前言
本文通过介绍canny边缘检测原理与代码解析,希望能让大家深入理解canny边缘检测
canny边缘检测算法主要流程
canny边缘检测主要分为4个部分,本文分别从每一个部分进行解析并附代码。
- 图像降噪
- 梯度计算
- 非极大值抑制
- 双阈值边界跟踪
一、高斯模糊
图像去噪是进行边缘检测的第一步,通过去噪可以去除图像中的一些噪点,从而使边缘检测时免受噪点干扰。
一般去噪卷积核中心点的值由周围点像素均值决定,以3×3卷积核的8邻域为例,卷积中心点坐标值由周围坐标与本身的均值决定。
然而这种均值决定中心点的方法本质是周围点均采用相同的权重,但是当卷积核变大时,离中心点最远的点与最近的点占有相同权重显然是不合适的,这就需要我们的高斯核出场啦。
高斯模糊就是将卷积核中不同位置的点按照高斯分布(正态分布)进行权重分配,二维高斯分布公式如下:
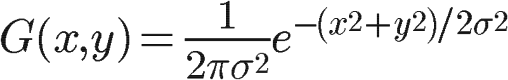
这边我们已σ=1为例生成一个3×3的高斯卷积核。如下图所示,首先将普通的卷积核按(x,y)坐标,σ=1,代入上述二维高斯分布公式,得到权重具有高斯分布特性的卷积核。其次,由于卷积核所有点的权重和为1,所以需要将卷积核每个点的权重值再除以所有点的权重合。最后就完成了高斯卷积核,可以对图像进行去噪卷积操作啦。
代码如下:
import numpy as np
from scipy import ndimage
from scipy.ndimage.filters import convolve
def gaussian_kernel(self, size, sigma=1):
size = int(size) // 2
x, y = np.mgrid[-size:size+1, -size:size+1]
normal = 1 / (2.0 * np.pi * sigma**2)
g = np.exp(-((x**2 + y**2) / (2.0*sigma**2))) * normal
return g
二、图像梯度计算
要进行边缘检测,就需要得到图像梯度信息,根据图像的梯度幅值和梯度方向来确定边缘,一般均采用sobel算子对图像进行梯度幅值与梯度方向计算。
sobel算子分为垂直方向和水平方向两个模板,模板如下:

梯度幅值G和梯度方向θ计算公式如下所示:
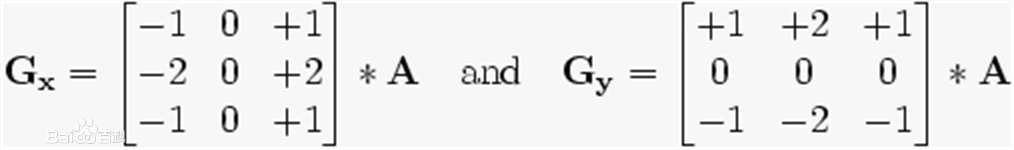
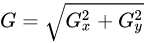
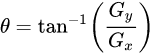
代码如下:
def sobel_filters(self, img):
Kx = np.array([[-1, 0, 1], [-2, 0, 2], [-1, 0, 1]], np.float32)
Ky = np.array([[1, 2, 1], [0, 0, 0], [-1, -2, -1]], np.float32)
Ix = ndimage.filters.convolve(img, Kx)
Iy = ndimage.filters.convolve(img, Ky)
G = np.hypot(Ix, Iy)
theta = np.arctan2(Iy, Ix)
return (G, theta)
三、非极大值抑制
在获取图像的梯度幅值和梯度方向后,需要通过获取的梯度幅值和梯度方向对图像边缘进行非极大值抑制操作,由于梯度方向与边缘方向是垂直的,所以非极大值抑制可以有效的剔除一大部分非边缘点。
如下图所示,在非极大值抑制中,梯度方向是一条无向直线,也就是正负两侧均为梯度方向(即下图红线),并将梯度方向分为四个部分:
- 垂直梯度方向(0,22.5]∪(-22.5,0]∪(157.5,180]∪(-180,157.5]
- 45°梯度方向 [22.5,67.5)∪[-157.5,-112.5)
- 水平梯度方向 [67.5,112.5]∪[-112.5,-67.5]
- 135°梯度方向 (112.5, 157.5]∪[-67.5, -22.5]
确定了梯度方向后,就需要通过这个梯度方向上交点q’和r’的值来确定是否将中心点抑制,但是实际上我们是得不到交点值的,以下图8邻域我们只能得到周围8个点,这时有两种办法,1)线性插值,通过p、q两点的线性插值求得q’,r’同理可得。2)取相近点作为极大值,即取q点取代q’点。下方代码是以方法2为基础的。

具体代码如下,
def non_max_suppression(self,img, D):
M, N = img.shape
Z = np.zeros((M,N), dtype=np.int32)
angle = D * 180. / np.pi
angle[angle < 0] += 180
for i in range(1,M-1):
for j in range(1,N-1):
try:
q = 255
r = 255
#angle 0
if (0 <= angle[i,j] < 22.5) or (157.5 <= angle[i,j] <= 180):
q = img[i, j+1]
r = img[i, j-1]
#angle 45
elif (22.5 <= angle[i,j] < 67.5):
q = img[i+1, j-1]
r = img[i-1, j+1]
#angle 90
elif (67.5 <= angle[i,j] < 112.5):
q = img[i+1, j]
r = img[i-1, j]
#angle 135
elif (112.5 <= angle[i,j] < 157.5):
q = img[i-1, j-1]
r = img[i+1, j+1]
if (img[i,j] >= q) and (img[i,j] >= r):
Z[i,j] = img[i,j]
else:
Z[i,j] = 0
except IndexError as e:
pass
return Z
四、双阈值边界跟踪
双阈值边界跟踪分为两个步骤:1)通过选取强弱阈值,将梯度幅值低与弱阈值的点置为0,大于强阈值的保留并标记为255。2)对于梯度幅值大于弱阈值但又小于高阈值的点,通过判断它的8邻域是否存在大于强阈值的点,若存在,则保留并置为255,若不存在,则舍弃并置为0。
具体代码如下:
步骤1:
def threshold(self, img):
highThreshold = img.max() * self.highThreshold
lowThreshold = highThreshold * self.lowThreshold
M, N = img.shape
res = np.zeros((M,N), dtype=np.int32)
weak = np.int32(self.weak_pixel)
strong = np.int32(self.strong_pixel)
strong_i, strong_j = np.where(img >= highThreshold)
zeros_i, zeros_j = np.where(img < lowThreshold)
weak_i, weak_j = np.where((img <= highThreshold) & (img >= lowThreshold))
res[strong_i, strong_j] = strong
res[weak_i, weak_j] = weak
return (res)
步骤2:
def hysteresis(self, img):
M, N = img.shape
weak = self.weak_pixel
strong = self.strong_pixel
for i in range(1, M-1):
for j in range(1, N-1):
if (img[i,j] == weak):
try:
if ((img[i+1, j-1] == strong) or (img[i+1, j] == strong) or (img[i+1, j+1] == strong)
or (img[i, j-1] == strong) or (img[i, j+1] == strong)
or (img[i-1, j-1] == strong) or (img[i-1, j] == strong) or (img[i-1, j+1] == strong)):
img[i, j] = strong
else:
img[i, j] = 0
except IndexError as e:
pass
return img
总体代码如下:
from scipy import ndimage
from scipy.ndimage.filters import convolve
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
import os
def rgb2gray(rgb):
r, g, b = rgb[:,:,0], rgb[:,:,1], rgb[:,:,2]
gray = 0.2989 * r + 0.5870 * g + 0.1140 * b
return gray
def load_data(dir_name):
imgs = []
for filename in os.listdir(dir_name):
if os.path.isfile(dir_name + '/' + filename):
img = mpimg.imread(dir_name + '/' + filename)
img = rgb2gray(img)
imgs.append(img)
return imgs
def visualize(imgs, format=None, gray=False):
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 20))
for i, img in enumerate(imgs):
if img.shape[0] == 3:
img = img.transpose(1,2,0)
plt_idx = i+1
plt.subplot(2, 2, plt_idx)
plt.imshow(img, format)
plt.show()
class cannyEdgeDetector:
def __init__(self, imgs, sigma=1, kernel_size=5, weak_pixel=75, strong_pixel=255, lowthreshold=0.05, highthreshold=0.15):
self.imgs = imgs
self.imgs_final = []
self.img_smoothed = None
self.gradientMat = None
self.thetaMat = None
self.nonMaxImg = None
self.thresholdImg = None
self.weak_pixel = weak_pixel
self.strong_pixel = strong_pixel
self.sigma = sigma
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.lowThreshold = lowthreshold
self.highThreshold = highthreshold
return
def gaussian_kernel(self, size, sigma=1):
size = int(size) // 2
x, y = np.mgrid[-size:size+1, -size:size+1]
normal = 1 / (2.0 * np.pi * sigma**2)
g = np.exp(-((x**2 + y**2) / (2.0*sigma**2))) * normal
return g
def sobel_filters(self, img):
Kx = np.array([[-1, 0, 1], [-2, 0, 2], [-1, 0, 1]], np.float32)
Ky = np.array([[1, 2, 1], [0, 0, 0], [-1, -2, -1]], np.float32)
Ix = ndimage.filters.convolve(img, Kx)
Iy = ndimage.filters.convolve(img, Ky)
G = np.hypot(Ix, Iy)
G = G / G.max() * 255
theta = np.arctan2(Iy, Ix)
return (G, theta)
def non_max_suppression(self, img, D):
M, N = img.shape
Z = np.zeros((M,N), dtype=np.int32)
angle = D * 180. / np.pi
angle[angle < 0] += 180
for i in range(1,M-1):
for j in range(1,N-1):
try:
q = 255
r = 255
#angle 0
if (0 <= angle[i,j] < 22.5) or (157.5 <= angle[i,j] <= 180):
q = img[i, j+1]
r = img[i, j-1]
#angle 45
elif (22.5 <= angle[i,j] < 67.5):
q = img[i+1, j-1]
r = img[i-1, j+1]
#angle 90
elif (67.5 <= angle[i,j] < 112.5):
q = img[i+1, j]
r = img[i-1, j]
#angle 135
elif (112.5 <= angle[i,j] < 157.5):
q = img[i-1, j-1]
r = img[i+1, j+1]
if (img[i,j] >= q) and (img[i,j] >= r):
Z[i,j] = img[i,j]
else:
Z[i,j] = 0
except IndexError as e:
pass
return Z
def threshold(self, img):
highThreshold = img.max() * self.highThreshold
lowThreshold = highThreshold * self.lowThreshold
M, N = img.shape
res = np.zeros((M,N), dtype=np.int32)
weak = np.int32(self.weak_pixel)
strong = np.int32(self.strong_pixel)
strong_i, strong_j = np.where(img >= highThreshold)
zeros_i, zeros_j = np.where(img < lowThreshold)
weak_i, weak_j = np.where((img <= highThreshold) & (img >= lowThreshold))
res[strong_i, strong_j] = strong
res[weak_i, weak_j] = weak
return (res)
def hysteresis(self, img):
M, N = img.shape
weak = self.weak_pixel
strong = self.strong_pixel
for i in range(1, M-1):
for j in range(1, N-1):
if (img[i,j] == weak):
try:
if ((img[i+1, j-1] == strong) or (img[i+1, j] == strong) or (img[i+1, j+1] == strong)
or (img[i, j-1] == strong) or (img[i, j+1] == strong)
or (img[i-1, j-1] == strong) or (img[i-1, j] == strong) or (img[i-1, j+1] == strong)):
img[i, j] = strong
else:
img[i, j] = 0
except IndexError as e:
pass
return img
def detect(self):
imgs_final = []
for i, img in enumerate(self.imgs):
self.img_smoothed = convolve(img, self.gaussian_kernel(self.kernel_size, self.sigma))
self.gradientMat, self.thetaMat = self.sobel_filters(self.img_smoothed)
self.nonMaxImg = self.non_max_suppression(self.gradientMat, self.thetaMat)
self.thresholdImg = self.threshold(self.nonMaxImg)
img_final = self.hysteresis(self.thresholdImg)
self.imgs_final.append(img_final)
return self.imgs_final
imgs = load_data(dir_name='faces_imgs')
visualize(imgs, 'gray')
detector = cannyEdgeDetector(imgs, sigma=1, kernel_size=5, lowthreshold=0.09, highthreshold=0.17, weak_pixel=100)
imgs_final = detector.detect()
visualize(imgs_final, 'gray')

效果还不错