土堆的pytorch学习记录
DAY 2 P15-P22 神经网络的层级结构
1.基本的nn.Module骨架
import torch
from torch import nn
# 定义一个类继承nn.Module
class Tudui(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
# super()可以代替父类,super().方法 = 父类.方法
# 对父类进行初始化
super().__init__()
# 接着可以在下面定义一下方法,主要是神经网络的层
# 定义一个前向传播的方法
# 有参数input要输入
def forward(self , input):
output = input + 1
return output
# 返回一个output
tudui = Tudui()
x = torch.tensor(1.0)
output = tudui(x)
print(output)
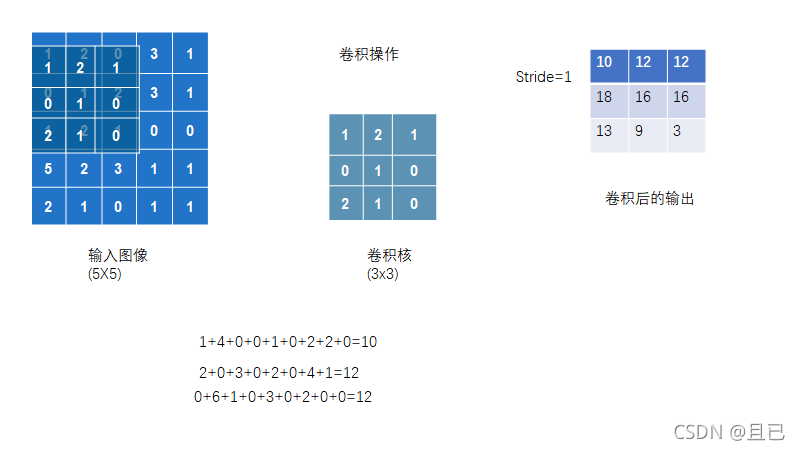
2.简单的卷积实现
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
# 多维矩阵可以这样表示,里面每个中括号表示一行,共有5行
input = torch.tensor([[1,2,0,3,1],
[0,1,2,3,1],
[1,2,1,0,0],
[5,2,3,1,1],
[2,1,0,1,1]])
# kernel指的是卷积核
kernel = torch.tensor([[1,2,1],
[0,1,0],
[2,1,0]])
# 因为input的格式要求是(minibatch, in_channels , iH , iW)
input = torch.reshape(input , (1,1,5,5))
kernel = torch.reshape(kernel , (1,1,3,3))
print(input.shape)
print(kernel.shape)
# conv2d是进行二维卷积操作
# 参数变量
# input – input tensor of shape (minibatch,in_channels,iH,iW) 输入矩阵
# weight – filters of shape (out_channels,groups,in_channels,kH,kW) 权值矩阵
# bias – optional bias tensor of shape (\text{out\_channels})(out_channels). Default: None 截距
# stride – the stride of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number or a tuple (sH, sW). Default: 1 卷积时每次移动的步长
# padding –implicit paddings on both sides of the input. Can be a string {‘valid’, ‘same’}, single number or a tuple (padH, padW). 周围填一圈0
output = F.conv2d(input , kernel , stride=1)
print(output)
output2 = F.conv2d(input , kernel , stride=2)
print(output2)
output3 = F.conv2d(input , kernel , stride=1 , padding=1)
print(output3)
3.pytorch里提供的卷积层conv2d
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Conv2d
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
# 数据集的下载与载入
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("dataseset_CIFAR10" , train=False ,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor() , download=True )
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset , batch_size=64)
class Tudui(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Tudui , self).__init__()
# 进入卷积层前channels为3 , 卷积操作后为6
self.conv1 = Conv2d(in_channels=3 , out_channels=6 ,kernel_size=3 , stride=1 ,padding=0)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.conv1(x)
return x
tudui = Tudui()
# 可视化展示
writer = SummaryWriter("logs")
step = 0
for data in dataloader:
imgs , targets = data
output = tudui(imgs)
print(imgs.shape)
print(output.shape)
#torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
# 注意如果是单张图片展示是writer.add_image()
# 注意如果是多张图片展示是writer.add_images()
writer.add_images("input" , imgs , step)
# torch.Size([64, 6, 30, 30]) ---> torch.Size([64 , 3 ,30 ,30])
# reshape里不知道第一个值是多少时就设为-1
output = torch.reshape(output ,(-1 , 3 , 30 , 30))
writer.add_images("output" , output , step)
step = step + 1
writer.close()
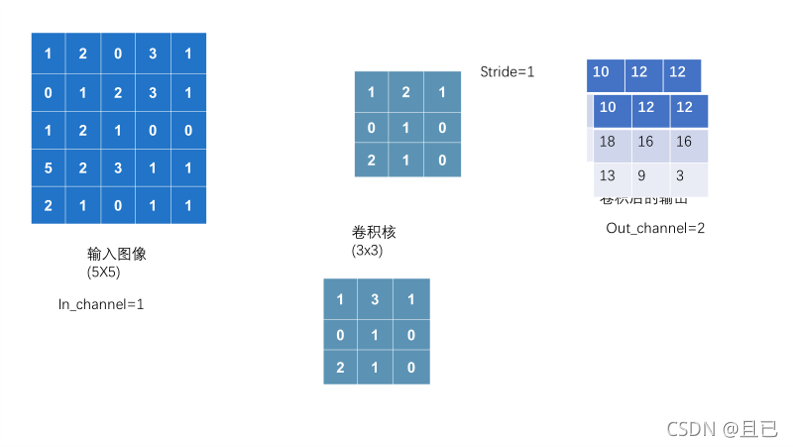
channels如何变多
4.激活函数
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import ReLU, Sigmoid
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
# 非线性变换的目的是引入非线性特征 , 从而训练出符合更多曲线或更多特征的模型 , 具备更强的泛化性
input = torch.tensor([[1 , -0.5],
[-1 , 3]])
# 注意 reshape里-1指的是batchsize(默认-1就行) , 1是channel值 , 2,2是矩阵维度
input = torch.reshape(input , (-1,1,2,2))
print(input.shape)
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("dataseset_CIFAR10" , train=False , transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=False)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset , batch_size=64 )
class Tudui(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Tudui, self).__init__()
# 定义激活函数
self.relu1 = ReLU()
self.sigmoid1 = Sigmoid()
def forward(self , input):
# 使用激活函数
output = self.sigmoid1(input)
return output
tudui = Tudui()
writer = SummaryWriter("logs")
step = 0
for data in dataloader:
imgs , targets = data
output = tudui(imgs)
writer.add_images("before" , imgs ,step)
writer.add_images("Sigmoid" , output ,step)
step = step + 1
writer.close()
常用的有Sigmoid 和Relu
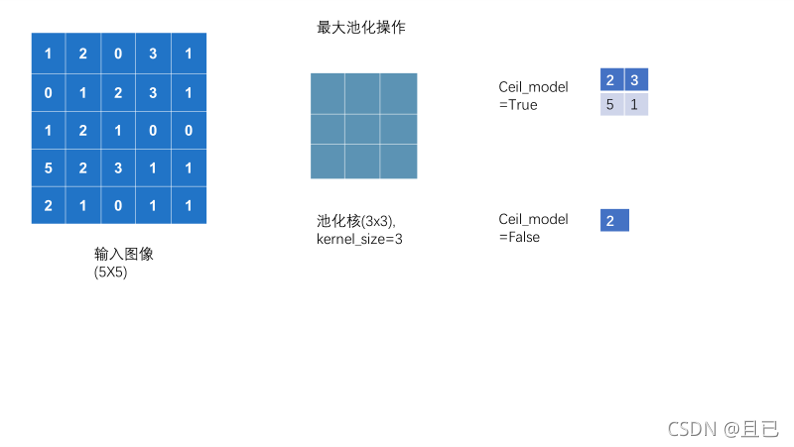
5.池化层
池化层的作用是去除不需要的像素点从而减少训练量
最大池化的卷积核是选取框框中最大的那一部分
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import MaxPool2d
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
# 池化层的作用是去除不需要的像素点从而减少训练量
# 最大池化的卷积核是选取框框中最大的那一部分
datdaset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("dataseset_CIFAR10" , train=False , transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()
,download=True)
dataloader = DataLoader(datdaset , batch_size=64 )
# input = torch.tensor([[1,2,0,3,1],
# [0,1,2,3,1],
# [1,2,1,0,0],
# [5,2,3,1,1],
# [2,1,0,1,1]], dtype=torch.float32)
#
# input = torch.reshape(input,(-1,1,5,5))
# print(input.shape)
class Tudui(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Tudui , self).__init__()
self.maxpool1 = MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3 , ceil_mode=True)
def forward(self,input):
output = self.maxpool1(input)
return output
tuidui = Tudui()
# output = tuidui(input)
# print(output)
writer = SummaryWriter("logs")
step = 0
for data in dataloader:
imgs , targets = data
writer.add_images("input" , imgs , step)
output = tuidui(imgs)
writer.add_images("output" , output ,step)
step = step +1
writer.close()
6.线性层或者说全连接层
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Linear
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("dataseset_CIFAR10" , train=False , transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=False)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset , batch_size=64)
class Tudui(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Tudui, self).__init__()
# 输入特征是196608 ,经过Linear变换变成特征为10的输出
self.linear1 = Linear(196608 , 10)
def forward(self , input):
output = self.linear1(input)
return output
tudui = Tudui()
for data in dataloader:
imgs , targets = data
print(imgs.shape)
# input = torch.reshape(imgs , (1,1,1,-1))
# torch.flatten()函数与上一行注释代码等效,表示把几行几列摊开成一行,用于展开成线性层的特征输入
input = torch.flatten(imgs)
print(input.shape)
output = tudui(input)
print(output.shape)
全连接层示意
flatten展平
padding,stride等的计算

7.Sequential的使用和简单模型的搭建
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Conv2d, MaxPool2d, Linear, Flatten, Sequential
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
class Tudui(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Tudui, self).__init__()
# self.conv1 = Conv2d(3 , 32 , 5, stride=1 , padding=2)
# self.maxpool1 = MaxPool2d(2)
# self.conv2 = Conv2d( 32 , 32 , 5 ,padding=2)
# self.maxpool2 = MaxPool2d(2)
# self.conv3 = Conv2d(32, 64 , 5 ,padding=2)
# self.maxpool3 = MaxPool2d(2)
# # 输入层到隐藏层
# self.linear1 = Linear(1024 , 64)
# # 隐藏层到输出层
# self.linear2 = Linear(64 , 10)
# self.flatten = Flatten()
# 引入一个Sequential,将做的操作打包成model1,以便下面使用
# 下面这段代码和上面注释的代码作用相同
self.model1 = Sequential(Conv2d(3 , 32 , 5, stride=1 , padding=2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Conv2d( 32 , 32 , 5 ,padding=2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Conv2d(32, 64 , 5 ,padding=2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Flatten(),
Linear(1024 , 64),
Linear(64 , 10))
def forward(self , x):
# x = self.conv1(x)
# x = self.maxpool1(x)
# x = self.conv2(x)
# x = self.maxpool2(x)
# x = self.conv3(x)
# x = self.maxpool3(x)
# x = self.flatten(x)
# x = self.linear1(x)
# x = self.linear2(x)
# 下面的代码作用和上面相同
x = self.model1(x)
return x
tudui = Tudui()
print(tudui)
input = torch.ones((64,3,32,32))
output = tudui(input)
print(output.shape)
writer = SummaryWriter("logs")
writer.add_graph(tudui , input)
writer.close()