1、
?
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
#直接创建
t1 = pd.Series([1, 2, 31, 12, 2, 2])
print(t1)
# 0 1
# 1 2
# 2 31
# 3 12
# 4 2
# 5 2
#index也可以赋予
t2 = pd.Series([1, 2, 31, 12, 2, 2], index=list("abcdef"))
print(t2)
# a 1
# b 2
# c 31
# d 12
# e 2
# f 2
#字典的形式
temp_dict = {"name":"zhangsan", "age":20, "tel":"95588"}
t3 = pd.Series(temp_dict)
print(t3)
# name zhangsan
# age 20
# tel 95588
#取数据:
print(t3["name"])
print(t3[1])
print(t3[:1])
print(t3[["name", "age"]])
print(t1[t1>10])
print(t3.index)
print(t3.values)2、DataFrame
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
t = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4))
print(t)
# 0 1 2 3
# 0 0 1 2 3
# 1 4 5 6 7
# 2 8 9 10 11
t2 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4), index=list('abc'), columns=list('qwer'))
print(t2)
# q w e r
# a 0 1 2 3
# b 4 5 6 7
# c 8 9 10 11
dic = {"name":["zhangsan", "lisi"], "age":[3, 4]}
t3 = pd.DataFrame(dic)
print(t3)
# name age
# 0 zhangsan 3
# 1 lisi 4
print(type(t3))
print(t3.index)
print(t3.columns)
print(t3.values)
print(t3.shape)
print(t3.dtypes)
print(t3.ndim)
print(t3.head)
#展示DataFrame的概览
print(t3.info())
print(t3.describe())
3、dataframe获取
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
t = pd.read_csv('./dogNames2.csv')
print(t.head())
print(t.describe())
#排序方法,按照by后边的排序
t = t.sort_values(by='Count_AnimalName', ascending = False)
print(t.head())
print('*' * 100)
#pandas取行或者列的注意点
# - 方括号写数组,表示取行,对行进行操作
# - 写字符串,表示的去列索引,对列进行操作
# print(t[:20])
# print('*' * 100)
# print(t["Row_Labels"])
# print('*' * 100)
# print(type(t["Row_Labels"]))
print(t[0:1])
#可以通过标签索引行数据
t = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4), index=list("abc"), columns=list("wxyz"))
print(t)
print('*' * 100)
print(t.loc['a'])
# w 0
# x 1
# y 2
# z 3
print('*' * 100)
#选择某一个数据
print(t.loc['a', 'w'])
# 0
#选择一行的某几列
print(t.loc['a', ['w', 'y']])
# w 0
# y 2
#选择连续几行的某列
print(t.loc['a':, ['w', 'y']])
# w y
# a 0 2
# b 4 6
# c 8 10
#选择几行几列,注意:后边也会选到
print(t.loc['a':'c', 'w':'y'])
# w x y
# a 0 1 2
# b 4 5 6
# c 8 9 10
#通过位置获取行数据
print(t.iloc[0, 0])
#0
print(t.iloc[0:1, 0])
# a 0
print(t.iloc[0:1, [0, 1]])
# w x
# a 0 1
4、bool运算以及nan填充
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
t = pd.read_csv('./dogNames2.csv')
print(t.head())
# 找到所有的使用次数超过700并且名字的字符串的长度大于4的狗的名字
#要将条件使用()括起来,然后使用 '&', '|' 链接
t1 = t[(t['Count_AnimalName'] > 700)&(t['Row_Labels'].str.len() > 4)]
print(t1)
#修复缺失数据
t2 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(16).reshape(4, 4))
print(t2)
t2.iloc[[0, 1], [1, 2]] = np.nan
print(t2)
print(pd.isnull(t2))
print(pd.notnull(t2))
#1.直接删除掉nan所在的行
t3 = t2[pd.notnull(t2.iloc[:, 1])]
print(t3)
#使用dropna 方法进行删除
#axis表明方向how:any是指只要有nan就删,all指必须全是nan才删inplace,表示是否会自己更新,true的话就不用再赋值了。
# t2.dropna(axis=0, how='any', inplace=True)
# print(t2)
#2.填充
#填充0
print('*' * 100)
print(t2.fillna(0))
#填充均值
print('*' * 100)
print(t2.fillna(t2.mean()))
#填充中值
print('*' * 100)
print(t2.fillna(t2.median()))
#如果是0的话,可以更新成nan,因为nan不参与mean等的运算
t2[t2==0] = np.nan
print(t2)
?
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
filname = 'IMDB-Movie-Data.csv'
t = pd.read_csv('./' + filname)
print(t.info())
print(t.head(1))
#获取平均评分
print(t['Rating'].mean())
#导演的人数
print(len(set(t['Director'].tolist())))
#获取演员的人数
temp_actors_list = t['Actors'].str.split(', ').tolist()
print(temp_actors_list)
actors_list = [i for j in temp_actors_list for i in j]
print(actors_list)
print(temp_actors_list[0])
actors_list1 = []
print('*' * 100)
for i in temp_actors_list:
for j in i:
actors_list1.append(j)
print(actors_list1)
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as py
file_path = './IMDB-Movie-Data.csv'
source = pd.read_csv(file_path)
# print(source.head())
print(source.info())
rating = source["Rating"].values
# print(rating)
max_rating = rating.max()
min_rating = rating.min()
print(max_rating - min_rating)
num_bin = (max_rating - min_rating)//0.5
print(type(int(num_bin)))
py.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80)
py.hist(rating, int(num_bin))
_x = [min_rating]
i = min_rating
while i<=max_rating+0.5:
i = i+0.5
_x.append(i)
py.xticks(_x)
py.show()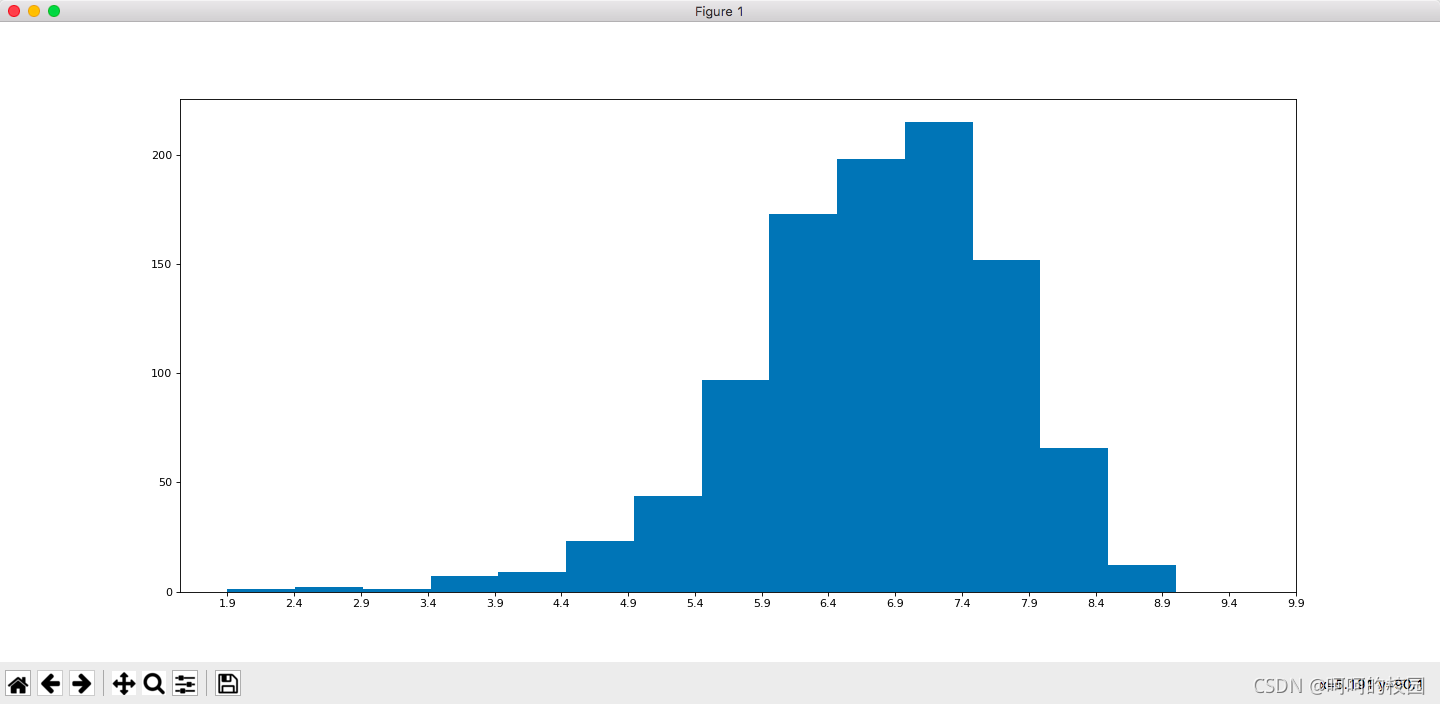
?