一、彩色图像文件转换为灰度文件
(一)使用opencv
1.通过cvtColor库将其转为灰度
(1)代码
import cv2 as cv
img = cv.imread('C:/Users/86199/Pictures/lena/lena.jpg',1)
img_1 = cv.cvtColor(img,cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv.imshow('gray',img_1)
cv.imshow('colour',img)
cv.waitKey(0)
(2)结果
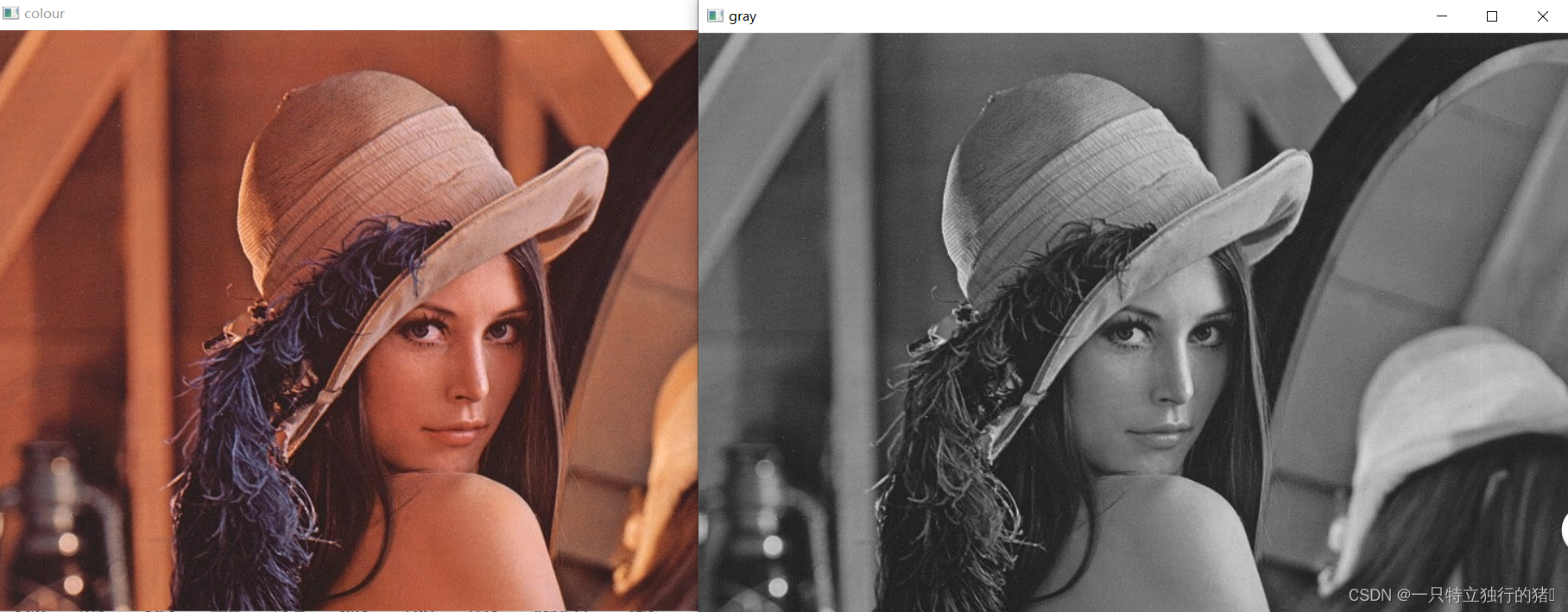

2通过分离RGB三个通道得到三个通道的灰度图
(1)代码
import cv2 as cv
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv.imread('C:/Users/86199/Pictures/lena/lena.jpg',1)
#cv2.imread读取图片格式是BGR
b,g,r = cv.split(img) #这个地方将图像拆分,把彩色图像分为3个颜色
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))
color = [b,g,r]
img_2 = cv.merge([r,g,b]) #这个地方我把bgr格式的图片转成了rgb,然后显示的时候会变成正常的彩色
for i in range(3):
plt.subplot(2,2,i+1)
plt.imshow(color[i],'gray')
plt.subplot(2,2,4)
plt.imshow(img_2)
plt.savefig('./三通道灰度.png')
plt.show()
(2)运行结果
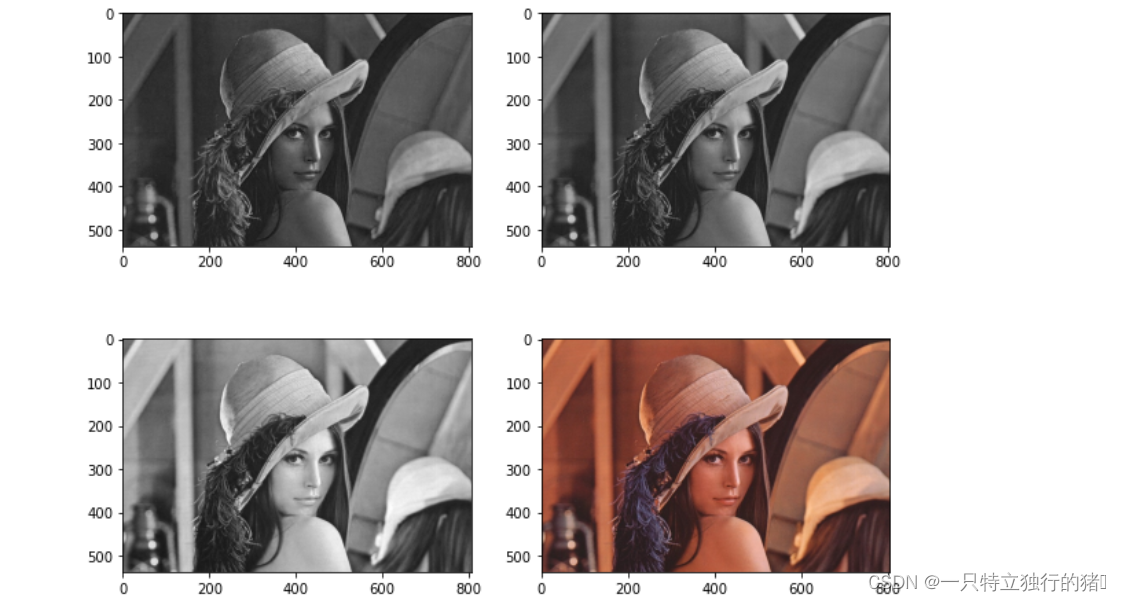

(二)不使用opencv
1.代码
from PIL import Image
I = Image.open('C:/Users/86199/Pictures/lena/lena.jpg')
L = I.convert('L')
L.show()
2.运行结果
二、将彩色图像转化为HSV、HSI 格式
(一)彩色图像转化为HSV格式
1.HSV介绍
HSV 格式: H 代表色彩,S 代表颜色的深浅,V 代表着颜色的明暗程度。
HSV 颜色空间可以很好地把颜色信息和亮度信息分开,将它们放在不同的通道中,减小了光线对于特定颜色识别的影响。
HSV (色相hue, 饱和度saturation, 明度value), 也称HSB
(B指brightness) 是艺术家们常用的,因为与加法减法混色的术语相比,使用色相,饱和度等概念描述色彩更自然直观。HSV
是RGB色彩空间的一种变形,它的内容与色彩尺度与其出处——RGB色彩空间有密切联系。对应的媒介是人眼。
在 OpenCV 视觉库中,HSV 的数值被做了一些小的修改, H 的范围调整为 0~180,S 和 V 的范围为 0~255。

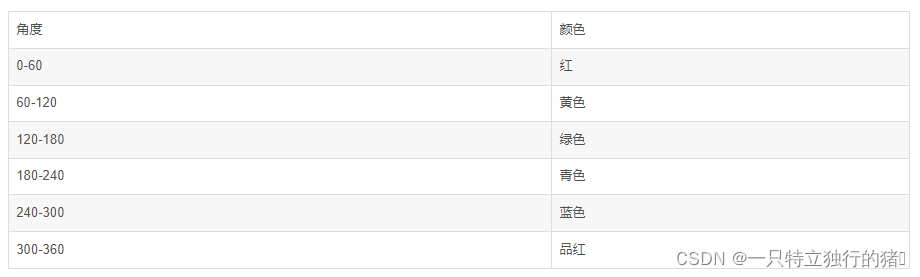
当我们采用 HSV 的图像阈值得到某一种颜色时,可以参考颜色分布表,先将 H 通道对应的颜色找到。表格中,每种颜色都对应了一个区间。
2.代码
# open-cv library is installed as cv2 in python
# import cv2 library into this program
import cv2 as cv
# read an image using imread() function of cv2
# we have to pass only the path of the image
img = cv.imread('C:/Users/86199/Pictures/lena/lena.jpg',1)
# displaying the image using imshow() function of cv2
# In this : 1st argument is name of the frame
# 2nd argument is the image matrix
cv.imshow('original image',img)
# converting the colourfull image into HSV format image
# using cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV argument of
# the cvtColor() function of cv2
# in this :
# ist argument is the image matrix
# 2nd argument is the attribute
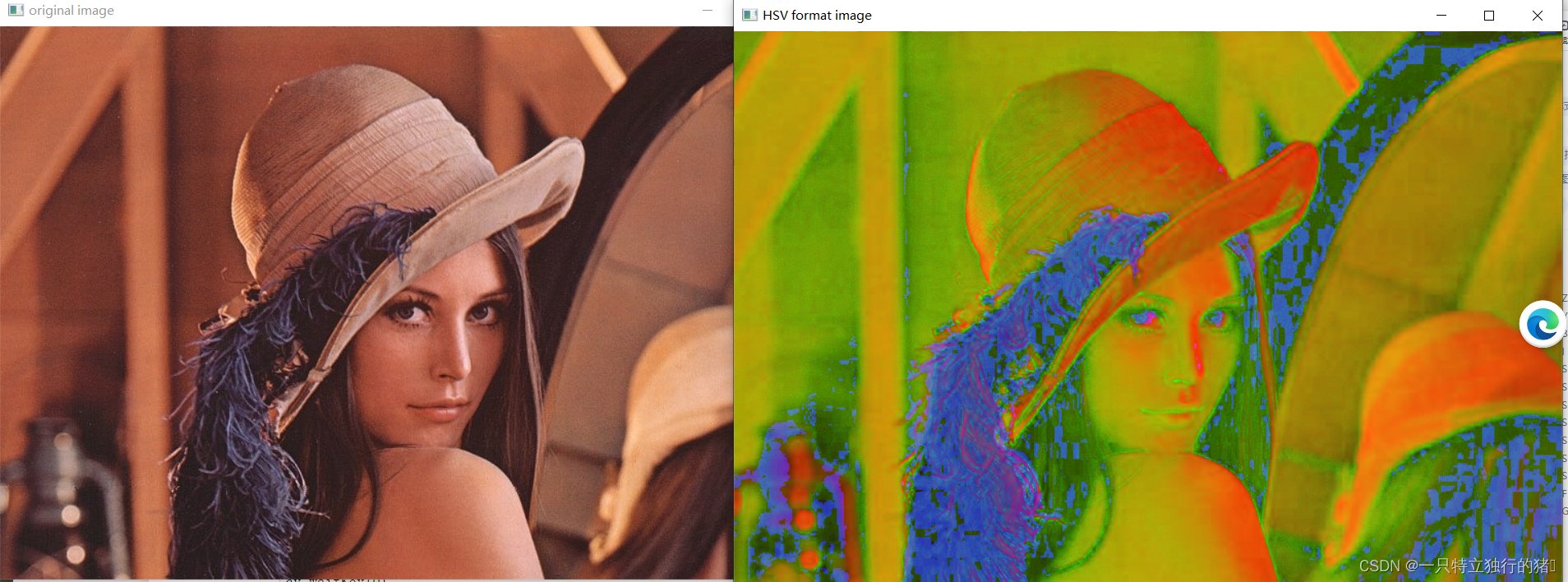
hsv = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
# displaying the Hsv format image
cv.imshow('HSV format image',hsv)
cv.waitKey(0)
3.运行结果
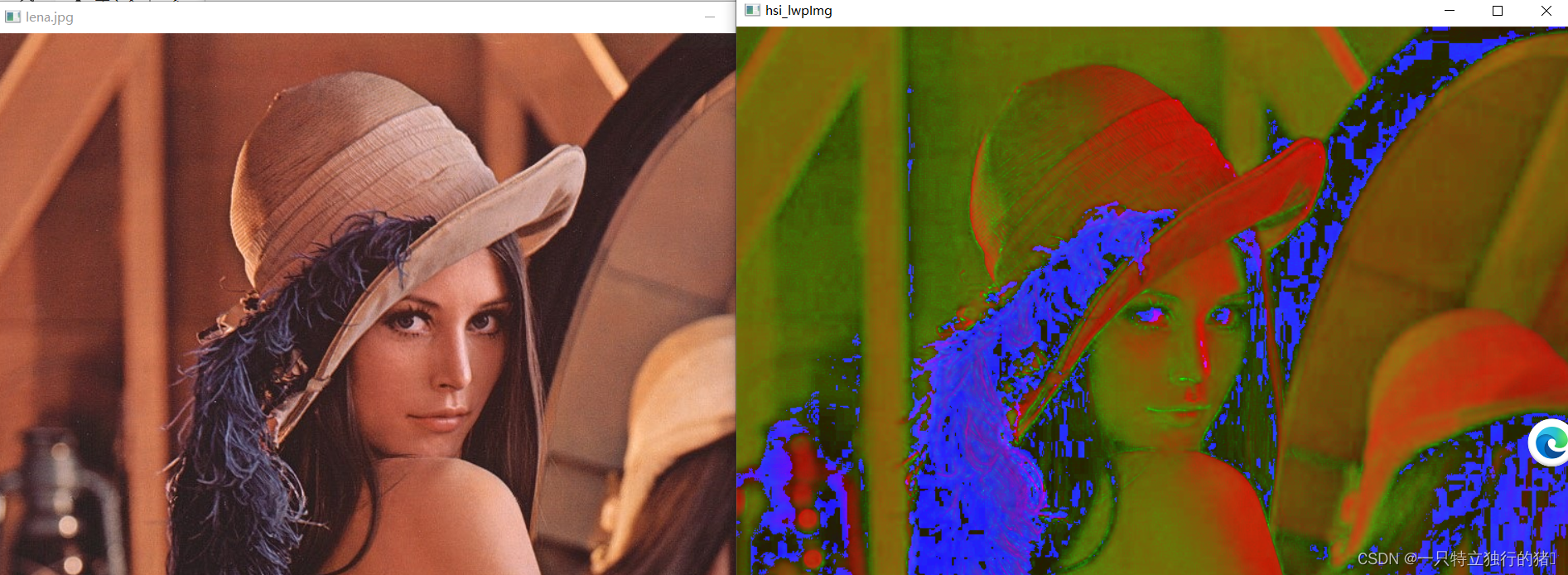
(二)彩色图像转化为HSI格式
1.HSI介绍
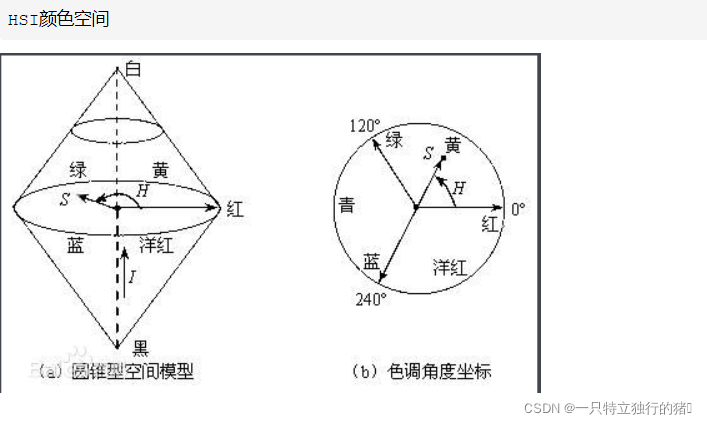
HSL (色相hue, 饱和度saturation, 亮度lightness/luminance),
也称HLS 或 HSI (I指intensity)
与 HSV非常相似,仅用亮度(lightness)替代了明度(brightness)。
人的视觉对亮度的敏感程度远强于对颜色浓淡的敏感程度,为了便于颜色处理和识别,人的市局系统经常采用HSI彩色空间,它比RGB空间更符合人的视觉特性。此外,由于HSI空间中亮度和色度具有可分离性,使得图像处理和机器视觉中大量灰度处理算法都可在HSI空间方便进行
2.代码
import cv2
import numpy as np
def rgbtohsi(rgb_lwpImg):
rows = int(rgb_lwpImg.shape[0])
cols = int(rgb_lwpImg.shape[1])
b, g, r = cv2.split(rgb_lwpImg)
# 归一化到[0,1]
b = b / 255.0
g = g / 255.0
r = r / 255.0
hsi_lwpImg = rgb_lwpImg.copy()
H, S, I = cv2.split(hsi_lwpImg)
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
num = 0.5 * ((r[i, j]-g[i, j])+(r[i, j]-b[i, j]))
den = np.sqrt((r[i, j]-g[i, j])**2+(r[i, j]-b[i, j])*(g[i, j]-b[i, j]))
theta = float(np.arccos(num/den))
if den == 0:
H = 0
elif b[i, j] <= g[i, j]:
H = theta
else:
H = 2*3.14169265 - theta
min_RGB = min(min(b[i, j], g[i, j]), r[i, j])
sum = b[i, j]+g[i, j]+r[i, j]
if sum == 0:
S = 0
else:
S = 1 - 3*min_RGB/sum
H = H/(2*3.14159265)
I = sum/3.0
# 输出HSI图像,扩充到255以方便显示,一般H分量在[0,2pi]之间,S和I在[0,1]之间
hsi_lwpImg[i, j, 0] = H*255
hsi_lwpImg[i, j, 1] = S*255
hsi_lwpImg[i, j, 2] = I*255
return hsi_lwpImg
if __name__ == '__main__':
rgb_lwpImg = cv2.imread("C:/Users/86199/Pictures/lena/lena.jpg")
hsi_lwpImg = rgbtohsi(rgb_lwpImg)
cv2.imshow('lena.jpg', rgb_lwpImg)
cv2.imshow('hsi_lwpImg', hsi_lwpImg)
key = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xFF
if key == ord('q'):
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
3.运行结果
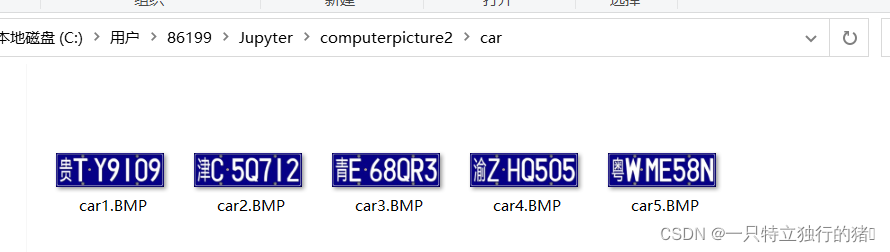
三、将车牌数字分割为单个的字符图片
车牌信息如下
1.分割字符步骤
- (1)灰度转换:将彩色图片转换为灰度图像,常见的R=G=B=像素平均值。
- (2)高斯平滑和中值滤波:去除噪声。
- (3)Sobel算子:提取图像边缘轮廓,X方向和Y方向平方和开跟。
- (4)二值化处理:图像转换为黑白两色,通常像素大于127设置为255,小于设置为0。
- (5)膨胀和细化:放大图像轮廓,转换为一个个区域,这些区域内包含车牌。
- (6)通过算法选择合适的车牌位置,通常将较小的区域过滤掉或寻找蓝色底的区域。
- (7)标注车牌位置
- (8)图像切割和识别
2.代码
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
def stackImages(scale, imgArray):
"""
将多张图像压入同一个窗口显示
:param scale:float类型,输出图像显示百分比,控制缩放比例,0.5=图像分辨率缩小一半
:param imgArray:元组嵌套列表,需要排列的图像矩阵
:return:输出图像
"""
rows = len(imgArray)
cols = len(imgArray[0])
rowsAvailable = isinstance(imgArray[0], list)
# 用空图片补齐
for i in range(rows):
tmp = cols - len(imgArray[i])
for j in range(tmp):
img = np.zeros((imgArray[0][0].shape[0], imgArray[0][0].shape[1]), dtype='uint8')
imgArray[i].append(img)
# 判断维数
if rows>=2:
width = imgArray[0][0].shape[1]
height = imgArray[0][0].shape[0]
else:
width = imgArray[0].shape[1]
height = imgArray[0].shape[0]
if rowsAvailable:
for x in range(0, rows):
for y in range(0, cols):
if imgArray[x][y].shape[:2] == imgArray[0][0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x][y] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x][y], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x][y] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x][y], (imgArray[0][0].shape[1], imgArray[0][0].shape[0]),
None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x][y].shape) == 2:
imgArray[x][y] = cv2.cvtColor(imgArray[x][y], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
imageBlank = np.zeros((height, width, 3), np.uint8)
hor = [imageBlank] * rows
hor_con = [imageBlank] * rows
for x in range(0, rows):
hor[x] = np.hstack(imgArray[x])
ver = np.vstack(hor)
else:
for x in range(0, rows):
if imgArray[x].shape[:2] == imgArray[0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (imgArray[0].shape[1], imgArray[0].shape[0]), None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x].shape) == 2: imgArray[x] = cv2.cvtColor(imgArray[x], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
hor = np.hstack(imgArray)
ver = hor
return ver
# 分割结果输出路径
output_dir = "./output"
# 车牌路径
file_path="./car/"
# 读取所有车牌
cars = os.listdir(file_path)
cars.sort()
# 循环操作每一张车牌
for car in cars:
# 读取图片
print("正在处理"+file_path+car)
src = cv2.imread(file_path+car)
img = src.copy()
# 预处理去除螺丝点
cv2.circle(img, (145, 20), 10, (255, 0, 0), thickness=-1)
cv2.circle(img, (430, 20), 10, (255, 0, 0), thickness=-1)
cv2.circle(img, (145, 170), 10, (255, 0, 0), thickness=-1)
cv2.circle(img, (430, 170), 10, (255, 0, 0), thickness=-1)
cv2.circle(img, (180, 90), 10, (255, 0, 0), thickness=-1)
# 转灰度
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 二值化
adaptive_thresh = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(gray, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV, 333, 1)
# 闭运算
kernel = np.ones((5, 5), int)
morphologyEx = cv2.morphologyEx(adaptive_thresh, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
# 找边界
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(morphologyEx, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# 画边界
img_1 = img.copy()
cv2.drawContours(img_1, contours, -1, (0, 0, 0), -1)
imgStack = stackImages(0.7, ([src, img, gray], [adaptive_thresh, morphologyEx, img_1]))
cv2.imshow("imgStack", imgStack)
cv2.waitKey(0)
# 转灰度为了方便切割
gray_1 = cv2.cvtColor(img_1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 每一列的白色数量
white = []
# 每一列的黑色数量
black = []
# 区域高度取决于图片高
height = gray_1.shape[0]
# 区域宽度取决于图片宽
width = gray_1.shape[1]
# 最大白色数量
white_max = 0
# 最大黑色数量
black_max = 0
# 计算每一列的黑白色像素总和
for i in range(width):
s = 0 # 这一列白色总数
t = 0 # 这一列黑色总数
for j in range(height):
if gray_1[j][i] == 255:
s += 1
if gray_1[j][i] == 0:
t += 1
white_max = max(white_max, s)
black_max = max(black_max, t)
white.append(s)
black.append(t)
# 找到右边界
def find_end(start):
end = start + 1
for m in range(start + 1, width - 1):
# 基本全黑的列视为边界
if black[m] >= black_max * 0.95: # 0.95这个参数请多调整,对应下面的0.05
end = m
break
return end
# 临时变量
n = 1
# 起始位置
start = 1
# 结束位置
end = 2
# 分割结果数量
num=0
# 分割结果
res = []
# 保存分割结果路径,以图片名命名
output_path= output_dir + car.split('.')[0]
if not os.path.exists(output_path):
os.makedirs(output_path)
# 从左边网右边遍历
while n < width - 2:
n += 1
# 找到白色即为确定起始地址
# 不可以直接 white[n] > white_max
if white[n] > 0.05 * white_max:
start = n
# 找到结束坐标
end = find_end(start)
# 下一个的起始地址
n = end
# 确保找到的是符合要求的,过小不是车牌号
if end - start > 10:
# 分割
char = gray_1[1:height, start - 5:end + 5]
# 保存分割结果到文件
cv2.imwrite(output_path+'/' + str(num) + '.jpg',char)
num+=1
# 重新绘制大小
char = cv2.resize(char, (300, 300), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
# 添加到结果集合
res.append(char)
# cv2.imshow("imgStack", char)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# 构造结果元祖方便结果展示
res2 = (res[:2], res[2:4], res[4:6], res[6:])
# 显示结果
imgStack = stackImages(0.5, res2)
cv2.imshow("imgStack", imgStack)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
3.运行结果


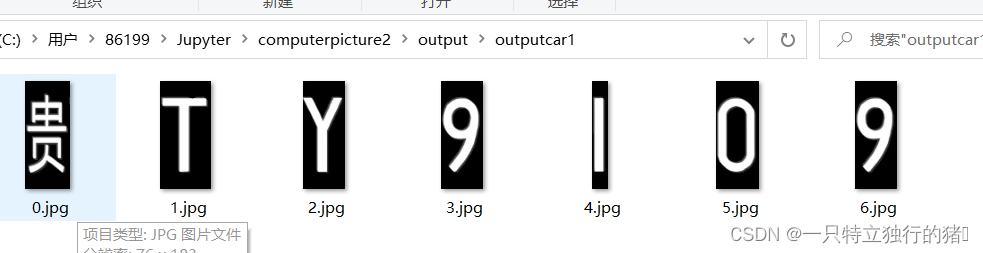

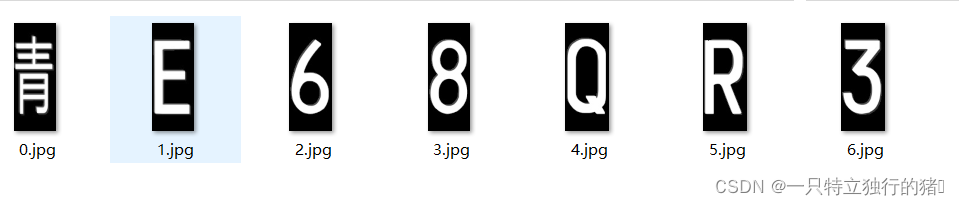


四、总结
本次实验了了解了图片转灰度图像的原理,HSI和HSV格式的组成, HSI 与 HSV非常相似,不同的是仅用HSI用亮度替代了明度。了解了分割车牌字符步骤,以及实现过程。