数据分析篇
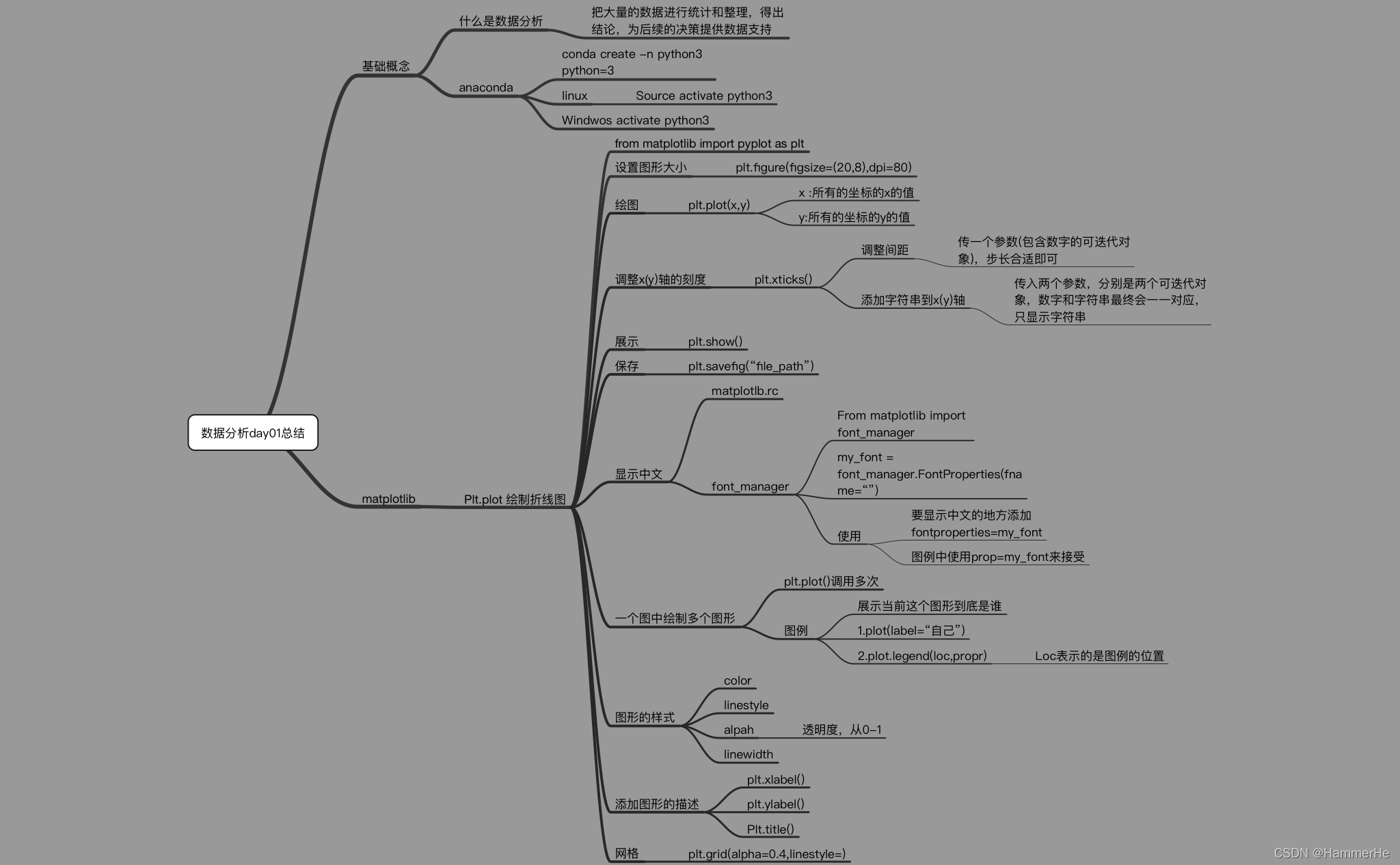
1 数据分析和环境介绍
1.1什么是数据分析
数据分析:是用适当的方法对收集来的大量数据进行分析,帮助人们作出判断,以便采取适当行动
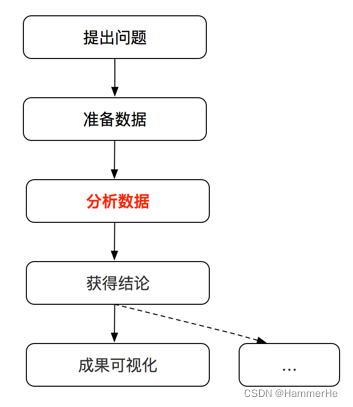
1.2 jupyter notebook
一些简单操作:
cmd-jupyter notebook
new python3文件
2 Matplotlib
2.1 Matplotlib介绍
最流行的Python底层绘图库,主要做数据可视化图表,名字取材于MATLAB,模仿MATLAB构建
2.2 Matplotlib基础操作(折线图为例)
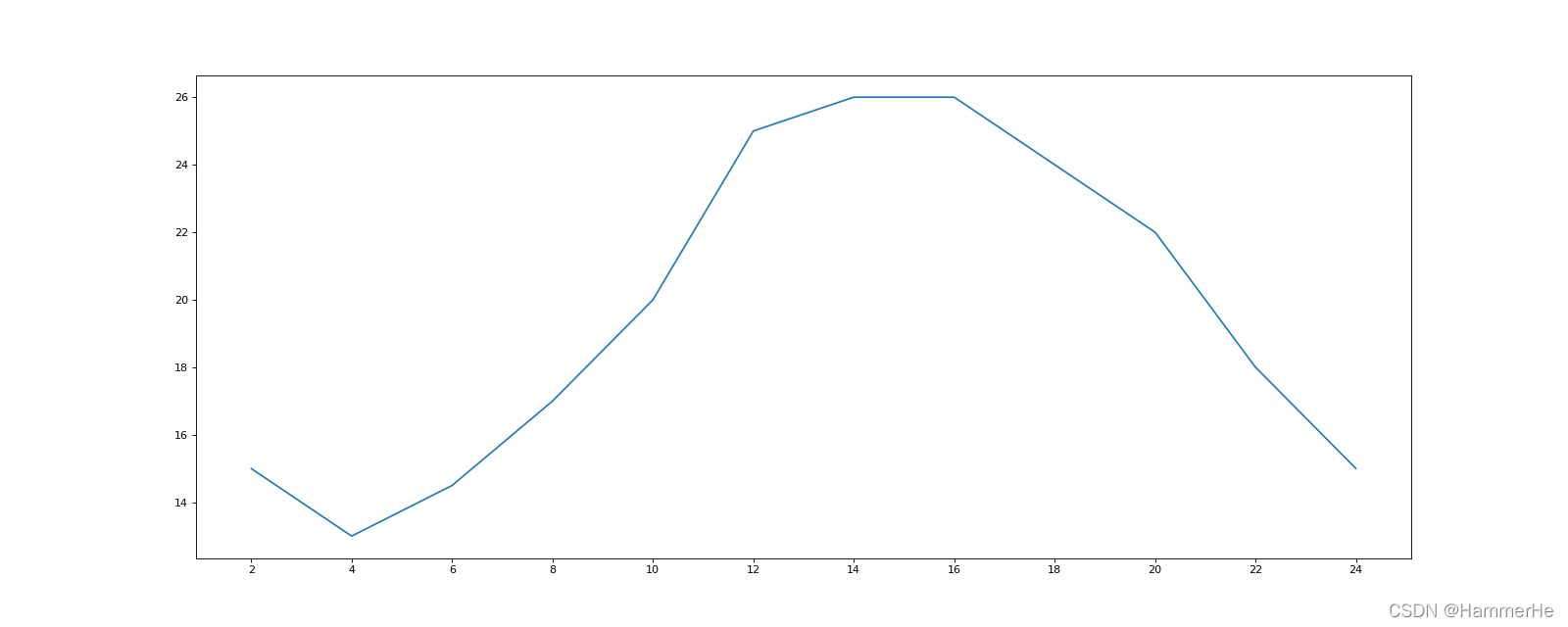
首先绘制简单无信息折线图:
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
x = range(2, 26, 2)
y = [15, 13, 14.5, 17, 20, 25, 26, 26, 24, 22, 18, 15]
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.show()
接下来我们希望实现如下操作:
2.2.1.设置图片大小
figure图形图标的意思,在这里指的就是我们画的图
通过实例化一个 figure并且传递参数,能够在后台自动使用该作figure实例
在图像模糊的时候可以传入dpi(每英寸上点的个数)参数,让图片更加清晰
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(50, 10), dpi=80)
2.2.2.保存图片到本地
保存格式有很多:png,svg(矢量图)…
plt.savefig("./t1.svg")
plt.savefig("./t2.png")
2.2.3.调整x或者y的刻度的间距
注意用xticks设置的刻度,只有设置范围内有刻度,非设置范围内不会有刻度
(1)直接以x的坐标间隔为横坐标
plt.xticks(x)
(2)可以自己建一个label,来表示横坐标的间隔
x_labels = [i/2 for i in range(0, 60)]
# x_labels=[0,0.5,1,1.5.....30]
plt.xticks(x_labels)
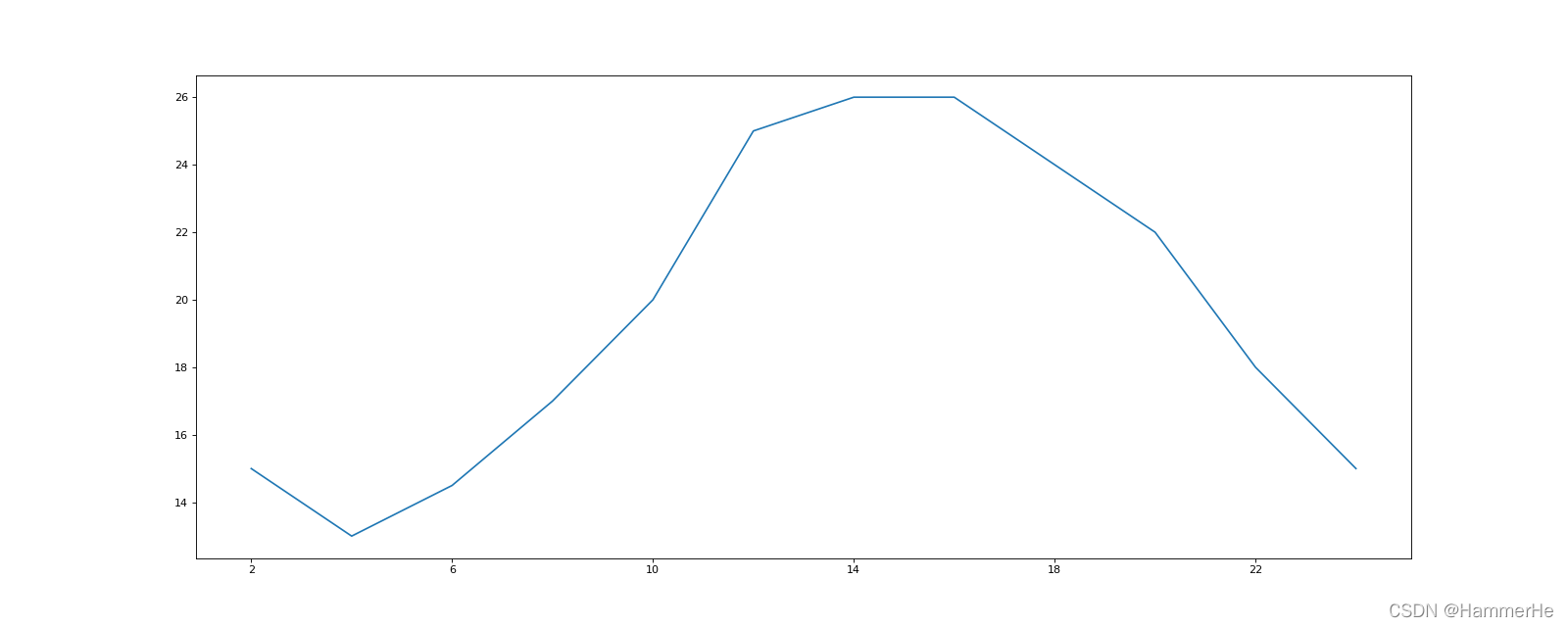
 (3)用断间隔的方式去处理X也可以
(3)用断间隔的方式去处理X也可以
plt.xticks(x[::2])
(4)如果要把新的label和原来的x对应:
x_labels = [i/2 for i in range(0, 12)]
plt.xticks(x,x_labels)
这样的话其中的x的横坐标显示会变成x_labels(x和x_label要对应关系)
2.2.4 转换matplotlib界面显示为中文
ctrl+B查看函数源码
方法1:
import matplotlib
font = {'family': 'Microsoft Yahei',
'weight': 'bold',
'size': '10'}
matplotlib.rc("font", **font)
方法2:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.rc("font", family='Microsoft Yahei', weight='bold')
方法3:通过ttc文件导入字体
from matplotlib import font_manager
my_font = font_manager.FontProperties(fname="\\Windows\\Fonts\\simfang.ttf")
plt.xticks(x[::5], x_labels[::5], rotation=90, fontproperties=my_font)
2.2.5.给图像添加描述信息(比如x轴和y轴表示什么,这个图表示什么)(画时温折线图)
plt.xlabel("时间", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.ylabel("温度", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.title("时温图", fontproperties=my_font)
例子(时温图)测试:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
# import matplotlib
from matplotlib import font_manager
# font = {'family': 'Microsoft Yahei',
# 'weight': 'bold',
# 'size': '10'}
# matplotlib.rc("font", **font)
# matplotlib.rc("font", family='Microsoft Yahei', weight='bold')
my_font = font_manager.FontProperties(fname="\\Windows\\Fonts\\simfang.ttf")
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
x = range(120)
random.seed(10) # 设置随机种子,让不同时候得到的随机结果一致(即每次运行的随机数一致)
a = [random.randint(20, 35) for i in range(120)]
x_labels = ["10点{}分".format(i) for i in range(60)]
x_labels += ["10点{}分".format(i) for i in range(60)]
plt.xticks(x[::5], x_labels[::5], rotation=90, fontproperties=my_font)
plt.xlabel("时间", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.ylabel("温度", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.title("时温图", fontproperties=my_font)
plt.plot(x, a)
plt.show()
2.2.6.样式(比如颜色,透明度等)
(1)加网格(alpha表示透明度。默认1)
plt.grid(alpha=0.4)
(2)加图例(legend是唯一一个插入字体要用prop的)
loc是图例位置
plt.legend(prop=my_font, loc="best")
(3)线条样式
plt.plot(x, a, label="1号", linestyle="--", linewidth=0.5, color="red", alpha=0.5)
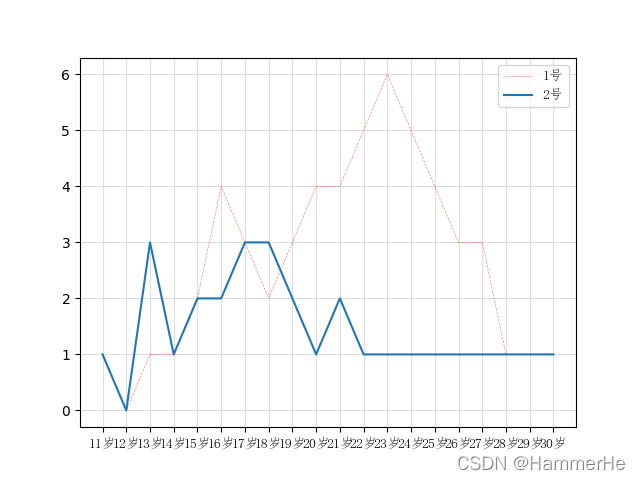
实际例子:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import font_manager
# 设置一个字体
my_font = font_manager.FontProperties(fname="\\Windows\\Fonts\\simfang.ttf")
x = range(11, 31)
a = [1, 0, 1, 1, 2, 4, 3, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 5, 4, 3, 3, 1, 1, 1]
b = [1, 0, 3, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
x_labels = ["{}岁".format(i) for i in x]
plt.xticks(x, x_labels, fontproperties=my_font)
plt.yticks(range(0, 9))
plt.grid(alpha=0.4)
plt.plot(x, a, label="1号", linestyle="--", linewidth=0.5, color="red", alpha=0.5)
plt.plot(x, b, label="2号")
plt.legend(prop=my_font, loc="best")
plt.show()
2.2matplotlib不同图的信息

Leetcode(13,14,20)
leetcode13:罗马数字转整数
先用字典(哈希表)记录对应键值关系
然后特殊情况只有一种,前项小于后项的时候需要减前项,所以直接遍历就可以。
class Solution:
def romanToInt(self, s: str) -> int:
Dic={'I':1,'V':5,'X':10,'L':50,'C':100,'D':500,'M':1000}
rx=0
for i in range(0,len(s)-1):
if(Dic[s[i]]<Dic[s[i+1]]):
rx-=Dic[s[i]]
else:
rx+=Dic[s[i]]
return rx+Dic[s[-1]]
leetcode14:最长公共前缀
方法1(朴实无华):先取出最小的字符串,然后遍历最小字符串和所有字符串对比,只要不相等就break。
class Solution:
def longestCommonPrefix(self, strs: List[str]) -> str:
LongStr=""
MatchStr=strs[0]
for i in range(len(strs)):
if(len(strs[i])<len(MatchStr)):
MatchStr=strs[i]
flag=True
for index in range(len(MatchStr)):
for j in range(len(strs)):
if(strs[j][index]!=MatchStr[index]):
flag=False
if(flag):
LongStr+=MatchStr[index]
else:
break
return LongStr
方法2:利用python的zip和set函数实现:
什么是zip函数?:
取出str列表里每一个列表的每一位,分别组成新的列表
什么是set函数?:
把列表里面相同的元素给消除或者说合并
class Solution:
def longestCommonPrefix(self, strs: List[str]) -> str:
res = ""
for tmp in zip(*strs):#zip取出一个list内所有数组相同位数的元素形成新的list
tmp_set = set(tmp)#把一个list内相同的元素做合并
if len(tmp_set) == 1:
res += tmp[0]
else:
break
return res
leetcode20:有效的括号
运用栈的思想来处理:
遍历括号列表
遇到括号前项入栈
遇到匹配的括号后项出栈(用哈希表做前后项括号匹配比较方便,也可以)
最终返回栈深=0,说明括号有效
class Solution:
def isValid(self, s: str) -> bool:
dic={')':'(',']':'[','}':'{'}
stack = []
#print("len=",len(stack)," stack=",stack)
if len(s)%2!=0:return False
#遍历s,前项入栈
for index in range(len(s)):
if(s[index]=='(' or s[index]=='[' or s[index]=='{'):
stack.append(s[index])
else:
if len(stack)>0 and stack[-1]==dic[s[index]]:#后项匹配出栈
del stack[-1]
else:
return False
#print("len=",len(stack)," stack=",stack)
return len(stack)==0