文章目录
SwinIR 论文

主要工作:将 Swin Transformer 在图像恢复中应用,降低参数量的同时取得很好的效果。
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2108.10257.pdf
源代码:https://github.com/JingyunLiang/SwinIR
SWinIR 网络结构
整体框架
SwinIR 的网络结构主要分为 3 个部分,分别是浅层特征提取模块,深层特征提取模块和高质量图像重建模块。其中前后两个模块都是基于 CNN 的,中间模块则主要使用 SwInTransformer。
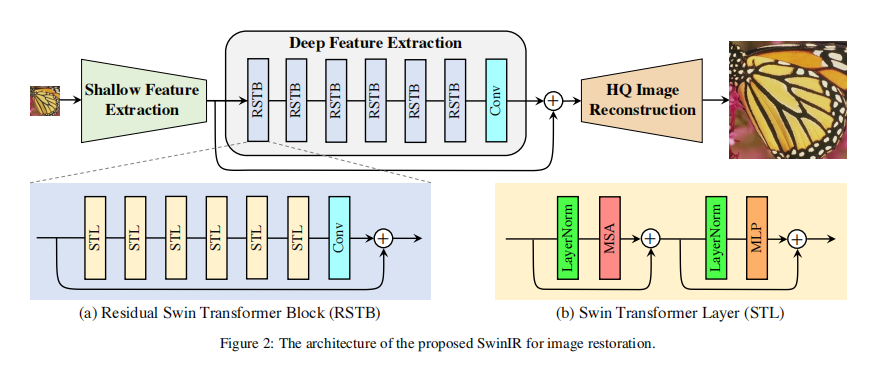
浅层特征提取
浅层特征提取只使用一层卷积进行提取。(注:这是一个容易改进的地方)
深层特征提取
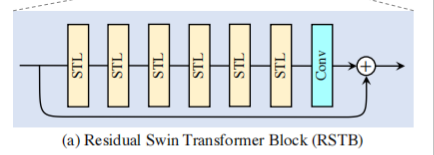
深层特征提取模块由若干个残差 SwInTransformer 块 (RSTB) 和卷积块构成,具体结构如下图。
(1) 首先将来自浅层特征提取模块的特征图分割成多个不重叠的 patch embeddings;
(2) 再通过多个串联的残差 SWin Transformer 块 (RSTB);
(3) 将多个不重叠的 patch embeddings 重新组合成与输入特征图分辨率一样;
(4) 最后通过一个卷积层 (1 层或3 层卷积) 输出;
(5) 在每个 RSTB 中都引入残差连接。
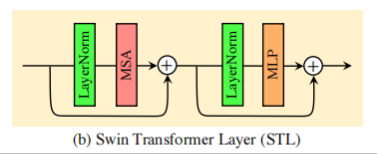
残差 SwInTransformer 块 (RSTB) 中的 STL 就是 SwIn Transformer Layer 的意思,具体结构如下图。
(1) 首先通过一个归一化层 LayerNorm;
(2) 再通过多头自注意力 (Multi-head Self Attention) 模块;
(3) 在多头自注意力结尾引入残差;
(4) 再通过一个归一化层 LayerNorm;
(5) 最后通过一个多层感知机 MLP;
(6) 结尾同样引入残差。
图像重建模块
图像重建模块其实就是卷积+上采样的组合,在这块论文提出 4 种结构。(注:这是一个容易改进的地方)
(1) 经典超分 (卷积 + pixelshuffle 上采样 + 卷积);
(2) 轻量超分 (卷积 + pixelshuffle 上采样);
(3) 真实图像超分 (卷积 + 卷积插值上采样 + 卷积插值上采样 + 卷积);
(4) 像去噪和 JPEG 压缩去伪影 (卷积 + 引入残差)。
主要代码理解
关于 SwinIR 中涉及 CNN 的部分代码非常简单,就不在此单独列出,这里主要注释一下其中有关 Swin Transformer 的实现代码。另外针对不构成主要网络结构的部分代码进行了删减,完整代码请移步:
(1) GitHub 链接:https://github.com/JingyunLiang/SwinIR
(2) CSDN 链接:https://download.csdn.net/download/Wenyuanbo/40284900
(3) 详尽注释代码:https://download.csdn.net/download/Wenyuanbo/40284085
SwinIR
SwinIR 主要由浅层特征提取,深层特征提取和高质量图像重建模块组成,具体原理如前所说,直接欣赏代码吧。
# SWinIR
class SwinIR(nn.Module):
r""" SwinIR
基于 Swin Transformer 的图像恢复网络.
输入:
img_size (int | tuple(int)): 输入图像的大小,默认为 64*64.
patch_size (int | tuple(int)): patch 的大小,默认为 1.
in_chans (int): 输入图像的通道数,默认为 3.
embed_dim (int): Patch embedding 的维度,默认为 96.
depths (tuple(int)): Swin Transformer 层的深度.
num_heads (tuple(int)): 在不同层注意力头的个数.
window_size (int): 窗口大小,默认为 7.
mlp_ratio (float): MLP隐藏层特征图通道与嵌入层特征图通道的比,默认为 4.
qkv_bias (bool): 给 query, key, value 添加可学习的偏置,默认为 True.
qk_scale (float): 重写默认的缩放因子,默认为 None.
drop_rate (float): 随机丢弃神经元,丢弃率默认为 0.
attn_drop_rate (float): 注意力权重的丢弃率,默认为 0.
drop_path_rate (float): 深度随机丢弃率,默认为 0.1.
norm_layer (nn.Module): 归一化操作,默认为 nn.LayerNorm.
ape (bool): patch embedding 添加绝对位置 embedding,默认为 False.
patch_norm (bool): 在 patch embedding 后添加归一化操作,默认为 True.
use_checkpoint (bool): 是否使用 checkpointing 来节省显存,默认为 False.
upscale: 放大因子, 2/3/4/8 适合图像超分, 1 适合图像去噪和 JPEG 压缩去伪影
img_range: 灰度值范围, 1 或者 255.
upsampler: 图像重建方法的选择模块,可选择 pixelshuffle, pixelshuffledirect, nearest+conv 或 None.
resi_connection: 残差连接之前的卷积块, 可选择 1conv 或 3conv.
"""
def __init__(self, img_size=64, patch_size=1, in_chans=3,
embed_dim=96, depths=[6, 6, 6, 6], num_heads=[6, 6, 6, 6],
window_size=7, mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None,
drop_rate=0., attn_drop_rate=0., drop_path_rate=0.1,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, ape=False, patch_norm=True,
use_checkpoint=False, upscale=2, img_range=1., upsampler='', resi_connection='1conv',
**kwargs):
super(SwinIR, self).__init__()
num_in_ch = in_chans # 输入图片通道数
num_out_ch = in_chans # 输出图片通道数
num_feat = 64 # 特征图通道数
self.img_range = img_range # 灰度值范围:[0, 1] or [0, 255]
if in_chans == 3: # 如果输入是RGB图像
rgb_mean = (0.4488, 0.4371, 0.4040) # 数据集RGB均值
self.mean = torch.Tensor(rgb_mean).view(1, 3, 1, 1) # 转为[1, 3, 1, 1]的张量
else: # 否则灰度图
self.mean = torch.zeros(1, 1, 1, 1) # 构造[1, 1, 1, 1]的张量
self.upscale = upscale # 图像放大倍数,超分(2/3/4/8),去噪(1)
self.upsampler = upsampler # 上采样方法
self.window_size = window_size # 注意力窗口的大小
#######################################################################################
################################### 1, 浅层特征提取 ###################################
self.conv_first = nn.Conv2d(num_in_ch, embed_dim, 3, 1, 1) # 输入卷积层
##########################################################################################
################################### 2, 深层特征提取 ######################################
self.num_layers = len(depths) # Swin Transformer 层的个数
self.embed_dim = embed_dim # 嵌入层特征图的通道数
self.ape = ape # patch embedding 添加绝对位置 embedding,默认为 False.
self.patch_norm = patch_norm # 在 patch embedding 后添加归一化操作,默认为 True.
self.num_features = embed_dim # 特征图的通道数
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio # MLP隐藏层特征图通道与嵌入层特征图通道的比
# 将图像分割成多个不重叠的patch
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(
img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=embed_dim, embed_dim=embed_dim,
norm_layer=norm_layer if self.patch_norm else None)
num_patches = self.patch_embed.num_patches # 分割得到patch的个数
patches_resolution = self.patch_embed.patches_resolution # 分割得到patch的分辨率
self.patches_resolution = patches_resolution
# 将多个不重叠的patch合并成图像
self.patch_unembed = PatchUnEmbed(
img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=embed_dim, embed_dim=embed_dim,
norm_layer=norm_layer if self.patch_norm else None)
# 绝对位置嵌入
if self.ape:
# 结构为 [1,patch个数, 嵌入层特征图的通道数] 的参数
self.absolute_pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, num_patches, embed_dim))
trunc_normal_(self.absolute_pos_embed, std=.02) # 截断正态分布,限制标准差为0.02
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_rate) # 以drop_rate为丢弃率随机丢弃神经元,默认不丢弃
# 随机深度衰减规律,默认为 [0, 0.1] 进行24等分后的列表
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))]
# Residual Swin Transformer blocks (RSTB)
# 残差 Swin Transformer 块 (RSTB)
self.layers = nn.ModuleList() # 创建一个ModuleList实例对象,也就是多个 RSTB
for i_layer in range(self.num_layers): # 循环 Swin Transformer 层的个数次
# 实例化 RSTB
layer = RSTB(dim=embed_dim,
input_resolution=(patches_resolution[0],
patches_resolution[1]),
depth=depths[i_layer],
num_heads=num_heads[i_layer],
window_size=window_size,
mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
drop=drop_rate, attn_drop=attn_drop_rate,
drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_layer]):sum(depths[:i_layer + 1])], # no impact on SR results
norm_layer=norm_layer,
downsample=None,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint,
img_size=img_size,
patch_size=patch_size,
resi_connection=resi_connection
)
self.layers.append(layer) # 将 RSTB 对象插入 ModuleList 中
self.norm = norm_layer(self.num_features) # 归一化操作,默认 LayerNorm
# 在深层特征提取网络中加入卷积块,保持特征图通道数不变
if resi_connection == '1conv': # 1层卷积
self.conv_after_body = nn.Conv2d(embed_dim, embed_dim, 3, 1, 1)
elif resi_connection == '3conv': # 3层卷积
# 为了减少参数使用和节约显存,采用瓶颈结构
self.conv_after_body = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(embed_dim, embed_dim // 4, 3, 1, 1), # 降维
nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(embed_dim // 4, embed_dim // 4, 1, 1, 0),
nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(embed_dim // 4, embed_dim, 3, 1, 1)) # 升维
# 高质量图像重建模块
if self.upsampler == 'pixelshuffle': # pixelshuffle 上采样
# 适合经典超分
self.conv_before_upsample = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(embed_dim, num_feat, 3, 1, 1),
nn.LeakyReLU(inplace=True))
self.upsample = Upsample(upscale, num_feat) # 上采样
self.conv_last = nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_out_ch, 3, 1, 1) # 输出卷积层
elif self.upsampler == 'pixelshuffledirect': # 一步是实现既上采样也降维
# 适合轻量级充分,可以减少参数量(一步是实现既上采样也降维)
self.upsample = UpsampleOneStep(upscale, embed_dim, num_out_ch,
(patches_resolution[0], patches_resolution[1]))
elif self.upsampler == 'nearest+conv': # 最近邻插值上采样
# 适合真实图像超分
assert self.upscale == 4, 'only support x4 now.' # 声明目前仅支持4倍超分重建
# 上采样之前的卷积层
self.conv_before_upsample = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(embed_dim, num_feat, 3, 1, 1),
nn.LeakyReLU(inplace=True))
# 第一次上采样卷积(直接对输入做最近邻插值变为2倍图像)
self.conv_up1 = nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat, 3, 1, 1)
# 第二次上采样卷积(直接对输入做最近邻插值变为2倍图像)
self.conv_up2 = nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat, 3, 1, 1)
self.conv_hr = nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_feat, 3, 1, 1) # 对上采样完成的图像再做卷积
self.lrelu = nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True) # 激活层
self.conv_last = nn.Conv2d(num_feat, num_out_ch, 3, 1, 1) # 输出卷积层
else:
# 适合图像去噪和 JPEG 压缩去伪影
self.conv_last = nn.Conv2d(embed_dim, num_out_ch, 3, 1, 1)
self.apply(self._init_weights) # 初始化网络参数
# 初始化网络参数
def _init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear): # 判断是否为线性 Linear 层
trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02) # 截断正态分布,限制标准差为 0.02
if m.bias is not None: # 如果设置了偏置
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0) # 初始化偏置为 0
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm): # 判断是否为归一化 LayerNorm 层
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0) # 初始化偏置为 0
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0) # 初始化权重系数为 1
# 检查图片(准确说是张量)的大小
def check_image_size(self, x):
_, _, h, w = x.size() # 张量 x 的高和宽
# h 维度要填充的个数
mod_pad_h = (self.window_size - h % self.window_size) % self.window_size
# w 维度要填充的个数
mod_pad_w = (self.window_size - w % self.window_size) % self.window_size
# 右填充 mod_pad_w 个值,下填充 mod_pad_h 个值,模式为反射(可以理解为以 x 的维度末尾为轴对折)
x = F.pad(x, (0, mod_pad_w, 0, mod_pad_h), 'reflect')
return x
# 深层特征提取网络的前向传播
def forward_features(self, x):
x_size = (x.shape[2], x.shape[3]) # 张量 x 的高和宽
x = self.patch_embed(x) # 分割 x 为多个不重叠的 patch embeddings
if self.ape: # 绝对位置 embedding
x = x + self.absolute_pos_embed # x 加上对应的绝对位置 embedding
x = self.pos_drop(x) # 随机将x中的部分元素置 0
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x, x_size) # x 通过多个串联的 RSTB
x = self.norm(x) # 对 RSTB 的输出进行归一化
x = self.patch_unembed(x, x_size) # 将多个不重叠的 patch 合并成图像
return x
# SWinIR 的前向传播
def forward(self, x):
H, W = x.shape[2:] # 输入图片的高和宽
x = self.check_image_size(x) # 检查图片的大小,使高宽满足 window_size 的整数倍
self.mean = self.mean.type_as(x) # RGB 均值的类型同 x 一致
x = (x - self.mean) * self.img_range # x 减去 RGB 均值再乘以输入的最大灰度值
if self.upsampler == 'pixelshuffle': # pixelshuffle 上采样方法
# 适合经典超分
x = self.conv_first(x) # 输入卷积层
x = self.conv_after_body(self.forward_features(x)) + x # 深度特征提取网络,引入残差
x = self.conv_before_upsample(x) # 上采样前进行卷积
x = self.conv_last(self.upsample(x)) # 上采样后再通过输出卷积层
elif self.upsampler == 'pixelshuffledirect': # 一步是实现既上采样也降维
# 适合轻量级超分
x = self.conv_first(x) # 输入卷积层
x = self.conv_after_body(self.forward_features(x)) + x # 深度特征提取网络,引入残差
x = self.upsample(x) # 上采样并降维后输出
elif self.upsampler == 'nearest+conv': # 最近邻插值上采样方法
# 适合真实图像超分,只适合 4 倍超分
x = self.conv_first(x) # 输入卷积层
x = self.conv_after_body(self.forward_features(x)) + x # 深度特征提取网络,引入残差
x = self.conv_before_upsample(x) # 上采样前进行卷积
# 第一次上采样 2 倍
x = self.lrelu(self.conv_up1(torch.nn.functional.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')))
# 第二次上采样 2 倍
x = self.lrelu(self.conv_up2(torch.nn.functional.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')))
x = self.conv_last(self.lrelu(self.conv_hr(x))) # 输出卷积层
else:
# 适合图像去噪和 JPEG 压缩去伪影
x_first = self.conv_first(x) # 输入卷积层
res = self.conv_after_body(self.forward_features(x_first)) + x_first # 深度特征提取网络,引入残差
x = x + self.conv_last(res) # 输出卷积层,引入残差
x = x / self.img_range + self.mean # 最后的 x 除以灰度值范围再加上 RGB 均值
return x[:, :, :H*self.upscale, :W*self.upscale] # 返回输出 x
MLP
多层感知机 MLP 是 transformer 比较基础的部分,具体原理也很简单。
# 多层感知机
class Mlp(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.GELU, drop=0.):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features # 输入特征的维度
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features # 隐藏特征维度
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features) # 线性层
self.act = act_layer() # 激活函数
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features) # 线性层
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop) # 随机丢弃神经元,丢弃率默认为 0
# 定义前向传播
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop(x)
return x
Patch Embedding
主要的操作就是将原始 2 维图像 (特征图的一个 plane 或者说一个 channel) 转变为 1 维的 patch embeddings,通过 Swin Transformer 学习处理之后再重新组合成与原来特征图结构一致的新特征图。
(1) 将 2 维图像转变成 1 维 patch embeddings。
# 图像转成 Patch Embeddings
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
r""" Image to Patch Embedding
输入:
img_size (int): 图像的大小,默认为 224*224.
patch_size (int): Patch token 的大小,默认为 4*4.
in_chans (int): 输入图像的通道数,默认为 3.
embed_dim (int): 线性 projection 输出的通道数,默认为 96.
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): 归一化层, 默认为N None.
"""
def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, embed_dim=96, norm_layer=None):
super().__init__()
img_size = to_2tuple(img_size) # 图像的大小,默认为 224*224
patch_size = to_2tuple(patch_size) # Patch token 的大小,默认为 4*4
patches_resolution = [img_size[0] // patch_size[0], img_size[1] // patch_size[1]] # patch 的分辨率
self.img_size = img_size
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.patches_resolution = patches_resolution
self.num_patches = patches_resolution[0] * patches_resolution[1] # patch 的个数,num_patches
self.in_chans = in_chans # 输入图像的通道数
self.embed_dim = embed_dim # 线性 projection 输出的通道数
if norm_layer is not None:
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim) # 归一化
else:
self.norm = None
# 定义前向传播
def forward(self, x):
x = x.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2) # 结构为 [B, num_patches, C]
if self.norm is not None:
x = self.norm(x) # 归一化
return x
(2) 将 1 维 patch embeddings 转变为 2 维图像。
# 从 Patch Embeddings 组合图像
class PatchUnEmbed(nn.Module):
r""" Image to Patch Unembedding
输入:
img_size (int): 图像的大小,默认为 224*224.
patch_size (int): Patch token 的大小,默认为 4*4.
in_chans (int): 输入图像的通道数,默认为 3.
embed_dim (int): 线性 projection 输出的通道数,默认为 96.
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): 归一化层, 默认为N None.
"""
def __init__(self, img_size=224, patch_size=4, in_chans=3, embed_dim=96, norm_layer=None):
super().__init__()
img_size = to_2tuple(img_size) # 图像的大小,默认为 224*224
patch_size = to_2tuple(patch_size) # Patch token 的大小,默认为 4*4
patches_resolution = [img_size[0] // patch_size[0], img_size[1] // patch_size[1]] # patch 的分辨率
self.img_size = img_size
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.patches_resolution = patches_resolution
self.num_patches = patches_resolution[0] * patches_resolution[1] # patch 的个数,num_patches
self.in_chans = in_chans # 输入图像的通道数
self.embed_dim = embed_dim # 线性 projection 输出的通道数
def forward(self, x, x_size):
B, HW, C = x.shape # 输入 x 的结构
x = x.transpose(1, 2).view(B, self.embed_dim, x_size[0], x_size[1]) # 输出结构为 [B, Ph*Pw, C]
return x
Window Attention
采用窗口注意力来减轻传统 Transformer 的全局注意力带来的计算负担,将注意力的计算限制在每一个窗口里,在每个窗口里其实还是原始的多头自注意力。(注:这个窗口注意力我之前也有过类似想法,主要是考虑到由于网络测试阶段的输入图像大小是不定的,如果在其中加入注意力机制得到的注意力图也是不定的,这一定程度上限制网络的泛化性能,将窗口注意力的思想迁移到 CNN 相信也能有不错的表现)
(1) 窗口分割
# 将输入分割为多个不重叠窗口
def window_partition(x, window_size):
"""
输入:
x: (B, H, W, C)
window_size (int): window size # 窗口的大小
返回:
windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C) # 每一个 batch 有单独的 windows
"""
B, H, W, C = x.shape # 输入的 batch 个数,高,宽,通道数
# 将输入 x 重构为结构 [batch 个数,高方向的窗口个数,窗口大小,宽方向的窗口个数,窗口大小,通道数] 的张量
x = x.view(B, H // window_size, window_size, W // window_size, window_size, C)
# 交换重构后 x 的第 3和4 维度, 5和6 维度,再次重构为结构 [高和宽方向的窗口个数乘以 batch 个数,窗口大小,窗口大小,通道数] 的张量
windows = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(-1, window_size, window_size, C)
return windows
# 这里比较有意思,不太理解的可以给个初始值,比如 x = torch.randn([1, 14, 28, 3])
(2) 窗口注意力
这里的相对位置索引比较有意思,有不明白的可以参考:图解Swin Transformer。
# 窗口注意力
class WindowAttention(nn.Module):
r""" 基于有相对位置偏差的多头自注意力窗口,支持移位的(shifted)或者不移位的(non-shifted)窗口.
输入:
dim (int): 输入特征的维度.
window_size (tuple[int]): 窗口的大小.
num_heads (int): 注意力头的个数.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): 给 query, key, value 添加可学习的偏置,默认为 True.
qk_scale (float | None, optional): 重写默认的缩放因子 scale.
attn_drop (float, optional): 注意力权重的丢弃率,默认为 0.0.
proj_drop (float, optional): 输出的丢弃率,默认为 0.0.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, window_size, num_heads, qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, attn_drop=0., proj_drop=0.):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim # 输入特征的维度
self.window_size = window_size # 窗口的高 Wh,宽 Ww
self.num_heads = num_heads # 注意力头的个数
head_dim = dim // num_heads # 注意力头的维度
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5 # 缩放因子 scale
# 定义相对位置偏移的参数表,结构为 [2*Wh-1 * 2*Ww-1, num_heads]
self.relative_position_bias_table = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros((2 * window_size[0] - 1) * (2 * window_size[1] - 1), num_heads))
# 获取窗口内每个 token 的成对的相对位置索引
coords_h = torch.arange(self.window_size[0]) # 高维度上的坐标 (0, 7)
coords_w = torch.arange(self.window_size[1]) # 宽维度上的坐标 (0, 7)
coords = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid([coords_h, coords_w])) # 坐标,结构为 [2, Wh, Ww]
coords_flatten = torch.flatten(coords, 1) # 重构张量结构为 [2, Wh*Ww]
relative_coords = coords_flatten[:, :, None] - coords_flatten[:, None, :] # 相对坐标,结构为 [2, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww]
relative_coords = relative_coords.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous() # 交换维度,结构为 [Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, 2]
relative_coords[:, :, 0] += self.window_size[0] - 1 # 第1个维度移位
relative_coords[:, :, 1] += self.window_size[1] - 1 # 第1个维度移位
relative_coords[:, :, 0] *= 2 * self.window_size[1] - 1 # 第1个维度的值乘以 2倍的 Ww,再减 1
relative_position_index = relative_coords.sum(-1) # 相对位置索引,结构为 [Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww]
self.register_buffer("relative_position_index", relative_position_index) # 保存数据,不再更新
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias) # 线性层,特征维度变为原来的 3倍
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop) # 随机丢弃神经元,丢弃率默认为 0.0
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim) # 线性层,特征维度不变
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop) # 随机丢弃神经元,丢弃率默认为 0.0
trunc_normal_(self.relative_position_bias_table, std=.02) # 截断正态分布,限制标准差为 0.02
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1) # 激活函数 softmax
# 定义前向传播
def forward(self, x, mask=None):
"""
输入:
x: 输入特征图,结构为 [num_windows*B, N, C]
mask: (0/-inf) mask, 结构为 [num_windows, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww] 或者没有 mask
"""
B_, N, C = x.shape # 输入特征图的结构
# 将特征图的通道维度按照注意力头的个数重新划分,并再做交换维度操作
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B_, N, 3, self.num_heads, C // self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2] # 方便后续写代码,重新赋值
# q 乘以缩放因子
q = q * self.scale
# @ 代表常规意义上的矩阵相乘
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) # q 和 k 相乘后并交换最后两个维度
# 相对位置偏移,结构为 [Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww, num_heads]
relative_position_bias = self.relative_position_bias_table[self.relative_position_index.view(-1)].view(
self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], self.window_size[0] * self.window_size[1], -1)
# 相对位置偏移交换维度,结构为 [num_heads, Wh*Ww, Wh*Ww]
relative_position_bias = relative_position_bias.permute(2, 0, 1).contiguous()
attn = attn + relative_position_bias.unsqueeze(0) # 带相对位置偏移的注意力图
if mask is not None: # 判断是否有 mask
nW = mask.shape[0] # mask 的宽
# 注意力图与 mask 相加
attn = attn.view(B_ // nW, nW, self.num_heads, N, N) + mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(0)
attn = attn.view(-1, self.num_heads, N, N) # 恢复注意力图原来的结构
attn = self.softmax(attn) # 激活注意力图 [0, 1] 之间
else:
attn = self.softmax(attn)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn) # 随机设置注意力图中的部分值为 0
# 注意力图与 v 相乘得到新的注意力图
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B_, N, C)
x = self.proj(x) # 通过线性层
x = self.proj_drop(x) # 随机设置新注意力图中的部分值为 0
return x
(3) 窗口合并
# 将多个不重叠窗口重新合并
def window_reverse(windows, window_size, H, W):
"""
输入:
windows: (num_windows*B, window_size, window_size, C) # 分割得到的窗口(已处理)
window_size (int): Window size # 窗口大小
H (int): Height of image # 原分割窗口前特征图的高
W (int): Width of image # 原分割窗口前特征图的宽
返回:
x: (B, H, W, C) # 返回与分割前特征图结构一样的结果
"""
# 以下就是分割窗口的逆向操作,不多解释
B = int(windows.shape[0] / (H * W / window_size / window_size))
x = windows.view(B, H // window_size, W // window_size, window_size, window_size, -1)
x = x.permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous().view(B, H, W, -1)
return x
残差 Swin Transformer 块 (RSTB)
SwinIR 主要是使用 Swin Transformer 的思想来实现,残差 Swin Transformer 块 (RSTB) 可以理解为:
(1) Swin Transformer 块是 RSTB 的基础组件;
(2) 多个 Swin Transformer 块构成基础网络;
(3) 基础网络结尾处加上卷积操作后再引入残差构成 RSTB。
(1) Swin Transformer 块
# Swin Transformer 块
class SwinTransformerBlock(nn.Module):
"""
输入:
dim (int): 输入特征的维度.
input_resolution (tuple[int]): 输入特征图的分辨率.
num_heads (int): 注意力头的个数.
window_size (int): 窗口的大小.
shift_size (int): SW-MSA 的移位值.
mlp_ratio (float): 多层感知机隐藏层的维度和嵌入层的比.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): 给 query, key, value 添加一个可学习偏置,默认为 True.
qk_scale (float | None, optional): 重写默认的缩放因子 scale.
drop (float, optional): 随机神经元丢弃率,默认为 0.0.
attn_drop (float, optional): 注意力图随机丢弃率,默认为 0.0.
drop_path (float, optional): 深度随机丢弃率,默认为 0.0.
act_layer (nn.Module, optional): 激活函数,默认为 nn.GELU.
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): 归一化操作,默认为 nn.LayerNorm.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, input_resolution, num_heads, window_size=7, shift_size=0,
mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0., drop_path=0.,
act_layer=nn.GELU, norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim # 输入特征的维度
self.input_resolution = input_resolution # 输入特征图的分辨率
self.num_heads = num_heads # 注意力头的个数
self.window_size = window_size # 窗口的大小
self.shift_size = shift_size # SW-MSA 的移位大小
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio # 多层感知机隐藏层的维度和嵌入层的比
if min(self.input_resolution) <= self.window_size: # 如果输入分辨率小于等于窗口大小
self.shift_size = 0 # 移位大小为 0
self.window_size = min(self.input_resolution) # 窗口大小等于输入分辨率大小
# 断言移位值必须小于等于窗口的大小
assert 0 <= self.shift_size < self.window_size, "shift_size must in 0-window_size"
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim) # 归一化层
# 窗口注意力
self.attn = WindowAttention(
dim, window_size=to_2tuple(self.window_size), num_heads=num_heads,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale, attn_drop=attn_drop, proj_drop=drop)
# 如果丢弃率大于 0 则进行随机丢弃,否则进行占位(不做任何操作)
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim) # 归一化层
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio) # 多层感知机隐藏层维度
# 多层感知机
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=mlp_hidden_dim, act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop)
if self.shift_size > 0: # 如果移位值大于 0
attn_mask = self.calculate_mask(self.input_resolution) # 计算注意力 mask
else:
attn_mask = None # 注意力 mask 赋空
self.register_buffer("attn_mask", attn_mask) # 保存注意力 mask,不参与更新
# 计算注意力 mask
def calculate_mask(self, x_size):
H, W = x_size # 特征图的高宽
img_mask = torch.zeros((1, H, W, 1)) # 新建张量,结构为 [1, H, W, 1]
# 以下两 slices 中的数据是索引,具体缘由尚未搞懂
h_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size), # 索引 0 到索引倒数第 window_size
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size), # 索引倒数第 window_size 到索引倒数第 shift_size
slice(-self.shift_size, None)) # 索引倒数第 shift_size 后所有索引
w_slices = (slice(0, -self.window_size),
slice(-self.window_size, -self.shift_size),
slice(-self.shift_size, None))
cnt = 0
for h in h_slices:
for w in w_slices:
img_mask[:, h, w, :] = cnt # 将 img_mask 中 h, w 对应索引范围的值置为 cnt
cnt += 1 # 加 1
mask_windows = window_partition(img_mask, self.window_size) # 窗口分割,返回值结构为 [nW, window_size, window_size, 1]
mask_windows = mask_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size) # 重构结构为二维张量,列数为 [window_size*window_size]
attn_mask = mask_windows.unsqueeze(1) - mask_windows.unsqueeze(2) # 增加第 2 维度减去增加第 3 维度的注意力 mask
# 用浮点数 -100. 填充注意力 mask 中值不为 0 的元素,再用浮点数 0. 填充注意力 mask 中值为 0 的元素
attn_mask = attn_mask.masked_fill(attn_mask != 0, float(-100.0)).masked_fill(attn_mask == 0, float(0.0))
return attn_mask
# 定义前向传播
def forward(self, x, x_size):
H, W = x_size # 输入特征图的分辨率
B, L, C = x.shape # 输入特征的 batch 个数,长度和维度
# assert L == H * W, "input feature has wrong size"
shortcut = x
x = self.norm1(x) # 归一化
x = x.view(B, H, W, C) # 重构 x 为结构 [B, H, W, C]
# 循环移位
if self.shift_size > 0: # 如果移位值大于 0
# 第 0 维度上移 shift_size 位,第 1 维度左移 shift_size 位
shifted_x = torch.roll(x, shifts=(-self.shift_size, -self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else:
shifted_x = x # 不移位
# 对移位操作得到的特征图分割窗口, nW 是窗口的个数
x_windows = window_partition(shifted_x, self.window_size) # 结构为 [nW*B, window_size, window_size, C]
x_windows = x_windows.view(-1, self.window_size * self.window_size, C) # 结构为 [nW*B, window_size*window_size, C]
# W-MSA/SW-MSA, 用在分辨率是窗口大小的整数倍的图像上进行测试
if self.input_resolution == x_size: # 输入分辨率与设定一致,不需要重新计算注意力 mask
attn_windows = self.attn(x_windows, mask=self.attn_mask) # 注意力窗口,结构为 [nW*B, window_size*window_size, C]
else: # 输入分辨率与设定不一致,需要重新计算注意力 mask
attn_windows = self.attn(x_windows, mask=self.calculate_mask(x_size).to(x.device))
# 合并窗口
attn_windows = attn_windows.view(-1, self.window_size, self.window_size, C) # 结构为 [-1, window_size, window_size, C]
shifted_x = window_reverse(attn_windows, self.window_size, H, W) # 结构为 [B, H', W', C]
# 逆向循环移位
if self.shift_size > 0:
# 第 0 维度下移 shift_size 位,第 1 维度右移 shift_size 位
x = torch.roll(shifted_x, shifts=(self.shift_size, self.shift_size), dims=(1, 2))
else:
x = shifted_x # 不逆向移位
x = x.view(B, H * W, C) # 结构为 [B, H*W, C]
# FFN
x = shortcut + self.drop_path(x) # 对 x 做 dropout,引入残差
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x))) # 归一化后通过 MLP,再做 dropout,引入残差
return x
(2) 基础网络
# 单阶段的 SWin Transformer 基础层
class BasicLayer(nn.Module):
"""
输入:
dim (int): 输入特征的维度.
input_resolution (tuple[int]): 输入分辨率.
depth (int): SWin Transformer 块的个数.
num_heads (int): 注意力头的个数.
window_size (int): 本地(当前块中)窗口的大小.
mlp_ratio (float): MLP隐藏层特征维度与嵌入层特征维度的比.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): 给 query, key, value 添加一个可学习偏置,默认为 True.
qk_scale (float | None, optional): 重写默认的缩放因子 scale.
drop (float, optional): 随机丢弃神经元,丢弃率默认为 0.0.
attn_drop (float, optional): 注意力图随机丢弃率,默认为 0.0.
drop_path (float | tuple[float], optional): 深度随机丢弃率,默认为 0.0.
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): 归一化操作,默认为 nn.LayerNorm.
downsample (nn.Module | None, optional): 结尾处的下采样层,默认没有.
use_checkpoint (bool): 是否使用 checkpointing 来节省显存,默认为 False.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, input_resolution, depth, num_heads, window_size,
mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0.,
drop_path=0., norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, downsample=None, use_checkpoint=False):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim # 输入特征的维度
self.input_resolution = input_resolution # 输入分辨率
self.depth = depth # SWin Transformer 块的个数
self.use_checkpoint = use_checkpoint # 是否使用 checkpointing 来节省显存,默认为 False
# 创建 Swin Transformer 网络
self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
SwinTransformerBlock(dim=dim, input_resolution=input_resolution,
num_heads=num_heads, window_size=window_size,
shift_size=0 if (i % 2 == 0) else window_size // 2,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
drop=drop, attn_drop=attn_drop,
drop_path=drop_path[i] if isinstance(drop_path, list) else drop_path,
norm_layer=norm_layer)
for i in range(depth)])
# patch 合并层
if downsample is not None: # 如果有下采样
self.downsample = downsample(input_resolution, dim=dim, norm_layer=norm_layer) # 下采样
else:
self.downsample = None # 不做下采样
#定义前向传播
def forward(self, x, x_size):
for blk in self.blocks: # x 输入串联的 Swin Transformer 块
if self.use_checkpoint:
x = checkpoint.checkpoint(blk, x, x_size) # 使用 checkpoint
else:
x = blk(x, x_size) # 直接输入网络
if self.downsample is not None:
x = self.downsample(x) # 下采样
return x
(3) 残差 Swin Transformer 块 (RSTB)
# 残差 Swin Transforme 块 (RSTB)
class RSTB(nn.Module):
"""
输入:
dim (int): 输入特征的维度.
input_resolution (tuple[int]): 输入分辨率.
depth (int): SWin Transformer 块的个数.
num_heads (int): 注意力头的个数.
window_size (int): 本地(当前块中)窗口的大小.
mlp_ratio (float): MLP隐藏层特征维度与嵌入层特征维度的比.
qkv_bias (bool, optional): 给 query, key, value 添加一个可学习偏置,默认为 True.
qk_scale (float | None, optional): 重写默认的缩放因子 scale.
drop (float, optional): D 随机丢弃神经元,丢弃率默认为 0.0.
attn_drop (float, optional): 注意力图随机丢弃率,默认为 0.0.
drop_path (float | tuple[float], optional): 深度随机丢弃率,默认为 0.0.
norm_layer (nn.Module, optional): 归一化操作,默认为 nn.LayerNorm.
downsample (nn.Module | None, optional): 结尾处的下采样层,默认没有.
use_checkpoint (bool): 是否使用 checkpointing 来节省显存,默认为 False.
img_size: 输入图片的大小.
patch_size: Patch 的大小.
resi_connection: 残差连接之前的卷积块.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, input_resolution, depth, num_heads, window_size,
mlp_ratio=4., qkv_bias=True, qk_scale=None, drop=0., attn_drop=0.,
drop_path=0., norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, downsample=None, use_checkpoint=False,
img_size=224, patch_size=4, resi_connection='1conv'):
super(RSTB, self).__init__()
self.dim = dim # 输入特征的维度
self.input_resolution = input_resolution # 输入分辨率
# SWin Transformer 基础层
self.residual_group = BasicLayer(dim=dim,
input_resolution=input_resolution,
depth=depth,
num_heads=num_heads,
window_size=window_size,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
drop=drop, attn_drop=attn_drop,
drop_path=drop_path,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
downsample=downsample,
use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
if resi_connection == '1conv': # 结尾用 1 个卷积层
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, 1, 1)
elif resi_connection == '3conv': # 结尾用 3 个卷积层
# 为了减少参数使用和节约显存,采用瓶颈结构
self.conv = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(dim, dim // 4, 3, 1, 1), nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(dim // 4, dim // 4, 1, 1, 0),
nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(dim // 4, dim, 3, 1, 1))
# 图像转成 Patch Embeddings
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(
img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=0, embed_dim=dim,
norm_layer=None)
# 从 Patch Embeddings 组合图像
self.patch_unembed = PatchUnEmbed(
img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_chans=0, embed_dim=dim,
norm_layer=None)
# 定义前向传播
def forward(self, x, x_size):
return self.patch_embed(self.conv(self.patch_unembed(self.residual_group(x, x_size), x_size))) + x # 引入残差
HQ Image Reconstruction
高质量图像重建模块其实就是卷积和上采样操作的组合,在这块论文提出 4 种结构。
(1) 经典超分 (卷积 + pixelshuffle 上采样 + 卷积);
(2) 轻量超分 (卷积 + pixelshuffle 上采样);
(3) 真实图像超分 (卷积 + 卷积插值上采样 + 卷积插值上采样 + 卷积);
(4) 像去噪和 JPEG 压缩去伪影 (卷积 + 引入残差)。
在这里主要看一下两种上采样操作:
(1) 先卷积再使用 pixelshuffle 上采样,特征图维度不是 3
# 上采样
class Upsample(nn.Sequential):
"""
输入:
scale (int): 缩放因子,支持 2^n and 3.
num_feat (int): 中间特征的通道数.
"""
def __init__(self, scale, num_feat):
m = []
if (scale & (scale - 1)) == 0: # 缩放因子等于 2^n
for _ in range(int(math.log(scale, 2))): # 循环 n 次
m.append(nn.Conv2d(num_feat, 4 * num_feat, 3, 1, 1)) # 卷积层
m.append(nn.PixelShuffle(2)) # pixelshuffle 上采样 2 倍
elif scale == 3: # 缩放因子等于 3
m.append(nn.Conv2d(num_feat, 9 * num_feat, 3, 1, 1)) # 卷积层
m.append(nn.PixelShuffle(3)) # pixelshuffle 上采样 3 倍
else:
# 报错,缩放因子不对
raise ValueError(f'scale {scale} is not supported. ' 'Supported scales: 2^n and 3.')
super(Upsample, self).__init__(*m)
(2) 一步既上采样也实现输出降维,特征图维度是 3,即最后的恢复图像
# 一步实现既上采样也降维
class UpsampleOneStep(nn.Sequential):
"""一步上采样与前边上采样模块不同之处在于该模块只有一个卷积层和一个 pixelshuffle 层
输入:
scale (int): 缩放因子,支持 2^n and 3.
num_feat (int): 中间特征的通道数.
"""
def __init__(self, scale, num_feat, num_out_ch, input_resolution=None):
self.num_feat = num_feat # 中间特征的通道数
self.input_resolution = input_resolution # 输入分辨率
m = []
m.append(nn.Conv2d(num_feat, (scale ** 2) * num_out_ch, 3, 1, 1)) # 卷积层
m.append(nn.PixelShuffle(scale)) # pixelshuffle 上采样 scale 倍
super(UpsampleOneStep, self).__init__(*m)
一个测试实例
虽然 SwinIR 的整体参数不大,但是计算负担比较大。
upscale = 4 # 图像放大因子
window_size = 8 # 窗口大小
height = (1024 // upscale // window_size + 1) * window_size # 输入图像的高
width = (720 // upscale // window_size + 1) * window_size # 输入图像的宽
# 实例化 SWinIR
model = SwinIR(upscale=2, img_size=(height, width),
window_size=window_size, img_range=1., depths=[6, 6, 6, 6],
embed_dim=60, num_heads=[6, 6, 6, 6], mlp_ratio=2, upsampler='pixelshuffledirect')
print(model) # 打印网络结构
print(height, width) # 打印输入图像的高和宽
x = torch.randn((1, 3, height, width)) #随机生成输入图像
x = model(x) # 送入网络
print(x.shape) # 打印网络输入的图像结构
参考文献
[1] Liang J, Cao J, Sun G, et al. SwinIR: Image restoration using swin transformer[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2021: 1833-1844.
[2] Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.14030, 2021.
结语
转载请注明出处。SwinIR 本身没有太多创新,主要还是 Swin Transformer 在图像恢复领域进行应用,但是整体网络对显卡的要求已经很接近纯 CNN 的网络。完整的 SwinIR 的注释代码可以移步链接:https://download.csdn.net/download/Wenyuanbo/40284085。既然现在 Swin Transfomer 已经公开,那相信不久就会如同当初的 ResNet 一样有许多改进方案不断出现,先到先得。如果我的这篇文章对你有所帮助,希望能不吝点赞关注一波。