目录
0 程序环境与所学函数
本章程序运行需要导入下面三个库,并定义了一个显示图像的函数
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
?
def show(img):
? ? if img.ndim == 2:
? ? ? ? plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
? ? else:
? ? ? ? plt.imshow(cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
? ? plt.show()
所学函数
Premitt、Roberts算子
cv.filter2D(img, -1, kernel)Sobel、Scharr算子
cv.Sobel(img, cv.CV_16S, 1, 0, ksize=3) cv.Scharr(img, cv.CV_64F, 0, 1, ksize=3)Laplacian、LoG算子
cv.Laplacian(img, cv.CV_16S)Canny边缘检测
cv.Canny(img, 20, 200)
1 Prewitt、Robert 算子
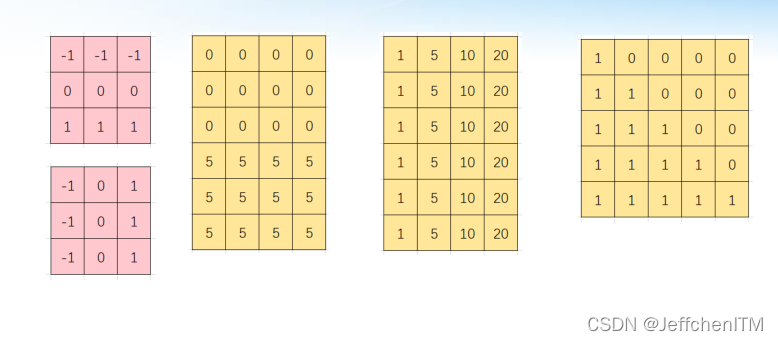
Prewitt原理:红色矩阵代表两个不同方向的算子(水平方向与竖直方向)
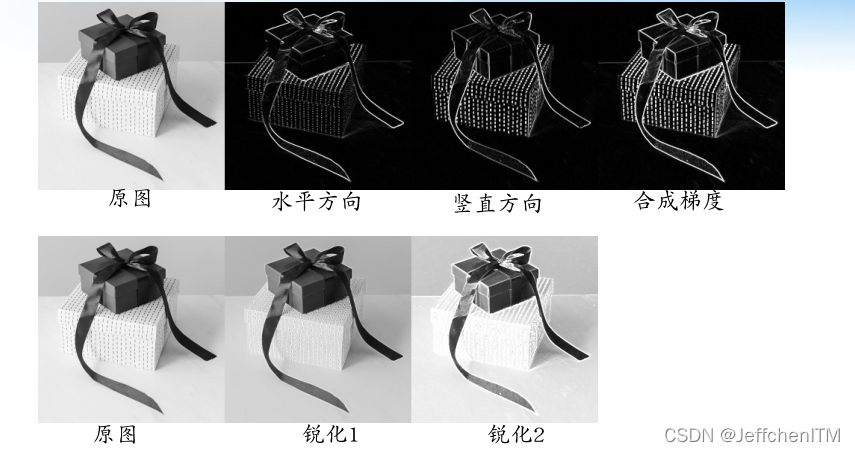
效果
?编程实现
# Prewitt算子
img = cv.imread('pic/gift500x500.jpg', 0)
kx = np.array([[1, 1, 1], [0, 0, 0], [-1, -1, -1]], dtype=np.float32)
ky = np.array([[-1,0, 1], [-1,0, 1], [-1, 0, 1]], dtype=np.float32)
imgx = cv.filter2D(img, cv.CV_16S, kx) #CV_16S是数据类型
imgy = cv.filter2D(img, cv.CV_16S, ky)
absX = cv.convertScaleAbs(imgx)
absY = cv.convertScaleAbs(imgy)
img_prewitt = cv.add(absX, absY) # np.uint8
show(img_prewitt)显示
# 锐化
img_pre_sharp1 = cv.addWeighted(img, 0.9, img_prewitt, 0.2, 0)
img_pre_sharp2 = cv.add(img, img_prewitt)
cv.imwrite('pic/gift_sharp.jpg', np.hstack([img, img_pre_sharp1, img_pre_sharp2]))?Roberts算子原理
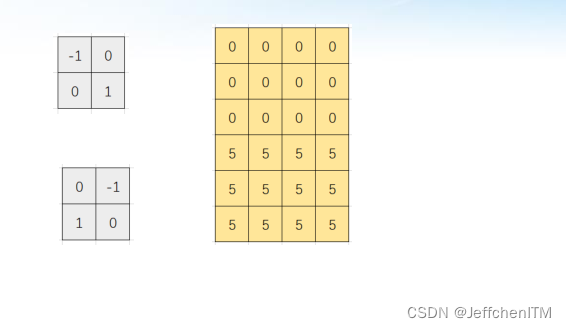
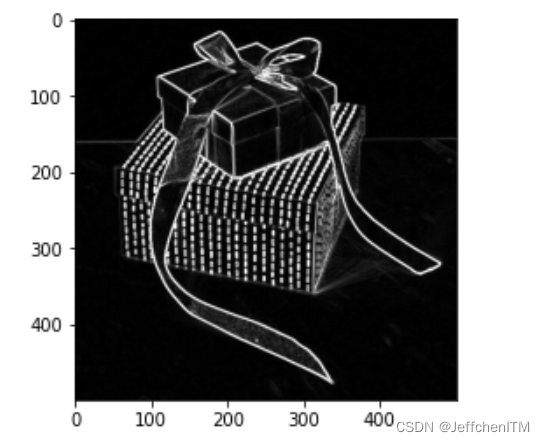
?效果

?程序实现
# Roberts算子
img = cv.imread('pic/gift500x500.jpg', 0)
kx = np.array([[-1, 0], [0, 1]], dtype=np.float32)
ky = np.array([[0, -1], [1, 0]], dtype=np.float32)
imgx = np.abs(cv.filter2D(img, cv.CV_16S, kx))
imgy = np.abs(cv.filter2D(img, cv.CV_16S, ky))
img_robert = cv.convertScaleAbs(np.abs(imgx) + np.abs(imgy)) # np.uint8
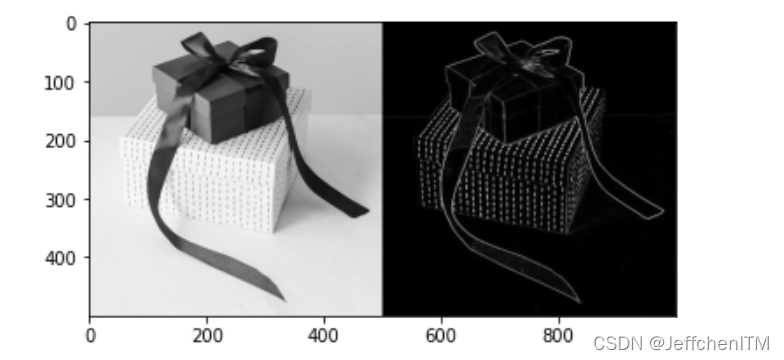
show(np.hstack([img, img_robert])) 显示
?2 sobel 、scharr算子
原理
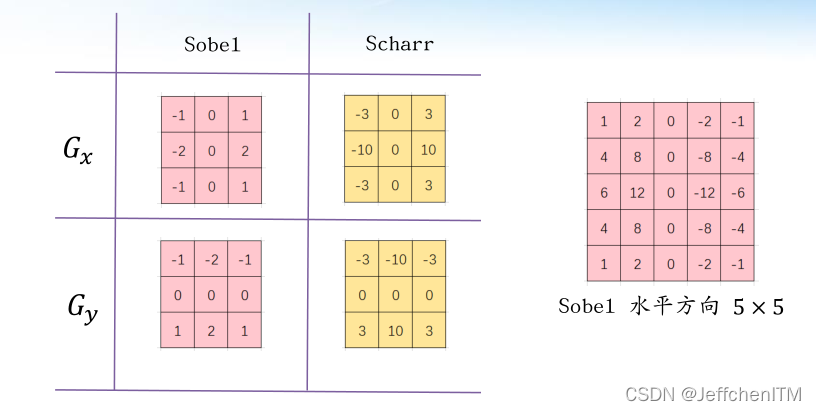
?sobel算子编程实现
#sobel算子
img = cv.imread('pic/bookshelf500x333.jpg', 0)
show(img)
grad_x = cv.Sobel(img, cv.CV_16S, 1, 0, ksize=3)#1表示dx工作0表示dy不工作
grad_y = cv.Sobel(img, cv.CV_16S, 0, 1, ksize=3)
grad_xabs = np.abs(grad_x)
grad_yabs = np.abs(grad_y)
grad_xy = grad_xabs + grad_yabs
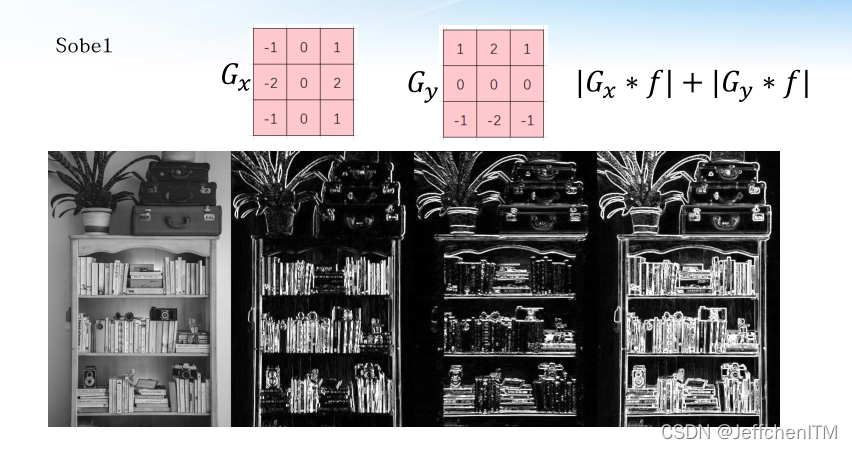
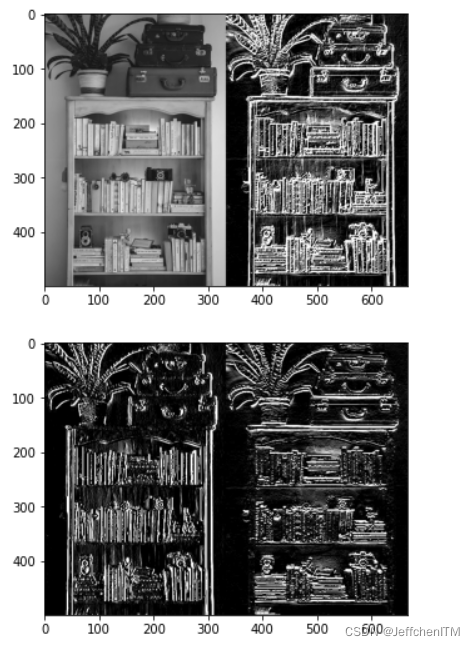
show(np.hstack([img, grad_xabs, grad_yabs, grad_xy]))
显示
??Scharr算子编程实现
img = cv.imread('pic/bookshelf500x333.jpg', 0)
grad_x = np.abs(cv.Scharr(img, -1, 1, 0))
grad_y = np.abs(cv.Scharr(img, -1, 0, 1))
img_grad = cv.add(grad_x, abs(grad_y))
show(np.hstack([img, img_grad]))
show(np.hstack([grad_x, grad_y]))显示

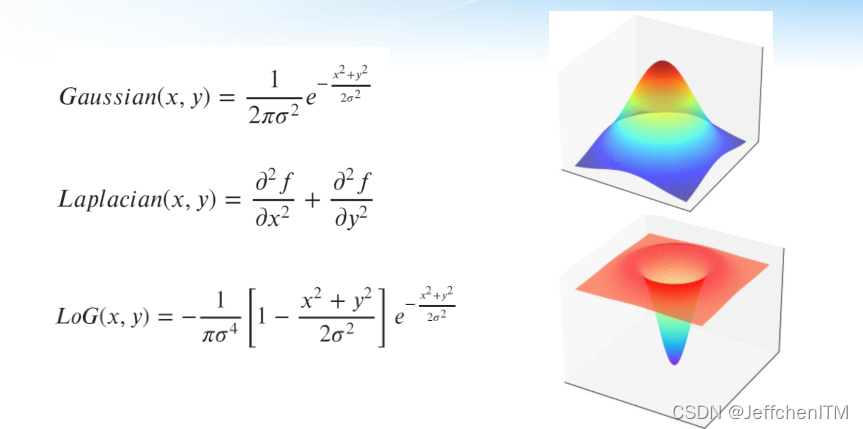
3 Laplacian 、 LoG算子
原理:
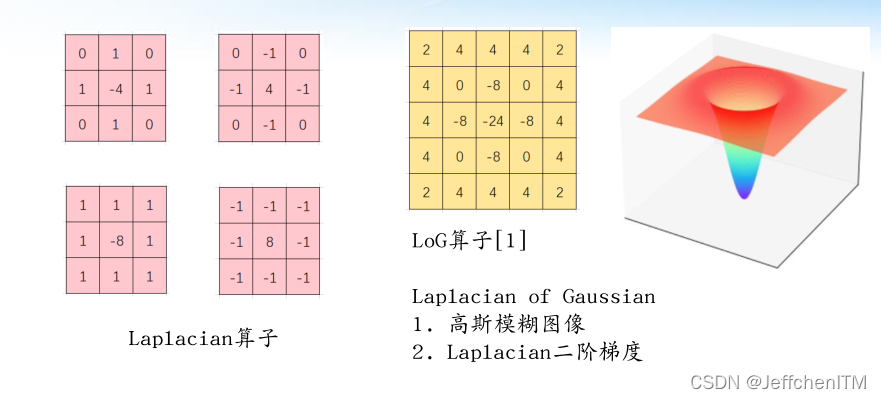
?
?效果
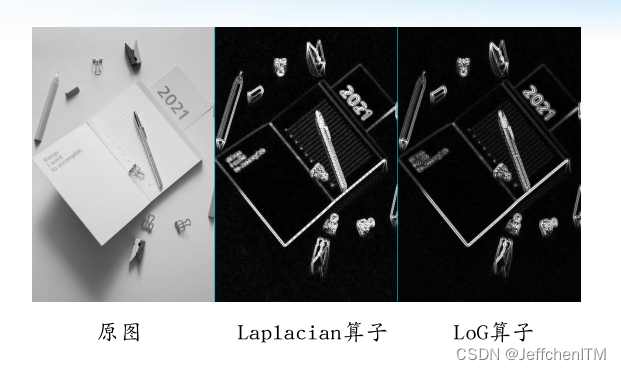
?Laplacian算子编程实现
img = cv.imread('pic/notebook500x333.jpg', 0)
img_lap = cv.Laplacian(img, cv.CV_16S, ksize=5, scale=0.2)
img_lap2 = np.abs(img_lap).clip(0, 255)
show(np.hstack([img, img_lap2]))显示
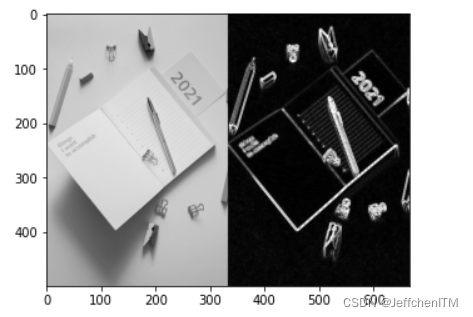
?LoG算子编程实现
img = cv.imread('pic/notebook500x333.jpg', 0)
img_g = cv.GaussianBlur(img, (3,3), 0)
img_log = cv.Laplacian(img_g, cv.CV_16S, ksize=5, scale=0.2)
img_log2 = np.abs(img_log).clip(0, 255)
show(np.hstack([img, img_log2]))显示
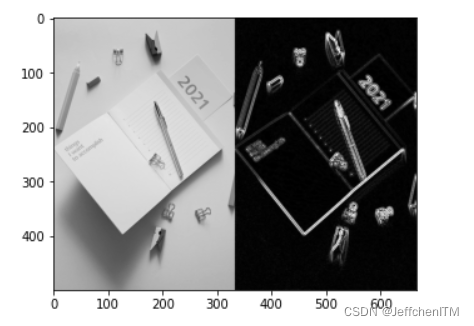
?4 Canny边缘检测
原理:

?效果

?编程实现
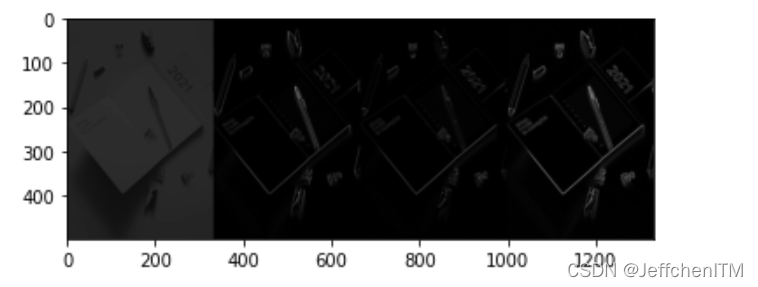
img = cv.imread('pic/notebook500x333.jpg', 0)
img_canny = cv.Canny(img, 20, 200) #小于20设为0大于200设为255
show(np.hstack([img, img_canny]))显示
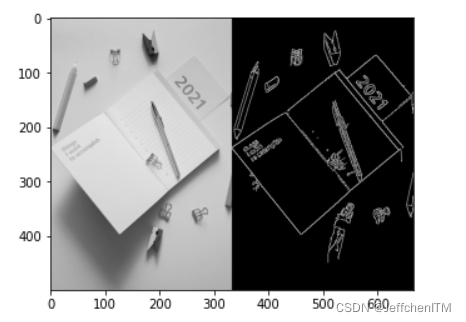
5 Canny边缘检测底层代码实现
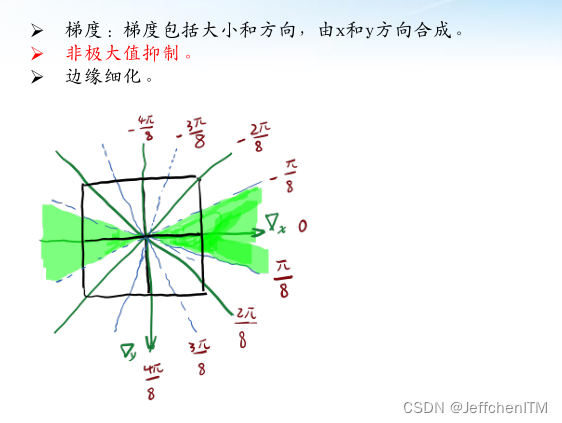
原理
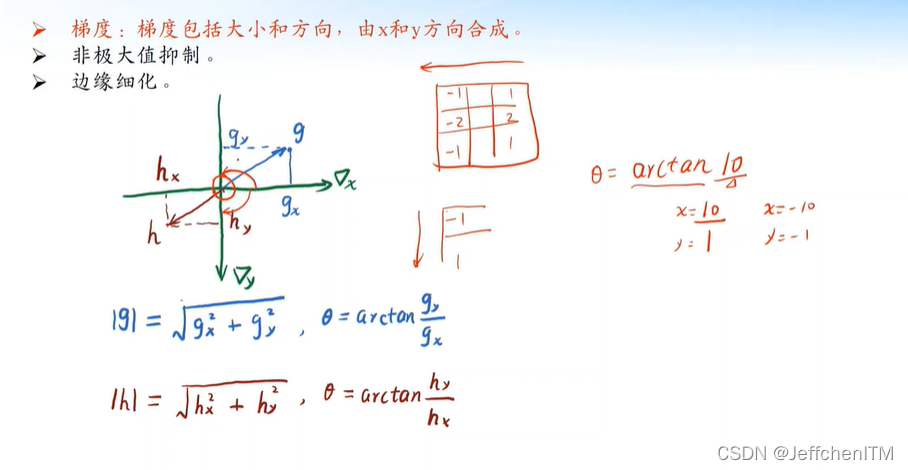
?
?代码实现
img = cv.imread('pic/notebook500x333.jpg', 0)
# 1. 平滑
img_blur = cv.GaussianBlur(img, (5,5), 2)
# 2. 计算梯度
gradx = cv.Sobel(img_blur, cv.CV_64F, 1, 0)
grady = cv.Sobel(img_blur, cv.CV_64F, 0, 1)
R = np.abs(gradx) + np.abs(grady)
T = np.arctan(grady / (gradx + 1e-3))
# 3. 细化边缘
h, w = R.shape
img_thin = np.zeros_like(R)
for i in range(1, h-1):
for j in range(1, w-1):
theta = T[i,j]
if -np.pi / 8 <= theta < np.pi / 8:
if R[i,j] == max([R[i,j], R[i,j-1], R[i, j+1]]):
img_thin[i,j] = R[i,j]
elif -3 * np.pi / 8 <= theta < -np.pi / 8:
if R[i,j] == max([R[i,j], R[i-1,j+1], R[i+1,j-1]]):
img_thin[i,j] = R[i,j]
elif np.pi / 8 <= theta < 3 * np.pi / 8:
if R[i,j] == max([R[i,j], R[i-1,j-1], R[i+1,j+1]]):
img_thin[i,j] = R[i,j]
else:
if R[i,j] == max([R[i,j], R[i-1,j], R[i+1,j]]):
img_thin[i,j] = R[i,j]
show(img_thin)
th1 = 20
th2 = 200
h, w = img_thin.shape
img_edge = np.zeros_like(img_thin, dtype=np.uint8)
for i in range(1, h-1):
for j in range(1, w-1):
if img_thin[i,j] >= th2:
img_edge[i,j] = img_thin[i,j]
elif img_thin[i,j] > th1:
around = img_thin[i-1:i+2, j-1:j+2]
if around.max() >= th2:
img_edge[i,j] = img_thin[i,j]
show(img_edge)?
?