一.概述
k均值聚类算法(k-means clustering algorithm)是一种迭代求解的聚类分析算法,属于无监督学习的一种,其步骤是,预先将数据分为K组,则随机选取K个对象作为初始的聚类中心,然后计算每个对象与各个聚类中心之间的距离,把每个对象分配给距离它最近的聚类中心。聚类中心以及分配给它们的对象就代表一个聚类。每分配一个样本,聚类中心会根据聚类中现有的对象被重新计算。这个过程将不断重复直到满足某个终止条件。
终止条件可以分为3中:
1. 没有(或最小数目)对象被重新分配给不同的聚类
2. 没有(或最小数目)聚类中心再发生变化
3. 误差平方和局部最小。
二.算法实现
"""
KMeans 实现
"""
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.switch_backend("TkAgg")
# pandas 打印所有的行列
pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 50)
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 500)
pd.set_option('display.width', 1000)
# 计算各个点距离聚簇中心的距离并归类
def classified(df_table, center):
distance_from_centroid_id = []
for i in center.keys():
# 记录下所有key值
distance_id = "distance_%d" % i
distance_from_centroid_id.append(distance_id)
# 计算各个点距离预设中心的距离
df_table[distance_id] = np.sqrt((df_table["x"] - center[i][0]) ** 2 + (df_table["y"] - center[i][1]) ** 2)
# 获取每个点到各聚簇中心的最小距离的 key, 并去掉前缀以归类
df_table["closest"] = df_table.loc[:, distance_from_centroid_id].idxmin(axis=1). \
map(lambda key: int(key.lstrip('distance_')))
return df
# 重新计算聚簇中心
def calculate_cluster_center(df_table, centroids):
for i in centroids.keys():
centroids[i][0] = np.mean(df_table[df_table['closest'] == i]['x'])
centroids[i][1] = np.mean(df_table[df_table['closest'] == i]['y'])
return centroids
# 一. 生成模拟数据, 生成5簇数据, 共 1000 个样本, 每个样本的特征值为2
x, y = make_blobs(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, centers=5, random_state=2)
# 整合为 pandas 表结构
df = pd.DataFrame({'x': x[:, 0], 'y': x[:, 1]})
# 二 .进行聚类
# 设置聚类中心为 5
k = 5
# 随机生成三个聚类中心
center_points = {i: [np.random.uniform(np.min(x[:, 0]), np.max(x[:, 0])),
np.random.uniform(np.min(x[:, 1]), np.max(x[:, 1]))] for i in range(k)}
# 计算各个点距离初始化的聚簇中心的距离并归类
df = classified(df, center_points)
# 进行迭代
for i in range(1000):
# 重新计算聚簇中心点
center_points = calculate_cluster_center(df, center_points)
# 计算各个点距离聚簇中心的距离并归类
df = classified(df, center_points)
# 三. 打印结果
# 设置各个簇的颜色
color_map = {0: "r", 1: "g", 2: "b", 3: "m", 4: "y"}
# 记录下每个种类所对应的颜色
df["color"] = df['closest'].map(lambda key: color_map[key])
plt.scatter(df['x'], df['y'], color=df['color'], alpha=0.5, edgecolor='b')
# 绘制各个聚簇中心点(中心点带颜色)
# for j in center_points.keys():
# plt.scatter(*center_points[j], color=color_map[j], linewidths=5)
# 绘制各个聚簇中心点(中心点为黑色)
center_points = np.array(list(center_points.values()))
plt.scatter(center_points[:, 0], center_points[:, 1], c='black', s=100)
plt.show()
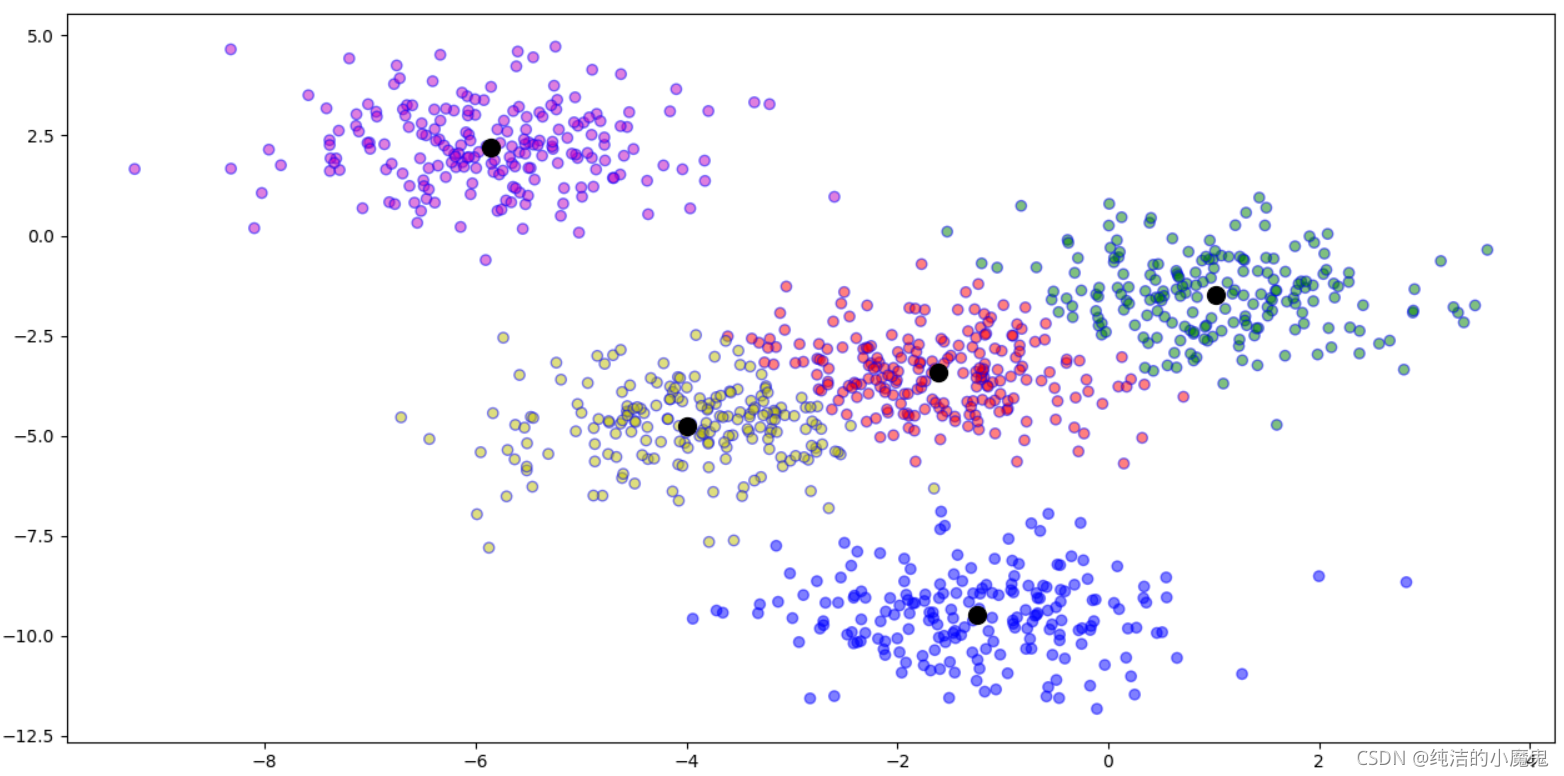
多次运行时,每次产生的结果可能会由于初始点的不同而不同,由此可以采用 k-means++,初始的聚类中心之间的相互距离要尽可能远。
三.sklearn KMeans 算法主要参数
n_clusters:k值,需要聚类的个数。
init:初始聚类中心的选择方式,共有三种, 随机从训练数据中选取(random),初始的聚类中心之间的相互距离要尽可能远的(k-means++), 自己指定的 k 个聚类中心。一般建议使用默认的 k-means++。
n_init:用不同的初始化质心运行算法的次数。因为 K-Means 的结果受初始值k的影响,因此需要多跑几次来选择一个比较好的聚类效果,如果k值较大,可以适当增大该值。
max_iter:最大迭代次数,如果是凸数据集(数据集中任意两点连线上的点,也在数据集内)可以不管这个值,如果是非凸数据集则可能很难收敛,此时可以指定最大迭代次数让算法及时退出循环。
tol:迭代终止条件,当误差小于 tol 时退出迭代。
precompute_distances:是否预计算距离(如果预算则更快但占用更多内存),共有auto,True,False三个参数可选, 选择 auto 则当 样本数*质心数 > 12兆 的时候,就不会提前进行计算,如果小于则会与提前计算。
verbose:是否输出详细信息,默认为0不输出详细信息,大于0时输出详细信息。
random_state:确定聚类中心初始化时的位置。使随机数具有确定性。
copy_x:在提前计算距离的情况,如果是True,则表示在源数据的副本上提前计算距离时,不会修改源数据。
n_jobs:指定计算所用的进程数。内部原理是同时进行 n_init 指定次数的计算。当值为1时,不进行并行运算,若值小于0,则使用的CPU个数为(CPU个数 + 1 + n_jobs),则-1表示用全部的CPU,-2表示为CPU的总数-1。
algorithm:有auto、full 和 elkan 三种选择,默认为 auto。full 就是我们传统的K-Means算法, elkan 是elkan K-Means算法。auto 会根据数据是否稀疏来选择 full 还是 elkan。如一般如果数据是稠密的,那么选择 elkan,否则选择 full。一般来说建议直接用默认的auto就可以。
四.sklearn Kmeans演示
1.数据点的聚类
"""
KMeans 聚类
"""
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
plt.switch_backend("TkAgg")
np.set_printoptions(suppress=True)
# 一. 生成模拟数据, 生成5簇数据, 共 1000 个样本, 每个样本的特征值为2
x, y = make_blobs(n_samples=1000, n_features=2, centers=5, random_state=2)
# 展现生成的点数据, 点大小设置为 50
# plt.scatter(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], s=50)
# plt.yticks(())
# plt.show()
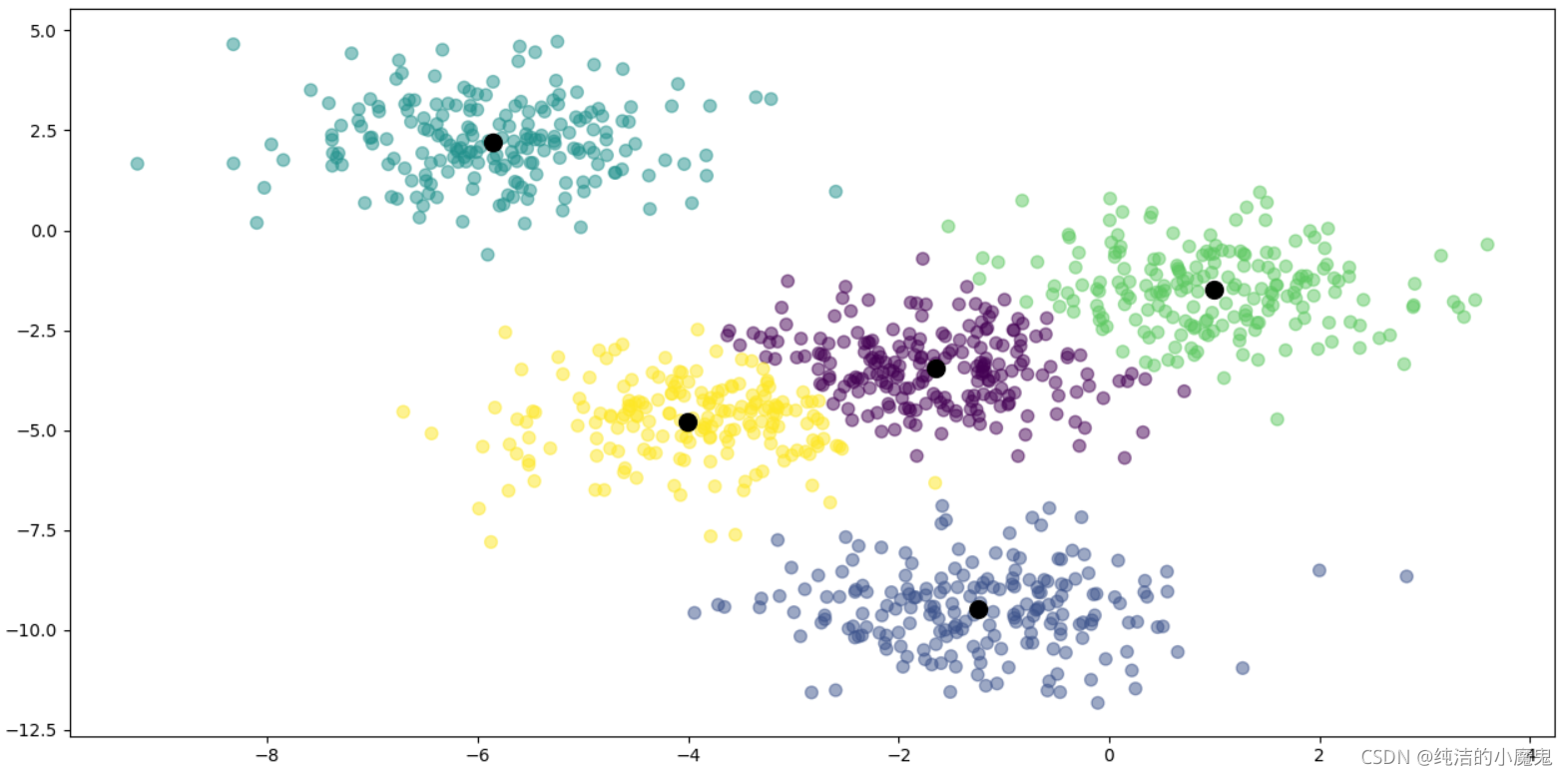
# 二. 构建 KMeans 模型, 聚簇数量为 5
km_model = KMeans(n_clusters=5, max_iter=30)
km_model.fit(x)
# 三.聚类并展现数据
# 进行聚类
y_predict = km_model.predict(x)
# 绘制聚类好的数据
plt.scatter(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], c=y_predict, alpha=0.5, s=50)
# 获取并绘制簇心
centers = km_model.cluster_centers_
plt.scatter(centers[:, 0], centers[:, 1], c='black', s=100)
plt.show()
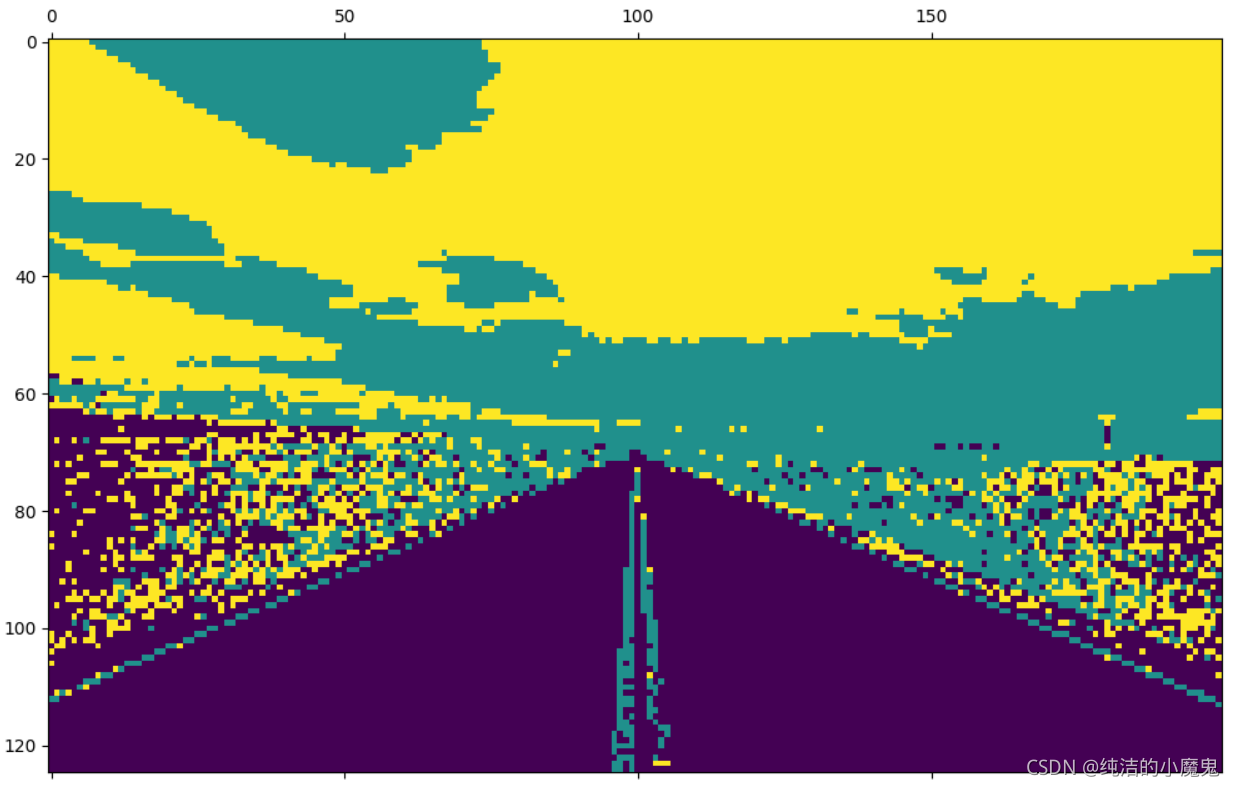
2.自动驾驶中的图片车道识别
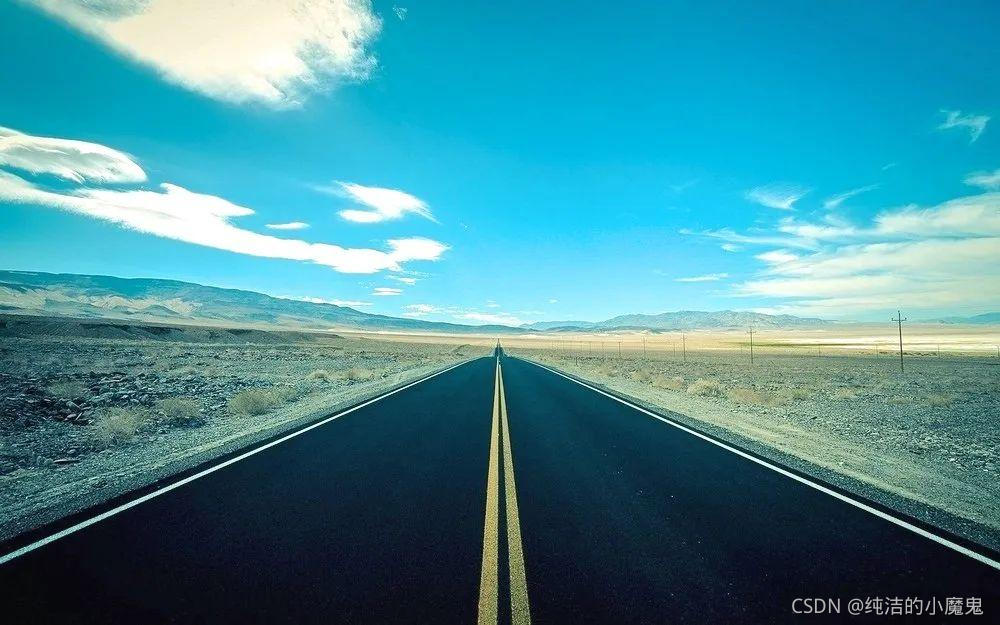

"""
车道聚类
"""
import cv2
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.switch_backend("TkAgg")
# 一. 准备数据
# 读取图片路径, 图片大小为 (625, 1000, 3)
img = cv2.imread("data/road.jpg")
# 将图片缩小 5 倍, 大小为 (125, 200, 3)
img = img[0:-1:5, 0:-1:5, :]
# 将 img 转化为 float32 类型
img = img.astype(np.float32)
# 求最大值最小值的均值
img_mean = (np.max(img) + np.min(img))/2
# 进行归一化, 标准化
img = (img - img_mean)/img_mean
# 获取图像的维度 125 200 3
h, w, c = img.shape
# 将图片证据整合为 [h*w, c] 大小的矩阵 即 [[红,绿,蓝], [......], [红,绿,蓝]]
img_2d = np.reshape(img, [h * w, c])
# 二. 建立模型
# 定义 Kmeans 聚类方法, 并分为 3 类
method = KMeans(n_clusters=3)
# 以像素作为基本单位,分割过程中以相同颜色作为聚类依据
d = method.fit_predict(img_2d)
print(d)
# 三. 展示结果
# 将数据整合为 h * w 大小, 类似于展示灰度图
d_img = np.reshape(d, [h, w])
# 类别输出后使用 matshow 进行可视化
plt.matshow(d_img)
plt.show()
3.从绿幕中抠图贴到其他图片中
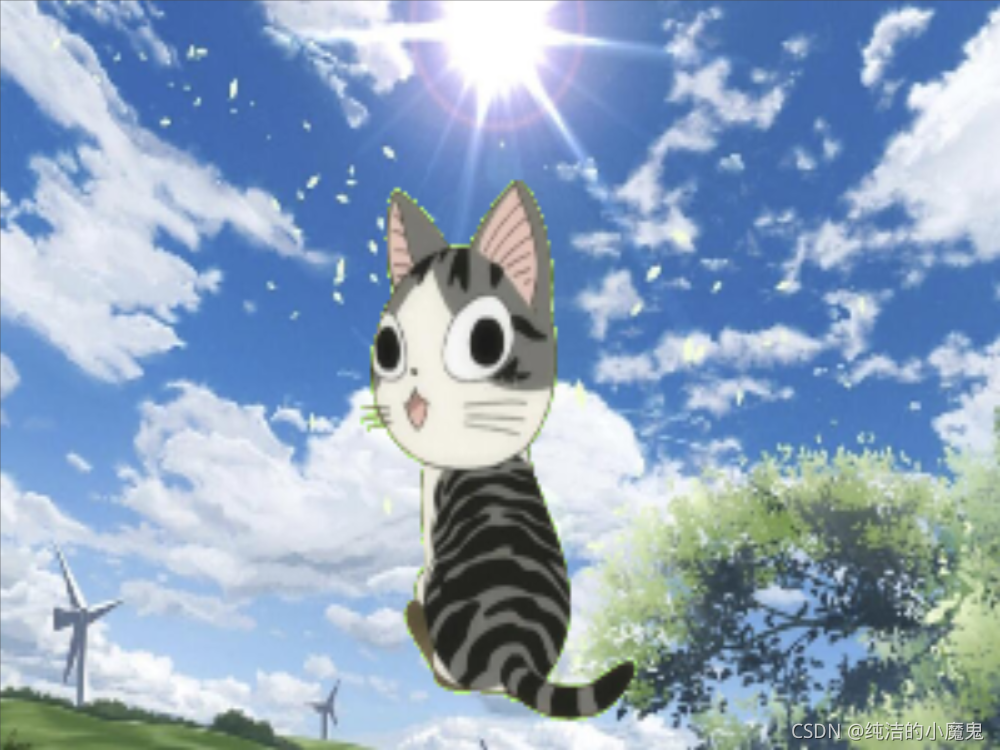
把绿幕中的卡通猫任务截图到另一张图片中
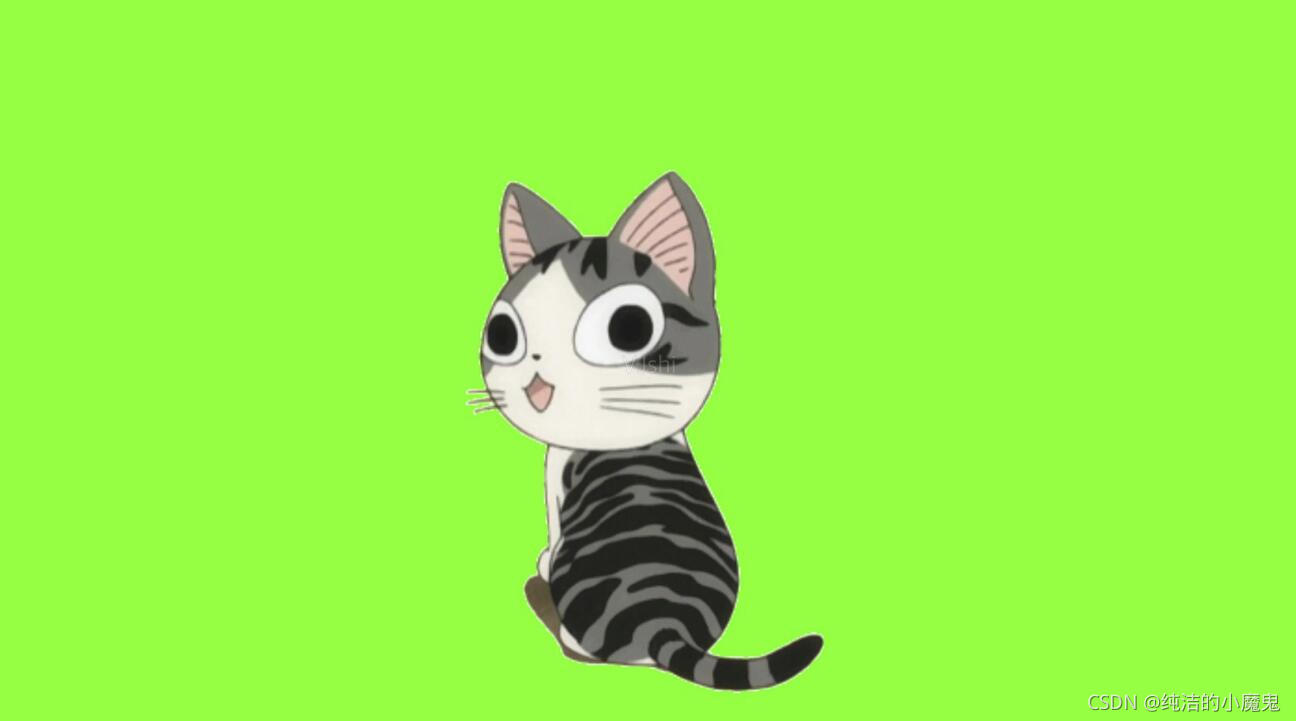
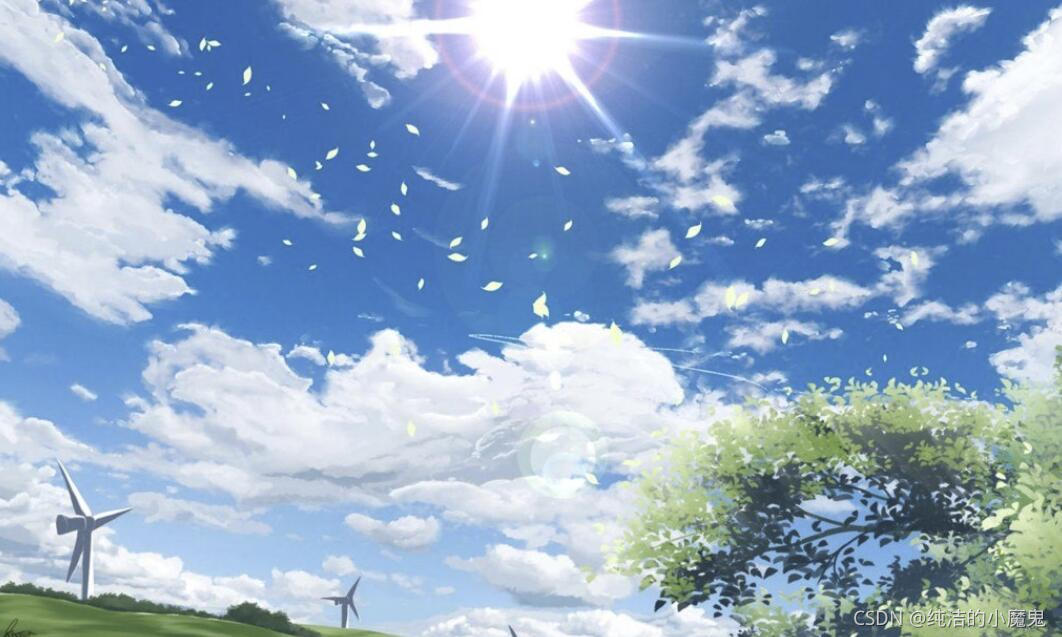


"""
绿幕聚类后拼图
"""
import cv2
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
import numpy as np
# 一.读取数据
# 分别读取两张图片
img1 = cv2.imread("data/aaa.jpg")
print(img1.shape)
img2 = cv2.imread("data/ccc.jpg")
# 转换后图像大小,进行图像放缩
img1, img2 = cv2.resize(img1, (300, 200)), cv2.resize(img2, (300, 200))
# 转换为浮点数,方便计算
img1 = img1.astype(np.float32)
# 求最大值最小值的均值
img_mean = (np.max(img1) + np.min(img1))/2
# 将图像进行归一化, 标准化
img_standard = (img1 - img_mean)/img_mean
# 获取图像的维度
h, w, c = img1.shape
# 将图片证据整合为 [h*w, c] 大小的矩阵 如: [[红,绿,蓝], [......], [红,绿,蓝]]
img_2d = np.reshape(img_standard, [h * w, c])
# 二. 建立模型
# 定义 KMeans 聚类方法
method = KMeans(n_clusters=5)
# 以像素作为基本单位,分割过程中以相同颜色作为聚类依据
d = method.fit_predict(img_2d)
# 三. 展示结果
# 将数据整合为 h * w * 1大小, 这个 1 是指训练好后它的类别(可能是0,1,2
# 类似于展示灰度图, 但是内层元素单独作为一个一维数组
d_img = np.reshape(d, [h, w, 1])
# 进行归一化, imshow() 显示图像时对浮点型是认为在0~1的范围,
# 而一开始的 255 是 unit8 类型
img1 = img1.astype(np.float32) / 255
img2 = img2.astype(np.float32) / 255
# 在计算机中,True代表 1, False代表 0,img1 * (d_img != 0) , 等于把img1的那些
# 颜色分类不为0的部位(即绿色除外的部位)切割了拿了出来,img2 * (d_img == 0)
# 等于把卡通猫那个图片的猫的位置的像素值都变成0,好把那个猫放到另一张图片的相同位置。
# img = img1 * (d_img != 0) + img2 * (d_img == 0)
img = img1 * (d_img != 0) + img2 * (d_img == 0)
img = cv2.resize(img, (800, 600))
cv2.imshow("img", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
