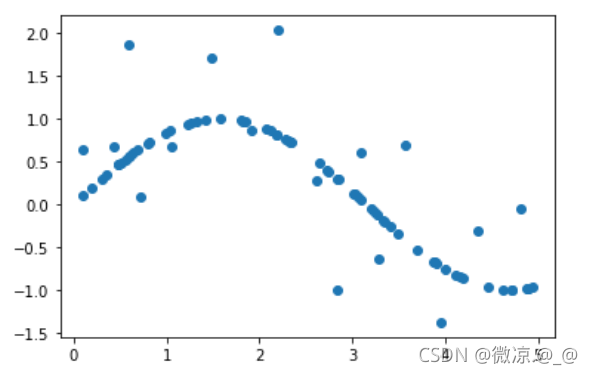
1.构造训练数据(80个)
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rng = np.random.RandomState(0) #随机数种子
X = np.sort(rng.rand(80,1)*5,axis=0) #创建x
y = np.sin(X).ravel() #创建y ravel()函数:降维,此处将二位数组转换为一维
y[::5] += 3*(0.5-rng.rand(16)) #增添噪音
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(X,y)
plt.show()
2.训练深度分别为3和8的两个决策树回归模型
tree_1 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=8)
tree_2 = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=3)
fit_1 = tree_1.fit(X,y)
fit_2 = tree_2.fit(X,y)
3.构造测试数据(50个)
X_test = np.arange(0,5,0.1)[:,np.newaxis]#[:,np.newaxis] :升维成 :行1列的二维数组
y_test = np.sin(X_test).ravel()#ravel()函数:降维,此处将二位数组转换为一维
4.输出各自的评分
predict_1 = fit_1.predict(X_test)
predict_2 = fit_2.predict(X_test)
print("深度为8:",tree_1.score(X_test,y_test))
print("深度为3:",tree_2.score(X_test,y_test))

5.画图,查看两个模型的拟合效果
plt.figure()#画布
plt.scatter(X,y,c="red",label="data")
plt.plot(X_test,predict_1,c="blue",label="predict_1_max=8",linewidth=3)
plt.plot(X_test,predict_2,c="green",label="predict_2_max=3",linewidth=3)
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.legend()#显示图例
plt.show()
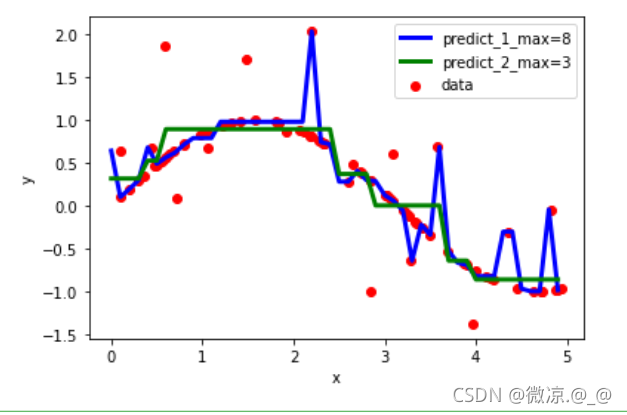
由图可知:当最大深度值设置越大,模型学习的细节越多,许多噪音点都被拟合进去,偏离正弦曲线,模型过拟合,当深度越小,模型拟合就比较好。