cifarc10图像下载地址:CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets
参考链接:HOG + SVM 进行图片分类(python)_程序员的点滴-CSDN博客_svm图片二分类python
cifar转图像操作
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
def unpickle(file):
import _pickle as cPickle
with open(file, 'rb') as f:
dict = cPickle.load(f, encoding='iso-8859-1')
return dict
def main(cifar10_data_dir):
train_txt=[]
test_txt=[]
for i in range(1, 2):
train_data_file = os.path.join(cifar10_data_dir, 'data_batch_' + str(i))
print(train_data_file)
data = unpickle(train_data_file)
print('unpickle done', data)
for j in range(10000):
img = np.reshape(data['data'][j], (3, 32, 32))
img = img.transpose(1, 2, 0)
img_name = 'train/' + str(data['labels'][j]) + '_' + str(j + (i - 1) * 10000) + '.jpg'
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(cifar10_data_dir, img_name), img)
train_txt.append(str(data['labels'][j]) + '_' + str(j + (i - 1) * 10000) + '.jpg' + ' ' + str(data['labels'][j]))
np.savetxt(r"./train.txt", np.reshape(train_txt, -1), delimiter=',', fmt='%5s')
test_data_file = os.path.join(cifar10_data_dir, 'test_batch')
data = unpickle(test_data_file)
for i in range(10000):
img = np.reshape(data['data'][i], (3, 32, 32))
img = img.transpose(1, 2, 0)
img_name = 'test/' + str(data['labels'][i]) + '_' + str(i) + '.jpg'
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(cifar10_data_dir, img_name), img)
test_txt.append(str(data['labels'][i]) + '_' + str(i) + '.jpg' + ' ' + str(data['labels'][i]))
np.savetxt(r"./test.txt", np.reshape(test_txt, -1), delimiter=',', fmt='%5s')
if __name__ == "__main__":
main('cifar-10-batches-py')如果遇到这个问题:
python 3以上版本使用pickle.load读取文件报UnicodeDecodeError: 'ascii' codec can't decode byte 0x8b in position 6
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
import glob
import platform
import time
from PIL import Image
from skimage.feature import hog
import numpy as np
import os
import joblib
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
import shutil
import sys
# 第一个是你的类别 第二个是类别对应的名称 输出结果的时候方便查看
label_map = {0: 'airplane',
1: 'automobile',
2: 'bird',
3: 'cat',
4: 'deer',
5: 'dog',
6: 'frog',
7: 'horse',
8: 'ship',
9: 'truck,'
}
# 训练集图片的位置
train_image_path = './database/train'
# 测试集图片的位置
test_image_path = './database/test'
# 训练集标签的位置
train_label_path = os.path.join('./labels', 'train.txt')
# 测试集标签的位置
test_label_path = os.path.join('./labels', 'test.txt')
image_height = 32
image_width = 32
train_feat_path = './feature/train/'
test_feat_path = './feature/test/'
model_path = 'model/'
# 获得图片列表
def get_image_list(filePath, nameList):
print('read image from ', filePath)
img_list = []
for name in nameList:
temp = Image.open(os.path.join(filePath, name))
img_list.append(temp.copy())
temp.close()
return img_list
# 提取特征并保存
def get_feat(image_list, name_list, label_list, savePath):
i = 0
for image in image_list:
try:
# 如果是灰度图片 把3改为-1
image = np.reshape(image, (image_height, image_width, -1))
except:
print('发送了异常,图片大小size不满足要求:', name_list[i])
continue
#gray = rgb2gray(image) / 255.0
# 如果直接就是灰度图
gray = image
# 这句话根据你的尺寸改改
fd = hog(gray, orientations=12, block_norm='L1', pixels_per_cell=[8, 8], cells_per_block=[4, 4], visualize=False,
transform_sqrt=True)
fd = np.concatenate((fd, [label_list[i]]))
fd_name = name_list[i] + '.feat'
fd_path = os.path.join(savePath, fd_name)
joblib.dump(fd, fd_path)
i += 1
print("Test features are extracted and saved.")
# 变成灰度图片
def rgb2gray(im):
gray = im[:, :, 0] * 0.2989 + im[:, :, 1] * 0.5870 + im[:, :, 2] * 0.1140
return gray
# 获得图片名称与对应的类别
def get_name_label(file_path):
print("read label from ", file_path)
name_list = []
label_list = []
with open(file_path) as f:
for line in f.readlines():
#一般是name label 三部分,所以至少长度为3 所以可以通过这个忽略空白行
if len(line) >= 3:
name_list.append(line.split(' ')[0])
label_list.append(line.split(' ')[1].replace('\n','').replace('\r',''))
if not str(label_list[-1]).isdigit():
print("label必须为数字,得到的是:",label_list[-1], "程序终止,请检查文件")
exit(1)
return name_list, label_list
# 提取特征
def extra_feat():
train_name, train_label = get_name_label(train_label_path)
test_name, test_label = get_name_label(test_label_path)
train_image = get_image_list(train_image_path, train_name)
test_image = get_image_list(test_image_path, test_name)
get_feat(train_image, train_name, train_label, train_feat_path)
get_feat(test_image, test_name, test_label, test_feat_path)
# 创建存放特征的文件夹
def mkdir():
if not os.path.exists(train_feat_path):
os.mkdir(train_feat_path)
if not os.path.exists(test_feat_path):
os.mkdir(test_feat_path)
# 训练和测试
def train_and_test():
t0 = time.time()
features = []
labels = []
correct_number = 0
total = 0
for feat_path in glob.glob(os.path.join(train_feat_path, '*.feat')):
data = joblib.load(feat_path)
features.append(data[:-1])
labels.append(data[-1])
# print("Training a Linear LinearSVM Classifier.")
# clf = LinearSVC()
# clf.fit(features, labels)
# # 下面的代码是保存模型的
# if not os.path.exists(model_path):
# os.makedirs(model_path)
# joblib.dump(clf, model_path + 'model')
# 下面的代码是加载模型 可以注释上面的代码 直接进行加载模型 不进行训练
clf = joblib.load(model_path+'model')
print("训练之后的模型存放在model文件夹中")
# exit()
result_list = []
for feat_path in glob.glob(os.path.join(test_feat_path, '*.feat')):
total += 1
if platform.system() == 'Windows':
symbol = '\\'
else:
symbol = '/'
image_name = feat_path.split(symbol)[1].split('.feat')[0]
data_test = joblib.load(feat_path)
data_test_feat = data_test[:-1].reshape((1, -1)).astype(np.float64)
result = clf.predict(data_test_feat)
print(result)
result_list.append(image_name + ' ' + str(result[0]) + '\n')
if int(result[0]) == int(data_test[-1]):
correct_number += 1
write_to_txt(result_list)
rate = float(correct_number) / total
t1 = time.time()
print('准确率是: %f' % rate)
print('耗时是 : %f' % (t1 - t0))
def write_to_txt(list):
with open('result.txt', 'w') as f:
f.writelines(list)
print('每张图片的识别结果存放在result.txt里面')
if __name__ == '__main__':
mkdir() # 不存在文件夹就创建
# need_input = input('是否手动输入各个信息?y/n\n')
if sys.version_info < (3,):
need_extra_feat = input('是否需要重新获取特征?y/n\n')
else:
need_extra_feat = input('是否需要重新获取特征?y/n\n')
if need_extra_feat == 'y':
shutil.rmtree(train_feat_path)
shutil.rmtree(test_feat_path)
mkdir()
extra_feat()
train_and_test()
cifar10的训练和测试结果,如下:
是否需要重新获取特征?y/n
y
read label from ./labels\train.txt
read label from ./labels\test.txt
read image from ./database/train
read image from ./database/test
Test features are extracted and saved.
Test features are extracted and saved.
Training a Linear LinearSVM Classifier.
训练之后的模型存放在model文件夹中
每张图片的识别结果存放在result.txt里面
准确率是: 0.460400
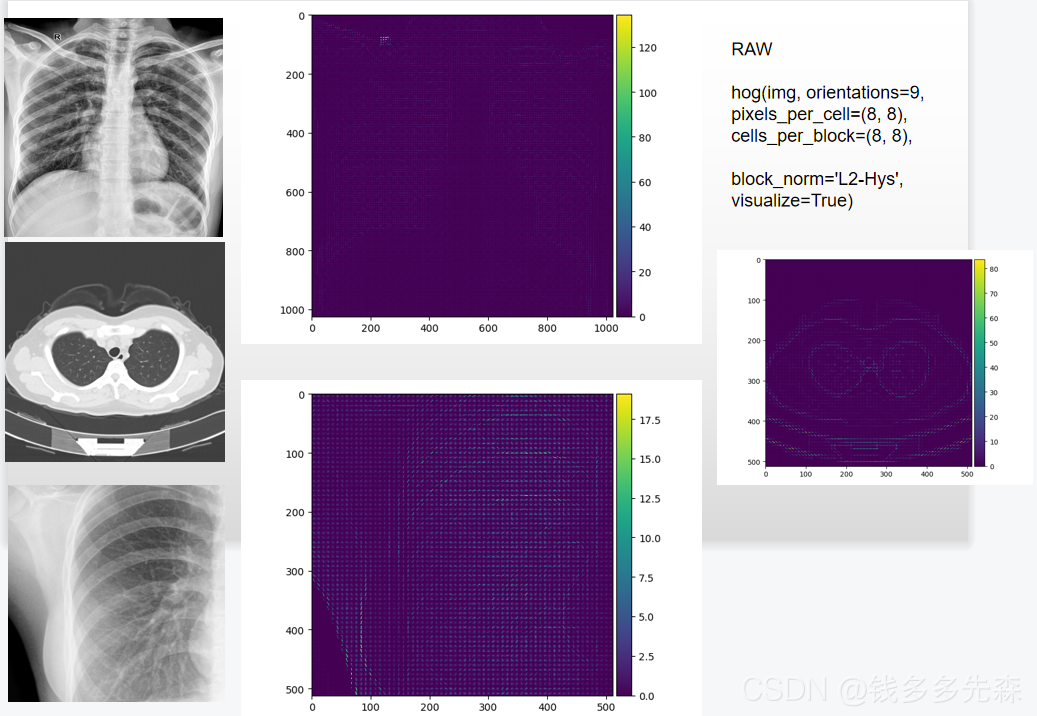
耗时是 : 12.241030from skimage.feature import hog
from skimage import io
from PIL import Image
import cv2
img = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread('./database/train_medical/DRCrop_3.png'), cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
print(img.shape)
normalised_blocks, hog_image = hog(img, orientations=9, pixels_per_cell=(8, 8), cells_per_block=(8, 8),
block_norm='L2-Hys', visualize=True)
io.imshow(hog_image)
io.show()