一、MATLAB基础
dir :列出当前目录下的所有文件;clc :清除命令窗口;clear all :清除环境(从内存中清除所有变量);who:将内存中的当前变量以简单形式列出;close all :关闭所有的 Figure 窗口。
Matlab 的变量名以字母打头,后面最多可跟 19 个字母或数字,不能使用内部函数或命令名作为变量名, Matlab 中的变量名区分大小写。
矩阵赋值:数值通常按行输入,行之间用分号隔开。省略最后的分号,Matlab 会回显矩阵值。
C=[-1,0,0;l,-1,0;0,0,2];
rand %无变量输入时只产生一个随机数
y = rand(n) %生成n x n随机矩阵,其元素在(0,1)内
y = rand (m, n) %生成m x n随机矩阵,其元素在(0,1)内
bitand(a,b) %按位与
bitor(a,b) %按位或
若 a= 2; b=3。a 的 二进制为 0100 ;b 的 二进制为 0110。比较该二进制,若相对应的位置都为1则为1其余为0。所以 bitand(2,3)=0100=2
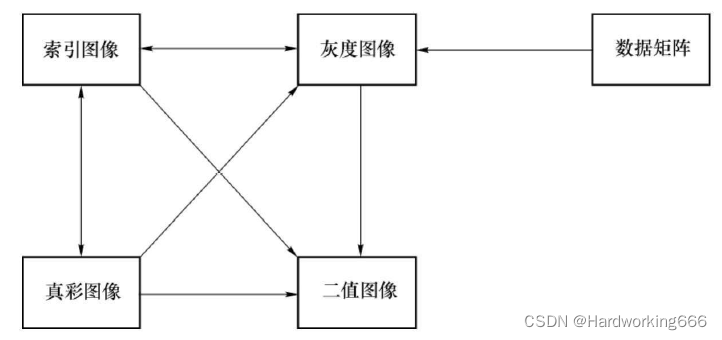
二、文件的读取与图像格式转换
imfinfo('binary.tif') 读取图像文件属性
I=imread('binary.tif'); 将指定图像文件读入工作区
figure; imshow(I); 新创建一个显示窗口,并显示图像文件
M=imread('football.jpg'); 读取 RGB图像 football.jpg
MR=M(:,:,1); 提取图像 R层数据矩阵
MG=M(:,:,2); 提取图像 G层数据矩阵
MB=M(:,:,3); 提取图像 B层数据矩阵
subplot(2,2,1); imshow(M); title('原始图像 ');
subplot(2,2,2); imshow(MR); title('R层灰度图像 ');
subplot(2,2,3); imshow(MG) ;title('G层灰度图像 ');
subplot(2,2,4); imshow(MB); title('B层灰度图像 ');
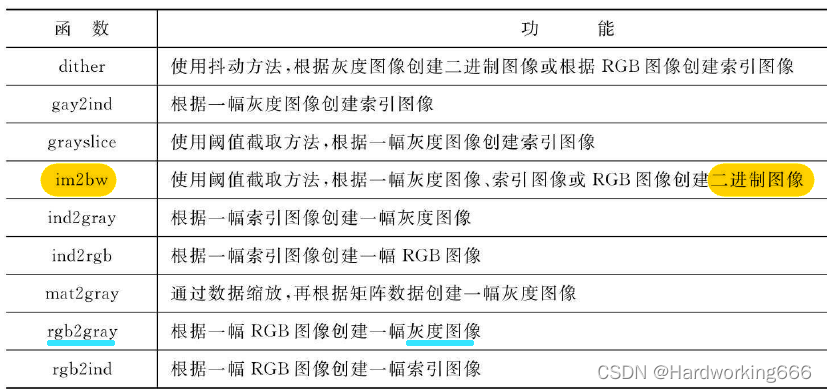
I=rgb2gray(M); 将真彩色图像转换为灰度图
figure;imshow(I);
[X,map]=rgb2ind(M,256); 将真彩色图像 football.jpg转换成 256色索引图像
[X1,map1]=rgb2ind(M,32);
[X2,map2]=rgb2ind(M,8);
subplot(2,2,1);imshow(M);
subplot(2,2,2);imshow(X,map);
subplot(2,2,3);imshow(X1,map1);
subplot(2,2,4);imshow(X2,map2);
imwrite(X1,map1,'footballind.bmp'); 将转换后的 32色索引图像保存为 footballind.bmp
subplot(m,n,p)或者subplot(m n p)。subplot是将多个图画到一个平面上的工具。其中,m表示是图排成m行,n表示图排成n列,也就是整个figure中有n个图是排成一行的,一共m行,如果m=2就是表示2行图。p表示图所在的位置,p=1表示从左到右从上到下的第一个位置。
clear;
clc;
[a,b]=imread('footballind.bmp'); 读取刚才保存的索引图像footballind.bmp
K=ind2gray(a,b); 将其转换为灰度图
subplot(1,2,1);imshow(a,b);
subplot(1,2,2);imshow(K);
level=graythresh(K); 取灰度图的一个合适阈值
BW=im2bw(K,level); 再将灰度图转换成二值图像
subplot(1,2,1);imshow(K);
subplot(1,2,2);imshow(BW);