前言
当公开的数据只有分割mask,没有json数据格式的时候,你的模型训练将会很受局限。为了突破,故撰写该文档,这样可用于检测的验证数据集又多了一些。


mask转labelme格式
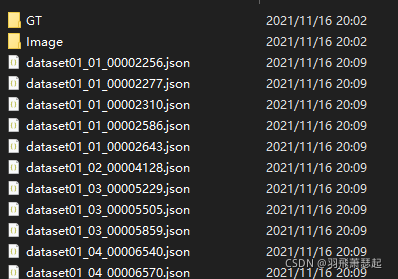
mask2Labelme\mask2labelme.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#功能批量将多个同类mask 转单个json
import datetime
import json
import os
import io
import re
import fnmatch
import json
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
from pycococreatortools import pycococreatortools
from PIL import Image
import base64
from base64 import b64encode
ROOT_DIR = 'C:/Users/awei/Desktop/mask2Labelme/tank/Tank_train/'
IMAGE_DIR = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "Image")
ANNOTATION_DIR = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "GT")
def img_tobyte(img_pil):
# 类型转换 重要代码
# img_pil = Image.fromarray(roi)
ENCODING='utf-8'
img_byte=io.BytesIO()
img_pil.save(img_byte,format='PNG')
binary_str2=img_byte.getvalue()
imageData = base64.b64encode(binary_str2)
base64_string = imageData.decode(ENCODING)
return base64_string
annotation_files=os.listdir(ANNOTATION_DIR)
for annotation_filename in annotation_files:
coco_output = {
"version": "3.16.7",
"flags": {},
"fillColor": [255, 0,0,128],
"lineColor": [0,255,0, 128],
"imagePath": {},
"shapes": [],
"imageData": {} }
print(annotation_filename)
class_id = 1
name = annotation_filename.split('.',3)[0]
name1=name+'.jpg'
coco_output["imagePath"]=name1
image = Image.open(IMAGE_DIR+'/'+ name1)
imageData=img_tobyte(image)
coco_output["imageData"]= imageData
binary_mask = np.asarray(Image.open(ANNOTATION_DIR+'/'+annotation_filename)
.convert('1')).astype(np.uint8)
segmentation=pycococreatortools.binary_mask_to_polygon(binary_mask, tolerance=3)
#筛选多余的点集合
for item in segmentation:
if(len(item)>10):
list1=[]
for i in range(0, len(item), 2):
list1.append( [item[i],item[i+1]])
label = "tank" #
seg_info = {'points': list1, "fill_color":'null' ,"line_color":'null' ,"label": label, "shape_type": "polygon","flags": {}}
coco_output["shapes"].append(seg_info)
coco_output[ "imageHeight"]=binary_mask.shape[0]
coco_output[ "imageWidth"]=binary_mask.shape[1]
full_path='{}/'+name+'.json'
with open( full_path.format(ROOT_DIR), 'w') as output_json_file:
json.dump(coco_output, output_json_file)
切分数据
总共有3类数据,每类文件夹下对应的就是jpg和对应的json标注文件,借助splidata_labelMe.py将每类切分为训练测试两部分
labelme2coco\splitData_labelMe.py
import os, random, shutil
fileDir = './hangar485/'
testDir = fileDir+'Test/'
trainDir = fileDir+'Train/'
def moveFile(fileDir,toTest=True):
dir = testDir
pathDir = [i for i in os.listdir(fileDir) if i.endswith('.json')] #取所有labelme标注名
rate=0.1 #自定义抽取图片的比例,比方说100张抽10张,那就是0.1
filenumber=len(pathDir)
if not toTest:
dir = trainDir
rate = 1 # 将剩下的都作为train
picknumber=int(filenumber*rate) #按照rate比例从文件夹中取一定数量图片
# picknumber=200 #直接取1000张
sample = random.sample(pathDir, picknumber) #随机选取picknumber数量的样本图片
print (sample)
for name in sample:
shutil.move(fileDir+name, dir+name)
jpgName = name.split(".")[0]+'.jpg'
shutil.move(fileDir+jpgName, dir+jpgName)
return
if __name__ == '__main__':
if not os.path.exists(testDir):
os.makedirs(testDir)
if not os.path.exists(trainDir):
os.makedirs(trainDir)
moveFile(fileDir)
moveFile(fileDir,toTest=False) # 剩下移动到train
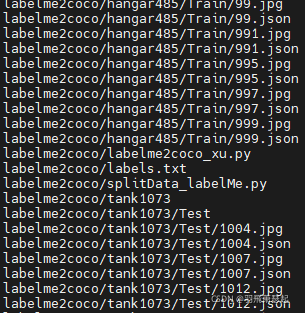
但是吧你会发现不同类下,文件名都是一样的,这样在后面会导致替换丢失
借助linux下的shell命令,增加对应类别名前缀:
for i in `ls`;do mv -f $i `echo "tank_"$i`; done
补充labelme的imageData
JPEGImages中的原始图片,是从labelme的json标注文件中ImageData解码产生
但是吧,有些labelme标注的json,该项为None,所以就会导致labelme2coco_xu无法解码生成原始图片
譬如:
{
"version": "4.5.13",
"flags": {},
"shapes": [
{
"label": "tank",
"points": [
[
1351.129363449692,
407.18685831622173
],
[
1361.1909650924024,
408.4188911704312
],
[
1375.359342915811,
415.4004106776181
],
[
1385.4209445585216,
422.17659137577
],
[
1373.100616016427,
435.3182751540041
],
[
1364.476386036961,
444.96919917864477
],
[
1361.3963039014372,
447.22792607802876
],
[
1358.7268993839834,
453.7987679671458
],
[
1351.9507186858316,
460.7802874743326
],
[
1339.2197125256673,
456.26283367556465
],
[
1325.4620123203285,
450.51334702258725
],
[
1320.3285420944558,
445.37987679671454
],
[
1321.1498973305954,
438.3983572895277
],
[
1324.640657084189,
433.88090349075975
],
[
1328.747433264887,
429.15811088295686
],
[
1331.006160164271,
425.87268993839837
],
[
1340.6570841889118,
421.5605749486653
]
],
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "polygon",
"flags": {}
}
],
"imagePath": "2235.jpg",
"imageData": null,
"imageHeight": 1080,
"imageWidth": 1920
labelme2coco\checkImgData_labelme.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#功能 填补labelme的json中缺失的imageData
import datetime
import json
import os
import io
import json
from PIL import Image
import base64
from base64 import b64encode
ROOT_DIR = './tank1073/Test'
IMAGE_DIR = ROOT_DIR
ANNOTATION_DIR = ROOT_DIR
def img_tobyte(img_pil):
# 类型转换 重要代码
# img_pil = Image.fromarray(roi)
ENCODING='utf-8'
img_byte=io.BytesIO()
img_pil.save(img_byte,format='PNG')
binary_str2=img_byte.getvalue()
imageData = base64.b64encode(binary_str2)
base64_string = imageData.decode(ENCODING)
return base64_string
annotation_files=[i for i in os.listdir(ANNOTATION_DIR) if i.endswith('.json')]
for annotation_filename in annotation_files:
with open(ANNOTATION_DIR+'/'+annotation_filename,'r') as f:
coco_output = json.load(f)
if coco_output["imageData"] is None:
print(annotation_filename+" without imageData")
name = annotation_filename.split('.',3)[0]
name1=name+'.jpg'
image = Image.open(IMAGE_DIR+'/'+ name1)
imageData=img_tobyte(image)
coco_output["imageData"]= imageData
full_path='{}/'+name+'.json'
with open( full_path.format(ROOT_DIR), 'w') as output_json_file:
json.dump(coco_output, output_json_file)
生成coco格式
labelme2coco\labelme2coco_xu.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
import argparse
import collections
import datetime
import glob
import json
import os
import os.path as osp
import sys
import uuid
import imgviz
import numpy as np
import labelme
try:
import pycocotools.mask
except ImportError:
print("Please install pycocotools:\n\n pip install pycocotools\n")
sys.exit(1)
#https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_29957455/article/details/82778306
def get_dir_path(root_path,dir_list):
#获取该目录下所有的文件名称和目录名称
dir_or_files = os.listdir(root_path)
for dir_file in dir_or_files:
#获取目录或者文件的路径
dir_file_path = os.path.join(root_path,dir_file)
#判断该路径为文件还是路径
if os.path.isdir(dir_file_path):
dir_list.append(dir_file_path)
#递归获取所有目录的路径
get_dir_path(dir_file_path,dir_list)
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter
)
parser.add_argument("--input_dir",type=str,default="./", help="input annotated directory")
parser.add_argument("--output_dir",type=str,default="./cocoFormat", help="output dataset directory")
parser.add_argument("--labels",type=str,default="./labels.txt", help="labels file")
parser.add_argument("--train_flag",type=bool,default=False, help="generate train or val") # True
parser.add_argument(
"--noviz", help="no visualization", action="store_true"
)
args = parser.parse_args()
if osp.exists(args.output_dir):
print("Output directory already exists:", args.output_dir)
sys.exit(1)
os.makedirs(args.output_dir)
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages"))
if not args.noviz:
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "Visualization"))
print("Creating dataset:", args.output_dir)
now = datetime.datetime.now()
data = dict(
info=dict(
description=None,
url=None,
version=None,
year=now.year,
contributor=None,
date_created=now.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f"),
),
licenses=[dict(url=None, id=0, name=None,)],
images=[
# license, url, file_name, height, width, date_captured, id
],
type="instances",
annotations=[
# segmentation, area, iscrowd, image_id, bbox, category_id, id
],
categories=[
# supercategory, id, name
],
)
class_name_to_id = {}
for i, line in enumerate(open(args.labels).readlines()):
class_id = i - 1 # starts with -1
class_name = line.strip()
if class_id == -1:
assert class_name == "__ignore__"
continue
class_name_to_id[class_name] = class_id
data["categories"].append(
dict(supercategory=None, id=class_id, name=class_name,)
)
dir_list = []
get_dir_path(args.input_dir,dir_list)
if args.train_flag:
out_ann_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "train_annotations.json")
dirs = [i for i in dir_list if i.endswith("Train")]
else:
out_ann_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "val_annotations.json")
dirs = [i for i in dir_list if i.endswith("Test")]
label_files = []
for dir in dirs:
label_files +=glob.glob(osp.join(dir, "*.json"))
for image_id, filename in enumerate(label_files):
print("Generating dataset from:", filename)
label_file = labelme.LabelFile(filename=filename)
base = osp.splitext(osp.basename(filename))[0]
out_img_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages", base + ".jpg")
img = labelme.utils.img_data_to_arr(label_file.imageData)
imgviz.io.imsave(out_img_file, img)
data["images"].append(
dict(
license=0,
url=None,
file_name=osp.relpath(out_img_file, osp.dirname(out_ann_file)),
height=img.shape[0],
width=img.shape[1],
date_captured=None,
id=image_id,
)
)
masks = {} # for area
segmentations = collections.defaultdict(list) # for segmentation
for shape in label_file.shapes:
points = shape["points"]
label = shape["label"]
group_id = shape.get("group_id")
shape_type = shape.get("shape_type", "polygon")
mask = labelme.utils.shape_to_mask(
img.shape[:2], points, shape_type
)
if group_id is None:
group_id = uuid.uuid1()
instance = (label, group_id)
if instance in masks:
masks[instance] = masks[instance] | mask
else:
masks[instance] = mask
if shape_type == "rectangle":
(x1, y1), (x2, y2) = points
x1, x2 = sorted([x1, x2])
y1, y2 = sorted([y1, y2])
points = [x1, y1, x2, y1, x2, y2, x1, y2]
if shape_type == "circle":
(x1, y1), (x2, y2) = points
r = np.linalg.norm([x2 - x1, y2 - y1])
n_points_circle = 12
i = np.arange(n_points_circle)
x = x1 + r * np.sin(2 * np.pi / n_points_circle * i)
y = y1 + r * np.cos(2 * np.pi / n_points_circle * i)
points = np.stack((x, y), axis=1).flatten().tolist()
else:
points = np.asarray(points).flatten().tolist()
segmentations[instance].append(points)
segmentations = dict(segmentations)
for instance, mask in masks.items():
cls_name, group_id = instance
if cls_name not in class_name_to_id:
continue
cls_id = class_name_to_id[cls_name]
mask = np.asfortranarray(mask.astype(np.uint8))
mask = pycocotools.mask.encode(mask)
area = float(pycocotools.mask.area(mask))
bbox = pycocotools.mask.toBbox(mask).flatten().tolist()
data["annotations"].append(
dict(
id=len(data["annotations"]),
image_id=image_id,
category_id=cls_id,
segmentation=segmentations[instance],
area=area,
bbox=bbox,
iscrowd=0,
)
)
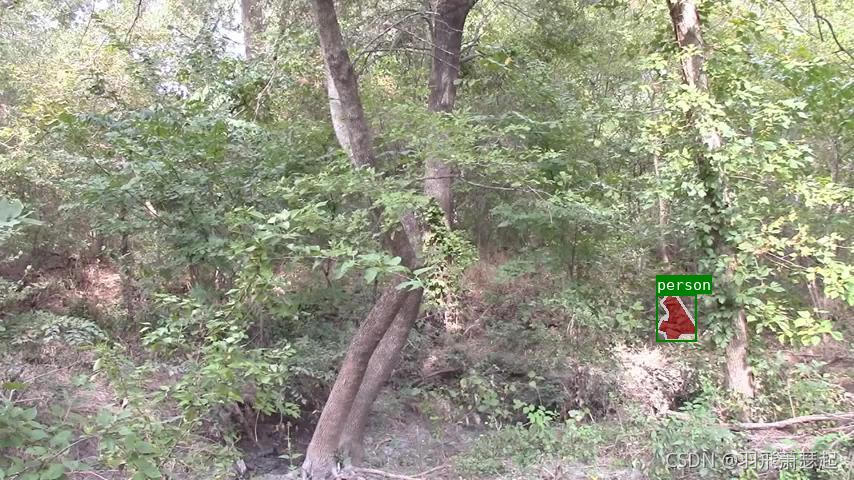
if not args.noviz:
viz = img
if masks:
labels, captions, masks = zip(
*[
(class_name_to_id[cnm], cnm, msk)
for (cnm, gid), msk in masks.items()
if cnm in class_name_to_id
]
)
viz = imgviz.instances2rgb(
image=img,
labels=labels,
masks=masks,
captions=captions,
font_size=15,
line_width=2,
)
out_viz_file = osp.join(
args.output_dir, "Visualization", base + ".jpg"
)
imgviz.io.imsave(out_viz_file, viz)
with open(out_ann_file, "w") as f:
json.dump(data, f)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
之后稍微调整下文件夹名方可,这里稍微注意下coco的instance_{train,val}2017.json文件中的"file_name": "JPEGImages/person_dataset07_08_00010578.jpg"故在train2017文件夹下得有个JPEGImages文件夹,然后再放原始图片