CBAM论文解读+CBAM-ResNeXt的Pytorch实现
本文参考了CBAM模块与ResNeXt实现的官方代码,给出代码GitHub地址如下:
1.CBAM
2.ResNeXt
3.CBAM论文地址
1.CBAM论文解读:
此处仅是本人对论文实现原理的理解,不涉及对整个论文的翻译及解读
注意机制的目标是关注重要的特征,抑制不必要的特征。在本文中,其提出了一种新的网络模块——卷积块注意模块。由于卷积运算通过混合跨通道和空间信息来提取信息特征,因此其模块强调沿通道和空间轴两个主要维度学习重要特征。如图1所示,卷积注意模块串联应用通道和空间注意模块,以便每个分支可以分别学习通道和空间轴上的“什么”和“在哪里”。
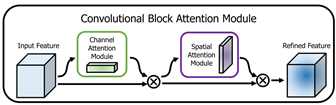
该文提出SENet网络通过全剧平均池化得出的全局信息为次优特征,在求取通道注意力时应当是使用最大池化,同时该文提出了空间注意力的计算方法。图2为通道注意力与空间注意力的计算模型。
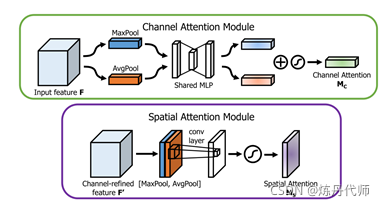
1) 通道注意力计算方法:
首先使用平均池和最大池操作聚合特征图的空间信息,生成两个不同的全局信息:Fc_avg和Fc_max,分别表示平均池特征和最大池特征。再将两个全局信息共享到一个多层感知器(MLP)和一个降维隐含层,输出值加权和即为通道注意力。计算公式如下:
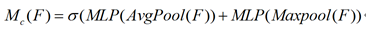
其中其结构可改写为avgpool/maxpool+FC(relu)+FC(sigmoid)。
2) 空间注意力计算方法:
首先沿通道方向取最大池化和平均池化得到1HW的特征图F_max及1*H
W的特征图F_avg,再通过一个77的卷积层将其连接并卷积生成空间注意力。计算公式如下:(其中激活函数为sigmoid函数)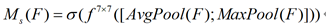
2.CBAM-ResNeXt的Pytorch实现
实现过程比较简单,与上一篇文章方法相似,在ResNeXt的残差块中加入CBAM模块即可。
import torch
import math
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchsummary import summary
class Flatten(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return x.view(x.size(0), -1)
class channel_Weight(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,inchannel,ratio=16,pool_type=["avg","max"]):
super(channel_Weight, self).__init__()
self.fc=nn.Sequential(Flatten(),
nn.Linear(inchannel,inchannel//ratio,bias=False),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(inchannel//ratio,inchannel,bias=False))
self.pool=pool_type
def forward(self,x):
sum=None
for i in self.pool:
if i=="avg":
avg=F.avg_pool2d(x,(x.size(2),x.size(3)),stride=(x.size(2),x.size(3)))
#C*H*W---->1*H*W
feature=self.fc(avg)
elif i=="max":
max=F.max_pool2d(x,(x.size(2),x.size(3)),stride=(x.size(2),x.size(3)))
feature=self.fc(max)
if sum is None:
sum=feature
else:
sum+=feature
weight=F.sigmoid(sum).unsqueeze(2).unsqueeze(3).expand_as(x)
return weight*x
class ChannelPool(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return torch.cat( (torch.max(x,1)[0].unsqueeze(1), torch.mean(x,1).unsqueeze(1)), dim=1 )
class Spatial_weight(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Spatial_weight, self).__init__()
self.pool=ChannelPool()
self.conv=nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels=2,out_channels=1,kernel_size=7,stride=1,padding=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(1,eps=1e-5, momentum=0.01, affine=True))
def forward(self,x):
spatial=self.pool(x)
weight=self.conv(spatial)
weight=F.sigmoid(weight)
return x*weight
class CBAM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,inchannel,ratio=16,pool_type=["avg","max"]):
super(CBAM, self).__init__()
self.channnel_Weight=channel_Weight(inchannel,ratio=ratio,pool_type=pool_type)
self.Spatial_weight=Spatial_weight()
def forward(self,x):
x=self.channnel_Weight(x)
x=self.Spatial_weight(x)
return x
class block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,inchannels,outchannels,stride=1,shortcut=False):
super(block, self).__init__()
self.layer1=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=inchannels,out_channels=outchannels//2,kernel_size=1,stride=stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannels//2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=outchannels//2, out_channels=outchannels // 2, kernel_size=3,padding=1,groups=32,stride=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannels // 2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=outchannels // 2, out_channels=outchannels, kernel_size=1,stride=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.layer4=CBAM(outchannels)
self.shortcut=shortcut
if shortcut:
self.shortcut=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=inchannels,out_channels=outchannels,kernel_size=1,stride=stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(outchannels)
)
def forward(self,x):
if self.shortcut:
resduial=self.shortcut(x)
else:
resduial=x
x=self.layer1(x)
x=self.layer2(x)
x=self.layer3(x)
x=self.layer4(x)
x=x+resduial
return x
class Resnext(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,layer_number,num_class):
super(Resnext, self).__init__()
if layer_number==50:
self.layer=[3,4,6,3]
elif layer_number==101:
self.layer=[3,4,23,3]
elif layer_number==152:
self.layer=[3,8,36,3]
self.layer1=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3,out_channels=64,kernel_size=7,stride=2,padding=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3,padding=1,stride=2)
)
self.layer2=self.make_layer(64,256,1,self.layer[0])
self.layer3 = self.make_layer(256, 512, 2, self.layer[1])
self.layer4 = self.make_layer(512, 1024, 2, self.layer[2])
self.layer5 = self.make_layer(1024, 2048, 2, self.layer[2])
self.layer6=nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=7,stride=1)
self.layer7=nn.Linear(2048,num_class)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
def make_layer(self,inchannels,outchannels,stride,num):
layers=[]
layers.append(block(inchannels,outchannels,stride=stride,shortcut=True))
for i in range(1,num):
layers.append(block(outchannels,outchannels,stride=1,shortcut=False))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self,x):
x=self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.layer5(x)
x = self.layer6(x)
x=torch.flatten(x,1)
print(x.size())
x=self.layer7(x)
return F.softmax(x,dim=1)
device=torch.device("cuda:0")
Xception=Resnext(50,10).to(device)
summary(Xception,(3,224,224))
3.模型实现结果及参数对比
此处只是用summary模拟了模型训练流程。
1)原始网络模型参数大小:
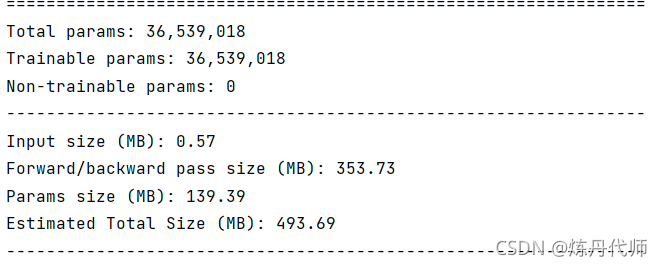
2)加入CBAM模块后模型参数大小:
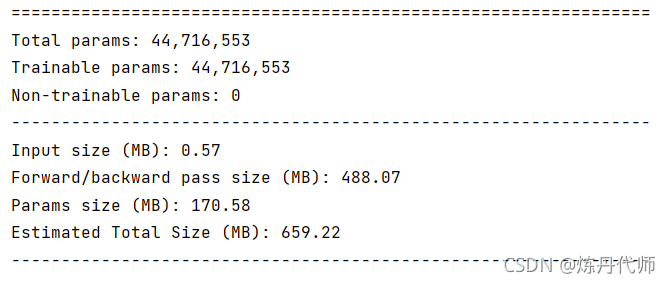
总结:加入CBAM模块后总参数数量由140M上升至170M,一张图片输入经前向传播与后向传播所需内存由493M提升至659M,在牺牲电脑内存的条件下,注意力机制可大幅提升模型性能,当然本文并未对模型性能提升进行验证,各位小伙伴可以用这个模型跑一跑(前提是你显卡内存够大)