支持向量机方法也是一种强大的机器学习分类方法。
在感知器算法中,我们的目标是最小化分类误差,而在SVM中,我们的优化目标是最大化分类间隔。
较大的分类间隔意味着模型有较小的泛化误差,较小的间隔则意味着模型可能会过拟合。
在SVM中的两条平行的决策边界为:
w
0
+
w
T
x
p
o
s
=
1
w_0+\bm{w}^T\bm{x}_{pos}=1
w0?+wTxpos?=1
w
0
+
w
T
x
n
e
g
=
?
1
w_0+\bm{w}^T\bm{x}_{neg}=-1
w0?+wTxneg?=?1
两式相减可得:
w
T
(
x
p
o
s
?
x
n
e
g
)
=
2
\bm{w}^T(\bm{x}_{pos}-\bm{x}_{neg})=2
wT(xpos??xneg?)=2
定义
∣
∣
w
∣
∣
=
∑
j
=
1
m
w
j
2
||\bm{w}||=\sqrt{\sum_{j=1}^{m}w_j^2}
∣∣w∣∣=j=1∑m?wj2??
可得
w
T
(
x
p
o
s
?
x
n
e
g
)
∣
∣
w
∣
∣
=
2
∣
∣
w
∣
∣
\frac{\bm{w}^T(\bm{x}_{pos}-\bm{x}_{neg})}{||\bm{w}||}=\frac{2}{||\bm{w}||}
∣∣w∣∣wT(xpos??xneg?)?=∣∣w∣∣2?
等式左侧为正负超平面间的距离,也就是所要最大化的间隔,故需使
2
/
∣
∣
w
∣
∣
2/||\bm{w}||
2/∣∣w∣∣最大。
SVM的目标函数记为:
w
0
+
w
T
x
i
≥
1
,
if?
y
(
i
)
=
1
w_0+\bm{w}^T\bm{x}^{i}\ge1, \text{if} \ y^{(i)}=1
w0?+wTxi≥1,if?y(i)=1
w
0
+
w
T
x
i
≤
1
,
if?
y
(
i
)
=
?
1
w_0+\bm{w}^T\bm{x}^{i}\le1, \text{if} \ y^{(i)}=-1
w0?+wTxi≤1,if?y(i)=?1
对于非线性可分的数据,需要放松线性约束条件,以保证在适当的罚项成本下,对错误的分类情况优化时能够收敛。
w
0
+
w
T
x
i
≥
1
,
if?
y
i
=
1
?
ξ
(
i
)
w_0+\bm{w}^T\bm{x}^{i}\ge1, \text{if} \ y^{i}=1-\xi^{(i)}
w0?+wTxi≥1,if?yi=1?ξ(i)
w
0
+
w
T
x
i
≤
1
,
if?
y
i
=
?
1
+
ξ
(
i
)
w_0+\bm{w}^T\bm{x}^{i}\le1, \text{if} \ y^{i}=-1+\xi^{(i)}
w0?+wTxi≤1,if?yi=?1+ξ(i)
通过引入
C
C
C值,新的目标优化为使下式最小:
1
2
∣
∣
w
∣
∣
2
+
C
(
∑
i
ξ
(
i
)
)
\frac{1}{2}||\bm{w}||^2+C(\sum_i\xi^{(i)})
21?∣∣w∣∣2+C(i∑?ξ(i))
通过这种方法我们也可以对鸢尾花进行分类,代码引自《python机器学习》
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, [2, 3]]
y = iris.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.3,random_state=0)
sc = StandardScaler()
sc.fit(X_train)
X_train_std = sc.transform(X_train)
X_test_std: object = sc.transform(X_test)
def plot_decision_regions(X, y, classifier, test_idx=None, resolution=0.02):
# 设置marker generator和color map
markers = ('s', 'x', 'o', '^', 'v')
colors = ('red', 'blue', 'lightgreen', 'gray', 'cyan')
cmap = ListedColormap(colors[:len(np.unique(y))])
x1_min, x1_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
x2_min, x2_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x1_min, x1_max, resolution),
np.arange(x2_min, x2_max, resolution))
Z = classifier.predict(np.array([xx1.ravel(), xx2.ravel()]).T)
Z = Z.reshape(xx1.shape)
plt.contourf(xx1, xx2, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap=cmap)
plt.xlim(xx1.min(), xx1.max())
plt.ylim = (xx2.min(), xx2.max())
X_test, y_test = X[test_idx, :], y[test_idx]
for idx, cl in enumerate(np.unique(y)): # np.unique:去除重复数据
plt.scatter(x=X[y == cl, 0], y=X[y == cl, 1], alpha=0.8, c=cmap(idx), marker=markers[idx], label=cl)
if test_idx:
X_test, y_test = X[test_idx, :], y[test_idx]
plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c='black', alpha=0.8, linewidths=1, marker='o', s=10, label='test set')
X_combined_std = np.vstack((X_train_std, X_test_std))
y_combined = np.hstack((y_train, y_test))
svm = SVC(kernel='linear', C=1.0, random_state=0)# 使用线性核函数,设置C值为1
svm.fit(X_train_std, y_train)
plot_decision_regions(X_combined_std, y_combined, classifier=svm, test_idx=range(105,150))
plt.xlabel('petal length {standardized}')
plt.ylabel('petal width {standardized}')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()
小黑点表示测试集数据,分类结果如下:
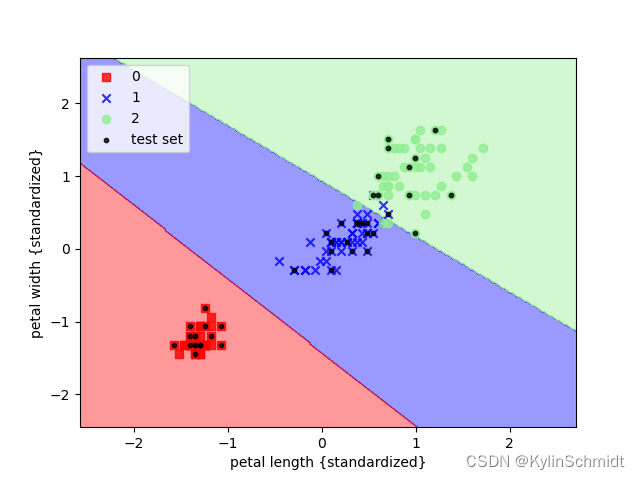
可以观察到分类结果较好。