k k k近邻法介绍与算法
参考文献:【KNN算法原理以及代码实现】,【KNN算法原理及实现】,【python 实现KNN算法】
1. 综述
k k k近邻法( k ? n e a r e s t ? n e i g h b o r , K N N k-nearest \ neighbor,KNN k?nearest?neighbor,KNN)是一种基本分类与回归方法。
- 输入:实例的特征向量,对应于特征空间的点;
- 输出:实例的类别,可以取多类。
k
k
k近邻法假设给定一个训练数据集,其中的实例类别已定。分类时,对新的实例,根据其
k
k
k最近邻的训练实例的类别,通过多数表决等方式进行预测。
k
k
k近邻法实际上利用训练数据集对特征向量空间进行划分,并作为其分类的”模型“。
k近邻法的三个基本要素:
- k k k值的选择
- 距离度量
- 分类决策规则
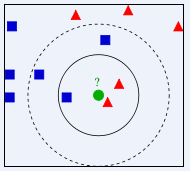
形象解释:
比如一个一定范围的平面随机分布着两种颜色的样本点,在这个平面内有个实例点不知道它是什么颜色,因此通过它周边的不同颜色的点分布情况进行推测,假设取
k
=
3
k=3
k=3,意思是在离这个实例点最近的样本点中去前三个最近的, 然后看这三个当中那种类别占比大,就判断该实例点属于那个类别的,当
k
=
5
k=5
k=5的时候也一样这样判断,因此
k
k
k的取值很关键,通常不会超过20。当然,因为每个样本有多个特征,因此实际工作中,这个平面就是三维甚至是多维的,道理是一样的。
2. 算法
k
k
k近邻算法的一大优点是简单、直观:
给定一个训练数据集,对新的输入实例,在训练数据集中找到与该实例最邻近的
k
k
k个实例,这
k
k
k个实例的多数属于某个类,就把该输入实例分为这个类。
2.1 标准解释
输入:训练数据集
T
=
{
(
x
1
,
y
1
)
,
(
x
2
,
y
2
)
,
.
.
.
,
(
x
N
,
y
N
)
}
(1)
T=\{(x_1,y_1),(x_2,y_2),...,(x_N,y_N)\} \tag 1
T={(x1?,y1?),(x2?,y2?),...,(xN?,yN?)}(1)
其中, x i ∈ χ ? R n x_i \in \chi \subseteq R^n xi?∈χ?Rn为实例的特征向量, y i ∈ γ = { c 1 , c 2 , . . . , c K } y_i \in \gamma = \{c_1,c_2,...,c_K\} yi?∈γ={c1?,c2?,...,cK?}为实例的类别, i = 1 , 2 , . . . , N i=1,2,...,N i=1,2,...,N;实例特征向量 x x x;
输出:实例 x x x所属的类 y y y。
- 根据给定的距离度量,在训练集 T T T中找出与 x x x最近邻的 k k k个点,涵盖这 k k k个点的 x x x的领域记作 N k ( x ) N_k(x) Nk?(x);
- 在
N
k
(
x
)
N_k(x)
Nk?(x)中根据分类决策规则(如多数表决)决定
x
x
x的类别
y
y
y:
y = arg ? ? max ? c j ∑ x i ∈ N k ( x ) I ( y i = c j ) , i = 1 , 2 , . . . , N ; j = 1 , 2 , . . . , K (2) y=\arg \ \max_{c_j} \sum_{x_i \in N_k(x)} I(y_i=c_j),i=1,2,...,N;j=1,2,...,K \tag 2 y=arg?cj?max?xi?∈Nk?(x)∑?I(yi?=cj?),i=1,2,...,N;j=1,2,...,K(2)
式
(
2
)
(2)
(2)中,
I
I
I为指示函数,即当
y
i
=
c
j
y_i=c_j
yi?=cj?时
I
I
I为1,否则
I
I
I为0。
特殊情况:
当
k
=
1
k=1
k=1的情形,称为最近邻算法。对于输入的实例点(特征向量)
x
x
x,最近邻法将训练数据集中与
x
x
x最近邻的类作为
x
x
x的类。
2.2 形象解释
在训练集中数据和标签已知的情况下,输入测试数据,将测试数据的特征与训练集中对应的特征进行相互比较,找到训练集中与之最为相似的前 K K K个数据,则该测试数据对应的类别就是 K K K个数据中出现次数最多的那个分类,其算法的描述为:
- 计算测试数据与各个训练数据之间的距离;
- 按照距离的递增关系进行排序;
- 选取距离最小的 K K K个点;
- 确定前 K K K个点所在类别的出现频率;
- 返回前 K K K个点中出现频率最高的类别作为测试数据的预测分类。
2.3 优缺点以及改进
优缺点:
- 简单,易于理解,是一个天然的多分类器;
- 不需要庞大的样本数据也可以完成一个简单的分类;
- 不需要训练和求解参数(既是优点也是缺点);
- 数据量大的时候,计算量也非常大(样本多,特征多);
- 不平衡样本处理能力差;
- 并没有学习和优化的过程,严格来说不算是机器学习。
改进:
进行加权平均,离得近的样本给予更大的权重,离得远的样本使其权重变小。
3. 模型
k k k近邻法中,当训练集、距离度量、 k k k值及分类决策规则(如多数表决)确定后,对于任何一个新的输入实例,它所属的类唯一地确定。
3.1 距离度量
特征空间中两个实例点的距离是两个实例点相似程度的反映。
k
k
k近邻模型的特征空间一般是
n
n
n维实数向量空间
R
n
R^n
Rn。使用的距离欧氏距离,也可以是更一般的
L
p
L_p
Lp?距离(
L
p
L_p
Lp? distance)或(Minkowski distance)。
设特征空间
χ
\chi
χ是
n
n
n维实数向量空间
R
n
R^n
Rn,
x
i
,
x
j
∈
χ
,
x
i
=
(
x
i
(
1
)
,
x
i
(
2
)
,
.
.
.
,
x
i
(
n
)
)
T
x_i,x_j \in \chi,x_i=(x_i^{(1)},x_i^{(2)},...,x_i^{(n)})^T
xi?,xj?∈χ,xi?=(xi(1)?,xi(2)?,...,xi(n)?)T,
x
j
=
(
x
j
(
1
)
,
x
j
(
2
)
,
.
.
.
,
x
j
(
n
)
)
T
x_j=(x_j^{(1)},x_j^{(2)},...,x_j^{(n)})^T
xj?=(xj(1)?,xj(2)?,...,xj(n)?)T,
x
i
,
x
j
x_i,x_j
xi?,xj?的
L
p
L_p
Lp?距离定义为:
L
p
(
x
i
,
x
j
)
=
(
∑
l
=
1
n
∣
x
i
(
l
)
?
x
j
(
l
)
∣
p
)
1
p
(3)
L_p(x_i,x_j)=(\sum_{l=1}^{n} |x_i^{(l)}-x_j^{(l)}|^p)^{\frac{1}{p}} \tag 3
Lp?(xi?,xj?)=(l=1∑n?∣xi(l)??xj(l)?∣p)p1?(3)
这里
p
≥
1
p \geq 1
p≥1。
当
p
=
2
p=2
p=2时,称为欧氏距离(Euclidean distance),即:
L
2
(
x
i
,
x
j
)
=
(
∑
l
=
1
n
∣
x
i
(
l
)
?
x
j
(
l
)
∣
2
)
1
2
(4)
L_2(x_i,x_j)=(\sum_{l=1}^{n} |x_i^{(l)}-x_j^{(l)}|^2)^{\frac{1}{2}} \tag 4
L2?(xi?,xj?)=(l=1∑n?∣xi(l)??xj(l)?∣2)21?(4)
当
p
=
1
p=1
p=1时,称为曼哈顿距离(Manhattan distance),即:
L
1
(
x
i
,
x
j
)
=
∑
l
=
1
n
∣
x
i
(
l
)
?
x
j
(
l
)
∣
(5)
L_1(x_i,x_j)=\sum_{l=1}^{n} |x_i^{(l)}-x_j^{(l)}| \tag 5
L1?(xi?,xj?)=l=1∑n?∣xi(l)??xj(l)?∣(5)
当
p
=
∞
p=\infty
p=∞时,它是各个坐标距离的最大值,即:
L
∞
(
x
i
,
x
j
)
=
max
?
l
∣
x
i
(
l
)
?
x
j
(
l
)
∣
(6)
L_{\infty}(x_i,x_j)=\max_{l}|x_i^{(l)}-x_j^{(l)}| \tag 6
L∞?(xi?,xj?)=lmax?∣xi(l)??xj(l)?∣(6)
当
p
p
p取不同值时,二维空间中,与原点的
L
p
L_p
Lp?距离为1(
L
p
=
1
L_p=1
Lp?=1)的点的图形。

例题:
已知二维空间的3个点
x
1
=
(
1
,
1
)
T
x_1=(1,1)^T
x1?=(1,1)T,
x
2
=
(
5
,
1
)
T
x_2=(5,1)^T
x2?=(5,1)T,
x
3
=
(
4
,
4
)
T
x_3=(4,4)^T
x3?=(4,4)T,试求在
p
p
p取不同值时,
L
p
L_p
Lp?距离下
x
1
x_1
x1?的最近邻点。
解:
因为
x
1
x_1
x1?和
x
2
x_2
x2?只有第一维的值不同,所以无论
p
p
p取什么值,
L
p
(
x
1
,
x
2
)
=
4
L_p(x_1,x_2)=4
Lp?(x1?,x2?)=4。而
L
1
(
x
1
,
x
3
)
=
6
,
L
2
(
x
1
,
x
3
)
=
4.24
,
L
3
(
x
1
,
x
3
)
=
3.78
,
L
4
(
x
1
,
x
3
)
=
3.57
L_1(x_1,x_3)=6,L_2(x_1,x_3)=4.24,L_3(x_1,x_3)=3.78,L_4(x_1,x_3)=3.57
L1?(x1?,x3?)=6,L2?(x1?,x3?)=4.24,L3?(x1?,x3?)=3.78,L4?(x1?,x3?)=3.57
于是得到:
p
p
p等于1或2时,
x
2
x_2
x2?是
x
1
x_1
x1?的最近邻点;
p
p
p大于等于3时,
x
3
x_3
x3?是
x
1
x_1
x1?的最近邻点。
3.2 k k k值的选择
- k k k值过小,相当于用较小的领域中的训练实例进行预测,”学习“的近似误差会减小,只有与输入实例较近的训练实例才会对预测结果起作用。但缺点是”学习“的估计误差会增大,预测结果会对近邻的实例点非常敏感。如果邻近的实例恰好是噪声,预测就会出错。( k k k值得减小就意味着整体模型变得复杂,容易发生过拟合)。
- k k k值过大,相当于用较大的领域中的训练实例进行预测,可以减少估计误差,但是缺点是学习的近似误差会增大。这时与输入实例较远的训练实例也会对预测起作用,使预测发生错误。( k k k增大,模型会比较简单)。
- 通常采用交叉验证法来选取最优的 k k k值
3.3 分类决策规则
k
k
k近邻法中的分类决策规则往往是多数表决,即由输入实例的
k
k
k个邻近的训练实例中的多数表决决定输入实例的类。
多数表决(majority voting rule)有如下解释:如果分类的损失函数为0-1损失函数,分类函数为:
f
:
?
R
n
→
{
c
1
,
c
2
,
.
.
.
,
c
K
}
(7)
f: \ R^n \rightarrow \{c_1,c_2,...,c_K\} \tag 7
f:?Rn→{c1?,c2?,...,cK?}(7)
那么误分类的概率是:
P
(
Y
=?
f
(
X
)
)
=
1
?
P
(
Y
=
f
(
X
)
)
(8)
P(Y \not= f(X))=1- P(Y=f(X)) \tag 8
P(Y?=f(X))=1?P(Y=f(X))(8)
对于给定的实例
x
∈
χ
x \in \chi
x∈χ,其最近邻的
k
k
k个训练实例点构成集合
N
k
(
x
)
N_k(x)
Nk?(x)。如果涵盖
N
k
(
x
)
N_k(x)
Nk?(x)的区域的类别是
c
j
c_j
cj?,那么误分类率是:
1
k
∑
x
i
∈
N
k
(
x
)
I
(
y
i
=?
c
j
)
=
1
?
1
k
∑
x
i
∈
N
k
(
x
)
I
(
y
i
=
c
j
)
(9)
\frac{1}{k} \sum_{x_i \in N_k(x)} I(y_i \not= c_j)=1- \frac{1}{k} \sum_{x_i \in N_k(x)} I(y_i=c_j) \tag 9
k1?xi?∈Nk?(x)∑?I(yi??=cj?)=1?k1?xi?∈Nk?(x)∑?I(yi?=cj?)(9)
要使误分类最小即经验风险最小,就要使
∑
x
i
∈
N
k
(
x
)
I
(
y
i
=
c
j
)
\sum_{x_i \in N_k(x)} I(y_i=c_j)
∑xi?∈Nk?(x)?I(yi?=cj?)最大,所以多数表决规则等价于经验风险最小化。
4. 基于鸢尾花数据集的KNN分类分析
4.1 简介
鸢尾花数据集包括鸢尾花的测量数据(特征属性)以及其所属的类别。
测量数据特征包括: 萼片长度、萼片宽度、花瓣长度、花瓣宽度。
所属类别有三类: Iris Setosa,Iris Versicolour,Iris Virginica ,用数字0,1,2表示。
4.2 导包
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
4.3 导入鸢尾花数据
iris = datasets.load_iris()
print('数据量',iris.data.shape)
4.4 拆分数据
拆分属性数据:
iris_X = iris.data
拆分类别数据:
iris_Y = iris.target
拆分数据集为训练集和测试集:
方法一:使用python的train_test_split库进行数据集拆分
iris_X_train , iris_X_test, iris_Y_train ,iris_Y_test = train_test_split(iris_X, iris_Y, test_size=0.2,random_state=0)
使用
help(train_test_split)查看详细用法
方法二:随机选择部分数据(20%)作为测试集
np.random.seed(0)
# permutation随机生成0-150的系列
indices = np.random.permutation(len(iris_Y))
iris_X_train = iris_X[indices[:-30]]
iris_Y_train = iris_Y[indices[:-30]]
iris_X_test = iris_X[indices[-30:]]
iris_Y_test = iris_Y[indices[-30:]]
4.5 分类器的初始化
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(algorithm='auto', leaf_size=30, metric='minkowski',
metric_params=None, n_jobs=1, n_neighbors=5, p=2,
weights='uniform')
参数介绍:
- n_neighbors=5,就是KNN中的k,默认为5。
- weights=‘uniform’,是距离计算中使用的权重,默认为uniform 是等权加权,也可以选distance是按照距离的倒数进行加权,也可以自己设置其他加权方式。(给距离增加权重,如果越近的距离权重越高,能在一定程度上避免样本分布不平均的问题)
- metric=‘minkowski’、p=2,表示采用的是欧氏距离的计算。
- algorithm=‘auto’,是分类时采取的算法,有brute、kd_tree和ball_tree,三种默认按照数据特征从这三种中选择最合适的。其中kd-tree基于欧氏距离的特性可以快速处理20维以内的数据集,ball_tree基于更一般的距离特性,适合处理高维数据。
- leaf_size=30,是kd_tree或ball_tree生成的树的树叶(二叉树中未分枝的节点)的大小。
- n_job=1,是并行计算的线程数量,默认是1,输入-1则设为CPU的内核数。
4.6 训练预测
提供数据集进行训练:
knn.fit(iris_X_train,iris_Y_train)
预测测试集数据鸢尾花类型:
predict_result = knn.predict(iris_X_test)
print('预测结果',predict_result)
计算预测的准确率:
print('预测准确率',knn.score(iris_X_test, iris_Y_test))
4.7 训练结果
数据量 (150, 4)
预测结果 [2 1 0 2 0 2 0 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 0 1 1 0 0 2 1 0 0 2 0 0 1 1 0]
预测准确率 0.9666666666666667
5. 基于欧式距离的KNN算法及代码分析
5.1 自定义数据及算法
import numpy as np
import operator
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def kNN(inX, dataSet, labels, k):
'''
kNN算法
:param inX: 需要分类的数据
:param dataSet: 样本数据集
:param labels: 样本数据的标签
:param k: 需要取出的前k个
:return: 最有可能的分类
'''
# 获取样本数据的个数
dataSetSize = dataSet.shape[0]
# np.tile函数将待分类的数据inX"广播"成和样本数据dataSet一样的形状
# 获取待分类数据inX与样本数据集中的每个数据之间的差
diffMat = np.tile(inX, (dataSetSize,1)) - dataSet
# 平方
sqDiffMat = diffMat**2
# 按行累加
sqDistances = sqDiffMat.sum(axis=1)
# 开方,得出距离(欧氏距离)
distances = sqDistances**0.5
# 从小到大排序,得到的是数据的index
sortedDistIndicies = distances.argsort()
classCount={}
# 取出前k个距离最小的
for i in range(k):
voteIlabel = labels[sortedDistIndicies[i]]
# 累计距离出现的次数,并做成字典
classCount[voteIlabel] = classCount.get(voteIlabel,0) + 1
# 将字典按值的大小排序,大的在前
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
# 返回最有可能的预测值
return sortedClassCount[0][0]
def createDataSet():
group = np.array([[1.0,1.1],[1.0,1.0],[0,0],[0,0.1]])
labels = ['A','A','B','B']
return group, labels
if __name__ == '__main__':
group, labels = createDataSet()
predict = kNN([0.1,0.1], group, labels, 3)
print(predict) # 预测结果为B
5.2 改进约会网站的配对效果
数据集介绍:
总共1000条,包含三个特征:
- 每年获得的飞行常客里程数;
- 玩视频游戏所耗时间百分比;
- 每周消费的冰淇淋公升数;
而标签类型为:
- 1代表“不喜欢的人”
- 2代表“魅力一般的人”
- 3代表“极具魅力的人”
代码:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import operator
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def file_Matrix(filename):
'''
将源数据规整为所需要的数据形状
:param filename: 源数据
:return: returnMat:规整好的数据;classLabelVector:数据类标签
'''
data = pd.read_csv(filename, sep='\t').as_matrix()
returnMat = data[:,0:3]
classLabelVector = data[:,-1]
return returnMat, classLabelVector
def autoNorm(dataSet):
'''
数据归一化
:param dataSet:
:return:
'''
# 每列的最小值
minVals = dataSet.min(0)
# 每列的最大值
maxVals = dataSet.max(0)
ranges = maxVals - minVals
# normDataSet = np.zeros(np.shape(dataSet))
m = dataSet.shape[0]
# np.tile(minVals,(m,1))的意思是将一行数据广播成m行
normDataSet = (dataSet - np.tile(minVals, (m,1))) / np.tile(ranges, (m,1))
# print(normDataSet)
return normDataSet, ranges, minVals
def kNN(inX, dataSet, labels, k):
'''
kNN算法
:param inX: 需要分类的数据
:param dataSet: 样本数据集
:param labels: 样本数据的标签
:param k: 需要取出的前k个
:return: 最有可能的分类
'''
# 获取样本数据的个数
dataSetSize = dataSet.shape[0]
# np.tile函数将待分类的数据inX“广播”成和样本数据dataSet一样的形状
# 获取待分类数据inX与样本数据集中的每个数据之间的差
diffMat = np.tile(inX, (dataSetSize,1)) - dataSet
# 平方
sqDiffMat = diffMat**2
# 按行累加
sqDistances = sqDiffMat.sum(axis=1)
# 开方,得出距离(欧氏距离)
distances = sqDistances**0.5
# 从小到大排序,得到的是数据的index
sortedDistIndicies = distances.argsort()
classCount={}
# 取出前k个距离最小的
for i in range(k):
voteIlabel = labels[sortedDistIndicies[i]]
# 累计距离出现的次数,并做成字典
classCount[voteIlabel] = classCount.get(voteIlabel,0) + 1
# 将字典按值的大小排序,大的在前
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
# 返回最有可能的预测值
return sortedClassCount[0][0]
def datingClassTest():
hoRatio = 0.10 #hold out 10%
datingDataMat,datingLabels = file_Matrix('datingTestSet2.txt') #load data setfrom file
normMat, ranges, minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat)
# print(normMat)
m = normMat.shape[0]
numTestVecs = int(m * hoRatio)
errorCount = 0.0
for i in range(numTestVecs):
classifierResult = kNN(normMat[i,:],normMat[numTestVecs:m,:],datingLabels[numTestVecs:m],4)
print("the classifier came back with: %d, the real answer is: %d" % (classifierResult, datingLabels[i]))
if (classifierResult != datingLabels[i]): errorCount += 1.0
print("测试集个数为%d ,分类错误的个数为%d"%(numTestVecs, errorCount))
print("the total error rate is: %f" % (errorCount/float(numTestVecs)))
print("accuracy: %f" % ((1-errorCount/float(numTestVecs))*100))
if __name__ == '__main__':
datingClassTest()
训练结果:
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 3, the real answer is: 3
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 2
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 1
the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1
测试集个数为99 ,分类错误的个数为4
the total error rate is: 0.040404
accuracy: 95.959596
数据集下载地址:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1UErV8D4Hrw557tjj9fyjlQ
提取码:o80d