一、拓扑概念
拓扑主要研究的对象为几何图形或空间结构,探究在连续改变形状后还能保持不变的一些性质。它只考虑物体间的位置关系而不考虑它们的形状和大小。简单的描述为:一些特殊的几何性质,在图形连续改变形状后还能继续保持不变。
二、拓扑数据分析
拓扑学研究的是一些特殊的几何性质,这些性质在图形连续改变形状后还能继续保持不变,称为“拓扑性质”。而在复杂的高维数据内部也存在着类似的结构性质,我们可以形象地称之为数据的形状(特征)。
拓扑数据分析(Topological data analysis, TDA),顾名思义,就是把拓扑学与数据分析结合的一种分析方法,用于深入研究大数据中潜藏的有价值的关系。
-
相比于主成分分析、聚类分析这些常用的方法,TDA不仅可以有效地捕捉高维数据空间的拓扑信息,而且擅长发现一些用传统方法无法发现的小分类。这种方法也因此曾在基因与癌症研究领域大显身手。
-
和通常研究的成对关系相比,这种相互关系的形状之中可能潜藏了巨大的研究价值。要理解数据的形状,就必须求助于拓扑学。TDA所做的就是抽取这种形状并进行分析。
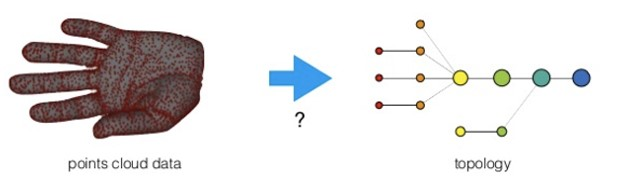
三、拓扑分析步骤
在TDA数据分析中,mapper算法是必须的。具体的实现过程如下。
数据矩阵
- 输入数据:输入数据可以是任何类型的数据,但是要满足一定的条件,即输入的数据必须要能够计算任何两数据之间的距离(这距离不局限于欧几里得距离,可以是用户定义的一些距离公式,目的就是要能够确定这个数据在总的输入数据中的一个大致“位置”)。
- 输出:一个关于输入数据的拓扑图。
Mapper算法
The Algorithm
Given a dataset of points, the basic steps behind Mapper are as follows:
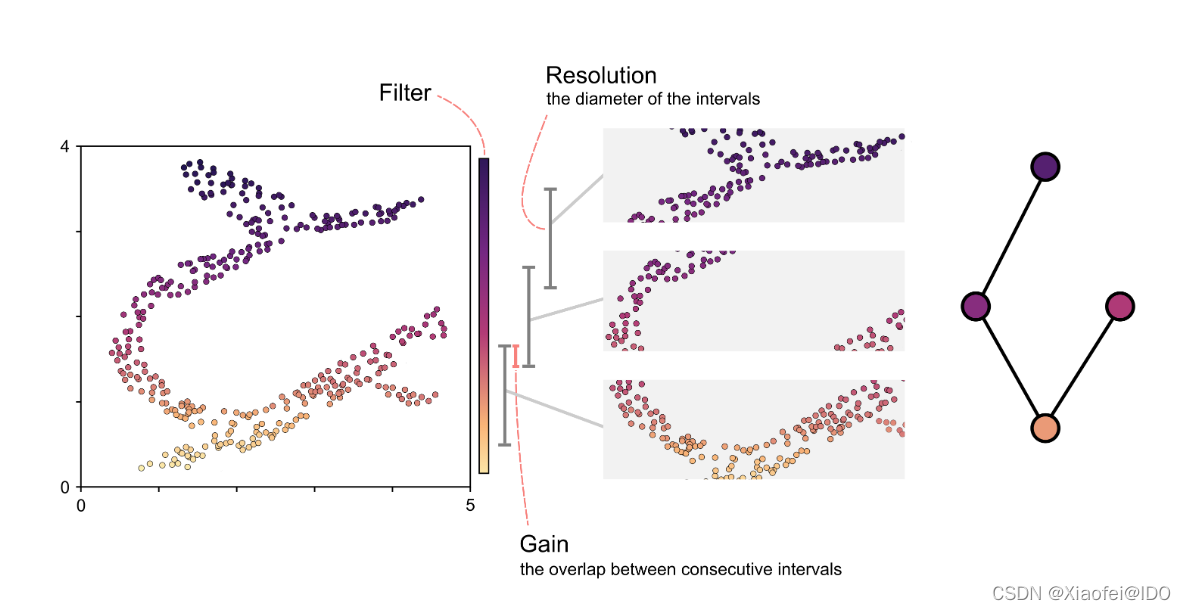
- Map to a lower-dimensional space using a filter function f f f, or lens. Common choices for the filter function include projection onto one or more axes via PCA or density-based methods.
- Construct a cover ( U i ) i ∈ I (U_i)_{i\in I} (Ui?)i∈I? of the projected space typically in the form of a set of overlapping intervals which have constant length.
- For each interval U_i cluster the points in the preimage f ? 1 ( U i ) f^{-1}(U_i) f?1(Ui?) into sets C i , 1 , … , C i , k i C_{i,1},\ldots,C_{i,k_i} Ci,1?,…,Ci,ki??.
- Construct the graph whose vertices are the cluster sets and an edge exists between two vertices if two clusters share some points in common.
- 使用一个(或多个)filter 函数,将输入数据X经过计算得到一个(或多个)值。即f(X) = a ,a是一个实数。
- 设置两个超参,分别是resolution(即intervals的间距大小)和overlap(重叠区间的大小)。(重要!!)
- 在每个intervals里面进行局部聚类,可以使用任何聚类算法。将聚在一起的类归并到一个拓扑节点。每一个拓扑节点中包含了不同的数据点。
- 基于第2步,resolution中设置的overlap(相邻intervals里面会有公共的数据点),将有overlap的两个拓扑节点,使用线连接起来。
优点
- 优点1:一般现有的算法,如果要对高维数据进行可视化,必然会有一个降维的过程,那么现有的算法在降维后对原始数据会有一些信息的损失(维数越高,越明显)。而mapper算法始终保留高维空间中数据的整体拓扑信息,在这个方面,它远胜于其他算法。
- 优点2:能够发现一些更小的类,检测传统方法无法找到的集群和有趣的拓扑结构
- 优点3:发现的特征具有鲁棒性,选择最能区分数据和模型可解释性的特征
基于python的实现
Nowadays there are a few python open source libraries implementing the main TDA tools, like GUDHI, scikit-tda and Giotto. For our test we chose to use one of the most recent: the Giotto library, which is scikit-learn compatible, oriented towards machine learning, fast-performing with C++ state-of-the-art implementations.
# Define filter function
filter_func = umap.UMAP(n_neighbors=5)
# Define cover
cover = CubicalCover(kind='balanced', n_intervals=10, overlap_frac=0.2)
# Choose clustering algorithm
clusterer = DBSCAN(eps=10)
# Initialise pipeline
pipe = make_mapper_pipeline(
filter_func=filter_func,
cover=cover,
clusterer=clusterer,
verbose=True,
n_jobs=-1,
)
# Plot Mapper graph
fig = plot_static_mapper_graph(pipe, X, color_by_columns_dropdown=True, color_variable=y)
fig.show(config={'scrollZoom': True})