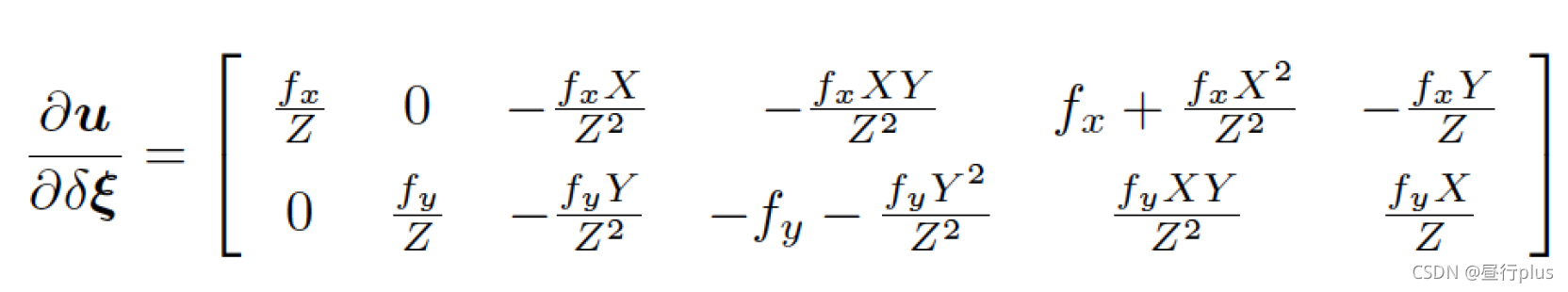首先关于递归方法做一个笔记:

这里的Bayes展开使用朴素贝叶斯的假设:这些条件事件之间是相互独立的
于是则有:
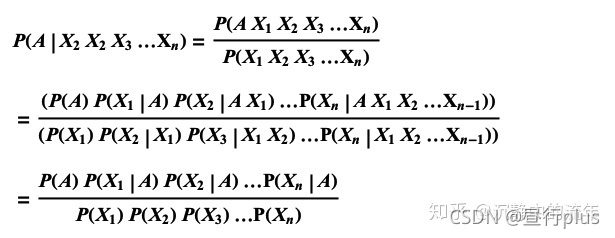
这样的话应该很容易推得:
P
(
x
k
∣
x
0
,
u
1
:
k
,
z
1
:
k
)
=
P
(
x
k
∣
x
0
,
u
1
:
k
,
z
1
:
k
?
1
)
?
P
(
z
k
∣
x
k
)
P
(
z
k
)
P(x_{k}| x_{0},u_{1:k}, z_{1:k}) = P(x_{k}| x_{0},u_{1:k}, z_{1:k-1}) *\frac{P(z_{k}|x_{k})}{P(z_{k})}
P(xk?∣x0?,u1:k?,z1:k?)=P(xk?∣x0?,u1:k?,z1:k?1?)?P(zk?)P(zk?∣xk?)?
由于
P
(
z
k
)
P(z_{k})
P(zk?)不会影响P(x_{k}),因而展开后省略该分母。
以上为个人理解,不保证准确,如有谬误还请指正!
2 Bundle Adjustment
2.1 文献阅读
我们在第五讲中已经介绍了Bundle Adjustment,指明它可以?于解PnP 问题。现在,我们又在后端中说明了它可以?于解?规模的三维重构问题,但在实时SLAM 场合往往需要控制规模。事实上,Bundle Adjustment 的历史远?我们想象的要长。请阅读Bill Triggs 的经典论?Bundle Adjustment: A Modern Synthesis(见paper/?录)(本??较长,建议选读1-5 节),了解BA 的发展历史,然后回答下列问题:
1. 为何说Bundle Adjustment is slow 是不对的?
The claimed slowness is almost always due to the unthinking use of a general-purpose optimization routine that completely ignores the problem structure and sparseness. Real bundle routines are much more efficient than this, and usually considerably more efficient and flexible than the newly suggested method.
答:不加思考地使用了一个通用的优化程序,完全忽略了问题的结构和稀疏性。(H矩阵具有稀疏性,可将H矩阵分为对角块对角块矩阵有加速计算技巧)实际的bundle例程应当更有效,而且通常比新建议的方法更有效和灵活
2. BA 中有哪些需要注意参数化的地方?Pose 和Point 各有哪些参数化方式?有何优缺点。
答:
① 相机内参(K) 位姿(SE3) 3D点坐标(Vector3) 投影后的像素坐标(Vector2);
②
- pose: 欧拉角/四元数/旋转矩阵/李代数+平移向量 or 变换矩阵
- 欧拉角有万向锁问题;
- 四元数/旋转矩阵/李代数都不够直观(很多都说旋转矩阵直观,不过个人觉得跟欧拉角比,差得远了,当然确实比另两个好理解点);
- 另外旋转矩阵的自由度过多
- point:
- 齐次仿射 homogeneous affine ( X , Y , Z , 1 ) T (X,Y,Z,1)^{T} (X,Y,Z,1)T:即使对于校准过的相机,视觉几何和视觉重建在本质上也是投影。如果一个 3D ( X , Y , Z ) T (X,Y,Z)^{T} (X,Y,Z)T 参数 (或等效的齐次仿射 ( X , Y , Z , 1 ) T (X,Y,Z,1)^{T} (X,Y,Z,1)T)用于非常遥远的3D点,需要大的 X,Y,Z 位移来显著改变图像。即,在(X Y Z)空间中, cost function 变得非常平坦,对于远距离的点,调整成本过大。
- 齐次投影参数化 homogeneous projective parametrization ( X , Y , Z , W ) T (X,Y,Z,W)^{T} (X,Y,Z,W)T:只要归一化使齐次 4-vector 在无穷远处保持有限(通过W→0),则其在无穷远处的行为是自然的、有限的和条件良好的。我们需要使用齐次参数化 ( X , Y , Z , W ) T (X,Y,Z,W)^T (X,Y,Z,W)T来处理远处的点,例如球形标准化 Σ X i 2 = 1 ΣX^2_i=1 ΣXi2?=1 。
3. * 本文写于2000 年,但是文中提到的很多内容在后面十几年的研究中得到了印证。你能看到哪些方向在后续工作中有所体现?请举例说明。
> 答:文中提到的“网络图”即“图优化”当下几乎代替了以往的滤波算法
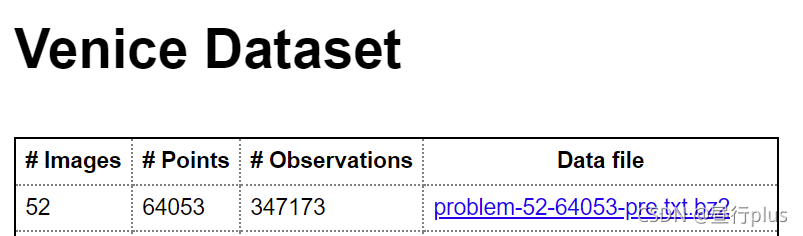
2.2 BAL-dataset
BAL(Bundle Adjustment in large)数据集是?个大型BA 数据集,它提供了相机与点初始值与观测,你可以用它们进行Bundle Adjustment。现在,请你使用g2o,自己定义Vertex 和Edge(不要使用自带的顶点类型,也不要像本书例程那边调用Ceres来求导),书写BAL 上的BA 程序。你可以挑选其中?个数据,运行你的BA,并给出优化后的点云图。
本题不提供代码框架,请独立完成。
提?:
- 注意BAL 的投影模型比教材中介绍的多了个负号;
所选数据:
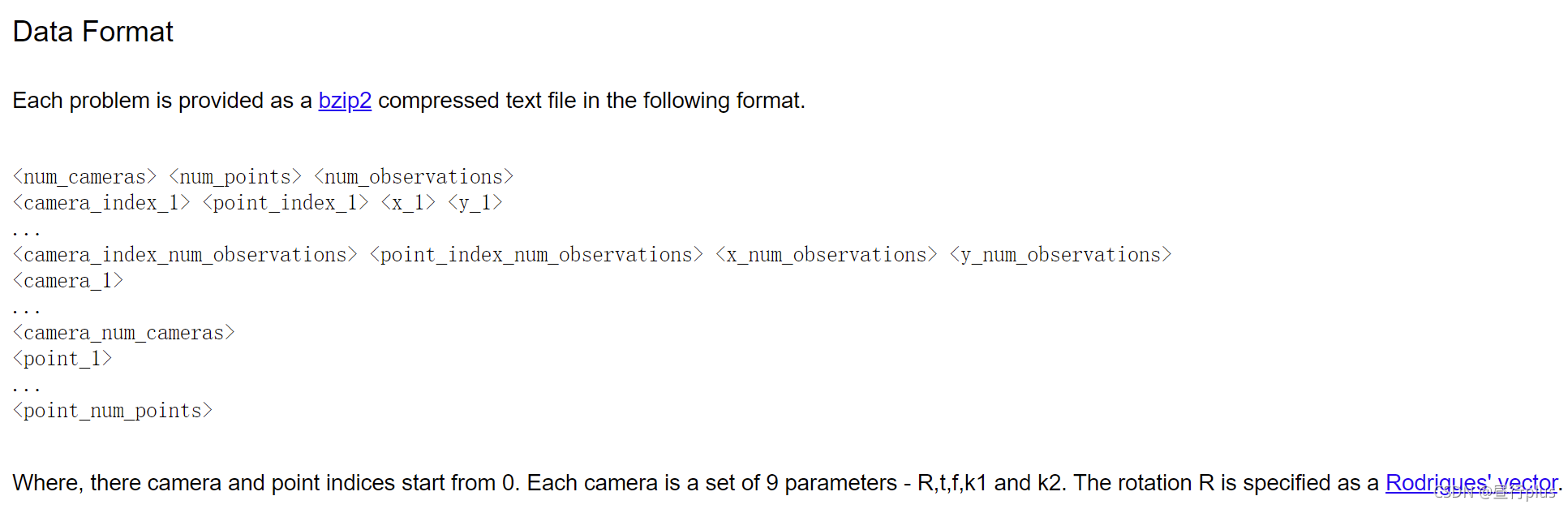
数据格式:
关于fatal error: cs.h: No such file or directory的问题,注意将github下载的g2o文件夹下的cmake_modules内的文件
都拷贝到工程文件的cmake文件夹下
然后CMakeLists.txt如下:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.17)
project(PA7)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release") # 这一句很关键,虽然不知道原因,但确实能令代码提速不少,可能release模式普遍比debug模式快吧
include_directories( "/usr/include/eigen3")
list(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake)
# g2o
find_package(G2O REQUIRED)
Find_Package(Ceres REQUIRED)
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
find_package(CSparse REQUIRED)
SET(G2O_LIBS g2o_csparse_extension g2o_stuff g2o_core cxsparse)
include_directories(
${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}
${CSPARSE_INCLUDE_DIR}
)
add_library(bal_common common.cpp)
add_executable(bundle_adjustment_g2o bundle_adjustment_g2o.cpp)
target_link_libraries(bundle_adjustment_g2o ${G2O_LIBS} bal_common)
add_executable(bundle_adjustment_ceres bundle_adjustment_ceres.cpp)
target_link_libraries(bundle_adjustment_ceres ${CERES_LIBRARIES} bal_common)
bundle_adjustment_g2o.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "common.h"
#include "sophus/se3.hpp"
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
//#include <g2o/solvers/dense/linear_solver_dense.h> // 之前用的是dense
#include <g2o/solvers/csparse/linear_solver_csparse.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_binary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/robust_kernel_impl.h>
using namespace Sophus;
using namespace Eigen;
using namespace std;
/// 姿态和内参的结构
struct PoseAndIntrinsics {
// PoseAndIntrinsics() {}
PoseAndIntrinsics() = default;
/// set from given data address
// explicit: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/52152355
explicit PoseAndIntrinsics(double *data_addr) {
rotation = SO3d::exp(Vector3d(data_addr[0], data_addr[1], data_addr[2]));
translation = Vector3d(data_addr[3], data_addr[4], data_addr[5]);
focal = data_addr[6];
k1 = data_addr[7];
k2 = data_addr[8];
}
/// 将估计值放入内存
void set_to(double *data_addr) {
auto r = rotation.log();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) data_addr[i] = r[i];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) data_addr[i + 3] = translation[i];
data_addr[6] = focal;
data_addr[7] = k1;
data_addr[8] = k2;
}
SO3d rotation;
Vector3d translation = Vector3d::Zero();
double focal = 0;
double k1 = 0, k2 = 0;
};
// 位姿加相机内参的顶点,9维,前三维为so3,接下去为t, f, k1, k2
class VertexPoseAndIntrinsics : public g2o::BaseVertex<9, PoseAndIntrinsics> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
VertexPoseAndIntrinsics() = default;
void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = PoseAndIntrinsics();
}
// void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
// _estimate.rotation = SO3d::exp(Vector3d(update[0], update[1], update[2])) * _estimate.rotation;
void oplusImpl(const number_t *update) override {
_estimate.rotation *= SO3d::exp(Vector3d(update[0], update[1], update[2]));
_estimate.translation += Vector3d (update[3], update[4], update[5]);
_estimate.focal += update[6];
_estimate.k1 += update[7];
_estimate.k2 += update[8];
}
/// 根据估计值投影一个点
// 公式:http://grail.cs.washington.edu/projects/bal/
Vector2d project(const Vector3d &point) {
Vector3d pc = _estimate.rotation * point + _estimate.translation;
pc = - pc / pc[2];
double r2 = pc.squaredNorm(); // 范数计算
double distortion = 1.0 + r2 * (_estimate.k1 + _estimate.k2 * r2); // 径向畸变
return Vector2d(_estimate.focal * distortion * pc[0],
_estimate.focal * distortion * pc[1]); //转换为像素坐标
}
// 存盘和读盘:留空
bool read(istream &in) override{}
bool write(ostream &out) const override{}
};
// vertex and edges used in g2o ba
// 模型的顶点,模板参数:优化变量维度和数据类型
class VertexPoint : public g2o::BaseVertex<3, Vector3d> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
VertexPoint() = default;
void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = Vector3d(0, 0, 0);
}
void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
_estimate += Vector3d(update[0], update[1], update[2]);
}
// 存盘和读盘:留空
bool read(istream &in) override{}
bool write(ostream &out) const override{}
};
// 误差模型 模板参数:观测值维度,类型,连接顶点类型
class EdgeProjection :
public g2o::BaseBinaryEdge<2, Vector2d, VertexPoseAndIntrinsics, VertexPoint> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
void computeError() override {
auto v0 = dynamic_cast<VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *>(_vertices[0]);
auto v1 = dynamic_cast<VertexPoint *>(_vertices[1]);
auto proj = v0->project(v1->estimate());
_error = proj - _measurement;
}
// 存盘和读盘:留空
bool read(istream &in) override{}
bool write(ostream &out) const override{}
};
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem);
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 2) {
cout << "usage: bundle_adjustment_g2o bal_data.txt" << endl;
return 1;
}
BALProblem bal_problem(argv[1]);
bal_problem.Normalize(); //数据归一化
bal_problem.Perturb(0.1, 0.5, 0.5); //加噪
bal_problem.WriteToPLYFile("initial.ply");
SolveBA(bal_problem);
bal_problem.WriteToPLYFile("final.ply");
return 0;
}
// pose dimension 9, landmark is 3
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<9, 3>> BlockSolverType;
//typedef g2o::LinearSolverDense<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType;
typedef g2o::LinearSolverCSparse<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType;
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem) {
const int point_block_size = bal_problem.point_block_size();
const int camera_block_size = bal_problem.camera_block_size();
double *points = bal_problem.mutable_points();
double *cameras = bal_problem.mutable_cameras();
// use LM //这里改用列文伯克-马夸尔特方法, 不用高斯牛顿了hh
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(
g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); // 设置求解器
optimizer.setVerbose(true); // 打开调试输出
/// build g2o problem
const double *observations = bal_problem.observations();
// vertex 往图中增加顶点
vector<VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *> vertex_pose_intrinsics;
vector<VertexPoint *> vertex_points;
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_cameras(); ++i) {
VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *v = new VertexPoseAndIntrinsics();
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size * i; // 移动地址运算
v->setId(i);
v->setEstimate(PoseAndIntrinsics(camera));
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertex_pose_intrinsics.push_back(v);
}
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_points(); ++i) {
VertexPoint *v = new VertexPoint();
double *point = points + point_block_size * i;
v->setId(i + bal_problem.num_cameras());
v->setEstimate(Vector3d(point[0], point[1], point[2]));
// g2o在BA中需要手动设置待Marg的顶点
v->setMarginalized(true);
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertex_points.push_back(v);
}
// edge // 往图中增加边
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_observations(); ++i) {
EdgeProjection *edge = new EdgeProjection;
edge->setVertex(0, vertex_pose_intrinsics[bal_problem.camera_index()[i]]);
edge->setVertex(1, vertex_points[bal_problem.point_index()[i]]);
edge->setMeasurement(Vector2d(observations[2*i + 0], observations[2*i + 1]));
edge->setInformation(Matrix2d::Identity());
edge->setRobustKernel(new g2o::RobustKernelHuber()); //设置鲁棒核函数 此处为Huber核
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
}
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(65);
// set to bal problem
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_cameras(); ++i) {
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size * i;
auto vertex = vertex_pose_intrinsics[i];
auto estimate = vertex->estimate();
estimate.set_to(camera);
}
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_points(); ++i) {
double *point = points + point_block_size * i;
auto vertex = vertex_points[i];
for (int k = 0; k < 3; ++k) point[k] = vertex->estimate()[k];
}
}
下载MeshLab(个人比较喜欢用AppImage)打开.ply文件(一种点云文件格式):
initial.ply
problem-16-22106-pre.txt(课本示例)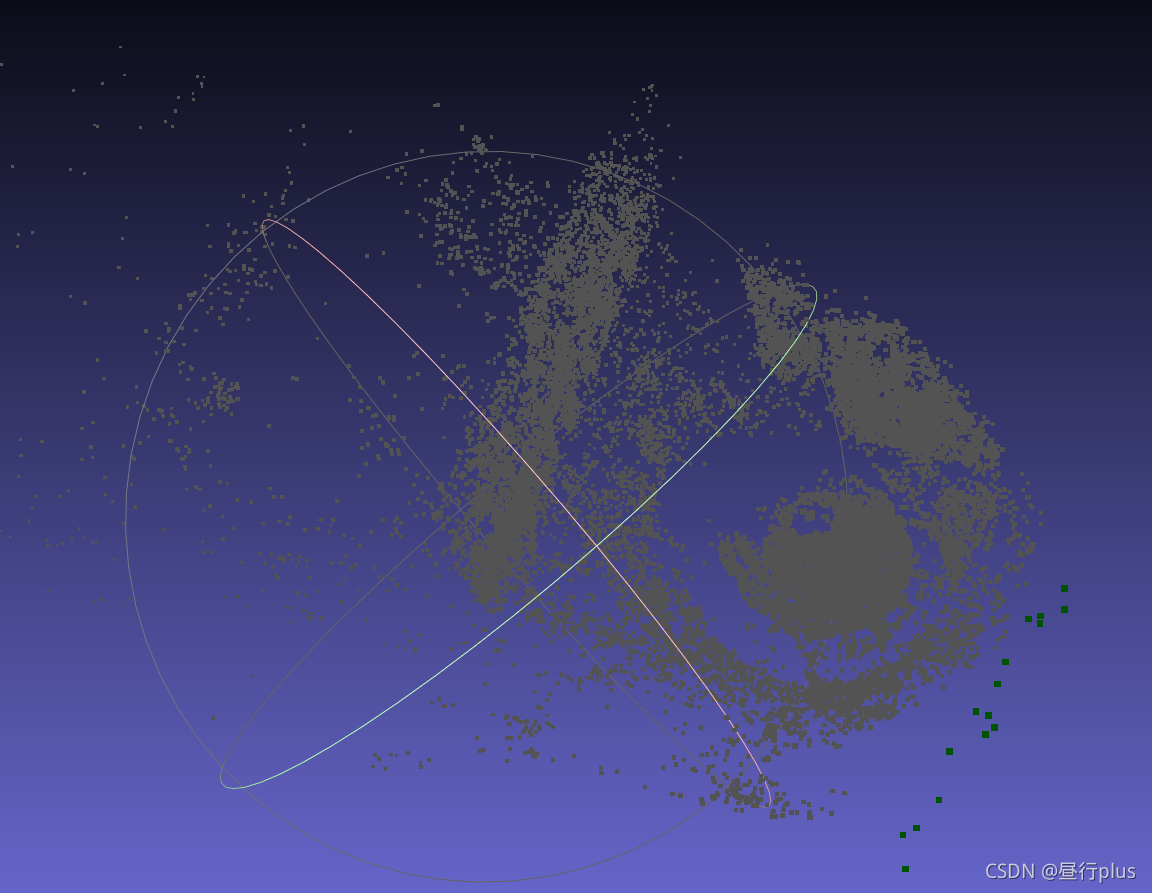
problem-52-64053-pre.txt
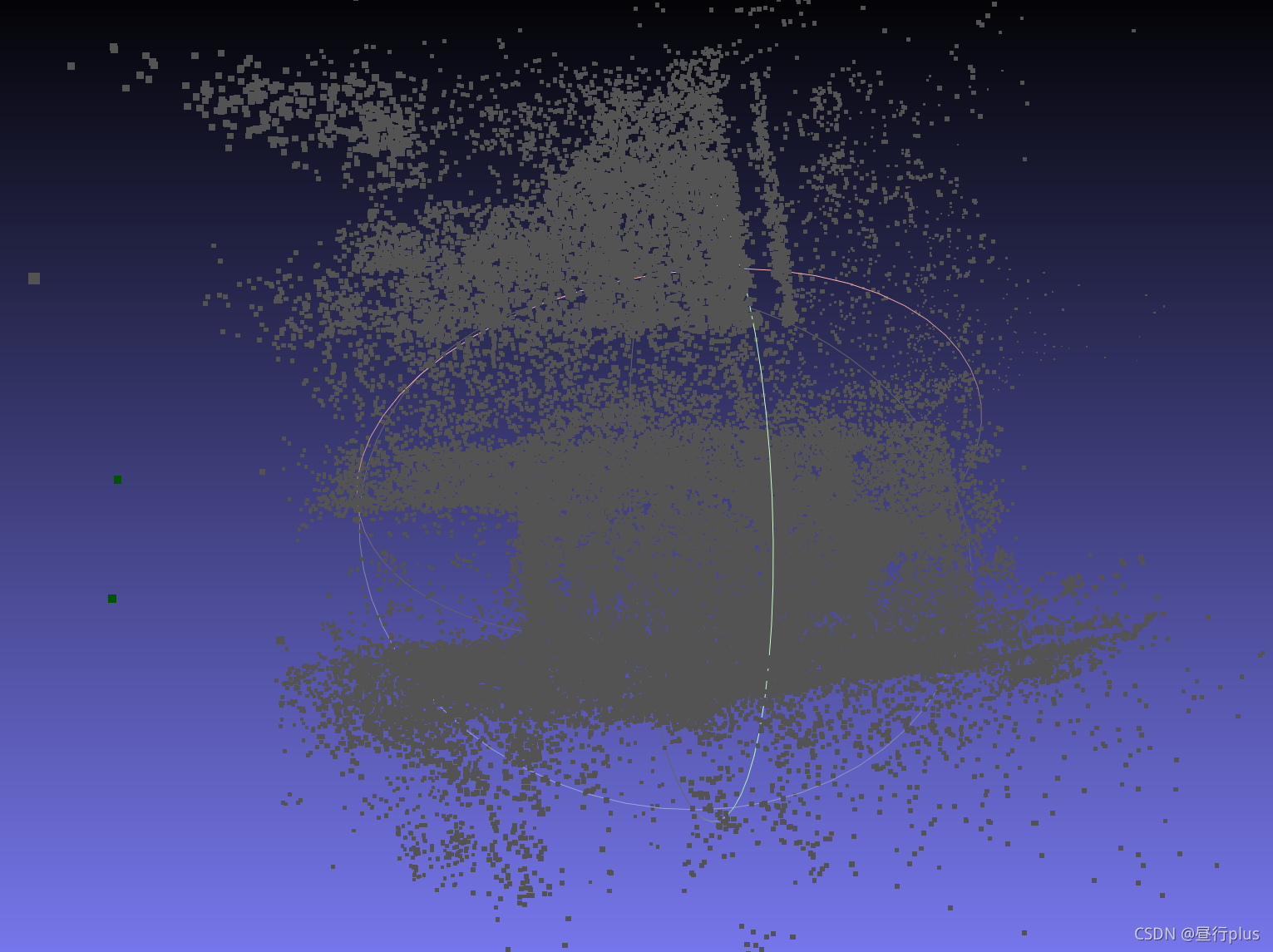
final.ply
problem-16-22106-pre.txt(课本示例)
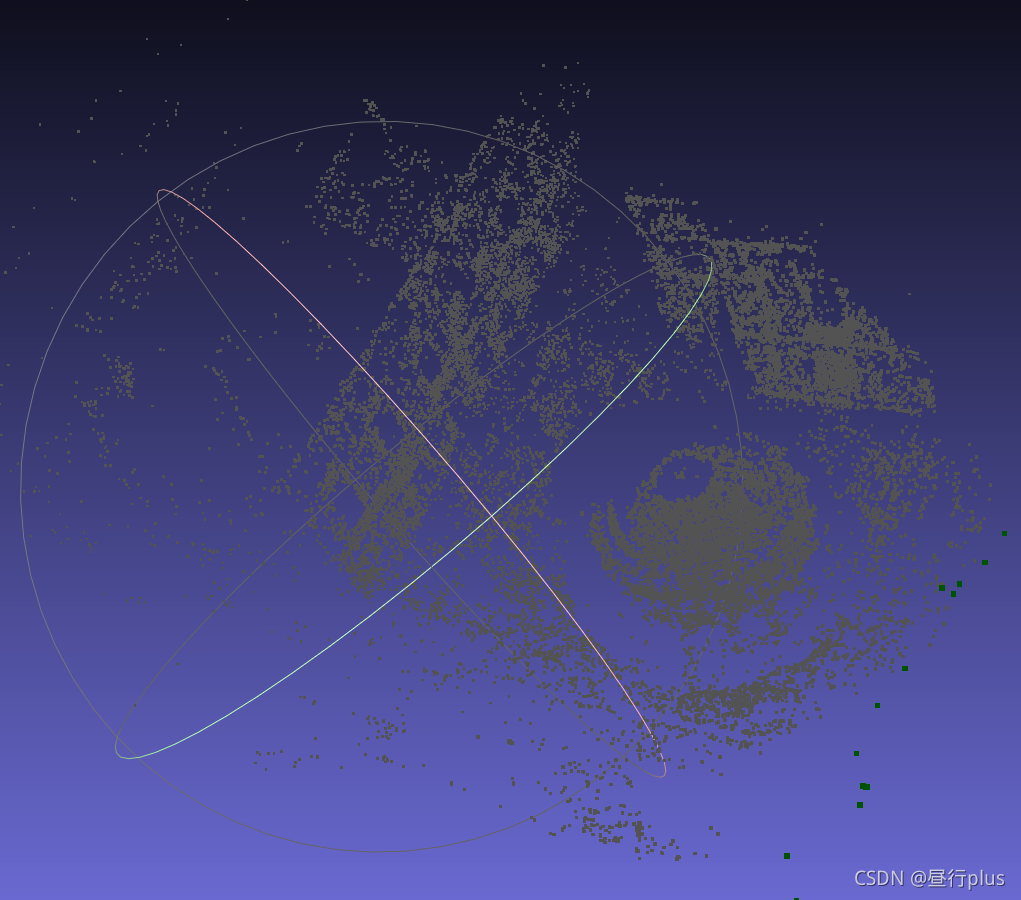
problem-52-64053-pre.txt
3 直接法的Bundle Adjustment
3.1 数学模型
特征点法的BA 以最小化重投影误差作为优化目标。相对的,如果我们以最?化光度误差为目标,就得到了直接法的BA。之前我们在直接法VO 中,谈到了如何?直接法去估计相机位姿。但是直接法亦可?来处理整个Bundle Adjustment。下面,请你推导直接法BA 的数学模型,并完成它的g2o 实现。
注意本题使用的参数化形式与实际的直接法还有?点不同,我们用x,y,z 参数化每?个3D 点,而实际的直接法多采用逆深度参数化(J. Engel, V. Koltun, and D. Cremers, “Direct sparse odometry,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1607.02565,2016.)。
本题给定7 张图片,记为0.png ?6.png,每张图片对应的相机位姿初始值为
T
i
T_{i}
Ti?,以
T
c
w
T_{cw}
Tcw? 形式存储在poses.txt 文件中,其中每一行代表?个相机的位姿,格式如之前作业那样:平移在前,旋转(四元数形式)在后。
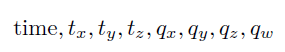
同时,还存在一个3D 点集P,共N 个点。其中每?个点的初始坐标记作
p
i
=
[
x
,
y
,
z
]
i
T
p_{i} = [x, y, z]_{i}^{T}
pi?=[x,y,z]iT?。每个点还有自己的固定灰度值,我们用16 个数来描述,这16 个数为该点周围4x4的小块读数,记作
I
(
p
i
)
I(p_{i})
I(pi?),顺序见图1 。换句话说,小块从(u - 2,v - 2) 取到(u + 1, v + 1),先迭代v。那么,我们知道,可以把每个点投影到每个图像中,然后再看投影后点周围小块与原始的4x4 小块有多大差异。
那么,整体优化?标函数为:
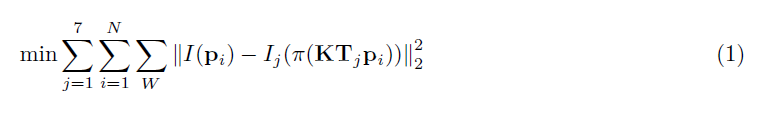
即最小化任意点在任意图像中投影与其本身颜色之差。其中K 为相机内参(在程序内以全局变量形式给定),
π
\pi
π为投影函数,W 指代整个patch。
图1: 直接法BA 的图例。左上:点颜颜色的定义顺序,其中11 号点是观测到的位置;右上:图片示例;中间:优化后的相机位置与点云。
下面,请回答:
1. 如何描述任意?点投影在任意?图像中形成的error?
答: e r r o r = ∑ M ( I ( p i ) ? I j ( π ( K T j p i ) ) ) error = \sum_{M}(I(p_{i}) - I_{j}(\pi (KT_{j}p_{i}))) error=∑M?(I(pi?)?Ij?(π(KTj?pi?)))
这里有个疑惑:这个相机内参矩阵K不应该是包含在 π ( ) \pi() π()里了吗,是否应该删掉?
自问自答: I j ( P ) I_{j}(P) Ij?(P)需要的参数P是图像的像素坐标(2D的),记住这点即可,无论带不带 K , 只要是能把无论是在什么坐标系下的3D点转换为目标相机坐标系下的2D像素坐标即可(这个转换过程必得需要K, 或许这里加上是给 内参矩阵K 刷个存在感吧hh )
2. 每个error 关联几个优化变量?
答:每个error关联两个优化变量:相机的李代数姿态ξ(6个自由度),三维空间点坐标 P=(x,y,z)(3个自由度)
3. error 关于各变量的雅可比是什么?
答:
先看 e r r o r = ∑ M ( I ( p i ) ? I j ( π ( K T j p i ) ) ) error = \sum_{M}(I(p_{i}) - I_{j}(\pi (KT_{j}p_{i}))) error=∑M?(I(pi?)?Ij?(π(KTj?pi?)))
令 q j i = T j p i q_{ji} =T_{j}p_i qji?=Tj?pi? , u i = π ( K q j i ) = 1 Z K q j i u_i = \pi(Kq_{ji}) = \frac{1}{Z}Kq_{ji} ui?=π(Kqji?)=Z1?Kqji?
则 e r r o r = ∑ M ( I ( p i ) ? I j ( π ( K q j i ) ) ) = ∑ M ( I ( p i ) ? I j ( u i ) ) error =\sum_{M}(I(p_{i}) - I_{j}(\pi (Kq_{ji}))) = \sum_{M}(I(p_{i}) - I_{j}(u_i)) error=∑M?(I(pi?)?Ij?(π(Kqji?)))=∑M?(I(pi?)?Ij?(ui?))
① error关于相机的李代数姿态ξ的雅可比:已经在视觉SLAM入门 – 学习笔记 - Part6的3.1单层直接法的第2问中推导过,结论是:
J = ? e ? T = ? ? I j ? u ? u ? q ? q ? δ ξ = ? ? I j ? u ? u ? δ ξ J = \frac{\partial e}{\partial T} = -\frac{\partial I_{j}}{\partial u}\frac{\partial u}{\partial q}\frac{\partial q}{\partial \delta \xi }= -\frac{\partial I_{j}}{\partial u}\frac{\partial u}{\partial \delta \xi } J=?T?e?=??u?Ij???q?u??δξ?q?=??u?Ij???δξ?u?
[ (1x2) x (2x6) = (1x6) ]其中 q = T j p q =T_{j}p q=Tj?p , u = π ( q ) = 1 Z K q u = \pi(q) = \frac{1}{Z}Kq u=π(q)=Z1?Kq
? I c u r ? u \frac{\partial I_{cur}}{\partial u} ?u?Icur??为图像的像素梯度
② error关于三维空间点坐标 P=(x,y,z)的雅可比:
J = ? e ? T = ? ? I j ? u ? u ? q ? q ? P = ? ? I j ? u ? u ? q R j J = \frac{\partial e}{\partial T} = -\frac{\partial I_{j}}{\partial u}\frac{\partial u}{\partial q}\frac{\partial q}{\partial P}= -\frac{\partial I_{j}}{\partial u}\frac{\partial u}{\partial q}R_j J=?T?e?=??u?Ij???q?u??P?q?=??u?Ij???q?u?Rj?
[ [ (1x2) x (2x3) x (3x3)= (1x3) ] ]
其中, R j R_j Rj? 为 T j T_j Tj? 的旋转向量部分
? I j ? u \frac{\partial I_{j}}{\partial u} ?u?Ij??
Eigen::Vector2d J_I_u = Eigen::Vector2d (
0.5*(GetPixelValue(targetImg, u+1+x, v+y) - GetPixelValue(targetImg, u-1+x, v+y)),
0.5*(GetPixelValue(targetImg, u+x, v+1+y) - GetPixelValue(targetImg,u+x, v-1+y))
);
// 注意:Vector2d是2x1的,计算时要用.transpose()转成1x2的
? u ? δ ξ \frac{\partial u}{\partial \delta \xi } ?δξ?u?
Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 6> J_pixel_xi; // pixel to \xi in Lie algebra
J_pixel_xi << fx/Z, 0, -fx*X/(Z*Z), -fx*X*Y/(Z*Z), fx+fx*X*X/(Z*Z), -fx*Y/Z,
0, fy/Z, -fy*Y/(Z*Z), -fy-fy*Y*Y/(Z*Z), fy*X*Y/(Z*Z), fy*X/Z;
? u ? q \frac{\partial u}{\partial q} ?q?u?
Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 3> J_u_Pc;
J_u_Pc(0, 0) = fx / Z;
J_u_Pc(0, 1) = 0;
J_u_Pc(0, 2) = -fx * X / (Z * Z);
J_u_Pc(1, 0) = 0;
J_u_Pc(1, 1) = fy / Z;
J_u_Pc(1, 2) = -fy * Y / (Z * Z);
linearizeOplus()
void linearizeOplus() override {
if (level() == 1) {
_jacobianOplusXi = Eigen::Matrix<double, 16, 3>::Zero();
_jacobianOplusXj = Eigen::Matrix<double, 16, 6>::Zero();
return;
}
const auto vertexPw = dynamic_cast<const g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ * >(vertex(0));
const auto vertexTcw = dynamic_cast<const VertexSophus * >(vertex(1));
Eigen::Vector3d Pc = vertexTcw->estimate() * vertexPw->estimate();
float X = Pc[0];
float Y = Pc[1];
float Z = Pc[2];
float u = fx * X / Z + cx;
float v = fy * Y / Z + cy;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 3> J_u_Pc;
J_u_Pc(0, 0) = fx / Z;
J_u_Pc(0, 1) = 0;
J_u_Pc(0, 2) = -fx * X / (Z * Z);
J_u_Pc(1, 0) = 0;
J_u_Pc(1, 1) = fy / Z;
J_u_Pc(1, 2) = -fy * Y / (Z * Z);
// Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 6> J_Pc_kesi = Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 6>::Zero();
// J_Pc_kesi(0, 0) = 1;
// J_Pc_kesi(0, 4) = Z;
// J_Pc_kesi(0, 5) = -Y;
// J_Pc_kesi(1, 1) = 1;
// J_Pc_kesi(1, 3) = -Z;
// J_Pc_kesi(1, 5) = X;
// J_Pc_kesi(2, 2) = 1;
// J_Pc_kesi(2, 3) = Y;
// J_Pc_kesi(2, 4) = -X;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 6> J_pixel_xi; // pixel to \xi in Lie algebra
J_pixel_xi << fx/Z, 0, -fx*X/(Z*Z), -fx*X*Y/(Z*Z), fx+fx*X*X/(Z*Z), -fx*Y/Z,
0, fy/Z, -fy*Y/(Z*Z), -fy-fy*Y*Y/(Z*Z), fy*X*Y/(Z*Z), fy*X/Z;
Eigen::Vector2d J_I_u; // image gradients
for (int x = -half_patch_size; x < half_patch_size; x++)
for (int y = -half_patch_size; y < half_patch_size; y++) {
int num = (x+2)*4 +(y+2); //这里根据图1左上:点颜颜色的定义顺序计算
J_I_u = Eigen::Vector2d (
0.5*(GetPixelValue(targetImg, u+1+x, v+y) - GetPixelValue(targetImg, u-1+x, v+y)),
0.5*(GetPixelValue(targetImg, u+x, v+1+y) - GetPixelValue(targetImg,u+x, v-1+y))
);
_jacobianOplusXi.block<1, 3>(num, 0) = -J_I_u.transpose() * J_u_Pc * vertexTcw->estimate().rotationMatrix();
// _jacobianOplusXj.block<1, 6>(num, 0) = -J_I_u * J_u_Pc * J_Pc_kesi;
_jacobianOplusXj.block<1, 6>(num, 0) = -J_I_u.transpose() * J_pixel_xi;
}
}
3.2 实现
下面,请你根据上述说明,使用g2o 实现上述优化,并用pangolin 绘制优化结果。程序框架见code/directBA.cpp 文件。实现过程中,思考并回答以下问题:
1. 能否不要以
[
x
,
y
,
z
]
T
[x, y, z]^T
[x,y,z]T 的形式参数化每个点?
答:可以,3.1有说实际的直接法多采用逆深度参数化(J. Engel, V. Koltun, and D. Cremers, “Direct sparse odometry,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1607.02565,2016.)的方法来参数化路标点。
2. 取4x4 的patch 好吗?取更大的patch 好还是取小?点的patch 好?
答:
① 4x4 的patch为较常用的值
② 取更大的patch会降低代码运行速度;而更小的patch会降低鲁棒性
3. 从本题中,你看到直接法与特征点法在BA 阶段有何不同?
答:
特征点法的BA 以最小化重投影误差作为优化目标;
直接法的BA以最小化光度误差为目标。
二者的误差形式和雅克比矩阵形式都不同
4. 由于图像的差异,你可能需要鲁棒核函数,例如Huber。此时Huber 的阈值如何选取?
答:可以先计算一步得到总误差,除以点数获得一个平均误差值,再根据该值设置Huber 阈值
在实践过程中,采用控制变量法对阈值可以做多次测验,取误差最小的阈值作为Huber的阈值。
或者根据经验来确定。
提示:
1. 构建Error 之前先要判断点是否在图像中,去除?部分边界的点。
2. 优化之后,Pangolin 绘制的轨迹与地图如图1 所示。
3. 你也可以不提供雅可比的计算过程,让g2o 自己计算?个数值雅可比。
4. 以上数据实际取自DSO([1] J. Engel, V. Koltun, and D. Cremers, “Direct sparse odometry,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1607.02565,
2016.)。
directBA.cpp
重要!!!
代码中最需要注意的是,无论是optimizer.addVertex(),还是edge->setVertex()都一定是3d的point在先,相机位姿poses在后,否则有数组访问溢出的报错Interupt by signal 11:SIGSEGV
这是我看别人代码推断出来的,具体原因怕是要看源码或者翻翻官方文档才可能知道了……
//
// Created by daybeha on 18/11/21.
// this program shows how to perform direct bundle adjustment
//
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/format.hpp>
using namespace std;
#include <g2o/core/base_binary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/dense/linear_solver_dense.h>
#include <g2o/core/robust_kernel_impl.h>
#include <g2o/types/sba/types_sba.h>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <sophus/se3.hpp>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <pangolin/pangolin.h>
typedef vector<Sophus::SE3d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Sophus::SE3d>> VecSE3d;
typedef vector<Eigen::Vector3d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Eigen::Vector3d>> VecVec3d;
// pose dimension 9, landmark is 3
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6,3> > BlockSolverType;
typedef g2o::LinearSolverDense<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType;
// global variables
string pose_file = "./poses.txt";
string points_file = "./points.txt";
// intrinsics 相机内参
float fx = 277.34;
float fy = 291.402;
float cx = 312.234;
float cy = 239.777;
// bilinear interpolation
inline float GetPixelValue(const cv::Mat &img, float x, float y) {
uchar *data = &img.data[int(y) * img.step + int(x)];
float xx = x - floor(x);
float yy = y - floor(y);
return float(
(1 - xx) * (1 - yy) * data[0] +
xx * (1 - yy) * data[1] +
(1 - xx) * yy * data[img.step] +
xx * yy * data[img.step + 1]
);
}
// g2o vertex that use sophus::SE3d as pose
class VertexSophus : public g2o::BaseVertex<6, Sophus::SE3d> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
// VertexSophus() {}
// ~VertexSophus() {}
void setToOriginImpl() override{
_estimate = Sophus::SE3d();
}
void oplusImpl(const double *update_) override{
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1>> update(update_);
// setEstimate(Sophus::SE3d::exp(update) * estimate());
_estimate *= Sophus::SE3d::exp(update);
}
Eigen::Vector2d project(const Eigen::Vector3d &point){
Eigen::Vector3d pc = _estimate * point;
double x = fx * pc[0]/pc[2] + cx;
double y = fy * pc[1]/pc[2] + cy;
return Eigen::Vector2d(x, y); //转换为像素坐标
}
// 存盘和读盘:留空
bool read(istream &in) override{}
bool write(ostream &out) const override{}
};
// TODO edge of projection error, implement it
// 16x1 error, which is the errors in patch
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double,16,1> Vector16d;
class EdgeDirectProjection : public g2o::BaseBinaryEdge<16, Vector16d, g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ, VertexSophus> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
EdgeDirectProjection(float *color, cv::Mat &target) {
this->origColor = color;
this->targetImg = target;
}
void computeError() override {
// TODO START YOUR CODE HERE
// compute projection error ...
const auto v_sophus = dynamic_cast<VertexSophus *>(_vertices[1]);
const auto v_point = dynamic_cast<g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ *>(_vertices[0]);
Eigen::Vector2d point_porj = v_sophus->project(v_point->estimate());
float u = point_porj[0];
float v = point_porj[1];
if(u-2<0 || v-2<0 || u+1>targetImg.cols-1 || v+1>targetImg.rows-1){
//边界点的处理(error设为0,setLevel(1))
this->setLevel(1);
for(int i=0; i<16; i++){
_error[i] = 0;
}
}else{
for (int i = -2; i < 2; ++i)
for (int j = -2; j < 2; ++j) {
int num = (i+2)*4 +(j+2); //这里根据图1左上:点颜颜色的定义顺序计算
_error[num] = origColor[num] - GetPixelValue(targetImg, u+i, v+j);
}
}
// END YOUR CODE HERE
}
// Let g2o compute jacobian for you
void linearizeOplus() override {
if (level() == 1) {
_jacobianOplusXi = Eigen::Matrix<double, 16, 3>::Zero();
_jacobianOplusXj = Eigen::Matrix<double, 16, 6>::Zero();
return;
}
const auto vertexPw = dynamic_cast<const g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ * >(vertex(0));
const auto vertexTcw = dynamic_cast<const VertexSophus * >(vertex(1));
Eigen::Vector3d Pc = vertexTcw->estimate() * vertexPw->estimate();
float X = Pc[0];
float Y = Pc[1];
float Z = Pc[2];
float u = fx * X / Z + cx;
float v = fy * Y / Z + cy;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 3> J_u_Pc;
J_u_Pc(0, 0) = fx / Z;
J_u_Pc(0, 1) = 0;
J_u_Pc(0, 2) = -fx * X / (Z * Z);
J_u_Pc(1, 0) = 0;
J_u_Pc(1, 1) = fy / Z;
J_u_Pc(1, 2) = -fy * Y / (Z * Z);
// Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 6> J_Pc_kesi = Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 6>::Zero();
// J_Pc_kesi(0, 0) = 1;
// J_Pc_kesi(0, 4) = Z;
// J_Pc_kesi(0, 5) = -Y;
// J_Pc_kesi(1, 1) = 1;
// J_Pc_kesi(1, 3) = -Z;
// J_Pc_kesi(1, 5) = X;
// J_Pc_kesi(2, 2) = 1;
// J_Pc_kesi(2, 3) = Y;
// J_Pc_kesi(2, 4) = -X;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 6> J_pixel_xi; // pixel to \xi in Lie algebra
J_pixel_xi << fx/Z, 0, -fx*X/(Z*Z), -fx*X*Y/(Z*Z), fx+fx*X*X/(Z*Z), -fx*Y/Z,
0, fy/Z, -fy*Y/(Z*Z), -fy-fy*Y*Y/(Z*Z), fy*X*Y/(Z*Z), fy*X/Z;
Eigen::Vector2d J_I_u; // image gradients
for (int x = -half_patch_size; x < half_patch_size; x++)
for (int y = -half_patch_size; y < half_patch_size; y++) {
int num = (x+2)*4 +(y+2); //这里根据图1左上:点颜颜色的定义顺序计算
J_I_u = Eigen::Vector2d (
0.5*(GetPixelValue(targetImg, u+1+x, v+y) - GetPixelValue(targetImg, u-1+x, v+y)),
0.5*(GetPixelValue(targetImg, u+x, v+1+y) - GetPixelValue(targetImg,u+x, v-1+y))
);
_jacobianOplusXi.block<1, 3>(num, 0) = -J_I_u.transpose() * J_u_Pc * vertexTcw->estimate().rotationMatrix();
// _jacobianOplusXj.block<1, 6>(num, 0) = -J_I_u * J_u_Pc * J_Pc_kesi;
_jacobianOplusXj.block<1, 6>(num, 0) = -J_I_u.transpose() * J_pixel_xi;
}
}
bool read(istream &in) override{}
bool write(ostream &out) const override{}
private:
cv::Mat targetImg; // the target image
float *origColor = nullptr; // 16 floats, the color of this point
int half_patch_size = 2;
};
// plot the poses and points for you, need pangolin
void Draw(const VecSE3d &poses, const VecVec3d &points);
// read poses points color and images
void ReadData(VecSE3d &poses, VecVec3d &points, vector<float *> &color, vector<cv::Mat> &images){
ifstream fin(pose_file);
while (!fin.eof()) {
double timestamp = 0;
fin >> timestamp;
if (timestamp == 0) break;
double data[7];
for (auto &d: data) fin >> d;
poses.push_back(Sophus::SE3d(
Eigen::Quaterniond(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]),
Eigen::Vector3d(data[0], data[1], data[2])
));
if (!fin.good()) break;
}
fin.close();
fin.open(points_file);
while (!fin.eof()) {
double xyz[3] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) fin >> xyz[i];
if (xyz[0] == 0) break;
points.push_back(Eigen::Vector3d(xyz[0], xyz[1], xyz[2]));
float *c = new float[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) fin >> c[i];
color.push_back(c);
if (!fin.good()) break;
}
fin.close();
boost::format fmt("./%d.png");
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
images.push_back(cv::imread((fmt % i).str(), CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE));
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
// read poses points color and images
VecSE3d poses;
VecVec3d points;
vector<float *> color;
vector<cv::Mat> images;
ReadData(poses, points, color,images);
cout << "poses: " << poses.size() << ", points: " << points.size() << endl;
// build optimization problem
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(
g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; // 图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); // 设置求解器
optimizer.setVerbose(true); // 打开调试输出
// TODO add vertices, edges into the graph optimizer 往图中增加顶点\边
// START YOUR CODE HERE
// vertex 往图中增加顶点
vector<VertexSophus *> vertex_poses;
vector<g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ *> vertex_points;
for (int j = 0; j < points.size(); ++j) {
auto v = new g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ();
v->setId(j);
v->setEstimate(points[j]);
// g2o在BA中需要手动设置待Marg的顶点
//使用稀疏优化时手动设置需要边缘化的顶点
//一般位姿结点更少,对应矩阵更小,为降低计算量,边缘化路标结点
v->setMarginalized(true);
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertex_points.push_back(v);
}
int camera_num = poses.size();
for (int i = 0; i < camera_num; ++i) {
auto v = new VertexSophus();
v->setId(i + points.size());
v->setEstimate(poses[i]);
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertex_poses.push_back(v);
}
for (int c = 0; c < poses.size(); c++)
for (int p = 0; p < points.size(); p++) {
auto edge = new EdgeDirectProjection(color[p], images[c]);
// point first and poses second !!!
edge->setVertex(0, vertex_points[p]);
edge->setVertex(1, vertex_poses[c]);
// edge->setVertex(0, dynamic_cast<g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ *>(optimizer.vertex(p+poses.size())));
// edge->setVertex(1, dynamic_cast<VertexSophus*>(optimizer.vertex(c)));
// 信息矩阵可直接设置为 error_dim*error_dim 的单位阵
edge->setInformation(Eigen::Matrix<double,16,16>::Identity()); //信息矩阵 Ω 是协方差矩阵的逆
// 设置Huber核函数,减小错误点影响,加强鲁棒性
// edge->setRobustKernel(new g2o::RobustKernelHuber()); //设置鲁棒核函数 此处为Huber核
auto rk = new g2o::RobustKernelHuber();
rk->setDelta(1.0);
edge->setRobustKernel(rk);
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
}
// END YOUR CODE HERE
// perform optimization
optimizer.initializeOptimization(0);
optimizer.optimize(200);
// TODO fetch data from the optimizer
// START YOUR CODE HERE
for (int c = 0; c < poses.size(); c++){
Sophus::SE3d Tcw = dynamic_cast<VertexSophus *>(optimizer.vertex(c + points.size()))->estimate();
poses[c] = Tcw;
}
for (int p = 0; p < points.size(); p++) {
Eigen::Vector3d Pw = dynamic_cast<g2o::VertexSBAPointXYZ *>(optimizer.vertex(p))->estimate();
points[p] = Pw;
}
// END YOUR CODE HERE
// plot the optimized points and poses
Draw(poses, points);
// delete color data
for (auto &c: color) delete[] c;
return 0;
}
void Draw(const VecSE3d &poses, const VecVec3d &points) {
if (poses.empty() || points.empty()) {
cerr << "parameter is empty!" << endl;
return;
}
// create pangolin window and plot the trajectory
pangolin::CreateWindowAndBind("Trajectory Viewer", 1024, 768);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glEnable(GL_BLEND);
glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
pangolin::OpenGlRenderState s_cam(
pangolin::ProjectionMatrix(1024, 768, 500, 500, 512, 389, 0.1, 1000),
pangolin::ModelViewLookAt(0, -0.1, -1.8, 0, 0, 0, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0)
);
pangolin::View &d_cam = pangolin::CreateDisplay()
.SetBounds(0.0, 1.0, pangolin::Attach::Pix(175), 1.0, -1024.0f / 768.0f)
.SetHandler(new pangolin::Handler3D(s_cam));
while (!pangolin::ShouldQuit()) {
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
d_cam.Activate(s_cam);
glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
// draw poses
float sz = 0.1;
int width = 640, height = 480;
for (auto &Tcw: poses) {
glPushMatrix();
Sophus::Matrix4f m = Tcw.inverse().matrix().cast<float>();
glMultMatrixf((GLfloat *) m.data());
glColor3f(1, 0, 0);
glLineWidth(2);
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glVertex3f(0, 0, 0);
glVertex3f(sz * (0 - cx) / fx, sz * (0 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(0, 0, 0);
glVertex3f(sz * (0 - cx) / fx, sz * (height - 1 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(0, 0, 0);
glVertex3f(sz * (width - 1 - cx) / fx, sz * (height - 1 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(0, 0, 0);
glVertex3f(sz * (width - 1 - cx) / fx, sz * (0 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (width - 1 - cx) / fx, sz * (0 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (width - 1 - cx) / fx, sz * (height - 1 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (width - 1 - cx) / fx, sz * (height - 1 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (0 - cx) / fx, sz * (height - 1 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (0 - cx) / fx, sz * (height - 1 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (0 - cx) / fx, sz * (0 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (0 - cx) / fx, sz * (0 - cy) / fy, sz);
glVertex3f(sz * (width - 1 - cx) / fx, sz * (0 - cy) / fy, sz);
glEnd();
glPopMatrix();
}
// points
glPointSize(2);
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
for (size_t i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {
glColor3f(0.0, points[i][2]/4, 1.0-points[i][2]/4);
glVertex3d(points[i][0], points[i][1], points[i][2]);
}
glEnd();
pangolin::FinishFrame();
usleep(5000); // sleep 5 ms
}
}
plus: linearizeOplus()也可以不重载,让g2o自己算,不过基本就更不动了……
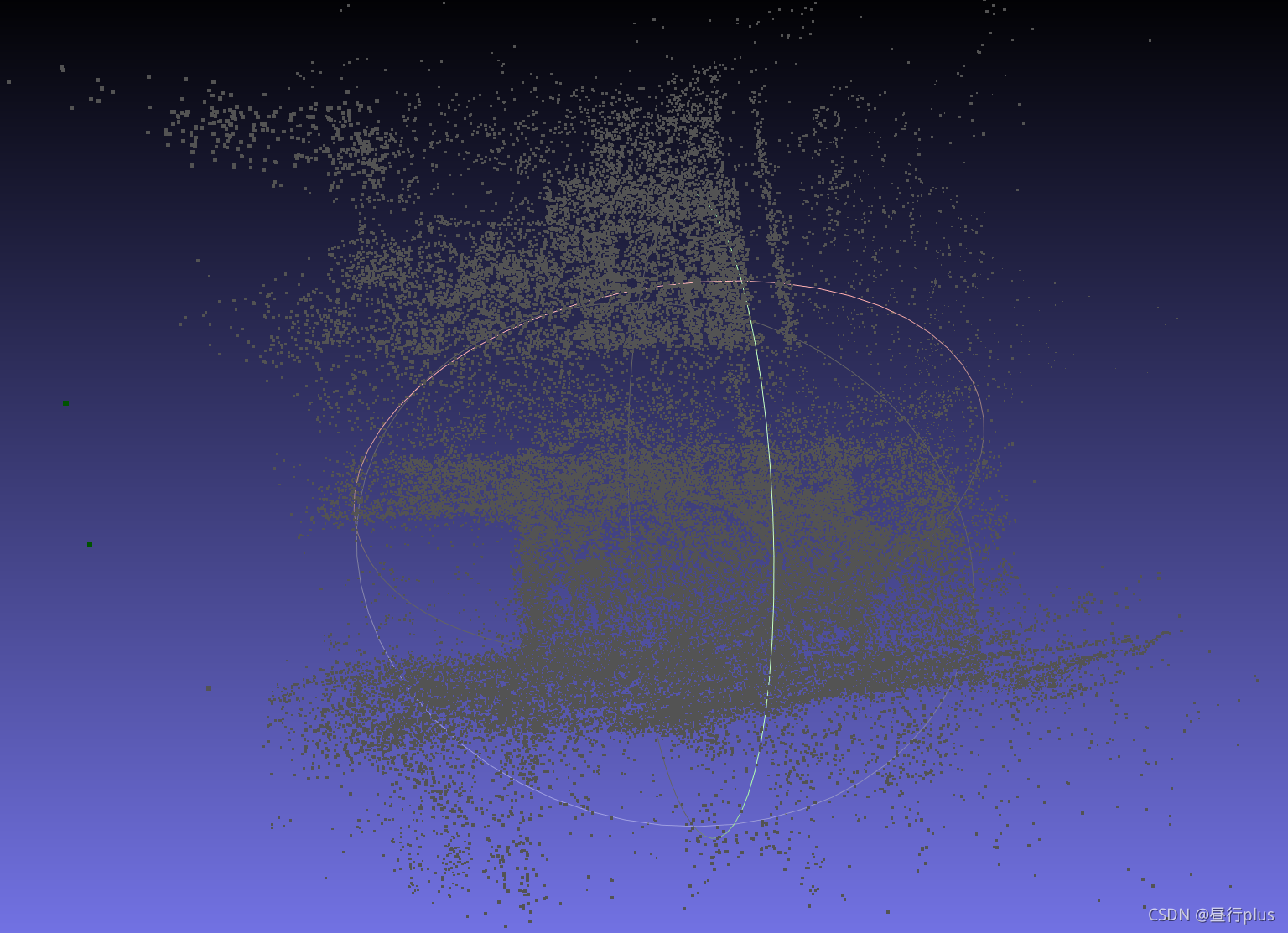
运行结果:
优化前:

优化后:

效果貌似不怎么样(error也忒大了点,并且优化后的点云看着和优化前没什么区别……)
如果报错:
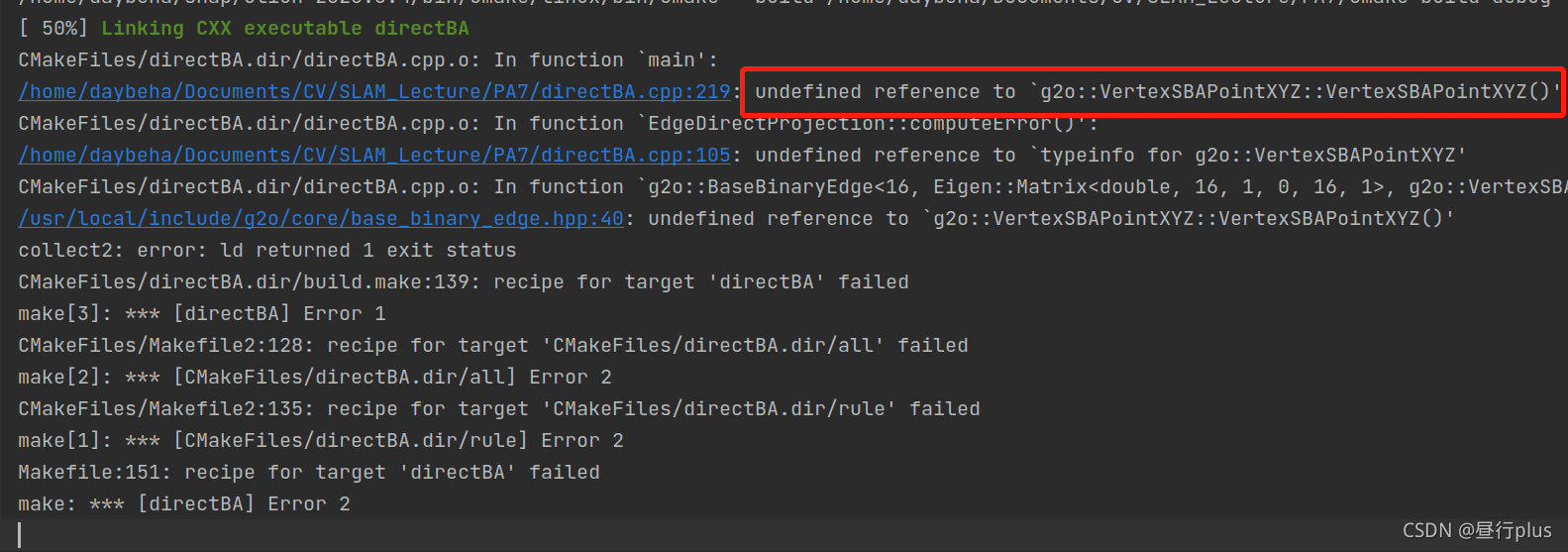
需要在CmakeList.txt中的target_link_libraries时加入 g2o_types_sba :
add_executable(directBA directBA.cpp)
target_link_libraries(directBA ${OpenCV_LIBRARIES} ${G2O_CORE_LIBRARY} ${G2O_STUFF_LIBRARY} g2o_types_sba
${Sophus_LIBRARIES} ${Pangolin_LIBRARIES})
完整CmakeList.txt :
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.17)
project(PA7)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release") # 这一句很关键,虽然不知道原因,但确实能令代码提速不少
include_directories( "/usr/include/eigen3")
list(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake)
# g2o
find_package(G2O REQUIRED)
find_package(CSparse REQUIRED)
Find_Package(Ceres REQUIRED)
find_package(Sophus REQUIRED)
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
find_package(Pangolin REQUIRED)
SET(G2O_LIBS g2o_csparse_extension g2o_stuff g2o_core cxsparse)
include_directories(
${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}
${CSPARSE_INCLUDE_DIR}
${Sophus_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}
${Pangolin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
add_library(bal_common common.cpp)
add_executable(bundle_adjustment_g2o bundle_adjustment_g2o.cpp)
target_link_libraries(bundle_adjustment_g2o ${G2O_LIBS} bal_common)
add_executable(bundle_adjustment_ceres bundle_adjustment_ceres.cpp)
target_link_libraries(bundle_adjustment_ceres ${CERES_LIBRARIES} bal_common)
add_executable(directBA directBA.cpp)
target_link_libraries(directBA ${OpenCV_LIBRARIES} ${G2O_CORE_LIBRARY} ${G2O_STUFF_LIBRARY} g2o_types_sba
${Sophus_LIBRARIES} ${Pangolin_LIBRARIES})
另外https://blog.csdn.net/hitljy/article/details/107544709有个手写雅可比的版本,时间较紧没有自己也写一个,先留个记号
参考:
3个范例带你读懂贝叶斯法则
https://blog.csdn.net/hitljy/article/details/107544709
https://www.cnblogs.com/guoben/p/13375128.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/yujingxiang/p/14459792.html
https://github.com/gaoxiang12/slambook2
高翔 张涛等 《视觉SLAM十四讲 第二版》
学习 点云格式(PLY)
g2o使用bug总结
https://gitee.com/ximing689/slam-learning