1. ffmpeg 视频解码一
2. ffmpeg 视频解码二
3. ffmpeg 音频解码一
4. ffmpeg 音频解码二
5. ffmpeg 音视频解码
6. ffmpeg 视频编码一
7. ffmpeg 视频编码一(精简版)
8. ffmpeg 视频编码二(基于 libswscale 转换视频)
前言
看了上篇文章的小伙伴应该都知道了编码的一些问题了,这篇文章我们就来解决它。
要解决上篇文章所述的问题,我们先了解一个扩展库 libswscale ,Libswscale里面实现了各种图像像素格式的转换(例如YUV与RGB之间的转换);以及图像大小缩放的功能(例如640x360拉伸为1280x720);以及前后图像的滤波处理(例如高斯模糊)。基于此,我们就可以解决我们上篇文章遇到的问题了。
libswscale的使用
要使用libswscale,我们必定要对齐有所了解,其核心函数主要有三个,下面分别介绍下他们的使用。
-
初始化(sws_getContext(…))
/** * 分配并返回一个SwsContext。 * * @param srcW 源图像的宽度 * @param srcH 源图像的高度 * @param srcFormat 源图像格式 * @param dstW 目标图像宽度 * @param dstH 目标图像高度 * @param dstFormat 目标图像格式 * @param flags 图像拉伸算法 * @param srcFilter 输入图像滤波器信息 * @param dstFilter 输出图像滤波器信息 * @param param 扩展算法需要的参数 * @return 返回一个指向SwsContext的指针, 出错则返回NULL * */ struct SwsContext *sws_getContext(int srcW, int srcH, enum AVPixelFormat srcFormat, int dstW, int dstH, enum AVPixelFormat dstFormat, int flags, SwsFilter *srcFilter, SwsFilter *dstFilter, const double *param);这里需要注意的是:
srcW,srcH,srcFormat 定义输入图像信息(宽、高、像素格式)
dstW,dstH,dstFormat 定义输出图像信息(宽、高、像素格式)
flags 定义转换的算法(只有当输入输出图像大小不同时有效)
srcFilter, dstFilter 定义输入/输出图像滤波器信息,如果不做前后图像滤波,输入NULL
param 扩展算法需要的额外参数(extra parameters to tune the used scaler For SWS_BICUBIC param[0] and [1] tune the shape of the basis function, param[0] tunes f(1) and param[1] f′(1) For SWS_GAUSS param[0] tunes the exponent and thus cutoff frequency For SWS_LANCZOS param[0] tunes the width of the window function)
-
转换(sws_scale(…))
/** * 缩放图像 * * @param c 之前用sws_getContext()创建的SwsContext 上下文 * @param srcSlice 输入图像的每个颜色通道的数据指针 * @param srcStride 数组中保存的是对应通道的数据宽度 * @param srcSliceY 图像上处理区域的起始位置 * @param srcSliceH 图像上需要处理的行数 * @param dst 类比输入,输出图像的每个颜色通道的数据指针 * @param dstStride 类比输入,数组中保存的是对应通道的数据宽度 * @return the height of the output slice */ int sws_scale(struct SwsContext *c, const uint8_t *const srcSlice[], const int srcStride[], int srcSliceY, int srcSliceH, uint8_t *const dst[], const int dstStride[]);这里需要注意的是:
-
srcSlice:
这个其实就是 AVFrame中的data[]数组。因为不同像素的存储格式不同,所以srcSlice[]维数也有可能不同。
以YUV420P为例,它是planar格式,它的内存中的排布如下:
YYYY UUUU VVVV
使用FFmpeg解码后存储在AVFrame的data[]数组中时:
data[0] —— Y分量, Y1, Y2, Y3, Y4……
data[1] —— U分量, U1, U2, U3, U4……
data[2] —— V分量, V1, V2, V3, V4……
linesize[]数组中保存的是对应通道的数据宽度 ,
linesize[0] —— Y分量的宽度
linesize[1] —— U分量的宽度
linesize[2] —— V分量的宽度 -
srcStride
这个其实就是 AVFrame中的linesize[]数组。存储的也就是每个通道的行字节数。比较特殊的是,这个大小和图像的宽度并不一定一直。
1.由于数据帧存储的对齐,有可能会向每行后面增加一些填充字节这样 stride = width + N;2.packet存错模式下,每个像素几个通道数据混合在一起,例如RGB24,每个像素3字节连续存放,因此下一行的位置需要跳过3*width字节。
srcSlice和srcStride的维数相同,由srcFormat值来。
p 维数 宽width 跨度stride 高 20 3 w, w/2, w/2 s, s/2, s/2 h, h/2, h/2 1 w, w/2, w/2 2s, 0, 0 h, h, h 2 w, w/2, w/2 s, s, 0 h, h/2 4 1 w, w, w 3s, 0, 0 h, 0, 0 -
srcSliceY 与 srcSliceH
这两个参数组合,既可以定义图像的处理区域,例如srcSliceY =0,srcSliceH =height,即代表一次性处理完整个图像。这种设置是为了多线程并行,例如可以创建两个线程,第一个线程处理 [0, h/2-1]行,第二个线程处理 [h/2, h-1]行。并行处理加快速度。
-
dst 与 dstStride
类比srcSlice和srcStride ,这里不多做解释。
-
-
释放(sws_freeContext(SwsContext*))
这个没什么说的,释放之前用sws_getContext()创建的SwsContext 上下文
流程图
流程图其实并不是完整代码逻辑,部分代码没在里面体现出来,主要是展示个大概流程。

源代码
#pragma once
#define __STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
extern "C"
{
#include <libavformat/avformat.h>
#include "libavcodec/avcodec.h"
#include <libswscale/swscale.h>
#include "libavutil/imgutils.h"
}
using namespace std;
#define INPUT_FILE_NAME "lh_online.yuv"
#define OUTPUT_FILE_NAME "lh_online.mp4"
//mp4
#define L_AVCODEID AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG4
//带编码视频类型
#define ENC_AV_PIX_FMT_YUV AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P
//编码之后的视频宽度
#define ENC_VIDEO_WIDTH 800
//编码之后的视频高度
#define ENC_VIDEO_HEIGHT 600
#define ENC_VIDEO_BITRATE 400000
//time_base AVRational{1,15}
//一秒多少张图片(原视频是15。)
#define ENC_TIME_BASE_DEN 15
AVFormatContext* i_fmt_ctx = NULL, * o_fmt_ctx = NULL;
AVCodecContext* enc_c = NULL;;
AVStream* out_stream;
AVFrame* frame, * tmp_frame;
AVPacket* enc_pkt;
int ret;
struct SwsContext* sws_ctx;
static void encode()
{
//发送待编码数据到编码器
ret = avcodec_send_frame(enc_c, tmp_frame);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error sending a frame for encoding\n");
exit(1);
}
while (ret >= 0) {
//编码一帧视频
ret = avcodec_receive_packet(enc_c, enc_pkt);
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF)
return;
else if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error during encoding\n");
exit(1);
}
//写入文件时流序号(这里只编码了视频流,而且也只实例化了一个输出流(avformat_new_stream),序号直接就是0)
//多输出流的时候需要注意,后面音视频同时处理的时候,再说这个吧
enc_pkt->stream_index = 0;
//时间基转换(编码器->输出流)
av_packet_rescale_ts(enc_pkt,
enc_c->time_base,
out_stream->time_base);
printf("Write packet %d (size=%d)\n", enc_pkt->pts, enc_pkt->size);
//写文件
ret = av_interleaved_write_frame(o_fmt_ctx, enc_pkt);
av_packet_unref(enc_pkt);
}
}
static int open_output_file()
{
int ret;
AVCodec* codec;
o_fmt_ctx = avformat_alloc_context();
avformat_alloc_output_context2(&o_fmt_ctx, NULL, NULL, OUTPUT_FILE_NAME);
if (!o_fmt_ctx) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Could not create output context\n");
return AVERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
//获取编码器
codec = avcodec_find_encoder(L_AVCODEID);
if (!codec) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_FATAL, "encoder Codec not found\n");
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
}
enc_c = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
if (!enc_c) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_FATAL, "Failed to allocate the encoder context\n");
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
//一些默认参数的设置
enc_c->codec_id = codec->id;
enc_c->pix_fmt = ENC_AV_PIX_FMT_YUV;
enc_c->bit_rate = ENC_VIDEO_BITRATE;
enc_c->width = ENC_VIDEO_WIDTH;
enc_c->height = ENC_VIDEO_HEIGHT;
enc_c->time_base.num = 1;
enc_c->time_base.den = ENC_TIME_BASE_DEN;
enc_c->gop_size = 12;
enc_c->max_b_frames = 4;
if (o_fmt_ctx->oformat->flags & AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER)
enc_c->flags |= AV_CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER;
//实例化输出流
out_stream = avformat_new_stream(o_fmt_ctx, NULL);
if (!out_stream) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Failed allocating output stream\n");
return AVERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
//复制编码器参数到输出流
ret = avcodec_parameters_from_context(out_stream->codecpar, enc_c);
if (0 != ret)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to copy codec parameters\n");
return -1;
}
out_stream->time_base = enc_c->time_base;
//打开编码器
ret = avcodec_open2(enc_c, codec, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Cannot open video encoder for stream\n");
return ret;
}
//打开输出文件
if (!(o_fmt_ctx->oformat->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE)) {
ret = avio_open(&o_fmt_ctx->pb, OUTPUT_FILE_NAME, AVIO_FLAG_WRITE);
if (ret < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Could not open output file\n", OUTPUT_FILE_NAME);
return ret;
}
}
//写文件头
ret = avformat_write_header(o_fmt_ctx, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Error occurred when opening output file\n");
return ret;
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
//-------初始化一些配置---start
int i = 0;
size_t data_size;
uint8_t* temp_buffer;
uint8_t* src_data[4];
int src_linesize[4];
//输入视频基本信息
const int src_w = 512, src_h = 288;
AVPixelFormat src_pixfmt = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P;
//获得YUV420P像素格式每个像素占用的比特数(Bit Per Pixel)
int src_bpp = av_get_bits_per_pixel(av_pix_fmt_desc_get(src_pixfmt));
//打开输入文件
FILE* src_file = fopen(INPUT_FILE_NAME, "rb");
//分配AVFrame
tmp_frame = av_frame_alloc();
if (!tmp_frame) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate video tmp_frame\n");
exit(1);
}
tmp_frame->format = ENC_AV_PIX_FMT_YUV;
tmp_frame->width = ENC_VIDEO_WIDTH;
tmp_frame->height = ENC_VIDEO_HEIGHT;
//计算 YUV420P 格式的图像需要占用的空间大小,分配内存空间
temp_buffer = (uint8_t*)av_malloc(av_image_get_buffer_size(src_pixfmt, src_w, src_h, 1));
//分配缓冲区并填入dst_data dst_linesize
if ((ret = av_image_alloc(src_data, src_linesize,
src_w, src_h, src_pixfmt, 1)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate source image\n");
goto end;
}
//分配缓冲区并填入dst_data dst_linesize
if ((ret = av_image_alloc(tmp_frame->data, tmp_frame->linesize,
ENC_VIDEO_WIDTH, ENC_VIDEO_HEIGHT, ENC_AV_PIX_FMT_YUV, 1)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate source image\n");
goto end;
}
//数初始化SwsContext结构体
//这里你可能发现我们源图像和目标图像的格式是一致的
//这里的话是正常的,因为我们只是拉伸图像的宽高
sws_ctx = sws_getContext(src_w, //源图像的宽度
src_h, //源图像的高度
src_pixfmt, //源图像格式
ENC_VIDEO_WIDTH, //目标图像宽度
ENC_VIDEO_HEIGHT, //目标图像高度
ENC_AV_PIX_FMT_YUV, //目标图像格式
SWS_BILINEAR, //图像拉伸算法
NULL, //输入图像滤波器信息
NULL, //输出图像滤波器信息
NULL //扩展算法需要的参数
);
if (!sws_ctx) {
fprintf(stderr, "could not allocate SwsContext.\n");
goto end;
}
//分配一个AVPacket
enc_pkt = av_packet_alloc();
if (!enc_pkt) {
goto end;
}
//-------初始化一些配置---end
//输出处理
if ((ret = open_output_file()) < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "could not open output file \s.\n", OUTPUT_FILE_NAME);
goto end;
}
while (!feof(src_file)) {
//读取数据 ,这里根据视频宽高和像素大小填充temp_buffer
data_size = fread(temp_buffer, 1, src_w * src_h * src_bpp / 8, src_file);
if (!data_size)
break;
//填充 frame
memcpy(src_data[0], temp_buffer, src_w * src_h); //Y
memcpy(src_data[1], temp_buffer + src_w * src_h, src_w * src_h / 4); //U
memcpy(src_data[2], temp_buffer + src_w * src_h * 5 / 4, src_w * src_h / 4); //V
//转换一帧图像。
sws_scale(sws_ctx, // 转换格式的上下文。也就是 sws_getContext 函数返回的结果
src_data, //输入图像的每个颜色通道的数据指针。其实就是解码后的AVFrame中的data[]数组
src_linesize, //数组中保存的是对应通道的数据宽度
0, //图像上处理区域的起始位置
src_h, //图像上需要处理的行数
tmp_frame->data, //类比输入,输出图像的每个颜色通道的数据指针
tmp_frame->linesize //类比输入,数组中保存的是对应通道的数据宽度
);
//添加pts
tmp_frame->pts = i++;
//送往编码
encode();
}
//写文件尾
av_write_trailer(o_fmt_ctx);
end:
//资源释放
sws_freeContext(sws_ctx);
avcodec_free_context(&enc_c);
av_frame_free(&frame);
av_packet_free(&enc_pkt);
avformat_close_input(&i_fmt_ctx);
avformat_free_context(o_fmt_ctx);
return 0;
}
这个程序里,我们把源视频(512 * 288也就是16:9)的视频,转码成640 * 360(16:9)的视频,并编码成MP4,下面来对比一下两个视频的差异:
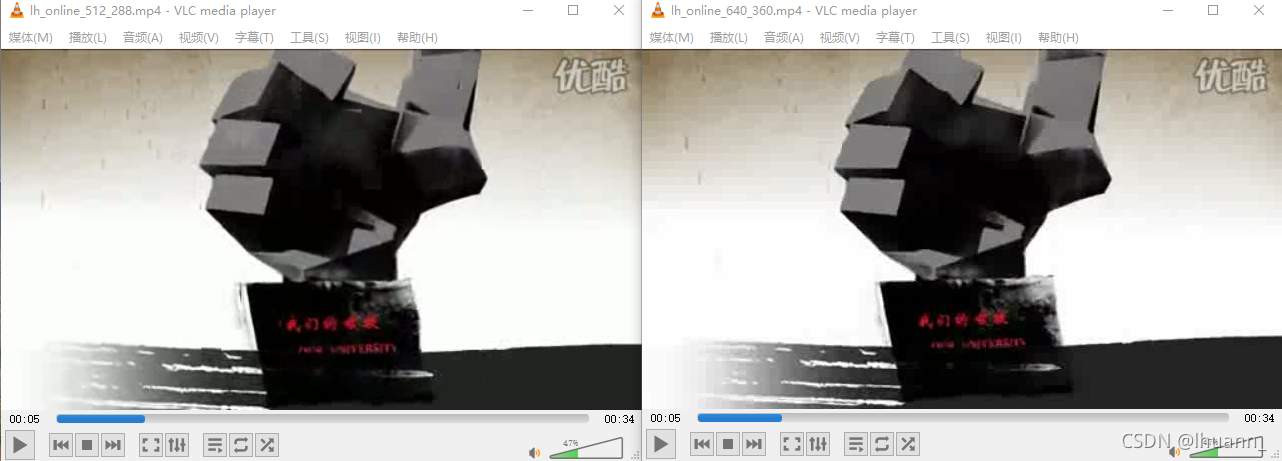
你可以发现,我们把图像拉伸成640*360之后,没有出现 ffmpeg 视频编码一(精简版)当中所展示的问题。
如果我们设置的比例不一致呢,我们实验一下,我们修改宏
//编码之后的视频宽度
#define ENC_VIDEO_WIDTH 800
//编码之后的视频高度
#define ENC_VIDEO_HEIGHT 600
为800*600,下面看下差异:
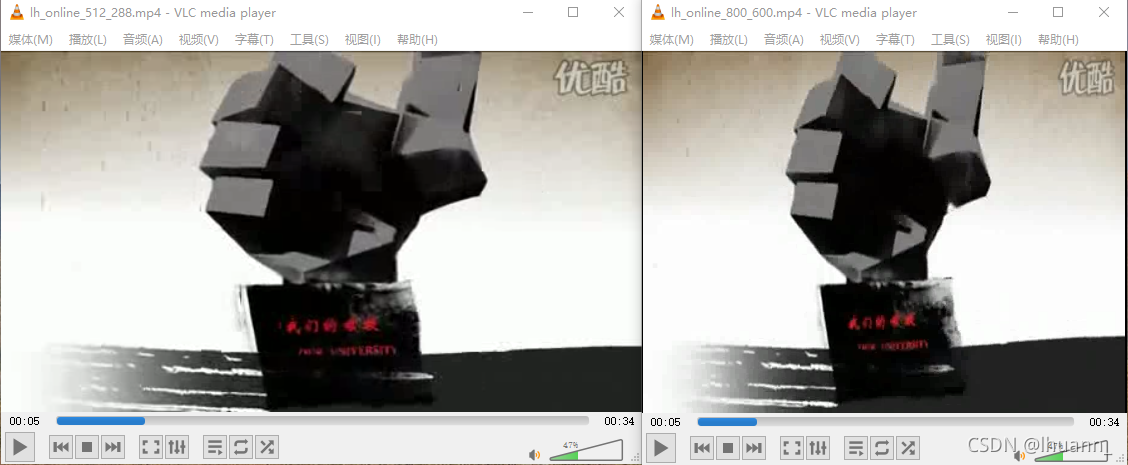
这里发现编码之后的视频,也没有出现花边和裁剪之类的问题,而且根据我们设置的宽高,自动的把视频拉伸了。
所以使用 libswscale 完美解决了ffmpeg 视频编码一(精简版)当中所展示的问题。
到此使用 libswscale的方式就介绍完了。