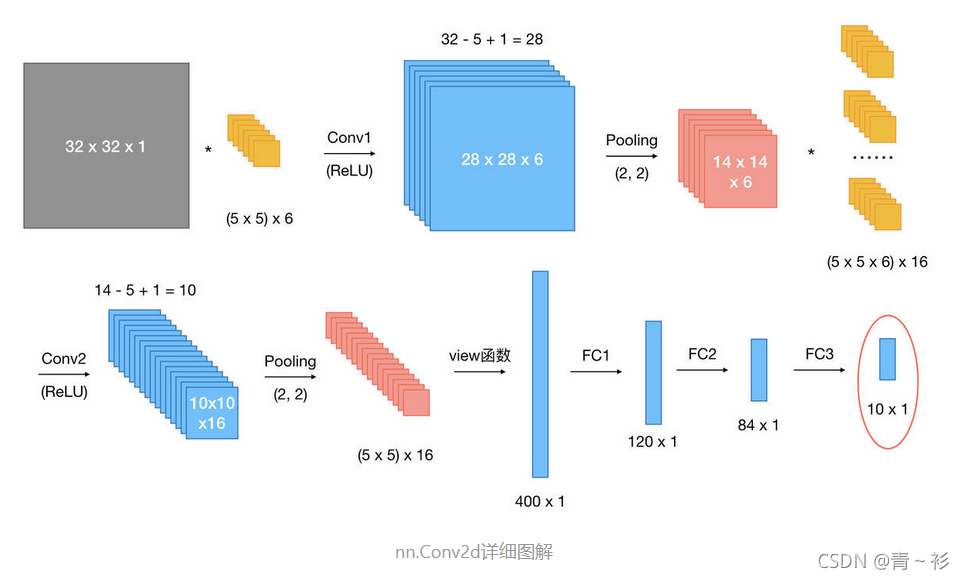
(图片来源)https://www.jianshu.com/p/45a26d278473
注意
在PyTorch中,池化操作默认的stride大小与卷积核的大小一致;
如果池化核的大小为一个方阵,则仅需要指明一个数,即kernel_size参数为常数n,表示池化核大小为n x n。
本文参考 链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/45a26d278473