- numpy和pandas区别
numpy:处理数值数据
pandas:字符串,时间数据等
1、Pandas概述
- pandas名称来源:面板数据(panel data)
Pandas是一个强大的分析结构化数据的工具集,基于Numpy构建,提供了高级数据结构和数据操作工作
1、基础是numpy,提供了高效性能矩阵的运算;
2、提供数据清洗功能
3、应用于数据挖掘,数据分析
4、提供了大量能快速便捷地处理数据的额函数和方法
2、Pandas数据结构
2.1、Series介绍
Series:是一种一维标记的数据型对象,能够保存任何数据类型(int,str,float,python object),包含了数据标签,称为索引
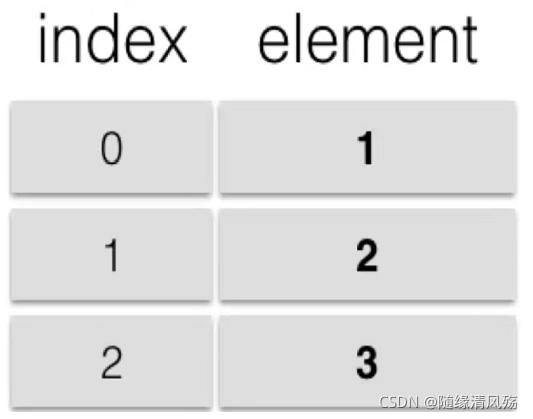
- 类似于一维数组的对象1,index=[“名字”,“年龄”,“班级”]
- 由数据和索引组成
- 索引在左边(index),数据在右边(values)
- 索引自动创建
3.2.2、Series创建
(1)通过列表创建
- 范例
# 1、通过list创建
s1 = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5])
s1
- 查询结果

(2)通过数组创建
- 范例
# 2、通过数组创建
arr1= np.arange(1,6)
s2 = pd.Series(arr1)
print(s2)
- 查询结果

? (3)通过字典创建
- 范例
# 3、通过字典创建
dict = {'name':'李宁','age':18,'class':'三班'}
s3 = pd.Series(dict,index = ['name','age','class','sex'])
s3
- 查询结果

2.3、Series用法
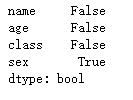
(1)空值判断
- 范例
# isnull和not null检测缺失值
s3.isnull()
- 查询结果
(2)获取数据
获取数据方式:索引,下标,标签名
- 范例
# 1、索引获取数据
print(s3.index)
print(s3.values)
# 2、下标获取数据
print(s3[1:3])
# 3、标签名获取数据
print(s3['age':'class'])
-

-
注意事项
标签切片和下标切片的区别
标签切片:包含末端数据
索引切片:不包含末端数据
(3)索引与数据的对应关系
索引和数据的对应关系不被运算结果影响
(4)name属性
- 范例
s3.name = "temp" #对象名
s3.index.name = 'values' #对象索引名
s3
- 查询结果

3、DateFrame数据结构
3.1、DataFrame概述
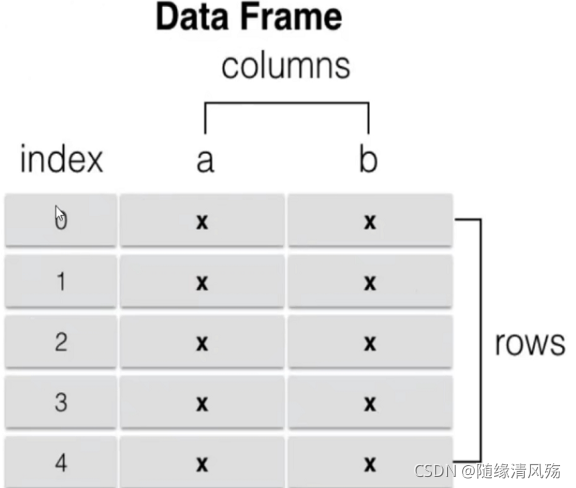
DataFrame是一个表格型的数据结构,它含有一组有序的列,每列可以是不同类型的索引值,DataFrame既有行索引也有列索引,它可以被看作是由series组成的字典,数据以二维结构存放
- 类似多维数组/表格数据(如,excel,R中的DataFrame)
- 每列数据可以是不同的数据类型
- 索引包含列索引和行索引
3.2、DataFrame创建
- 范例
# 数组、列表或元组构成的字典构造DataFrame
data = {'a':[1,2,3,4],
'b':(5,6,7,8),
'c':np.arange(9,13)}
frame = pd.DataFrame(data)
# 相关属性
print(frame.index)
print(frame.columns)
print(frame.values)
- 查询结果

3.3、DataFrame基本用法
1、T转置
2、通过列索引获取列数据(Series类型)
3、增加列数据
4、删除列
- 范例
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3,3),index = ['a','c','d'],columns=['A','C','B'])
# 1、T转置
df1 = df.T
print(df1)
print("========")
# 2、列索引获取数据
print(df['B'])
print("========")
# 3、增加列数据
df['D']=[1,2,3]
print(df)
# 4、删除列
df.drop('D',axis=1)
- 查询结果

4、索引相关操作
4.1、索引对象概述
1、Series和DataFrame中的索引都是index对象
2、索引对象不可改变,保证数据安全
- 范例
ps = pd.Series(range(5))
pd = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3,3),index = ['a','b','c'],columns = ['A','B','C'])
type(ps.index)
- 运行结果
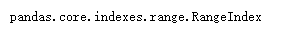
- 注意事项
常见索引类型
:1、Index - 索引
:2、Inet64index - 整数索引
:3、MultiIndex - 层级索引
:4、DatetiemIndex - 时间戳索引
4.2、索引基本操作
(1)重新索引
reindex:创建一个符合新索引的新对象
- 范例
s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(5),index=['a','b','c','d','e'])
print(s)
s.reindex(['e','b','f','d'])
- 运行结果

(2)增
1、在原有数据结构上增加数据
2、在新建数据结构上增加数据
- 范例 - series增加数据
s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(5),index=['a','b','c','d','e'])
s['f'] = 100
print(s)
- 查询结果

(3)删
1、del:删除,会更改原有结构
2、drop:删除轴上数据,产生新的对象
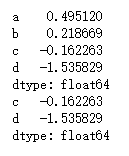
- 范例 - Series数据
# 删除
ps = pd.Series(np.random.randn(5),index=['a','b','c','d','e'])
del ps['e']
print(ps)
ps2 = ps.drop(['a','b'])
print(ps2)
- 查询结果
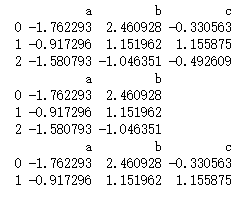
- 范例 - DF数据
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
pd = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(9).reshape(3,3),columns=['a','b','c'])
print(pd)
# 删除列
pd1 = pd.drop(['c'],axis=1)
print(pd1)
# 删除行
pd2 = pd.drop(2)
print(pd2)
- 查询结果
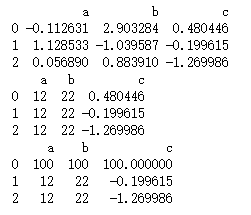
(4)改
1、修改列:对象.索引,对象.列
2、修改行:标签索引loc
- 范例
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
pd = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(9).reshape(3,3),columns=['a','b','c'])
print(pd)
# 修改列
pd['a'] = 12
pd.b = 22
print(pd)
# 修改行
pd.loc[0] = 100
print(pd)
- 运行结果
(5)查
1、行索引
2、切片索引:位置切片,标签切片
3、不连续索引
- 范例
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
ps = pd.Series(np.random.randn(5),index=['a','b','c','d','e'])
# 行索引
print(ps['a'])
# 位置切片索引
print(ps[1:3])
# 标签切片索引,包含终止索引
print(ps['a':'c'])
# 不连续索引
print(ps[['a','c']])
# 布尔索引
print(ps[ps>0])
- 运行结果

4.3、高级索引
1、loc标签索引:基于标签名的索引 pd.loc[2:3,'a']
2、iloc位置索引:基于索引编号索引
3、ix标签与位置混合索引:知道就行
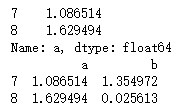
- 范例
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
pd = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(9).reshape(3,3),index = [7,8,9],columns=['a','b','c'])
# 标签索引 - 第一个参数索引行,第二个参数是列
print(pd.loc[7:8,'a'])
# 位置索引 - 两个参数,行列
print(pd.iloc[0:2,0:2])
- 查询结果
5、Pandas运算
5.1、算术运算
Pandas进行数据运算时,会按照索引进行一一对应,对应后进行相应的算术运算,没有对齐的位置就会用NaN进行填充。

- 范例
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
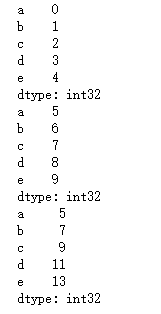
s1 = pd.Series(np.arange(5),index=['a','b','c','d','e'])
s2 = pd.Series(np.arange(5,10),index=['a','b','c','d','e'])
print(s1)
print(s2)
print(s1+s2)
- 运行结果
5.2、缺失值值填充
待补充
5.3、混合运算
DataFrame和Series混合运算:Series的行索引匹配DataFrame的列索引进行广播运算,index属性可沿列运算
- 范例
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
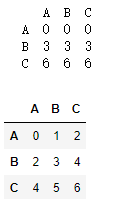
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3,3),index = ['A','B','C'],columns=['A','B','C'])
ds = df.iloc[0]
# 行运算,列广播
print(df-ds)
# 列运算,行广播
df.sub(ds,axis = 'index')
- 运行结果
- 注意事项
运算规则:索引匹配运算
5.4、函数应用
(1)apply函数
apply:将函数应用到行或列
- 范例
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3,3),index = ['A','B','C'],columns=['A','B','C'])
f = lambda x:x.max()
# 应用在行上,进行列运算
print(df.apply(f))
# 应用在列上,进行行运算
print(df.apply(f,axis=1))
- 运行结果

(2)applymap函数
applymap:将函数应用到每个数据
- 范例
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3,3),index = ['A','B','C'],columns=['A','B','C'])
f = lambda x:x**2
print(df.applymap(f))
- 运行结果

(3)排序
索引排序:sort_index(ascending,axis)
按值排序:sort_values(by,sacending,axis)
- 范例
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
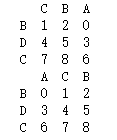
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3,3),index = ['B','D','C'],columns=['A','C','B'])
# 按行索引排序
print(df.sort_index(ascending=False,axis=1))
# 按列值进行排序
print(df.sort_values(by = 'A'))
- 查询结果
(4)唯一值和成员属性
| 函数名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| unique | 返回一个Series,用于去重 |
| value_counts | 返回Series,包括元素及其个数 |
| isin | 判断是否存在,返回布尔类型 |
(5)处理缺失值
- 范例
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame([np.random.randn(3),[1,2,np.nan],[np.nan,4,np.nan]])
# 1、判断是否存在缺失值
print(df.isnull())
# 2、丢弃缺失数据,默认丢弃行
print(df.dropna())
# 3、填充缺失数据
print(df.fillna(-100))
- 运行结果

3.6、层级索引
层级索引:在输入索引Index时,输入了由两个子list组成的list,第一个子list是外层索引,第二个list是内层索引。
作用:通过层级索引配合不同等级的一级索引使用,可以将高维数组转化为Series或DataFrame对向形式
- 范例
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
ser_obj = pd.Series(np.random.randn(12),index=[
['a', 'a', 'a', 'b', 'b', 'b', 'c', 'c', 'c', 'd', 'd', 'd'],
[0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2]
])
# 选取子集
'''
根据索引获取数据。因为现在有两层索引,当通过外层索引获取数据的时候,可以直接利用外层索引的标签来获取。
当要通过内层索引获取数据的时候,在list中传入两个元素,前者是表示要选取的外层索引,后者表示要选取的内层索引。
'''
print(ser_obj['a',1])
# 交换内外层
print(ser_obj.swaplevel())
- 运行结果

3.7、Pandas统计计算
统计计算:默认按列计算
- 范例
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(32).reshape(8,4))
# 选取
df.sum()
- 运行结果

- 常用统计函数
平均数:np.mean()
总和:np.sum()
中位数:np.median()
最大值:np.max()
最小值:np.min()
频次(计数): np.size()
方差:np.var()
标准差:np.std()
乘积:np.prod()
协方差: np.cov(x, y)
偏度系数(Skewness): skew(x)
峰度系数(Kurtosis): kurt(x)
正态性检验结果: normaltest(np.array(x))
四分位数:np.quantile(q=[0.25, 0.5, 0.75], interpolation=“linear”)
四分位数:describe() – 显示25%, 50%, 75%位置上的数据
相关系数矩阵(Spearman/ Person/ Kendall)相关系数: x.corr(method=“person”))
8、数据读取与存储
8.1、读写文本格式文件
-
读取csv文件
read_csv(file_path or buf,usecols,encoding):file_path:文件路径,usecols:指定读取的列名,encoding:编码 -
范例
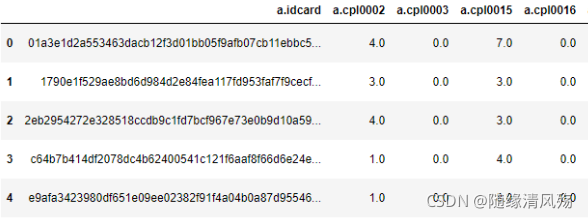
data = pd.read_csv('D:/jupyter_notebook/bfms_w2_out.csv',encoding='utf8')
data.head()
- 运行结果
9、数据连接/合并
9.1、数据连接
pd.merge:(left, right, how='inner',on=None,left\_on=None, right\_on=None \)
left:合并时左边的DataFrame
right:合并时右边的DataFrame
how:合并的方式,默认'inner', 'outer', 'left', 'right'
on:需要合并的列名,必须两边都有的列名,并以 left 和 right 中的列名的交集作为连接键
left\_on: left Dataframe中用作连接键的列
right\_on: right Dataframe中用作连接键的列
* 内连接 inner:对两张表都有的键的交集进行联合
- 范例
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
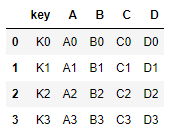
left = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['K0', 'K1', 'K2', 'K3'],
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']})
right = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['K0', 'K1', 'K2', 'K3'],
'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3'],
'D': ['D0', 'D1', 'D2', 'D3']})
pd.merge(left,right,on='key') #指定连接键key
- 运行结果
9.2、数据合并
concat:可指定轴进行横向或者纵向合并
- 范例
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(6).reshape(3,2),index=list('abc'),columns=['one','two'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(4).reshape(2,2)+5,index=list('ac'),columns=['three','four'])
print(df1)
print(df2)
pd.concat([df1,df2],axis='columns') #指定axis=1连接
- 运行结果

9.3、数据重塑
stack:stack函数会将数据从”表格结构“变成”花括号结构“,即将其行索引变成列索引
unstack:unstack函数将数据从”花括号结构“变成”表格结构“,即要将其中一层的列索引变成行索引。
- 范例
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df_obj = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(0,10, (5,2)), columns=['data1', 'data2'])
print(df_obj)
print("stack")
stacked = df_obj.stack()
print(stacked)
print("unstack")
# 默认操作内层索引
print(stacked.unstack())
# 通过level指定操作索引的级别
print(stacked.unstack(level=0))
- 运行结果
