文章目录
1. DataFrame数据结构
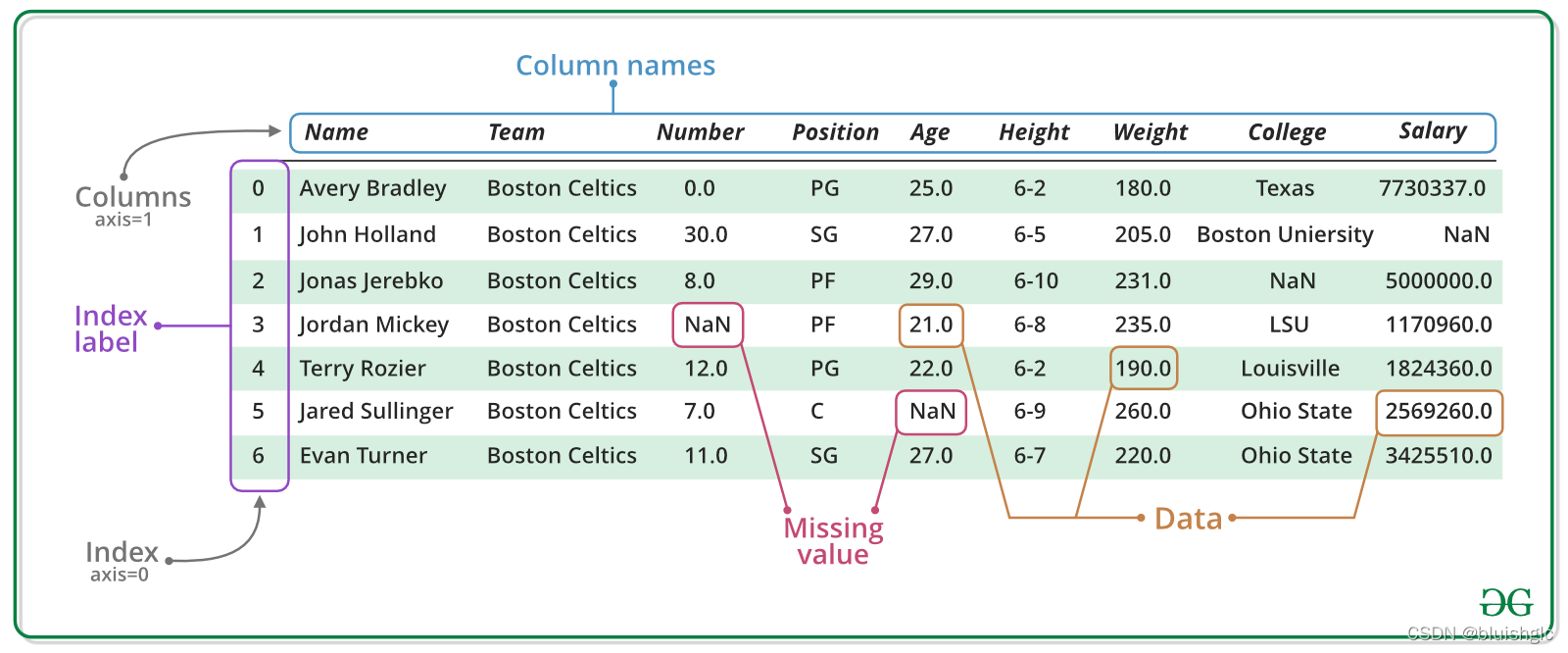
DataFrame的数据结构与一张数据表是非常相似的,上图对于DataFrame的解释已经一目了然了。唯一需要特别解释一下的是Index。在DF中,如不特别指定,DF总是默认为每一行数据生成Index,这个Index就是从0开始的自增索引,和数组中的Index是一样的。与此同时,用户还可以使用某一列(甚至多列)来作为Index,取代默认的索引值。细节可参考下一节。
2. 如何构建DataFrame
对于DataFrame的构建,下图给了非常形象地总结:
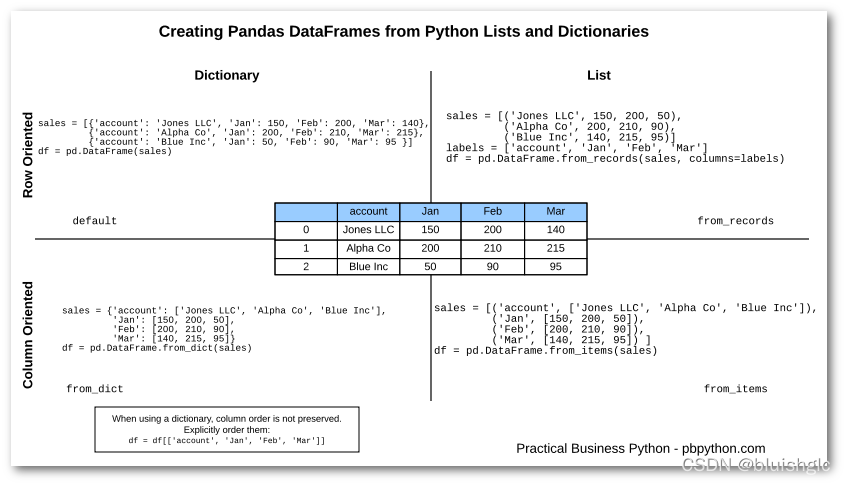
以下是参考代码:
import pandas as pd
from collections import OrderedDict
from datetime import date
2.1. 按行构建
2.1.1. 使用Dictionary按行构建
sales = [{'account': 'Jones LLC', 'Jan': 150, 'Feb': 200, 'Mar': 140},
{'account': 'Alpha Co', 'Jan': 200, 'Feb': 210, 'Mar': 215},
{'account': 'Blue Inc', 'Jan': 50, 'Feb': 90, 'Mar': 95 }]
df = pd.DataFrame(sales)
使用Dictionary按行构建,就是典型的KV模式,一个Dict一行,K是列名,V是对应值。这一方式易读,最符合人们的常规习惯,但是列名重复出现多次,比较繁琐。
2.1.2. 使用List按行构建
sales = [('Jones LLC', 150, 200, 50),
('Alpha Co', 200, 210, 90),
('Blue Inc', 140, 215, 95)]
labels = ['account', 'Jan', 'Feb', 'Mar']
df = pd.DataFrame.from_records(sales, columns=labels)
使用List按行构建时,是一行一行的纯数据填写,列名单独指定,这样构建效率要高很多!
2.2. 按列构建
2.2.1. 使用Dictionary按列构建
sales = {'account': ['Jones LLC', 'Alpha Co', 'Blue Inc'],
'Jan': [150, 200, 50],
'Feb': [200, 210, 90],
'Mar': [140, 215, 95]}
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(sales)
使用Dictionary按列构建时,Dict的K是列名,V是这一列的所有值。 这一方式也很高效,没有冗余数据输入。
2.2.2. 使用List按列构建
sales = [('account', ['Jones LLC', 'Alpha Co', 'Blue Inc']),
('Jan', [150, 200, 50]),
('Feb', [200, 210, 90]),
('Mar', [140, 215, 95]),
]
df = pd.DataFrame.from_items(sales)
使用List按列构建时,与使用Dictionary按列构建类似,但是比较扭曲,这时的List只有两个元素,第一个是K,第二个是V!
本章节参考自:https://pbpython.com/pandas-list-dict.html
3. 使用set_index重置索引
如上所述,DF总会生成一个默认的类似数组索引的默认索引,但是用户可以灵活的使用数据本身的一些列作为索引。比如当数据是从数据表中导出的时候,完全可以使用原始表中的ID列作为DF的Index。
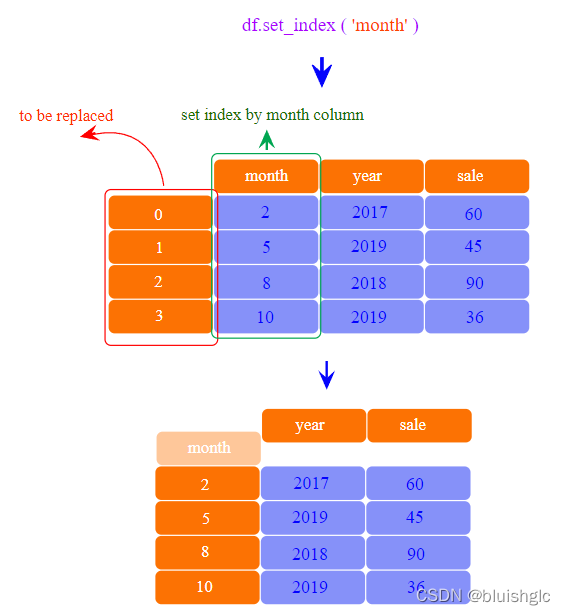
重置索引使用set_index方法。如下示意图形象地演示了它的处理逻辑:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'month': [2, 5, 8, 10],
'year': [2017, 2019, 2018, 2019],
'sale': [60, 45, 90, 36]})
df.set_index('month')
本章节参考自: https://www.w3resource.com/pandas/dataframe/dataframe-set_index.php